HPS771 - Research Methods in Psychology A
Deakin University Research Methods in Psychology A (HPS201/HPS771) Laboratory Assignment ANOVA Post-Hoc Tests **** ASSIGNMENT 6: ANOVA POST-HOC QUESTIONS **** Experiment
Cognitive theory suggests that college students learn best if they study later in the day (https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00188/full). Your task as a researcher is to test this idea. To this end, you recruit 45 undergraduate students of similar cognitive and academic ability. You then randomly allocate each student to one of three groups (Group A, Group B and Group C). All students study for the same exam over a two-week period (all students study for the same number of hours). Students in Group A study in the morning. Students in Group B study in the afternoon. Students in Group C study in the evening. At the end of the two-week period, all students sit the same exam. Scores on the exam range from 0 to 40 with higher scores indicating better exam performance. Finally, you conduct a one-way ANOVA to test if the three groups differ in their mean exam scores. You obtain the following output from the analysis:
Questions
The first question does not require you to use the SPSS output.
- If an ANOVA has been conducted, when is it appropriate to conduct post-hoc analyses and why? (2 Marks)
- The remaining questions relate to the above research scenario and/or the SPSS output.
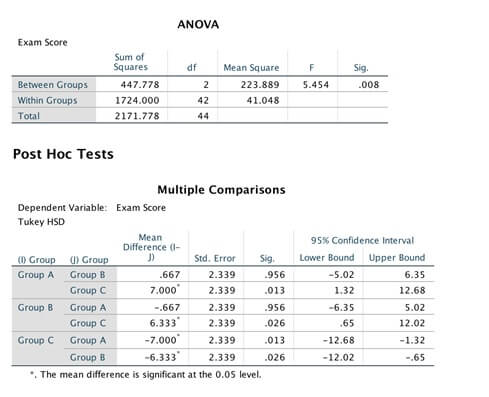
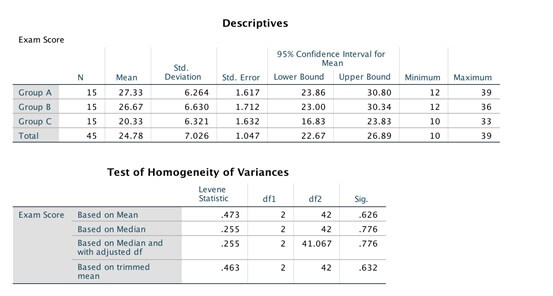
- Based on a visual inspection of the descriptive statistics (do not interpret the inferential statistics), do students appear to learn best if they study later in the day? Justify your response. (2 Marks)
- With help from the unit materials, report the results of the analysis (including relevant post-hoc analyses if applicable) in APA format including all relevant information. (4 Marks)
- Assume you are a Cognitive Psychologist. Based on the results of this study, what would be your recommendation to students studying for an exam? Justify your response. (2 Marks)
TOTAL: /10 Marks
Deakin University Research Methods in Psychology A (HPS201/HPS771) Laboratory Assignment One-Way ANOVA **** ASSIGNMENT 5: One-Way ANOVA QUESTIONS **** Experiment
Jurors place heavy weight on eyewitness testimony when deciding whether a suspect is guilty. Legal evidence suggests that jurors tend to give more weight to the testimony of eyewitnesses who report that they were confident in remembering the event. (http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/do-the-eyes-have-it/) Still, there is mixed evidence in the literature whether the confidence with which people remember an event is related to the accuracy of their memories. Your task as a researcher is to clarify this. To this end, you show a crime scene to 63 randomly selected individuals. You then count the number of mistakes they make in recalling the crime scene. Finally, you ask participants to rate how confident they were in recalling the crime scene. Based on their ratings, you assign each participant to either the low confidence group (n = 21), the medium confidence group (n = 21) or the high confidence group (n = 21). You then run a one-way ANOVA to test if the three groups differ in the number of mistakes made when recalling the crime scene. You obtain the following output from the analysis:
Questions
Note that these questions do not require SPSS output.
- Complete the table below. (2 Marks)
Source
SS
df
MS
F
Between Groups (Treatment)
2
Within Groups (Error)
180
Total
- With your alpha level (α) set at .05, what is the critical F value for the above data? (1 Mark)
- With help from the unit materials, report the results of the analysis in APA format including all relevant information. (3 Marks)
- In the present study, the three groups could have been compared using t-tests. Why is it more appropriate however to analyze the data from the experiment using a one-way ANOVA? (2 Marks)
- Assume you are a Forensic Psychologist. What would be your advice to jurors based on the results of the above research? Justify your response. (2 Marks)
TOTAL: /10 Marks
Deakin University Research Methods in Psychology A (HPS201/HPS771) Laboratory Assignment Regression **** ASSIGNMENT 4: REGRESSION QUESTIONS **** Experiment
In recent years, mental skills techniques such as motor (kinesthetic) imagery have become popular tools to enhance performance on the football field. (http://www.theage.com.au/afl/st-kilda-saints/saints-training-to-win-mind-games-20150624-ghwxoi.html) For example, the St Kilda Football Club now teaches players how to imagine (visualize) their kicking action with the aim of improving kicking accuracy. The theory behind this approach is that imagining an action activates similar brain processes to actually performing that action. Your task as a researcher is to test if we can predict a player’s kicking accuracy from their ability to imagine kicking a football. To this end, you ask a sample of 60 St Kilda players to imagine kicking a football. You then asses the vividness of their mental (kicking) image using the Vividness of Movement Imagery Questionnaire (VMIQ-2), a well-validated imagery measure. Scores on the VMIQ-2 range from 12 to 60 with higher scores indicating better imagery ability (i.e., increased vividness of the imagined kick). You also measure each player’s kicking accuracy (scores range from 0-100 with higher scores indicating higher kicking accuracy). Finally, you run a regression analysis on the data to test the hypothesis that imagery ability (as assessed by VMIQ-2 scores) will be a significant predictor of kicking accuracy. You obtain the following output from the analysis:
Questions
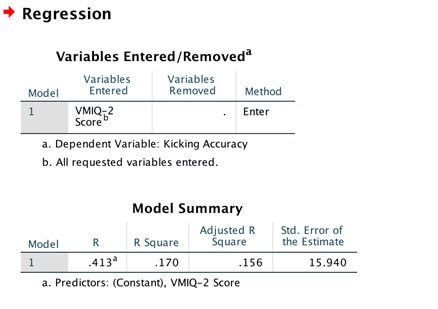
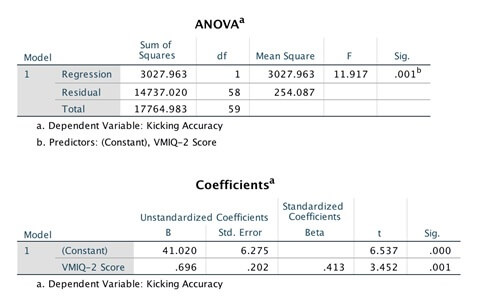
- With help from the unit materials, report the results of the analysis in APA format including all relevant information. (3 Marks)
- What percentage of the variability in kicking accuracy is not explained by imagery ability? Name one other factor that could reasonably be expected to influence kicking accuracy. (2 Marks)
- Based on the SPSS output, state the unstandardized regression equation that allows you to predict kicking accuracy from VMIQ-2 scores. (1 Mark)
- Kicking accuracy scores in the AFL are normally distributed with a mean of 60 (SD = 10). Jason, who has just nominated for the national draft, scores 56 on the VMIQ-2. Should the St Kilda Football Club recruit Jason based on his kicking accuracy? Justify your response? (2 Marks)
- Assume you are a Sports Psychologist. Would you recommend imagery training as a technique for improving kicking accuracy? Justify your response. (2 Marks)
TOTAL: /10 Marks

