007 supporting holistic development readings
Contents
Workbook 3 Completion Options 1
Submitting Assessment Workbooks 3
Activity Checklist and Declaration 4
001 Learning frameworks readings 12
002 Pedagogy, principles and practices 17
002 Pedagogy, principles and practices readings 17
003 Using the framework readings 22
CHCECE010 Support holistic development of children in early childhood 27
CHCECE010 Support holistic development of children in early childhood readings 28
002 Theories of development assessment tasks 36
003 Physical development readings 42
003 Physical development assessment tasks 43
004 Social and emotional development 50
007 Supporting holistic development readings 69
007 Supporting holistic development assessment tasks 70
CHCECE011 Provide experiences to support children’s play and learning 78
002 Following interests readings 86
003 Participations and interactions readings 90
003 Participations and interactions assessment tasks 91
004 Play environments and safety 96
004 Play environments and safety readings 96
005 Learning through play readings 102
CHCECE013 Use information about children to inform practice readings 107
002 Observing children readings 114
002 Observing children assessment tasks 115
003 Mitch assessment tasks 121
006 Misha assessment tasks 130
Workbook 3 Completion Options
Self-Paced Delivery
About this Workbook
The work you complete in this workbook is used as evidence to contribute to your overall competence in the underpinning knowledge requirements for this qualification. There are 18 Units of Competency that form a full Certificate III in Early Childhood Education and Care.
Once you have successfully completed all workbooks and been assessed as competent by HBA, you will have achieved your Certificate III in Early Childhood Education and Care.
CHCECE002 Ensure the health and safety of children
CHCECE003 Provide care for children
CHCECE010 Support the holistic development of children in early childhood
CHCECE011 Provide experiences to support children’s play and learning
HLTHIR404D Work effectively with Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander people
Chosen Electives:
Elements of Assessment
In undertaking an activity in this workbook you may be asked to:
Answer questions
NOTE:
Checking off Assessment Tasks
Submitting Assessment Workbooks
Only completed assessment activity items with appropriate evidence which is valid under the Registering Authority guidelines, and the terms of the RTO and its authorised delegates will be used toward determining competence.
You must submit your assessments in the Workbooks provided in their original format.
NOTE:
CHC30113 Workbook 3 Attempt #, your full name as per enrolment form
Note: Ensure that you change the attempt number with each submission
Activity Checklist and Declaration
Learner Declaration
I understand that competency will not be given if I do not meet the assessment evidence and activity requirements or if it is discovered that I have not undertaken all expected tasks.
I understand that HBA reserves the right to immediately withdraw a qualification if it is found that I provided false or misleading evidence, this includes any declaration, resource or tool I have submitted as being authored by me that I have submitted.
| Signed: | Date: | ||
| Name (print): | |||
Completing Assessment Tasks
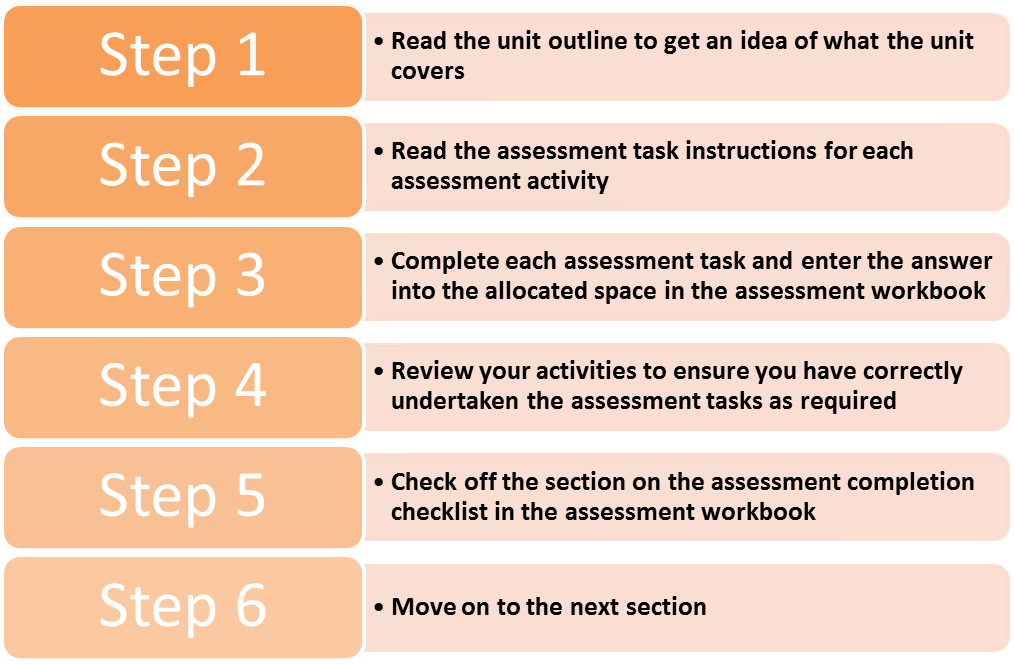
Assessment Task Tips
Shortcut Keys:
** Mac Users – Note your ‘Control’ Key is the ‘Command’ key
Other tips:
** Mac Users: Your ‘View’ tab is the ‘Window’ tab
Use the Contents Page to find the topic/activity number by clicking on it in the list.
Undertaking Assessment Tasks
Employability Skills
Nationally Recognised Training is attached to employability skills. These are soft skills that are required to be demonstrated by a Learner to prove their ability to work effectively in the role in industry. For the Certificate III in Early Childhood and Care the Employability Skills include:
The assessments have been designed to capture these soft skills and it is essential these skills are in the forefront of your mind when you are completing the assessment requirements for this qualification.
Locked Documents
Assessment Tasks
This workbook:
It is essential that your answer addresses all components of the question adequately, simply copying and pasting content that more or less answers the question is not appropriate. You can copy and paste content from other sources, but you must modify/paraphrase it to meet the question requirements and demonstrate your understanding of key concepts, ideas and models.
TIPS:
Read the questions to ensure you are providing what has been asked for.
Section 1 – Unit 1
CHCECE009 Use an approved learning framework to guide practice
This unit applies to educators working in a range of education and care services.
To achieve competency in this unit you will need to provide evidence that you can:
Reflecting on and discussing practice with supervisor and others
Investigated and documented their own involvement in at least three examples of pedagogical practices in the service.
CHCECE009 Use an approved learning framework guide to practice readings
Australian Children’s Education and Care Quality Authority. (2011). Guide to the Education and Care Services National Law and the Education and Care Services National Regulations. ACT: Commonwealth of Australia.
Australian Children’s Education and Care Quality Authority. (2011). Guide to the National Quality Standard. ACT: Commonwealth of Australia.
Early Childhood Australia. (2011). Learning Outcomes. The Early Years Learning Framework Professional Learning Program e-Newsletter, 6. Retrieved from http://www.earlychildhoodaustralia.org.au/nqsplp/wp-content/uploads/2012/05/EYLFPLP_E-Newsletter_No6.pdf
001 Learning frameworks
001 Learning frameworks readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
Australian Children’s Education and Care Quality Authority. (2011). Guide to the National Quality Standard. ACT: Commonwealth of Australia.
Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations. (2010). Educators’ Guide to the Early Years Learning Framework for Australia. Canberra: DEEWR.
001 Learning frameworks assessment tasks
Question 1
Readings
Question 1 (a)
| List the four requirements of the National Law and National Regulations in regards to the program that services provide. |
Question 1 (b)
Question 1 (c)
| List the two national approved learning frameworks? |
Question 1 (d)
Question 1 (e)
The Early Years Learning Framework (EYLF) reinforces the principles laid out in the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child.
In the table below list whether each Article from the UN Convention relates to the concept of Belonging, Being or Becoming as they are defined in the EYLF.
| Article from the UN Convention of the Rights of the Child | Link to EYLF |
| Article 12 (Respect for the views of the child): When adults are making decisions that affect children, children have the right to say what they think should happen and have their opinions taken into account. | |
| Article 13 (Freedom of expression): Children have the right to get and share information, as long as the information is not damaging to them or others. In exercising the right to freedom of expression, children have the responsibility to also respect the rights, freedoms and reputations of others. The freedom of expression includes the right to share information in any way they choose, including by talking, drawing or writing. | |
| Article 29 (Goals of education): Children’s education should develop each child’s personality, talents and abilities to the fullest. It should encourage children to respect others, human rights and their own and other cultures. It should also help them learn to live peacefully, protect the environment and respect other people. | |
| Article 30 (Children of minorities/indigenous groups): Minority or indigenous children have the right to learn about and practice their own culture, language and religion. The right to practice one’s own culture, language and religion applies to everyone; the Convention here highlights this right in instances where the practices are not shared by the majority of people in the country. | |
| Article 31 (Leisure, play and culture): Children have the right to relax and play, and to join in a wide range of cultural, artistic and other recreational activities |
Question 2
Readings
Question 2 (a)
Question 2 (b)
| What does Standard 1.1 of the NQS aim to achieve? |
Question 3
Readings
Question 3 (a)
Question 3 (b)
| What is involved in meaningful curriculum decision making? |
Question 3 (c)
002 Pedagogy, principles and practices
002 Pedagogy, principles and practices readings
Refer to Section 9 in the HBA Learner Guide for CHC30113 Certificate III in Early Childhood Education and Care
You will also need to access the following readings:
002 Pedagogy, principles and practices assessment tasks
Question 1
Readings
Belonging, Being and Becoming: The Early Years Learning Framework for Australia (pp. 11- 12), Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations (2009).
Question 1 (a)
| How does the EYLF define the term ‘pedagogy’? |
Question 1 (b)
Question 1 (c)
| Theoretical Perspective | Description | |
| Developmental Theories | ||
| Socio-cultural theories |
|
|
| Socio-behaviourist theories |
|
|
| Critical theories | ||
| Post-structuralist theories |
Question 2
Question
Question 3
Readings
Belonging, Being and Becoming: The Early Years Learning Framework for Australia, Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations (2009).
Guide to the National Quality Standard (p. 42- 43), ACECQA (2011).
Question 3 (a)
| List the eight pedagogical practices educators use to deliver educational programs to support and enhance children’s learning and development. |
Question 3 (b)
Question 3 (c)
003 Using the framework
003 Using the framework readings
HBA Learner Guide
Refer to Section 9 in the HBA Learner Guide for CHC30113 Certificate III in Early Childhood Education and Care
003 Using the framework assessment tasks
Question 1
Readings
To complete this task refer to the following reading:
Belonging, Being and Becoming: The Early Years Learning Framework for Australia, Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations (2009).
Question 1 (a)
Question 1 (b)
For each of the following situations describe possible strategies educators can use to be responsive to children. |
| Arrive time: |
| Painting at the easels: |
| Lunch time: |
| Completing an obstacle course outdoors: |
Question 2
Readings
To complete this task refer to the following reading:
Question 2 (a)
Readings
Question 2 (b)
| Learning Outcomes | Ways educators can promote learning for the outcome |
| Children have a strong sense of identity | |
| Children are connected with and contribute to their world | |
| Children have a strong sense of wellbeing | |
| Children are confident and involved learners | |
| Children are effective communicators | |
Question 2 (c)
Question 2 (d)
| List three strategies for supporting and facilitating children’s learning within Outcome 5: Children are effective communicators - Children express ideas and make meaning using a range of media. |
Section 2 – Unit 2
CHCECE010 Support holistic development of children in early childhood
Interacting with children to holistically support development and learning appropriate to the child’s abilities and age
Providing a variety of experiences and environments to support the different areas of children’s development (including a combination of physical, creative, social, emotional , language and cognitive)
CHCECE010 Support holistic development of children in early childhood readings
Australian Children’s Education and Care Quality Authority. (2011). Guide to the National Quality Standard. ACT: Commonwealth of Australia.
Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations. (2009). Belonging, Being and Becoming: The Early Years Learning Framework for Australia. Canberra: DEEWR.
001 Child development
001 Child development readings
Refer to Section 10 in the HBA Learner Guide for CHC30113 Certificate III in Early Childhood Education and Care
001 Child development assessment tasks
Question 1
Question
Match definition with the corresponding term.
Question 2
Question
All children have needs that must be met if they are to thrive and develop to their potential.
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
Question 3
Question
Question 4
Question
The following factors may influence physical growth and development. For each factor give a short explanation and example.
| Factor | Explanation | Example |
| Maturation − Readiness: | ||
| Heredity: | ||
| Culture/family: | ||
| Prenatal development: | ||
| Diet: |
Question 5
Question
Tick the column to indicate the stage of development when you would typically expect to observe the following behaviours.
002 Theories of development
002 Theories of development readings
002 Theories of development assessment tasks
Question 1
Question
| Stage | Piaget Stages of Cognitive Development | Approximate Ages Related to Stage |
| 1. | ||
| 2. | ||
| 3. | ||
| 4. |
Question 2
Question
Choose the correct word to complete each sentence.
Question 3
Readings
Question
Question 4
Readings
To complete this task refer to the following readings:
Question 4 (a)
| Explain the term Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD). Give an example to support your answer. |
Question 4 (b)
Question 5
Question
| Describe the two key functions of language which Vygotsky believed to be important to the learning process. |
| Private speech: |
| Public speech: |
Question 6
Question
Question 7
Question
Choose the correct word to complete each sentence.
| Missing Words | ||||
| Social | Information | Partnership | Abilities | Development |
| Needs | Significant | Positive | Relationship | Support |
Question 8
Question
Question 9
Question
| Term | Definition | |
| Critical periods | ||
| Sensitive periods |
|
|
| Synapses |
|
|
| Neurons | ||
| Limbic hypothalamus pituitary adrenal | ||
| Plasticity | ||
| Genes |
Question 10
Question
Describe each of the following stages of Erikson’s theory.
003 Physical development
003 Physical development readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
HBA Learner Guide
003 Physical development assessment tasks
Question 1
Readings
Question
Tick the key motor skills being demonstrated by Alyssa as she washes her hands.
| Key Motors Skills | ü |
|
|
Question 2
Question 2 (a)
Question 2 (b)
| Suggest two other experiences (not involving the use of scissors) that may assist preschool children to develop the fine motor skills necessary for manipulating scissors. |
Question 3
Question 3 (a)
Listed below are some general characteristics of the physical development of infants and toddlers.
Question 3 (b)
| Infant /Toddler Physical Development | Skills being developed |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Question 4
Question 4 (a)
| Preschool Descriptors | |
|
|
|
|
Question 4 (b)
Listed below are some of the general characteristics of the physical development of Pre-schoolers.
For each characteristic, list two experiences and/or resources that you can use to support children’s development and mastery of these skills.
Question 5
Readings
Question 5 (a)
Question 5 (b)
004 Social and emotional development
004 Social and emotional development readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
HBA Learner Guide
004 Social and emotional development assessment tasks
Question 1
Question 1 (a)
| What does social and emotional development include? |
Question 1 (b)
Question 2
Question 2 (a)
| Aspect of Social Development | Strategy/Experience/Environmental Factor | |
| Self–help skills promote autonomy, confidence and self-esteem. | ||
| Children learn that friendships are based on shared interests and care for others. | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Question 2 (b)
Question 3
Question
| Statement | ü ü | |
| Providing children with genuine choices supports social development. | False |
|
| Consistent, predictable routines support children’s emotional and psychological development. | ||
| Preschool children are too young to be encouraged to take responsibility for their own actions. | True |
|
| Actively involving children in decision-making supports their emotional and psychological development. | False |
|
| Requiring children to care for and respect the centre’s resources supports children’s social development. | ||
| Educators should always step in and quickly resolve preschool children’s conflicts. | True |
|
| Educators should allow children to give up on tasks that they find too challenging. | False |
|
| To provide a quality program for a child an Educator needs to understand the child, and family’s background, circumstances, experiences and needs. | ||
Question 4
Question 4 (a)
Match the Educator strategy to each scenario to support the development of friendships with pre-schoolers.
Question 4 (b)
Read each of the following scenarios and suggest a strategy that the Educator could use to support the child’s social and emotional development.
| Scenario | Educator Strategy |
| Tilly (4years 6 months) is crying because the other girls have excluded her from their play because Tilly was being too bossy and would not share the equipment. | |
| Harry (4 years) is quiet and shy. He tends to talk so softly he can barely be heard. He usually talks with his head bowed. | |
| Clancy (4years 7months) complains that nobody every listens to her. Clancy tends to talk over others and has a loud voice. | |
| Arran (4years 4months) appears unaware of how others might be feeling . He does not seem to pick up on body language/facial expressions. |
005 Thinking and talking
005 Thinking and talking readings
Readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
005 Thinking and talking assessment tasks
Question 1
Readings
To complete this task go to your text and refer to the following reading:
Belonging, Being and Becoming: The Early Years Learning Framework for Australia, Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations (2009).
Question 1 (a)
Question 1 (b)
| The Early Years Learning Framework Learning Outcome 5: Children are effective communicators, is demonstrated when Anshul: |
Question 1 (c)
Question 1 (d)
| Suggest one question that the Educator could ask Anshul about his structure or construction techniques to promote language and his cognitive learning. |
Question 2
Question
Question 3
Question 3 (a)
Match the descriptor to the correct cognitive development term.
| Descriptor | Cognitive Term | |
| The ability to turn thoughts into actions marks the beginning of. | ||
| This is when a toddler looks for and tries to find an object in the last place they saw it. | ||
| The ability to imitate actions by remembering past events that have been observed is known as. | ||
| Receiving and storing individual pieces of sensory data in the memory is. | ||
| When a toddler pretends to pour a cup of tea and drink from an empty cup it’s called. |
|
|
| The toddler’s activities become more purposeful as the child plans and experiments. |
|
|
| By 18 months, most children know how to use different tools such as utensils for eating, pens for drawing and keys to open doors. | ||
| A two year old can now identify themselves as a separate person and begin to show empathy for others. |
Question 3 (b)
Question 4
Question 4 (a)
In the following scenario, the Educator has used the technique known as ‘scaffolding’ to help Nailah persevere and achieve success. Explain how the Educator scaffolds Nailah’s learning? |
Question 4 (b)
006 Communication
006 Communication readings
Readings
006 Communication assessment tasks
Question 1
Question 1 (a)
| Language development refers to: |
Question 1 (b)
Question 1 (c)
| Language development is divided into two areas – receptive language and expressive language. |
|
Question 2
Readings
For each of the following scenarios consider how the Educator could respond to the child to promote the development of verbal communication skills.
Question 2 (a)
Question 2 (b)
| Suggest what you could say to Owen to encourage him to speak in a complete sentence. |

Readings
Question 2 (c)
Question 2 (d)
| Suggest a response that allows you to model language skills by expanding upon what Perri is doing. |
Question 3
Question
Question 4
Question
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
Question 5
Question
007 Supporting holistic development
007 Supporting holistic development readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
HBA Learner Guide
007 Supporting holistic development assessment tasks
Question 1
Question 1 (a)
| Answer | Scenario | Effective Encouragement Strategy |
| The ‘Reptile Show’ had come to the centre. Noah (3 years) began to hide behind the Educator, Sue, and refuse to sit in the circle with the other children. Sue said “Yes it is a bit scary isn’t it, Noah. When I’m scared, I find it best to take a big deep breath and stand next to someone who helps me feel safe. Would you like to sit next to me in the circle?” | ||
| Gillian watched Tess (4 years) walk, arms outstretched, along the balance beam. As Tess looked up at her, Gillian, the Educator, nodded and smiled broadly and stayed close by to show an interest in Tess’s efforts. |
|
|
| Michelle (3 years) was sitting at the top of the slide, holding on to the sides with both hands. Some other children were waiting for her to go down and she was becoming anxious. Peta, the Educator, came over to the slide and said calmly “I saw you go down the slide yesterday, Shelly, so I know you can do it. I’ll wait down here for you. Off you go!” |
|
|
| Megan, the Educator, was about to teach her group of four year old children a new circle game. They already knew ‘Punchinello’ so she wanted to introduce ‘Skip to My Lou’, a partner game. Today, Megan taught the song to sing with the game and the children practiced it a few times before standing up, to find a partner. The children learnt the first verse and in future group times, Megan will introduce the rest of the verses, one at a time. |
|
|
| “Wow. This is a hard puzzle, isn’t it Sara?” said Kylie the Educator. “You’re very clever with puzzles it’s one of your strengths. So, I’m sure that if you take your time and think about it carefully, you’ll finish it.” |
|
|
| Melanie, the Educator, smiled warmly Chrissy (11 months). Chrissy stretched out to reach the table top and attempted to pull herself up “You can do it” said Melanie, but she slipped back down. Chrissy started to frown. “Try again. That was close. You are such a clever girl. Give it one more try.” Chrissy gave a gigantic push up and successfully grasped the table top and stood up. Melanie clapped and cheered. |
Question 1 (b)
Suggest an experience that you could plan to support the child’s development in this area.
Question 2
Question
Choose one routine experience (such as morning tea, toileting, lunch) and list the possible learning opportunities for a child to acquire and practice skills in each of the areas listed in the table below.
| Routine Experience: | |
| Social Development: | Language/Communication Development: |
| Health and Physical Development: | Emotional Development: |
| Sustainable Practices: | Cognitive Development: |
Question 3
Readings
Question 3 (a)
Question 3 (b)
| How does the experience support creative development? |
Question 3 (c)
Question 3 (d)
| How does the experience support language development? |
 Question 4
Question 4
Readings
Question 4 (a)
Readings

Question 4 (b)
| Identify the positive and negative impacts each family may be having on the child’s development. |
Section 3 – Unit 3
CHCECE011 Provide experiences to support children’s play and learning
This unit describes the skills and knowledge required to support children’s play and learning. This unit applies to educators working in a range of education and care services.
Creating an environment that allows for individual and collaborative experiences
Providing a range of experiences to stimulate children and aid learning, including those that allow exploration of natural materials, environments and experiences.
CHCECE011 Provide experiences to support children’s play and learning readings
Australian Children’s Education and Care Quality Authority. (2011). Guide to the Education and Care Services National Law and the Education and Care Services National Regulations. ACT: Commonwealth of Australia.
Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations. (2009). Belonging, Being and Becoming: The Early Years Learning Framework for Australia. Canberra: DEEWR.
001 Playing
001 Playing readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
HBA Learner Guide
001 Playing assessment tasks
Question 1
Readings
Belonging, Being, Becoming: The Early Years Learning Framework
Question 1 (a)
Question 1 (b)
| How does play promote development (i.e. play as a context for learning)? |
Question 1 (c)
Complete the following sentences.
Question 1 (d)
Question 2
Question
| What are the important features of play? |
Question 3
Question
Match the type of play with the social play scenarios.
Types of Play |
|
| Social Play Scenarios | |
|
|
Question 4
Question
Match the type of play with the cognitive play scenarios.
| Cognitive Play Scenarios | |
|
|
Question 5
Question
Question 6
Question
Dramatic play provides children with a wide range of opportunities to promote learning and development.
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
002 Following interests
002 Following interests readings
002 Following interests assessment tasks
Question 1
Readings
Question 1 (a)
Question 1 (b)
Readings
| (ii) List three different play resources and equipment that you could place in the block area to foster children’s interest. |
Question 2
Question
003 Participations and interactions
003 Participations and interactions readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
HBA Learner Guide
003 Participations and interactions assessment tasks
Question 1
Question 1 (a)
| List the five key functions of Educators in relation to children’s play. |
Question 1 (b)
Question 2
Readings
Question 2 (a)
| How would address Eva’s behaviour whilst respecting her choice not to participate? |
Readings

Question 2 (b)
Readings

Question 2 (c)
| How would you address Harry whilst respecting his choice not to participate? |
Readings
Question 2 (d)
Question 3
Question
| Scenarios | Educator Response ü |
| Justin (3 years) offers you a wooden block and says, “Have a cup of tea.” | Say “You are always making cups of tea. Why don't you make coffee or cake, just for a change?'” “Thanks Justin. I've just got time for a quick cuppa before I wash the paint pots. I take milk though, do you have any?” |
| Catherine (5 years) kicks a ball towards you. | |
| Josh (4 years) tells you there is a monster under the bed. | Offer him a pretend biscuit and ask if he thinks the monster would like to eat it. Change the topic of conversation to something real and non-imaginary. |
| Madison (13 months) picks up a pair of dress up pants, puts them on her head and grins at you. | |
| The group of preschool children (3 - 5 years) are ready for the Educator to present the music session. She gets called to the office and you are left supervising the children while they wait for her return. | Encourage the children to sit quietly and wait Sing some familiar songs with the children, like ‘Open Shut Them’. |
Question 4
Readings
Question 4 (a)
Question 4 (b)
| Suggest an experience that Anne could plan to follow on from this discussion. |
Question 4 (c)
004 Play environments and safety
004 Play environments and safety readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
004 Play environments and safety assessment tasks
Question 1
Question 1 (a)
The objective of National Quality Standard (NQS) 3.2 is for services and Educators to provide an environment that is inclusive, promotes competence, independent exploration and learning through play. List six features Educators should provide when structuring the learning environment to meet this standard? |
Question 1 (b)
Question 2
| Example | Principle | |
| The room is divided into learning areas and each area is partially enclosed by furniture and equipment with clearly defined areas for traffic flow. Active areas are separate from quiet areas. | ||
| Learning areas are set up permanently with certain provisions always available within each area for children e.g. Blocks in block area. | ||
| The area is designed with low furniture and easily accessible toileting and hand washing facilities so that Educators can oversee all areas |
|
|
| Table and chairs are set up to define how many children can engage in an activity at any time; learning areas provide opportunities for children to be alone and play with others. There are multiples of resources to prevent conflicts. Soft furnishings reduce noise levels. |
|
|
| An indoor/outdoor program is utilised to allow maximum opportunities for children to interact with a variety of materials and engage in sustained play. | ||
| Outdoor areas are fenced, include self-closing gates and provide adequate shade. Climbing structures are kept away from fences. | ||
| The learning environment has photographs of all children and their families displayed Learning areas have wide access points to ensure all children can access the area. There are artefacts and displays from the local Aboriginal people available to children. | ||
| Furniture is at child height and resources are placed within children’s reach. |
Question 3
Readings
To assist you with this task refer to the reading:
Toy safety for pre-school, The Royal Children’s Hospital Safety Centre (2008).
Question 3 (a)
Question 3 (b)
| Statement | ü ü | |
| Play spaces for infants and toddlers need to take into account safety aspects such as choking hazards, trips and falls. | ||
| Children do not learn as much in outdoor environments as they do in the indoor environment. | True |
|
| The Regulations and Standards require all centre-based services to provide an outdoor play space that allows children to explore and experience the natural environment. | False |
|
| Educators should involve children in establishing routines that keep them safe. | ||
| Open-ended materials should be avoided for babies and toddlers. | True |
|
| Environments for young children should be aesthetically pleasing, invite participation, and stimulate interest, curiosity and explorations. | False |
|
| Educators need to assess safety within play environments whilst at the same time ensuring they provide challenging and promote risk taking. | ||
Question 3 (c)
005 Learning through play
005 Learning through play readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations. (2009). Belonging, Being and Becoming: The Early Years Learning Framework for Australia. Canberra: DEEWR.
Early Childhood Australia. (2011). Learning Outcomes. The Early Years Learning Framework Professional Learning Program e-Newsletter, 6. Retrieved from http://www.earlychildhoodaustralia.org.au/nqsplp/wp-content/uploads/2012/05/EYLFPLP_E-Newsletter_No6.pdf
005 Learning through play assessment tasks
Question 1
Readings
Question 1 (a)
This scenario links to the EYLF Outcome 4: Children are confident and involved learners. Children develop dispositions for learning such as curiosity, cooperation, confidence, creativity, commitment, enthusiasm, persistence, imagination and reflexivity |
Question 1 (b)
Question 1 (c)
| List three reasons why this experience would be appealing to preschool children (3 – 5 years). |
Question 1 (d)
Question 1 (e)
| What additional teaching strategies or resources can the Educator use to promote the children’s learning and engagement? |
Section 4 – Unit 4
CHCECE013 Use information about children to inform practice
This unit describes the skills and knowledge required to gather information about children through observation and other sources as a basis to inform program-planning cycles and to share with children and their families.
To achieve competency in this unit you will need to provide evidence of:
discussion with families
anecdotal information
Analysing observations of the children’s behaviour, including:
aspects of child’s development
Using information to contribute to program/planning.
CHCECE013 Use information about children to inform practice readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
Early Childhood Australia. (2011). Documenting Learning 2. The Early Years Learning Framework Professional Learning Program e-Newsletter, 10. Retrieved from http://www.earlychildhoodaustralia.org.au/nqsplp/wp-content/uploads/2012/05/EYLFPLP_E-Newsletter_No10.pdf
Early Childhood Australia. (2012). Observing Children. National Quality Standard Professional Learning Program e-Newsletter, 39. Retrieved from http://www.earlychildhoodaustralia.org.au/nqsplp/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/NQS_PLP_E-Newsletter_No39.pdf
001 Observation skills
001 Observation skill readings
HBA Learner Guide
Refer to Section 12 in the HBA Learner Guide for CHC30113 Certificate III in Early Childhood Education and Care
001 Observation skill assessment tasks
Question 1
Question
Question 2
Question
| List the types of narrative observations that may be used in a children’s service. |
Question 3
Readings
Question 3 (a)
Question 3 (b)
The reading describes how Educators can collaborate with families, other Educators and the child to gather information to build a holistic picture of children.
Match the strategy used to gather information with the type of information that may be gathered.
|
|
|
|
|
Question 3 (c)
Question 4
Question
| Child’s situation | Purpose of observation | |
| Kasim (3 years 6 months) has been attending the centre for 18 months. He tends to spend a great deal of time standing and watching others but does not join in their play. | ||
| Nadia (8 months) has only been at the centre for 2 weeks. Her mother asks how she is coping. | ||
| Erin (4 years) loves puzzles. The Educator has presented her with a new geometric puzzle that he thinks will challenge Erin. | ||
| The Educator in the 2’s room is reviewing her goals for the children in relation to the children’s developing independence. |
|
|
| Jie (2 years) seems to fall over quite often when playing outdoors. |
|
|
| The Educators are working on a design to revamp the outdoor area. They need to decide what elements of the play space to replace and what elements to keep. |
Question 5
Question
Question 6
Question
Objective: Presents facts without opinion
Subjective: Represents personal opinion which may not be accurate
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
|
|
Question 7
Question
Match each statement with the descriptor that best defines why the statement is unprofessional.
Descriptors:
002 Observing children
002 Observing children readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
HBA Learner Guide
Early Childhood Australia. (2012). Summative Assessment. National Quality Standard Professional Learning Program e-Newsletter, 40. Retrieved from http://www.earlychildhoodaustralia.org.au/nqsplp/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/NQS_PLP_E-Newsletter_No40.pdf
002 Observing children assessment tasks
Question 1
Question
Look at each photo and scenario.
Troy is jumping on the trampoline, counting each jump ‘one two three…. |
||
 The Educator and the children
are discussing plants whilst gardening together. The Educator and the children
are discussing plants whilst gardening together. |
Language – talking/listening Gross Motor- eye-foot coordination |
Language- Literacy Social – interactions with others |
|||
Gross Motor- dynamic balance Social - interactions |
|||
Question 2
Readings
Question
This task requires you to look closely at each photograph and tick the two correct statements.
003 Elyse
003 Elyse readings
Refer to Section 12 in the HBA Learner Guide for CHC30113 Certificate III in Early Childhood Education and Care
003 Mitch assessment tasks
Question 1
Question 1 (a)
Look at the photos of Elyse (9 months) who is an active crawler. Match the observations of Elyse’’s motor skills to the photographs.
| Photograph | Observation |
| Elyse holds on with one hand while manipulating another object on the table. | |
| Elyse shifts to a crouching position while manipulating the objects. | |
| Elyse is able to sit without support, move her body forward and reach out with his arm while maintaining balance |
Question 1 (b)
004 Ryan
004 Ryan readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
HBA Learner Guide
004 Ryan assessment tasks
Question 1
Readings
you. Can you see the cow? Here it comes. Here comes the cow Ryan, it’s getting close! Do you think when a cow says beep that’s funny? Here it is. Here’s the cow Ryan. |
Question 1 (a)
Question 1 (b)
| How does Kate know she has Ryan’s attention? |
Question 1 (c)
Question 1 (d)
| What does this observation tell us about Ryan’s social development? |
Question 1 (e)
Question 1 (f)
| The Educator would like to extend support and foster the development of Ryan’s social and/or language development. |
|
005 Mr Crocodile
005 Mr Crocodile readings
To complete these tasks you will need to refer to the relevant chapter in your Learner guide for underpinning knowledge:
005 Mr Crocodile assessment tasks
Question 1
Readings
Question
006 Misha
006 Misha readings
Readings
Early Childhood Australia. (2011). Documenting Learning. The Early Years Learning Framework Professional Learning Program e- Newsletter, 9. Retrieved from http://www.earlychildhoodaustralia.org.au/nqsplp/wp-content/uploads/2012/05/EYLFPLP_E-Newsletter_No9.pdf
Early Childhood Australia. (2011). Documenting Learning 2. The Early Years Learning Framework Professional Learning Program e-Newsletter, 10. Retrieved from http://www.earlychildhoodaustralia.org.au/nqsplp/wp-content/uploads/2012/05/EYLFPLP_E-Newsletter_No10.pdf
006 Misha assessment tasks
Question 1
Question 1 (a)
Misha’s personality, temperament, her self-confidence/self-esteem
Misha’s ability to make purposeful play choices
| Example Observation | Analysis/interpretation |
Educator: “Well done, Misha!” Misha sat astride for a moment at the top and carefully climbed When she reached the bottom of the slide she smiles, gave herself a clap and said “Misha clever girl!” |
Seeks approval of Educator. |
| Observation 1 | Analysis/interpretation |
Misha is pushing a doll around the room in a pram. She has a shopping basket over her arm and is wearing a hat and shoes from dress-up. As she walks along Misha stops to look at her doll, she smiles and sometimes gives the doll a kiss. |
. |
| Observation 2 | Analysis/interpretation |
Misha nods, takes Alec’s hand and drags him towards the door. She looks up at Alec and says, “Dolly.” Alec: “Would you like me to get you a teddy Misha?” Misha: “Teddy” (Nods) |
Question 1 (b)
An example skill/knowledge has been provided for each domain of development.
Question 1 (c)
| Suggest two areas of play that are of interest to Misha: |
Question 1 (d)
Question 1 (e)
| Describe an experience that will achieve this goal utilising one of Misha’s Interest area from Question 1c. |




