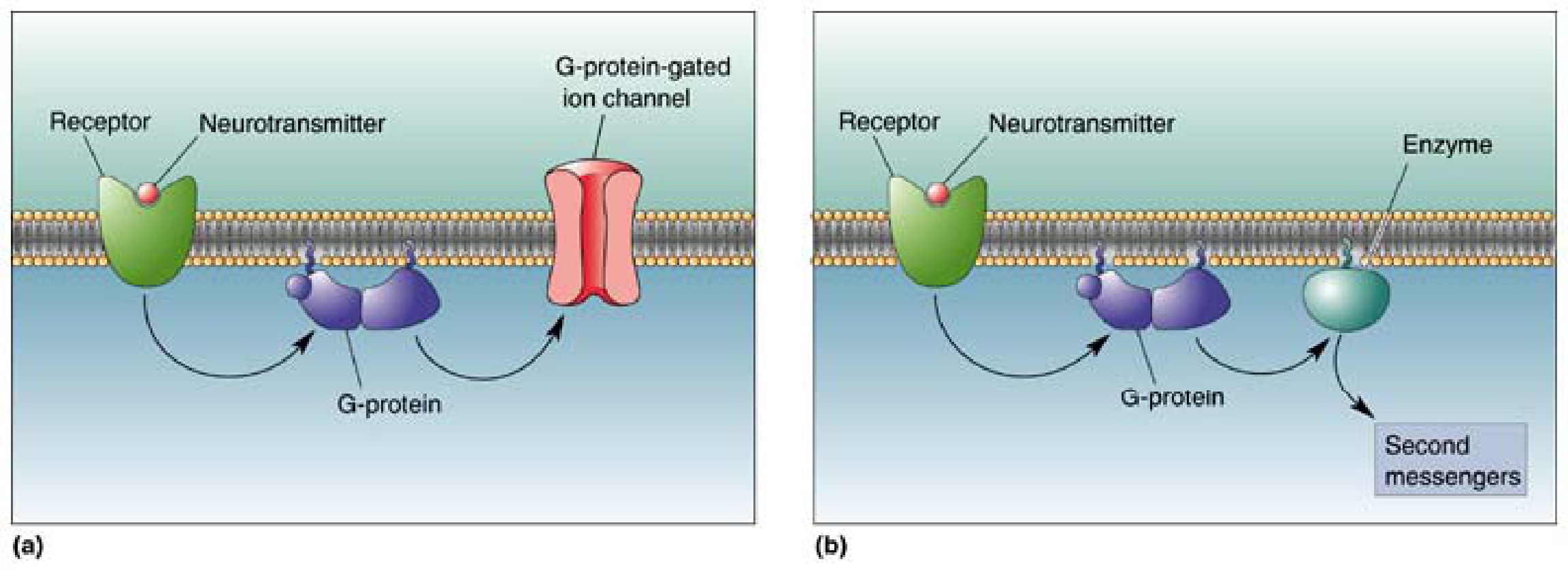
Ach receptors heart are metabotropic and inhibitory
• Chemical synapses: release of transmitter which binds to postsynaptic receptor
– Slow but __________; postsynaptic cells add up signals from many presynaptic inputs
• Fast EPSPs & Fast IPSPs + ‘modulatory’ postsynaptic effects – Type of response depends on receptor _____ionotropic & metabotropic.e.g. ACh receptors on heart are metabotropic and inhibitory, but ACh receptors on skeletal muscle are ionotropic & excitatory
2. Action potential depolarizes terminal causing opening of voltage-gated
________ channels
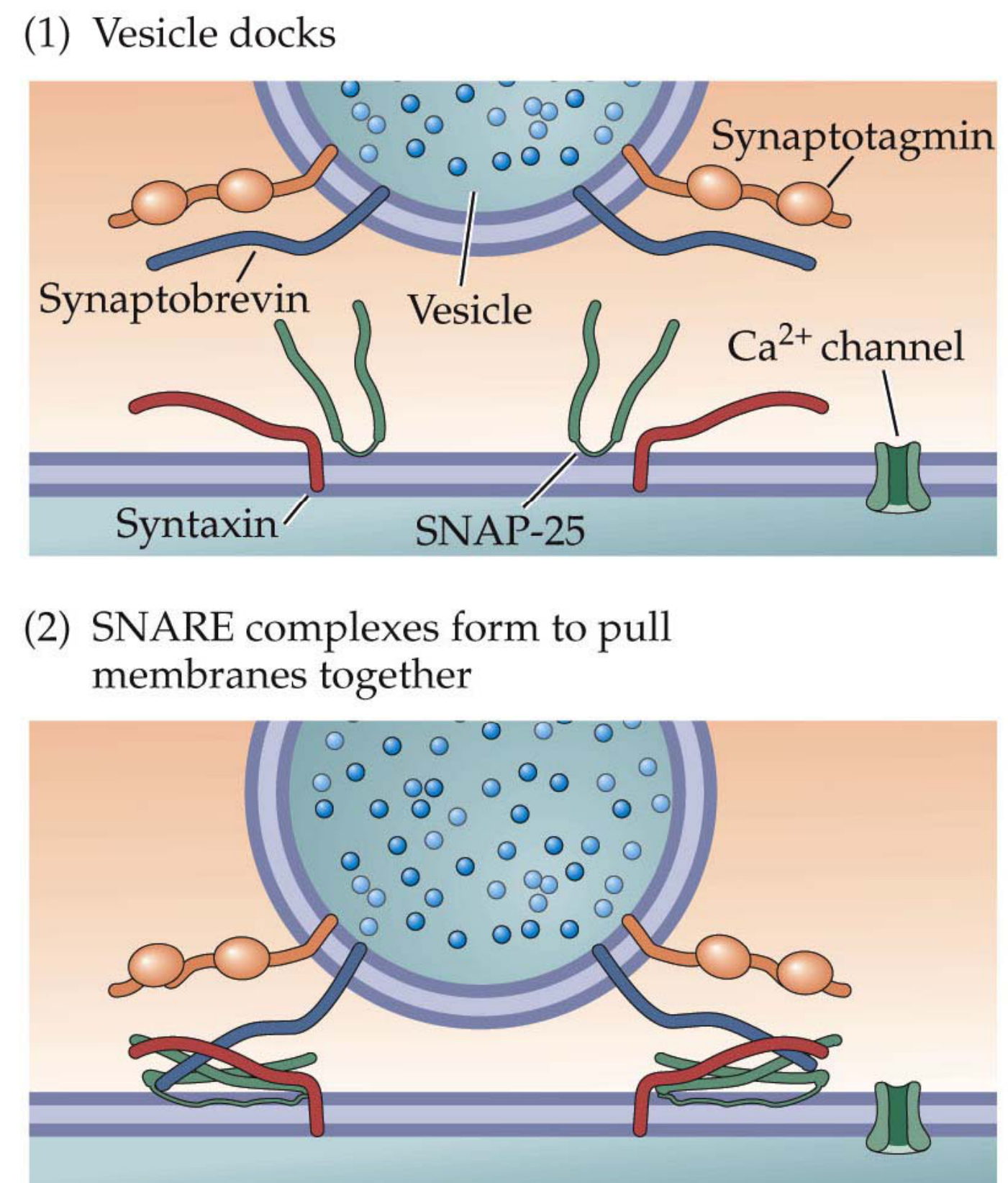
Snare Complex & Vesicle Fusion Fig. 5.14B
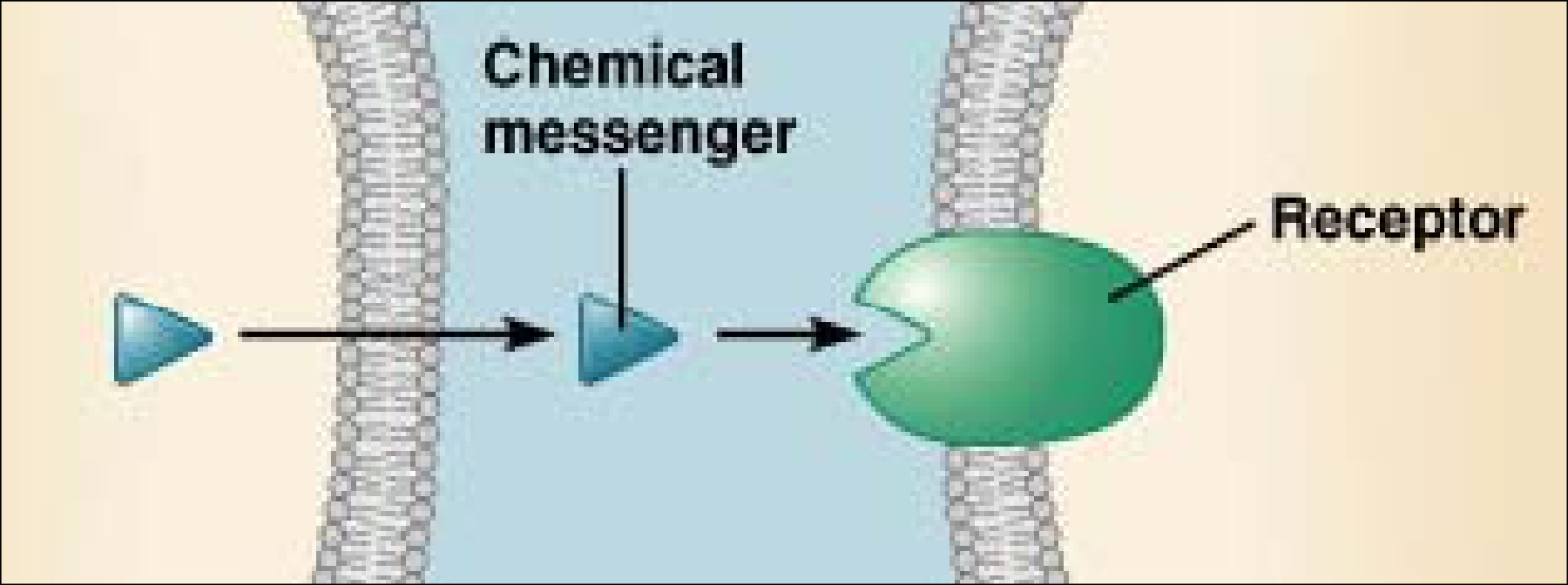
Receptors for chemical messengers
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
|---|
Acetylcholine receptor structure and other
transmitter-gated ion channel receptors similarTransmitter-gated ACh receptor
Excitatory postsynaptic potential: EPSP
• Neurotransmitter-gated ion channels permeable to both Na+& K+ bring Vm toward __________
Result is an ‘excitatory postsynaptic
potential’: ‘EPSP’
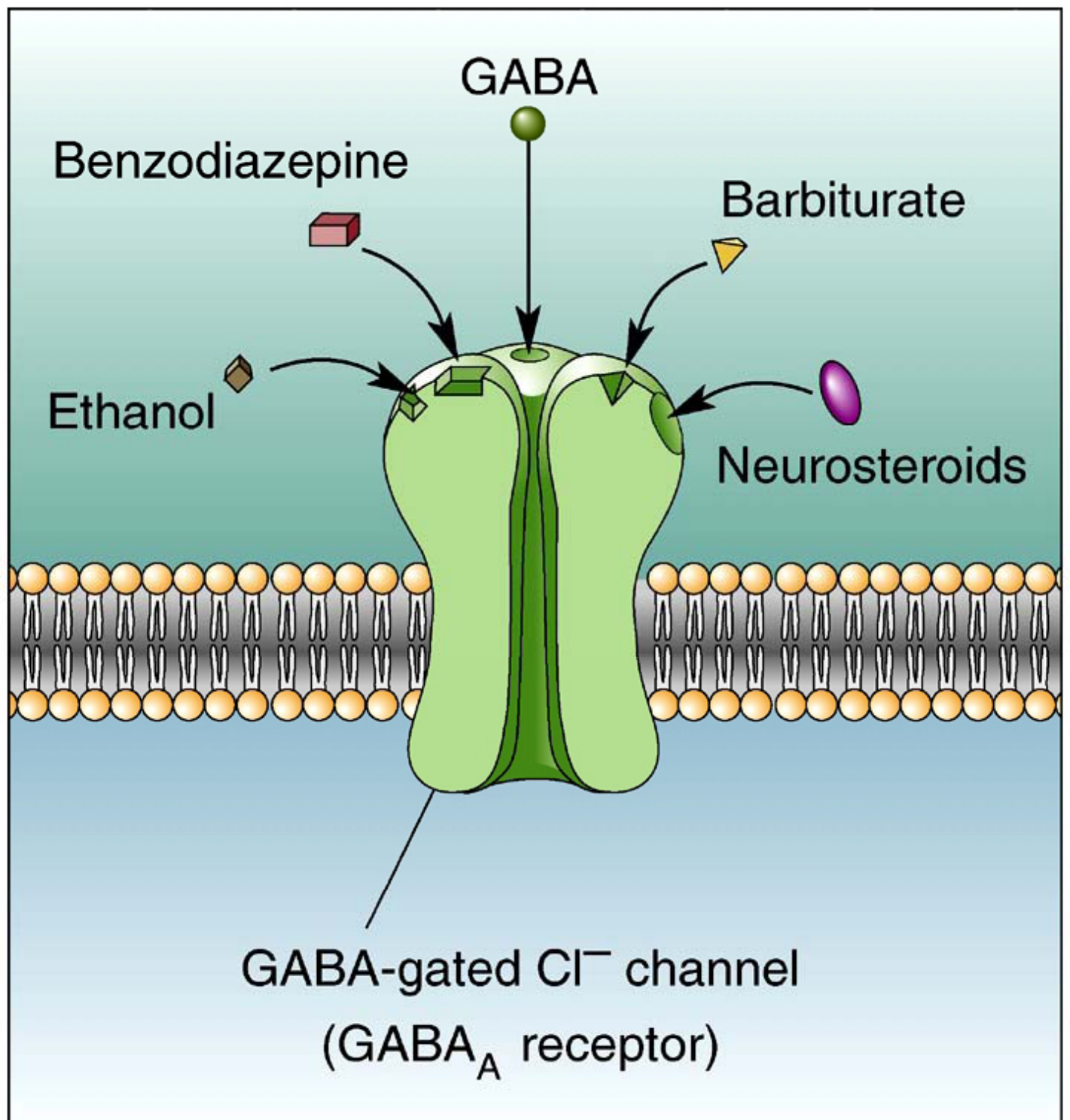
– ACh- and __________gated ion channels result in EPSPs
ECl- = _______
– Result is an IPSP– _____-gated ion channel receptors
• ACh cleared from neuromuscular junction by acetylcholinesterase: Nerve gases inhibit this enzyme
• After reuptake, monoamine oxidase (MAO) metabolizes the amines serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine. MAO inhibitors are used to treat Parkinson s disease and also as antidepressants
|
|---|
at same synapse
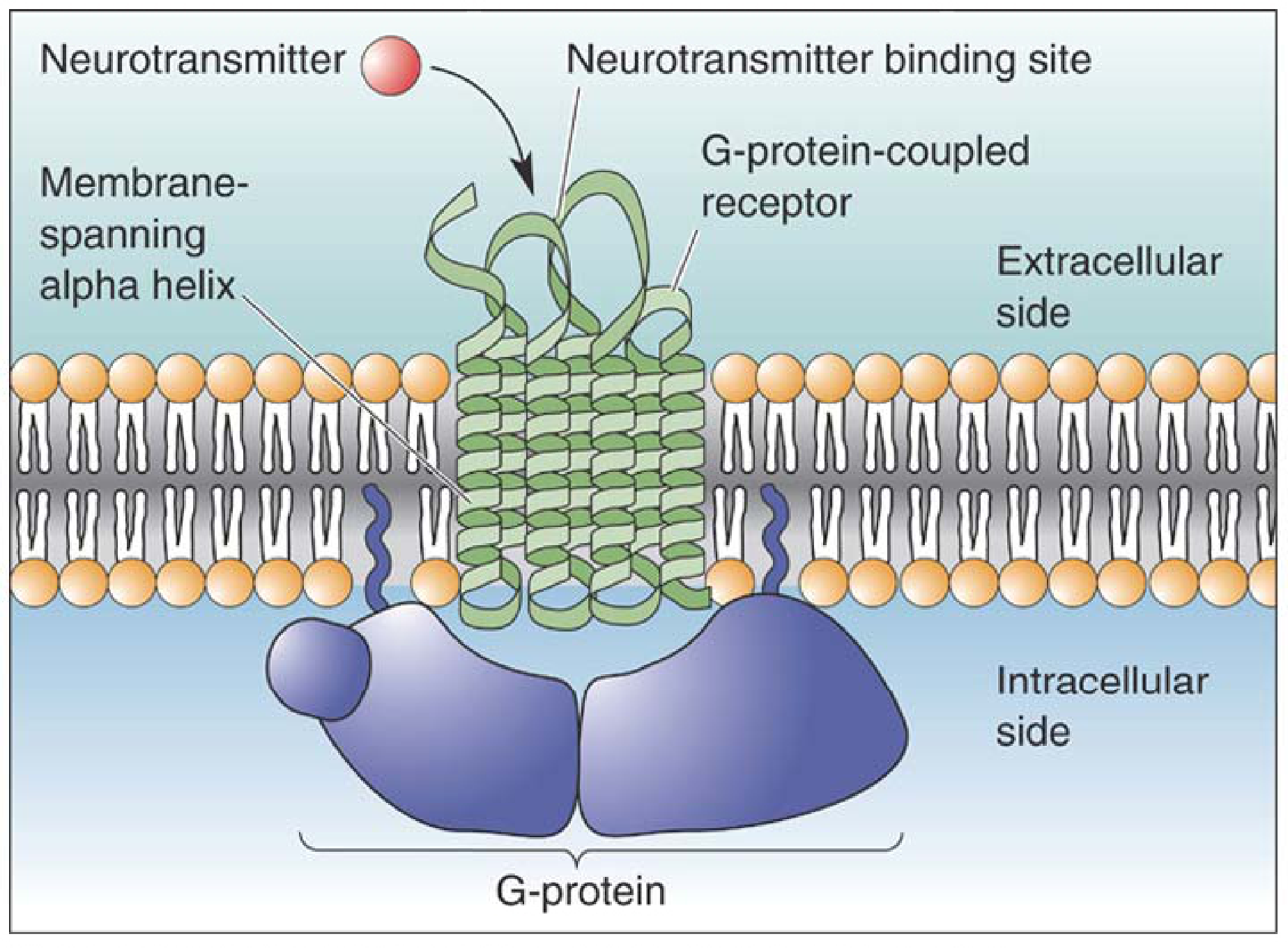
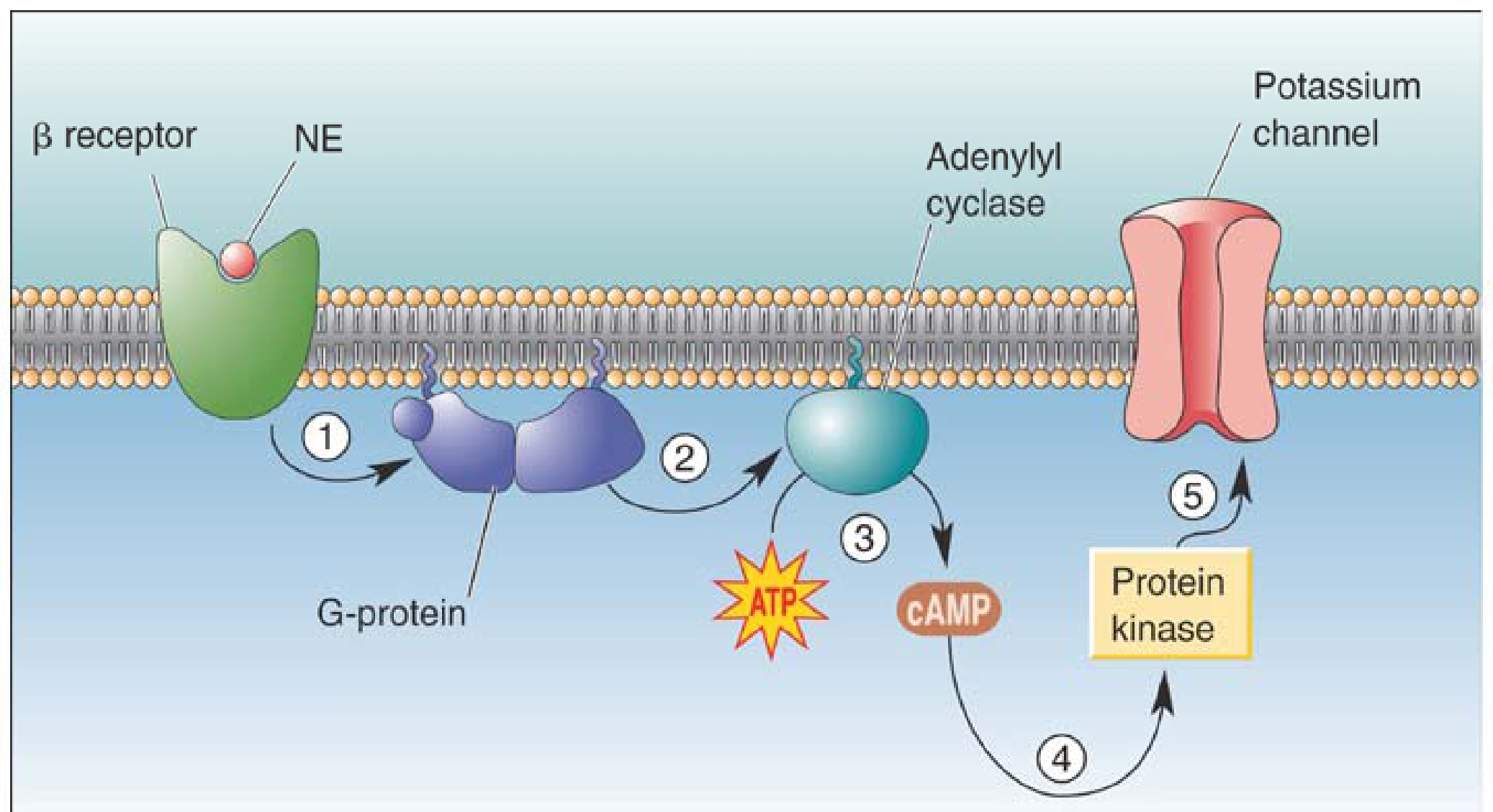
G-protein coupled receptors GPCRs)• Single protein with _ membrane spanning domains
| • |
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| 1. | ||
| 2. | ||
| 3. | ||
receptor __________
Acetylcholine (ACh)
|
|---|
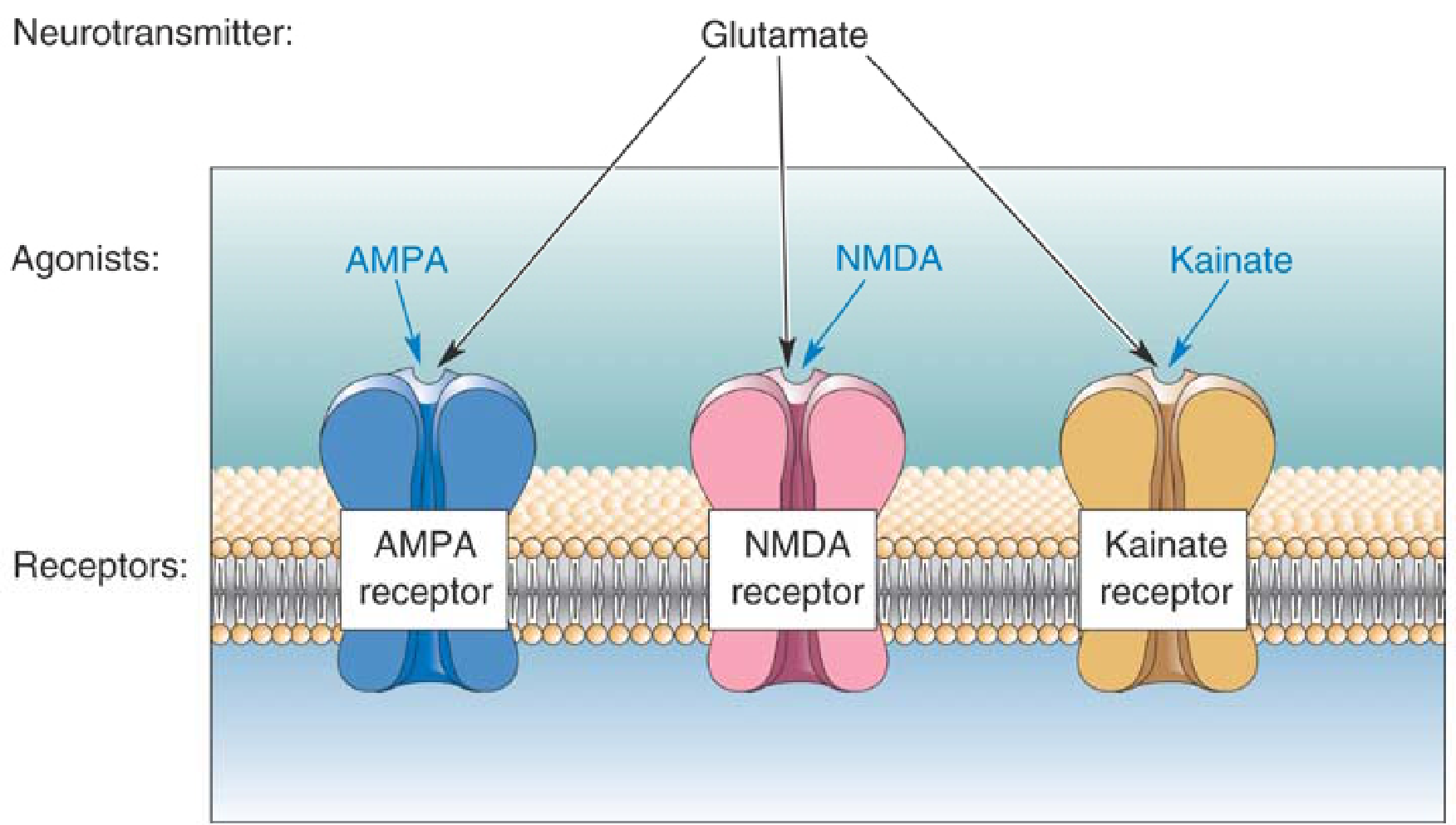
Glutamate
| – |
|---|
 |
|
|---|
• On Sakai
– Quiz 2
– Submission deadline: Friday, Sept 24 at 10 PM