And default gateway settings pc-b configure the router


This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted
to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive
use by instructors in the CCNA Routing and Switching: Routing and Switching
Essentials course as part of an official Cisco Networking Academy Program.

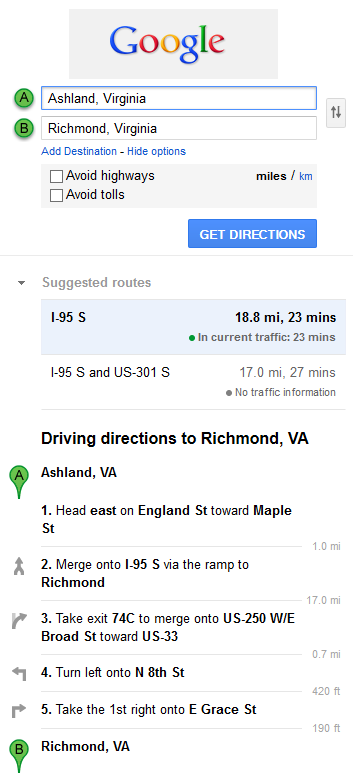
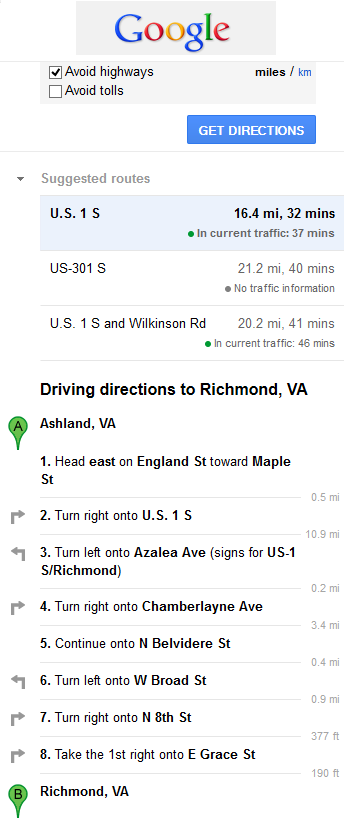
Routers send and receive information from networks they recognize. The routing table is a very important
tool to supply the network administrator with information about how a network delivers data from source to
Notice that in many cases, Google Maps suggests more than one route between the two locations you chose. It also allows you to put additional constraints on the route, such as avoiding highways or tolls.
|
|---|
• Internet connection
• Web browser
These instructions closely resemble information in routing tables of IP-based routers. Each crossing can be likened to a router on which the next path selection takes place. The overall length and duration of the route correspond to the route metric, or a measure of its usefulness, from the source to the destination. The advice on which next direction to take from a particular crossing resembles an entry in the particular router’s routing table that contains information about the nearest next hop router on the path towards the destination. The distance to the next crossroad is similar to the so-called cost of an interface that is used by routing protocols to compute the resulting metric of a route.
2. If Google Maps offered a set of different routes, what makes this route different from the first? Why would you choose one route over another?
3. What criteria can be used to evaluate the usefulness of a route?
_______________________________________________________________________________________ Criteria could include:
Modeling Activity Graphic Representation (designs will vary)
Instructor Note: Listed below is representative output from the Google Maps site for Instructor use only.
 |
 |
|---|
• Routing Table
• Bandwidth
• Static Route
© 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 3 of 3
Part 1: Determine Network Connectivity to a Destination Host
Part 2: Trace a Route to a Remote Server Using Tracert
(Microsoft Windows systems)
or
The displayed list can help identify data flow problems when trying to access a service such as a website. It can also be useful when performing tasks, such as downloading data. If there are multiple websites (mirrors) available for the same data file, one can trace each mirror to get a good idea of which mirror would be the fastest to use.
Command-line based route tracing tools are usually embedded with the operating system of the end device. This activity should be performed on a computer that has Internet access and access to a command line.
To trace the route to a distant network, the PC used must have a working connection to the Internet. Use the ping command to test whether a host is reachable. Packets of information are sent to the remote host with instructions to reply. Your local PC measures whether a response is received to each packet, and how long it takes for those packets to cross the network.
© 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 3
Africa: www.afrinic.net
Australia: www.apnic.net
Part 2: Trace a Route to a Remote Server Using Tracert
After you determine if your chosen websites are reachable by using ping, you will use tracert to determine the path to reach the remote server. It is helpful to look more closely at each network segment that is crossed.
a. At the command-line prompt, trace the route to Save the tracert output in a text file. Alternatively, you can redirect the output to a te or >>.
C:\Users\User1> tracert www.cisco.com
Tracing route to e144.dscb.akamaiedge.net [23.67.208.170] over a maximum of 30 hops:
1 1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 192.168.1.1
2 14 ms 7 ms 7 ms 10.39.0.1
3 10 ms 8 ms 7 ms 172.21.0.118
4 11 ms 11 ms 11 ms 70.169.73.196
5 10 ms 9 ms 11 ms 70.169.75.157
6 60 ms 49 ms * 68.1.2.109
7 43 ms 39 ms 38 ms Equinix-DFW2.netarch.akamai.com [206.223.118.102] 8 33 ms 35 ms 33 ms a23-67-208-170.deploy.akamaitechnologies.com [23.67.208.170]Europe: www.ripe.net
South America: www.lacnic.net
Answers will vary. cox.net, level3.com, registro.br
c. Compare the lists of domains crossed to reach the final destinations.
Answer will vary but could include network outages, high traffic loads, firewall blocking ICMP packets, ACL on intermediary devices prevents ICMP packets and asymmetric forwarding paths.
© 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 3 of 3
activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide additional practice.
Topology
Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices
• Cable equipment to match the network topology.
• Verify network connectivity.
• Configure the router for SSH.
• Verify the status of the interfaces.
Part 4: Configure IPv6 and Verify Connectivity
Lab – Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
In Part 3, you will use SSH to connect to the router remotely and utilize IOS commands to retrieve information from the device to answer questions about the router. In Part 4, you will configure IPv6 on the router so that PC-B can acquire an IP address and then verify connectivity.
• 1 Router (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable)
• 1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Part 2: Configure Devices and Verify Connectivity
Step 1: Configure the PC interfaces.
Router> enable
Router#
Router(config)# hostname R1
d. Disable DNS lookup to prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were hostnames.R1(config)# no ip domain-lookup
e. Require that a minimum of 10 characters be used for all passwords.R1(config)# line con 0
R1(config-line)# password ciscoconpass
R1(config-line)# exec-timeout 5 0
R1(config-line)# login
R1(config-line)# logging synchronous
R1(config-line)# exit
R1(config)#
For the exec-timeout command, what do the 5 and 0 represent?____________________________________________________________________________________ The session will timeout in 5 minutes and 0 seconds.
© 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 3 of 17
Lab – Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
R1# copy running-config startup-config
Destination filename [startup-config]?Building configuration...
configuration. Upon a reboot, a user would be asked if they would like to enter initial configuration dialog.
Step 3: Verify network connectivity.
____________________________________________________________________________________
Telnet
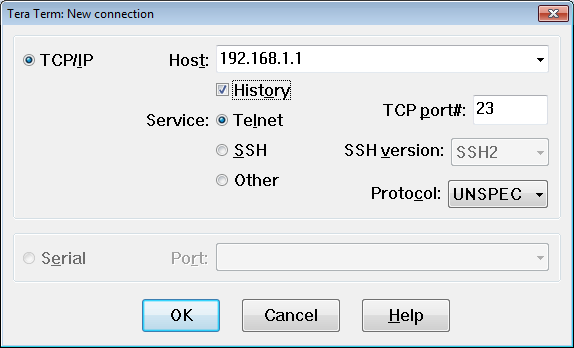
Was remote access successful? ____ Yes
a. Enable SSH connections and create a user in the local database of the router.
R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# ip domain-name CCNA-lab.com
R1(config)# username admin privilege 15 secret adminpass1 R1(config)# line vty 0 4
R1(config-line)# transport input ssh
R1(config-line)# login local
R1(config-line)# exit
R1(config)# crypto key generate rsa modulus 1024
R1(config)# exit
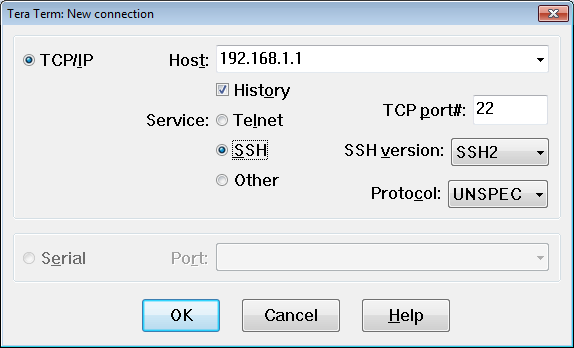
Was remote access successful? ____ Yes
Step 2: Retrieve important hardware and software information.
a. Use the show version command to answer questions about the router.
This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to United States and local country laws governing import, export, transfer and use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply
third-party authority to import, export, distribute or use encryption.© 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 6 of 17
Cisco CISCO1941/K9 (revision 1.0) with 446464K/77824K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID FTX1636848Z
2 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
2 Serial(sync/async) interfaces
1 terminal line
DRAM configuration is 64 bits wide with parity disabled. 255K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
| Device# |
|
|
|---|
What is the name of the IOS image that the router is running?
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Answers may vary, but the output from the show version on 1941 router is: 255K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
b. The show commands often provide multiple screens of outputs. Filtering the output allows a user to display certain sections of the output. To enable the filtering command, enter a pipe (|) character after a show command, followed by a filtering parameter and a filtering expression. You can match the output to the filtering statement by using the include keyword to display all lines from the output that contain the filtering expression. Filter the show version command, using show version | include register to answer the following question.
R1# show version | include register
Configuration register is 0x2142Use the show startup-config command on the router to answer the following questions.
R1# show start
Using 1674 out of 262136 bytes
!security passwords min-length 10
enable secret 4 3mxoP2KRPf3sFHYl6Vm6.ssJJi9tOJqqb6DMG/YH5No !no aaa new-model
!no ip domain lookup
ip domain name CCNA-lab.com
ip cef
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!!
interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0
no ip address
shutdown
!interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description Connection to PC-B
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!control-plane
!Lab – Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
exec-timeout 5 0
password 7 060506324F410A160B0713181F
logging synchronous
login
line aux 0
line 2
no activation-character
no exec
transport preferred none
transport input all
transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 5 0
password 7 060506324F411F0D1C0713181F
logging synchronous
login local
transport input ssh
!____________________________________________________________________________________
Passwords are encrypted due to the service password-encryption command. The line con password of ciscoconpass is encrypted as 060506324F410A160B0713181F. The line vty password of ciscovtypass is encrypted as 060506324F411F0D1C0713181F.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Lab – Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
R1# show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override_______________________________________________________________________________________
The C designates a directly connected subnet. An L designates a local interface. Both answers are correct.
What command changed the status of the Gigabit Ethernet ports from administratively down to up?
____________________________________________________________________________________
© 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 11 of 17
Lab – Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
If no IPv6 address is assigned to G0/1, why is it listed as [up/up]?
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Answers will vary. IPv6 address of 2001:db8:acad:a:d428:7de2:997c:b05a
1. In researching a network connectivity issue, a technician suspects that an interface was not enabled. What show command could the technician use to troubleshoot this issue?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________ show startup-config or show running-config
3. After configuring IPv6 on the R1 G0/0 PC-B LAN, if you were to ping from PC-A to the PC-B IPv6 address, would the ping succeed? Why or why not?_______________________________________________________________________________________ The ping would fail because R1 interface G0/1 was not configured with IPv6 and PC-A only has an IPv4 address.
Appendix A: Initializing and Reloading a Router and Switch
© 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 13 of 17
