And the price level michael parkin modular level
Questions 1 through 18 relate to Ethical and Professional Standards.
Answer = A
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard III (B) Fair Dealing
Study Session 1–2–c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard I (B) Independence and Objectivity
Study Session 1–2–c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.C is correct because Standard I (B) Independence and Objectivity requires members and candidates to use reasonable care and judgment to maintain their independence and objectivity in their professional activities. Best practice dictates that Kumar only accept transportation to the remote mining sites in that it is unlikely he would be able to source commercial flights to the locations and ground transport may not be viable. Because Kumar would normally visit mining sites around the world as part of his job and because he is combining this trip with trip to other mine sites in different countries, it would be inappropriate for Cerberus to pay for the analyst’s travel expenses from London. Although Kumar could go on safari with the group of analysts, he should pay his own way so as to restrict any influence such a gift could possibly have when making his investment recommendations on Cerberus.
B is correct because Naib knowingly misrepresented his qualifications by stating he had obtained an MBA degree at the time of his hire when in fact he had not. This reflects adversely on his professional integrity, violating Standard I (D) Misconduct. Stating he passed his CFA exams in three consecutive years is not a violation of Standard VII (B) Reference to CFA Institute,
the CFA Designation, and the CFA Program if it is factual. There is no evidence given to indicate he did not pass as claimed.
C is correct because Standard III (A) Loyalty, Prudence and Care stipulates that the client owns the brokerage. Therefore members and candidates are required to only use client brokerage to the benefit of the clients (soft commissions policy). Because the firm specializes in domestic equity, an offshore investment database service would not benefit clients.
5.Elbie Botha, CFA, an equity research analyst at an investment bank, disagrees with her research team’s buy recommendation for a particular company’s rights issue. She acknowledges the recommendation is based on a well-developed process and extensive research but feels the valuation is overpriced based on her assumptions. Despite her contrarian view, her name is included on the research report to be distributed to all of the investment bank’s clients. To avoid violating any CFA Institute standards, it would be least appropriate for Botha to undertake which of the following?
C is correct because Standard IV (A) calls for employees to be loyal to their employer by not causing harm. If Botha released a contradictory research recommendation report to clients, it could possibly cause confusion amongst clients and embarrassment to the firm.
6.Colleen O’Neil, CFA, manages a private investment fund with a balanced global investment mandate. Her clients insist that her personal investment portfolio replicate the investments within their portfolio to assure them she is willing to put her money at risk. By undertaking which of the following simultaneous investment actions for her own portfolio would O’Neil most likely be in violation of Standard VI (B) Priority of Transactions?
7.Christina Ng, a Level I CFA candidate, defaulted on a bank loan she obtained to pay for her Master’s degree tuition when her wedding cost more than expected. A micro finance loan company lent her money to pay off the tuition loan in full, including penalties and interest. The micro finance loan company even extended further credit to pay for her parents’ outstanding medical bills. Unfortunately, her parents’ health problems escalated to the point where Ng had to take extensive time away from work to deal with the issues. She was subsequently fired and consequently defaulted on the second loan. Because she was no longer employed, Ng decided to file for personal bankruptcy. Do the loan defaults leading up to Ng’s bankruptcy most likely violate Standard I (D) Misconduct?
A. No
B. Yes, with regard to the first loan default8.Charles Mbuwanga, a Level III CFA Candidate, is the business development manager for Sokoza Investment Group, an investment management firm with high-net-worth retail clients
throughout Africa. Sokoza introduced listed Kenyan Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) to its line of investment products based on new regulations introduced in Kenya so as to diversify its product offering to clients. The product introduction comes after months of researching Kenyan property correlations with other property markets and asset classes in Africa. Sokoza assigns Mbuwanga as part of the sales team in introducing this product to its clients across Africa.Mbuwanga subsequently determines most of Sokoza’s clients’ portfolios would benefit from having a small Kenyan property exposure to help diversify their investment portfolios. By promoting the Kenyan REITs for Sokoza’s client portfolios as planned, Mbuwanga would least likely violate which of the following standards?
done. He may also be in violation of Standard I (A) Knowledge of the Law in that he would need to determine if the Kenyan REIT product is allowable in each of the countries where his clients reside.
9.Victoria Christchurch, CFA, is a management consultant currently working with a financial services firm interested in curtailing its high staff turnover, particularly amongst CFA
charterholders. In recent months, the company lost 5 of its 10 most senior managers, all of whom have cited systemic unethical business practices as the reason for their leaving. To curtail staff turnover by encouraging ethical behavior, it would be least appropriate for Christchurch to recommend the company do which of the following?Under Standard I (A) Knowledge of the Law, CFA charterholders and candidates must
disassociate themselves from unethical behavior. Because the unethical business practices are seen as systemic, it would likely require them to leave the firm. Implementing a whistleblowing policy and adopting a corporate code of ethics would likely help to build a foundation of strong ethical behavior.10.Henrietta Huerta, CFA, writes a weekly investment newsletter to market her services and obtain new asset management clients. A third party distributes the free newsletter on her behalf to those individuals on its mailing list. As a result, it is widely read by thousands of individual investors. The newsletter recommendations reflect most of Huerta’s investment actions. After completing further research on East-West Coffee Roasters, Huerta decides to change her initial buy recommendation to a sell. To avoid violating the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct it would be most appropriate for Huerta to distribute the new investment
recommendation to:“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Section Standard III (A) Loyalty, Prudence, and Care Study Session 1–2–c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.B is correct because according to Standard III (A) Loyalty, Prudence and Care members and candidates must place their clients’ interests first before their own interests. The temptation may be to release the changed recommendation to newsletter recipients simultaneously with or even before the asset management clients to try to obtain new clients. However, to avoid violating Standard III (A) Loyalty, Prudence and Care, Huerta must ensure any change in an investment recommendation is first distributed to her asset management clients before any newsletter recipients, who are not necessarily clients (that is, they receive the newsletter for free from a third party distribution list).
C is correct because Deschutes most likely violated Standard III (E) Preservation of
Confidentiality by failing to preserve the confidentiality of client records when she disclosed specific details about clients in the equity portfolio.12.When Abdullah Younis, CFA, was hired as a portfolio manager at an asset management firm two years ago, he was told he could allocate his work hours as he saw fit. At that time, Younis served on the board of three non-public golf equipment companies and managed a pooled investment fund for several members of his immediate family. Younis was not compensated for his board
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard IV (B) Additional Compensation Arrangements, Standard VI (A) Disclosure of Conflicts
Study Session 1–2–c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.A is correct because golf equipment is a business independent of the financial services industry such that any board obligations would not likely be considered a conflict of interest requiring disclosure according to Standard IV (B) Additional Compensation Arrangements. Standard IV (B) requires members and candidates to obtain permission from their employer before accepting compensation or other benefits from third parties for the services that might create a conflict with their employer’s interests. Managing investments for family and non-family members could likely create a conflict of interest for Younis’ employer and should be disclosed to his employer.
“Guidance for Standards I–VII”, CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard IV (C) Responsibilities of SupervisorsStudy Session 1–2–b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard III (B) Fair Dealing, Standard V (A) Diligence and Reasonable Basis, Standard VI (B) Priority of Transactions
Study Session 1–2–b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.A is correct because the analyst violated Standard III (B) Fair Dealing by selectively distributing the recommendation only to investment banking clients despite being responsible for making investment recommendations to all group clients. Schleif should distribute the change in recommendation to all clients who received the initial recommendation, not just those within the investment banking division of the group.
Answer = A
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard V (A) Selecting External Advisers and Subadvisers
Study Session 1–2–b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard VI (C) Referral Fees
Study Session 1–2–c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.C is correct because the referral arrangements should be disclosed to potential clients “before entry into any formal agreement for services” and not after the fact. This allows potential clients to consider whether the arrangement causes them any potential harm as a result of the arrangement (e.g., higher fees and potential conflicts of interests).
Answer = C
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard VII (A) Confidential Program Information Study Session 1–2–b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.A. Statement 1
B. Statement 2
C. Statement 3Answer = C
19.The nominal (quoted) annual interest rate on an automobile loan is 10%. The effective annual rate of the loan is 10.47%. The frequency of compounding periods per year for the loan is closest to:
A.weekly.
B is correct. Use the formula for effective annual rate: EAR = (1 + Periodic interest rate)m – 1.
Iteratively substitute the possible frequency of compounding until the EAR is 10.47%.
C.mesokurtotic (identical to the normal distribution in peakedness).
Answer = B
| Observation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | –3 | –11 | 3 | –18 | 18 | 20 | –6 | 9 | 2 | –16 |
The sample standard deviation is closest to:
A. 11.92.
B.12.50.
C.13.18.The sample standard deviation is the (positive) square root of the sample variance.
A.0.1.
B.0.3.
C.0.7.Answer = A
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Sud,du = 79.2 | ||
|
The initial value of the stock is $80. The probability of an up move in any given period is 75% and the probability of a down move in any given period is 25%. Using the binomial model, the probability that the stock’s price will be $79.20 at the end of two periods is closest to:
Construct a binomial tree to describe stock price movement.
B is correct. Across two periods, there are four possibilities: • an up move followed by an up move ($96.8 end value), • an up move followed by a down move ($79.2 end value),
24.Which of the following statements of null and alternative hypotheses requires a two-tailed test?
A.H0: θ = θ0 versus Ha: θ ≠θ0
B.H0: θ ≤ θ0 versus Ha: θ >θ0
C.H0: θ ≥ θ0 versus Ha: θ <θ0A.support level.
B.resistance level.
26.You are given the following discrete uniform probability distribution of gross profits from purchase of an option:
“Common Probability Distributions,” Richard A. DeFusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 9, Section 2.1
Study Session 3– 9– d
Calculate and interpret probabilities for a random variable, given its cumulative distribution function.C is correct. There are two ways to find P(1 ≤ X ≤ 4):
1)Find the sum of four probabilities: P(1), P(2), P(3), and P(4), 0.2 + 0.2 + 0.2 + 0.2 = 0.8.A. 0.00096.
B. 0.00710.
C. 0.01485.Answer = C
|
||
|---|---|---|
| Here, |
|
|
If he assumes that the S&P return this year will be the same as it was last year, which of the following is the best estimate of the 95% confidence interval for this year’s S&P return?
A. –0.11600 to +0.34400
B. +0.05024 to +0.17775
C. +0.06110 to +0.16690With sample variance of 0.0529, .The estimated interval is
(√ ) ) = +0.05024 to +0.17775.
“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. DeFusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 5, Section 2
Study Session 2–5–b
Explain an interest rate as the sum of a real risk-free rate and premiums that compensate investors for bearing distinct types of risk.A is correct. “The liquidity premium compensates investors for the risk of loss relative to an investment’s fair value if the investment needs to be converted to cash quickly.”
| 9.81 |
|
13.99 | ||
|
10.12 | 14.47 | ||
| 10.84 | 14.85 | |||
| 11.33 |
|
15.00 | ||
|
12.25 | 17.36 | ||
| 13.39 | 17.98 | |||
| 13.42 |
The value of the first quintile is closest to:
A. 10.70%.
B. 10.84%.
C. 11.09%Therefore, the location of the first quintile is between the volatility of Fund 2 and Fund 3 (because they are ranked in ascending order).
Then, use linear interpolation to find the approximate value of the first quintile: P20 ≈ X2 + (2.80 – 2) × (X3– X2),
where
X2 is the volatility of Fund 2
X3 is the volatility of Fund 3
P20 is the approximate value of the first quintile
P20 ≈ 10.12% + (2.80 – 2) × (10.84% –10.12%) = 10.70%
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. DeFusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 7, Section 7.2 (Example 10)
Study Session 2–7–g
Calculate and interpret (1) a range and a mean absolute deviation and (2) the variance and standard deviation of a population and of a sample.A is correct. The mean absolute deviation (MAD) for a sample is calculated as follow:
| ∑ |
|---|
32.Consider the following information in relation to a portfolio composed of Fund A and Fund B:
| Fund A | ||
|---|---|---|
| 70 | 30 | |
| 10 | 16 | |
| 7 | 13 | |
|
0.80 | |
The portfolio standard deviation of returns is closest to:
B is correct. First, calculate the covariance between Fund A and Fund B given the standard deviation of returns and the correlation between the two funds:
Cov(RA, RB) = ρ(RA, RB)σ(RA)σ(RB),
where
σ(RA) = 7%. This is the standard deviation of returns of fund A
σ(RB) = 13%. This is the standard deviation of returns of fund B
ρ(RA, RB) = 0.80. This is the correlation between the returns of Fund A and Fund B. Cov(RA, RB) = 0.80 × 7% × 13%= 0.00728.Then calculate the portfolio standard deviation of returns as follow:
| . |
|---|
Alternatively, use correlation directly in the formula for portfolio standard deviation: σRPortfolio=[ 2σ2 RA+ 𝐵2σ2 RB+2𝐵𝜌RA, RB σRA σRB]0.5
σRPortfolio= [(0.70)2×0.072+0.302×0.132+2∗0.70×0.30×0.80×0.07×0.13]0.5=8.35%.
Questions 33 through 44 relate to Economics
The student’s current monthly food budget is $500, the price of a pizza is $5 and the price of cola is $1.25/bottle. If the student’s monthly food budget were to increase to $700, the slope of her demand curve for pizza would be closest to:
B is correct.
|
|---|
|
|
C. greater than 60.
Answer = C
|
|---|
60.
A.$6.00, all firms should exit the market in the long run.
B.$3.50, firm X should continue to operate in the short run, but firms Y and Z should shut down production.
B is correct.
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
A.106.2.
B.106.8.
C.113.4.Answer = C
| Nominal GDP | Real GDP | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
“Understanding Business Cycles,” Michele Gambera, CFA, Milton Ezrati, and Bolong Cao, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, Reading 18, Section 5.1, Exhibit 7
Study Session 5-18-i, j
Describe economic indicators, including their uses and limitations.Identify the past, current, or expected future business cycle phase of an economy based on economic indicators.
|
 |
|---|
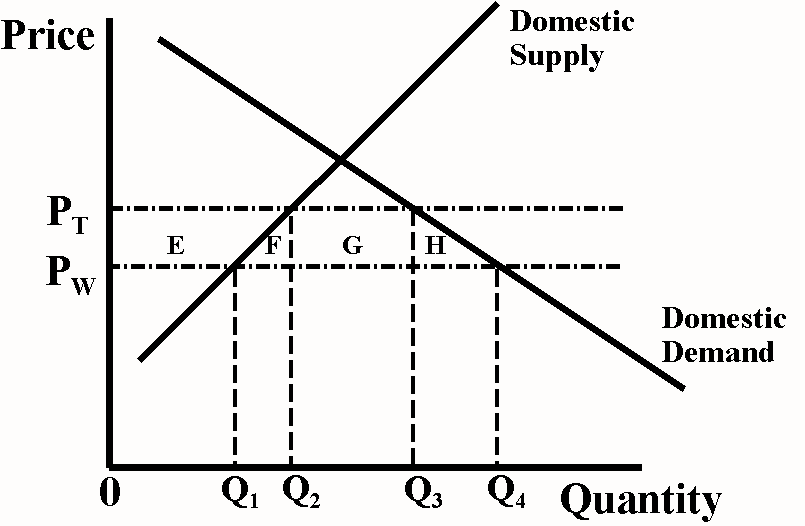
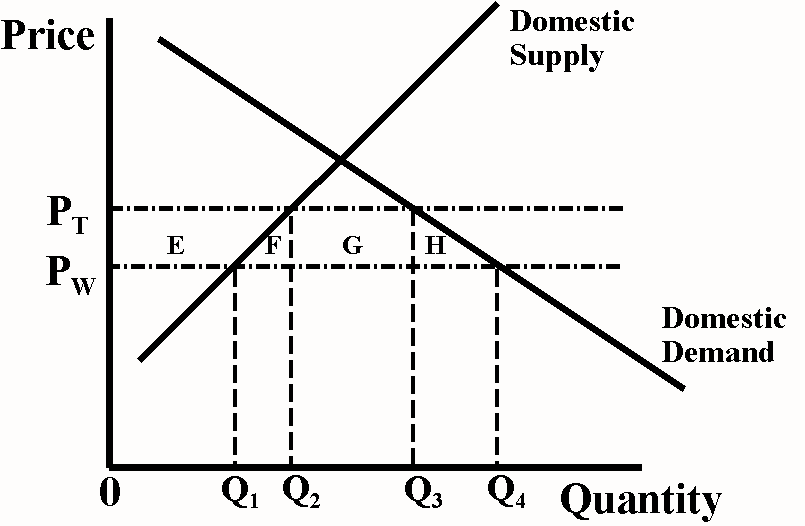
C is correct. The loss in consumer surplus because of higher prices is represented by area E+F+G+H. This exceeds the gains from producer surplus (E) and government revenues on imports (G). Hence, the net welfare effect to the country is a deadweight loss of [E + F + G + H] – [E] – [G] = F+H.
39.The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development most likely:
A is correct. Closely affiliated with The World Bank Group, the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) provides low or no-interest loans and grants to developing countries that have unfavorable or no access to international credit markets.
40.An investor examines the following rate quotes for the Brazilian real and the Australian dollar:
Answer = B
“Currency Exchange Rates,” William A. Barker, CFA, Paul D. McNelis, and Jerry Nickelsburg 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, Reading 21, Section 3.3
Study Session 6–21–f, g
Explain the arbitrage relationship between spot rates, forward rates and interest rates. Calculate and interpret a forward rate consistent with a spot rate and the interest rate in each currency.
| ) | ⁄( ) ( |
|---|
Arbitrage profit = BRL521,844 (right side above) – BRL520,500 (left side above) = 1,344.
41.The demand and supply functions for a leading smartphone are furnished below:
| Qd sp = 1,000 – 20Psp+ 2I; |
|---|
A. $250.
B. $300.
C. $425.Answer = B
A. shut down in the short run and exit in the long run. B. increase its level of production to enter profit territory. C. decrease its level of production to enter profit territory.
Answer = C
Answer = A
“Understanding Business Cycles,” Michele Gambera, CFA, Milton Ezrati, and Bolong Cao, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, Reading 18, Section 4.2.2
Study Session 5-18-f, g
Explain the construction of indices used to measure inflation.
Compare inflation measures, including their uses and limitations.Answer = B
“Understanding Business Cycles,” Michele Gambera, CFA, Milton Ezrati, and Bolong Cao, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, Reading 18, Section 3.3.1
Study Session 5–18–c
Describe theories of the business cycle.
| £ ‘000s | |
|---|---|
|
200 |
|
350 |
| 1,250 | |
| 300 | |
| 200 | |
| 600 |
Using the current ratio, when compared with the industry, the firm is best described as being:
A. as liquid.
Study Session 8-26-i, 11-40-b
Calculate and interpret liquidity and solvency ratios.Compare a company’s liquidity measures with those of peer companies.
The higher the current ratio the more liquid the company. Thus, with a current ratio of 2.6 (1,800 ÷ 700), the company is less liquid than the industry, with a current ratio of 3.2.
Answer = A
“Understanding Income Statements,” Elaine Henry, CFA and Thomas R. Robinson, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Reading 25, Section 5.3
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Elaine Henry, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, and Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol.4, Reading 28, Section 4.6.2
“Introduction to Industry and Company Analysis,” Patrick W. Dorsey, CFA, Anthony M. Fiore, CFA and Ian Rossa O’Reilly, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol.5, Reading 50, Section 5.1.2
Study Sessions: 8-25-e, 8-28-d, 14-50-g
Describe the financial reporting treatment and analysis of non-recurring items (including discontinued operations, extraordinary items, and unusual or infrequent items) and changes in accounting standards.47.In 2011, a software company recorded unearned revenue related to a software license that it will recognize as revenue during 2012. Ignoring income taxes, this recognition of the software revenue will most likely have which of the following effects on cash from operations in 2012?
A. No effect
B. A decrease
C. An increaseA is correct. The company received the cash in 2011 when it recorded the unearned revenue and it was a part of the cash from operations in that year. In 2012, the revenue is earned but there is no cash exchanged and hence no effect of the cash from operations, ignoring taxes.
48.The following information for the current year is available for a company that prepares its financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
| 7,000 | |
| 4,200 | |
| 500 | |
|
250 |
|
200 |
49.Which of the following activities would an analyst least likely complete as part of the processing data phase of a financial analysis?
A. Analyzing the prospects of the industry
B. Preparing common-sized financial statement data C. Making adjustments for different accounting policiesA. Form 10-K
B. Annual report
C. Proxy statementAnswer = B
• Company 2 has been offering the same products throughout the period, and the demand and cost structures for its products have not experienced any significant changes.
• Company 3 has recently restructured its product offerings focusing on high margin products only.
“Financial Statement Analysis: Applications,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Reading 35, Section 3.1 Example 3
Study Session 10–35–b
Prepare a basic projection of a company’s future net income and cash flow.B is correct. Company 2 because it has been offering the same products and its demand and cost structures have been stable too. Therefore, the relationship between sales and gross profit (i.e., gross margin) should be stable and most reliable.
| Component | Cost | Useful Life |
|---|---|---|
| A | $500,000 | 10 years |
| B | $500,000 | 5 years |
Answer = C
“Long-Lived Assets” Elaine Henry, CFA and Elizabeth A Gordon 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Reading 30, Section 3.1, Example 5 Study Session 9–30–d
Calculate depreciation expense.
A. Investing
B. Financing
C. OperatingAnswer = C
| $ millions | |
|---|---|
| 90.0 | |
|
15.2 |
|
28.0 |
| 34.3 | |
| 13.0 |
Answer = B
“Understanding Cash Flow Statements,”Elaine Henry, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, and Michael A Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Section 4.3
Study Session: 8–27-i
Calculate and interpret free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to equity, and performance and coverage cash flow ratios.
| 74.7 |
|---|
“Financial Analysis Techniques,”Elaine Henry, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, and Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Section 5.1.1, Exhibit 18
Study Session: 8-28-e
Calculate and interpret ratios used in equity analysis, credit analysis, and segment analysis.B is correct.
|
|
|
“Inventories,”Michael A Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Section 6, Example 5
Study Session: 9-29-h
Calculate and interpret ratios used to evaluate inventory management.B is correct. All else held constant, in a period of rising costs the ending inventory would be lower under weighted average and cost of goods sold (CGS) will be higher (compared to FIFO) resulting in lower net income and retained earnings. There will be no impact on the debt level, current or long-term. Therefore the debt-to-equity ratio (Total debt ÷ Total shareholder’s equity) will increase due to the decrease in retained earnings (and lower shareholders’ equity).
“Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction,” Elaine Henry, CFA and Thomas R. Robinson, CFA 2013 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, Reading 22, Section 3.1.6
Study Session: 7-22-e
Identify and explain information sources that analysts use in financial statement analysis besides annual financial statements and supplementary information.C is correct. Forward-looking information such as those about planned capital expenditures is typically provided in the management discussion and analysis (MD&A).
Answer = B
“Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, Reading 23, Sections 3.2, 4.2
Study Session: 7-23-b, e
|
||
|---|---|---|
| $ 50,000 | ||
| 225,000 | ||
| 450,000 | ||
| 5,000 | ||
|
(402,000) | |
|
53,000 | |
| (10,000) | ||
| 43,000 | 43,000 | |
| $318,000 | ||
A. timeliness and accrual accounting.
B. understandability and verifiability.
C. relevance and faithful representation.A. U.S. GAAP, intangibles must be valued at historical cost.
B. IFRS, a commercial real estate company should use a liquidity based presentation. C. IFRS, a classified balance sheet must present current assets before non-current assets.
61. A company recorded the following events in 2012:
A is correct.
“Understanding Cash Flow Statements,” Elaine Henry, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Reading 27, Section 2.1
Study Session 8-27-a
Compare cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities and classify cash flow items as relating to one of those three categories given a description of the items.
| $ millions | |
|---|---|
| 4,800 | |
| 2,880 |
B. 120.
C. 138.Answer = B
| Accounts receivable | Inventory |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Days in Sales (DSO) | Days on hand (DHO) |
|
|
| Sales | Purchases | ||
| A/R | Inventory | Payables | |
| 4,800 ÷ 625 | 2,880 ÷ 710 | 2,940 ÷ 145 | |
| = 7.68 times | |||
| = 4.06 times | = 20.3 times | ||
| 365 ÷ 7.68 | |||
| 365 ÷ 4.06 | 365 ÷ 20.3 | ||
| = 48 days | = 90 days | = 18 days |
| 300 | 7.70 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 600 | 12.00 | ||
|
400 |
If the company used a perpetual system versus a periodic inventory system, the gross margin would most likely be:
“Inventories,” Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, Reading 29, Section 3.6
Study Session: 9-29-d, e
Calculate and compare cost of sales, gross profit, and ending inventory using perpetual and periodic inventory systems.Compare and contrast cost of sales, ending inventory and gross profit using different inventory valuation methods.
"Long-Lived Assets,” Elaine Henry, CFA and Elizabeth A. Gordon 2013 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, Reading 30, Section 8
Study Session: 9-30-g, kDescribe the revaluation model.
B. U.S. GAAP if there is doubt about recovering a deferred tax asset.
C. both IFRS and U.S. GAAP on tax differences arising from the translation of foreign operations.
A. increase in gross margin.
B. decrease in the LIFO reserve.
67. Selected information about a company is as follows:
|
2011 December 31 |
|
|---|---|---|
| 2,200 | 2,500 | |
| 28% | 30% | |
| 1,400 | 1,400 | |
|
25% | 25% |
|
55 | 60 |
| 500 | 500 |
“Financial Statement Analysis: Applications,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, Reading 35, Section 3.2, Example 5
Study Session: 10-35-b
Prepare a basic projection of a company’s future net income and cash flow.C is correct. Forecasted net income is calculated as follows: Sales $2,500 Given
Variable costs (750) 30% of sales Fixed costs (1,400) Given
“Understanding Cash Flow Statements,” Elaine Henry, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Reading 27, Section 4.3
"Long-Lived Assets,” Elaine Henry, CFA and Elizabeth A. Gordon
2013 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, Reading 30, Section 2.1, Example 1,
Study Session 8-27-i, 9-30-a,
Calculate and interpret free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to equity, and performance and coverage cash flow ratios.Distinguish between costs that are capitalised and costs that are expensed in the period in which they are incurred.
| Example | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
Questions 69 through 78 relate to Corporate Finance
69. Two mutually exclusive projects have the following cash flows (€) and internal rates of return (IRR):
Study Session 11-36-c, d, e
Explain how the evaluation and selection of capital projects is affected by mutually exclusive projects, project sequencing, and capital rationing.
| ) | ) | ) | ) |
|---|
B is correct because Project A has a higher NPV and the projects are mutually exclusive, only Project A should be accepted.
70. A company’s asset beta is 1.2 based on a debt-to-equity ratio of 50%. If the company’s tax rate increases, the associated equity beta will most likely:
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, CFA, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela Peterson Drake, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol.4, Reading 37, Section 4.1.
Study Session 11-37-h
Calculate and interpret the cost of equity capital using the capital asset pricing model approach, the dividend discount model approach, and the bond-yield-plus risk-premium approach.
| [ ( ) |
|---|
A.declaration date.
B.ex-dividend date.
B is correct. The ex-dividend date is normally determined by the Securities Exchange on which the shares are listed. The corporation determines the holder-of-record date and declaration date.
72. A firm’s price-to-earnings ratio (P/E) is 12.5. The firm has decided to repurchase shares using external funds that have an after-tax cost of 9%. After the repurchase, the earnings per share (EPS) will most likely:
“Dividends and Share Repurchases: Basics,” George H. Troughton, CFA and Gregory Noronha, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol.4, Reading 39, Section 4.2.1.Study Session 11-39-d
Calculate and compare the effects of a share repurchase on earnings per share when 1) the repurchase is financed with the company’s excess cash and 2) the company uses funded debt to finance the repurchase.“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., CFA, Kenneth L. Parkinson, and Pamela Peterson Drake, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol.4, Reading 40, Section 2.1.3.Study Session 11-40-a
Describe primary and secondary sources of liquidity and factors that influence a company’s liquidity position.Answer = B
“The Corporate Governance of Listed Companies: A Manual for Investors,” Kurt Schacht, CFA, James C. Allen, CFA, and Matthew Orsagh, CFA, CIPM
2013 Modular Level I, Vol.4, Reading 41, Section: Board Independence.B.1,000.
C.1,250.Answer = B
Answer = A
“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., CFA, Kenneth L. Parkinson, and Pamela Peterson Drake, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, Reading 40, Section 8.4., Example 7
Study Session 11-40-g
Evaluate the choices of short-term funding available to a company and recommend a financing method.
B.All committees within the firm should benefit from the direct guidance of management. C.Appropriate controls and procedures exist that cover management’s activities in running the daily operations of the firm.
Answer = C
78. Which of the following is the least appropriate method for an external analyst to estimate a company’s target capital structure for determining WACC? Using the:
A.averages of comparable companies’ capital structure.
B is correct. An external analyst does not know a company’s actual target capital structure. Consequently, the analyst should rely on market value (not book value) weights for the components of the company’s current capital structure.
Questions 79 through 90 relate to Equity Investments
Answer = C
“Market Organization and Structure,” Larry Harris
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 46, Section 10
Study Session 13-46-l
Describe the objectives of market regulation.“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Elaine Henry, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, and Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Reading 28, Sections 4.5.2, 4.6.2.“Introduction to Industry and Company Analysis,” Patrick W. Dorsey, CFA, Anthony M. Fiore, CFA and Ian Rossa O’Reilly, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 50, Section 6.1
Study Session 8-28-c, d, e; 14-50-k
Describe the relationships among ratios and evaluate a company using ratio analysis.A. FCFE is a measure of the firm’s dividend paying capacity.
B. FCFE models provide more accurate valuations than the dividend discount models. C. A firm’s borrowing activities could influence dividend decisions but they would not impact FCFE.
The current value per share of the company’s common stock according to the two-stage dividend discount model is closest to:
A is correct.
Net profit margin = Net earnings ÷ Sales
Net earnings = Net profit margin × Sales;
Dividends per share (“Dn”) = (Net earnings × Payout ratio) ÷ # of outstanding shares; Therefore, D1 = ($180 million × 0.15 × 0.60) ÷ 8 million = $2.00
D2 = $2.00 ×(1+ 0.25) = $2.50
D3 = $2.00 × (1+ 0.25)2 = $3.13
D4 = $2.00 × (1+ 0.25)2 × (1+0.05) = $3.28
| V3 = | ) = $46.86 | ) + | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V0 = | ) + | ) + | ||
“Market Organization and Structure,” Larry Harris
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 46, Section 5.2, Example 20
Study Session 13-46-f
Calculate and interpret the leverage ratio, the rate of return on a margin transaction, and the security price at which the investor would receive a margin call.A is correct.
“Market Organization and Structure,” Larry Harris
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 46, Sections 4.1, 4.2
Study Session 13-46-d
Describe types of financial intermediaries and services they provide.A is correct. The service that dealers provide is liquidity. Liquidity is the ability to buy or sell with low transaction costs when you want to trade. By allowing their clients to trade when they want to trade, dealers provide liquidity to them.
Compare market orders with limit orders.
B is correct. An order is filled at the best available price as long as this price is lower than the limit price. In this case, the best available price is the market ask price = $49.49 x (1+ 0.7%) = $49.84. Since this price is lower than the limit price of $49.94, the order will be filled at this price
Answer = C
“Market Organization and Structure,” Larry Harris
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 46, Section 9
Study Session 13-46-k
Describe characteristics of a well-functioning financial system.
The value of the index as of January 1, 2012 is closest to:
A. 1,047.
B. 1,070.
C. 1,094.TRI = (VPRI1 − VPRI0 + IncI) ÷ VPRI0
where
TRI = the total return of the index portfolio (as a decimal number)
VPRI1= the value of the price return index at the end of the period
VPRI0 = the value of the price return index at the beginning of the period
IncI = the total income (dividends and/or interest) from all securities in the index held over the period
-4.5% = (1000 - VPRI0 + 23.5 + 21.5) ÷ VPRI0;
VPRI0 = 1000 + 23.5 + 21.5 ÷ (1 - 4.5%) = 1,094.88. After the public announcement of the merger of two firms an investor makes abnormal returns by going long on the target firm and short on the acquiring firm. This most likely violates which form of market efficiency?
B is correct. In a semi-strong efficient market, prices adjust quickly and accurately to new information. In this case, prices would quickly adjust to the merger announcement and if the market is semi-strong efficient market, investors acting after the merger announcement would not be able to earn abnormal returns. Therefore, it is a violation of the semi-strong form of market efficiency. Note that the semi-strong form of market efficiency encompasses the weak form. Therefore, both weak and semi-strong forms of market efficiency are violated.
89. An analyst gathers the following information about two companies in the same industry:
| Company A | Company B | |
|---|---|---|
| $20 | $10 | |
| $22 | $13 | |
| 16% | 13% | |
| 40% | 60% |
What is the most appropriate conclusion regarding investors’ expectations? Compared to Company B, Company A has:
A. higher intrinsic value as reflected by its higher market price.
C is correct. The price-to-book ratio, which is also referred to as the market-to-book ratio, provides an indication of investors’ expectations about a company’s future investment and cash flow-generating opportunities. The larger the price-to-book ratio (i.e., the greater the
divergence between market value per share and book value per share), the more favorably investors will view the company’s future investment opportunities. In this case, as shown below, Company A has lower price-to-book ratio than Company B and therefore an expectation of lower future investment opportunities.
| $1.47 | |
|---|---|
|
$4.00 |
| Estimate of long-run return on equity (ROE) | 15% |
|
40% |
| 12% |
“Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools,” John J. Nagorniak, CFA, and Stephen E. Wilcox, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 51, Section 5.1, Example 11
Study Session 14-51-hCalculate and interpret the following multiples: price to earnings, price to an estimate of operating cash flow, price to sales, and price to book value.
91. A corporation issues 5-year fixed-rate bonds. Its treasurer expects interest rates to decline for all maturities for at least the next year. She enters into a 1-year agreement with a bank to receive quarterly fixed-rate payments and to make payments based on floating rates benchmarked on 3-month LIBOR. This agreement is best described as a:
A.swap.
92. A portfolio manager is required to sell 31,250 shares of XYZ Inc. in two months. She is concerned the price of XYZ shares will decline during the 2-month period, so she enters into a
deliverable equity forward contract to sell 31,250 shares of XYZ in two months for EUR 160 per share. When the contract expires, XYZ is trading at EUR 138 per share. The portfolio manager will most likely:
C is correct because the portfolio manager entered into a contract to sell the stock to the dealer at $160 per share in 2 months time. 31,250 shares x EUR 160 = EUR 5,000,000.
93. A trader takes a long position in 40 futures contracts on Day 1. The futures have a daily price limit of $5 and closes with a settlement price of $106. On Day 2, the futures trade at $111 and the bid and offer move to $113 and $115, respectively. The futures price remains at these price levels until the market closes. The marked-to-market amount the trader receives in his account at the end of Day 2 is closest to:
94. An investor is long an in-the-money American call option on a dividend paying stock. Would this option most likely ever be exercised early?
A.No.
C is correct because a cash flow such as a dividend payment is required for an early exercise. A dividend payment doesn’t guarantee early exercise, as the dividend also needs to be large enough to justify the early exercise.
95. A European company issues a 5-year euro-denominated bond with a face value of EUR 50,000,000. The company then enters into a 5-year currency swap with a bank to convert the EUR exposure into USD exposure. The notional principals of the swap are EUR 50,000,000 and USD 70,000,000. The European company pays a fixed rate of 5% and the bank pays a fixed rate of 4.5%. Payments are made semiannually on a basis of 30 days per month and 360 days per year. What is the payment from the bank to the company at the end of year 4?
96. An investor with $5000 to invest believes that the price of ABC Corp. stock will appreciate by $7 to $95 in two months. The two-month at-the-money put on one share of ABC stock costs $1.76, while the two-month at-the-money call costs $1.56. In order to profit from his view on ABC stock, he will most likely:
A.sell calls on shares of ABC.
B.sell puts on shares of ABC.
C.buy calls on shares of ABC.
97. If a bond’s issuer is required to retire a specified portion of the issue each year, the bond most likely:
A.is callable.
C is correct because a sinking fund provision requires retirement of a portion of the bond issue each year, rather than retirement of the entire issue at maturity.
98. One reason why the duration of a portfolio of bonds does not properly reflect that portfolio’s yield curve risk is the duration measure:
Describe yield-curve risk and explain why duration does not account for yield-curve risk.
A is correct because duration assumes all interest rates across the yield curve change by the same amount and therefore each bond’s yield changes by the same amount.
Answer = B
“Understanding Yield Spreads”, Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 55, Section 4.6.1
Study Session 15-55-i
Calculate the after-tax yield of a taxable security and the tax-equivalent yield of a tax-exempt security.Answer = A
“Understanding Yield Spreads”, Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 55, Section 3.3 Study Session 15-55-d
Define a spot rate.C.stay the same.
Answer = A
Answer = A
“Introduction to the Valuation of Debt Securities”, Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 56, Section 2.6
Study Session 16-56-c
Calculate the value of a bond (coupon and zero-coupon).
103. All else equal, the difference between the nominal spread and the Z-spread for a non-Treasury security will most likely be larger when the:
A.yield curve is flat.
B is correct because the main factor causing any difference between the nominal spread and the Z-spread is the shape of the Treasury spot rate curve. The steeper the spot rate curve, the greater the difference.
104. Assume the following six-month forward rates (presented on an annualized, bond-equivalent basis) were calculated from the yield curve.
| Notation | Forward Rate |
|---|---|
| 1f0 | 0.50% |
| 1f1 | 0.70% |
| 1f2 | 1.00% |
| 1f3 | 1.50% |
| 1f4 | 2.20% |
| 1f5 | 3.00% |
| 1f6 | 4.00% |
A.increases measurement accuracy.
B.is easier to model than scenario analysis.
106. An analyst uses a valuation model to estimate the value of an option-free bond at 92.733 to yield 11%. If the value is 94.474 for a 60 basis point decrease in yield and 91.041 for a 60 basis point increase in yield, the effective duration of the bond is closest to:
A.1.85.
B.3.09.
C.6.17.
| D | = | 2 | V | − | − | , | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
× | V 0 | × | ∆y | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| D | = | 2 | 94 . 474 | − | = | |||||||||
| × | 92 . 733 | × | .0 0060 | |||||||||||
A.put the issue.
B.call the issue.
108. The bonds issued by ALS Corp. are currently priced at 108.00 and are option free. Based on a portfolio manager’s valuation model, a 10 basis points rise in interest rates will result in the bond price falling to 106.50 while a 10 basis points fall in interest rates will result in the bond price rising to 110.00. The market value of the portfolio manager’s holdings of ALS bonds is $2 million. The expected change in the market value of this holding for a 100 basis point change in interest rates will be closest to:
A.$124,000.
B.$322,600.
C.$645,200.The approximate percent change in the value of the holdings (the dollar duration) is: 0.1613 × 2,000,000 = $322,600.
Questions 109 through 114 relate to Alternative Investments.
“Introduction to Alternative Investments,” Terri Duhon, George Spentzos, CFA, and Scott D.
Stewart, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, Reading 66, Sections 2.1 Study Session 18-66-b
Describe categories of alternative investments.C. convenience yield.
Answer = B
C. reduce exposure to inflation.
Answer = C
A. assets are not marked to market.
B. data are subject to survivorship bias.
C is correct. Since commodity indices are constructed using commodity futures and not the underlying commodities there can be differences between commodity index returns and the returns of the underlying commodities.
113. Which of the following investments most likely provides an investor with indirect, equity exposure to real estate?
“Introduction to Alternative Investments,” Terri Duhon, George Spentzos, CFA, and Scott D.
Stewart, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, Reading 66, Sections 5.1, 5.2 Study Session 18-66-dexposure. Real estate investment partnerships are a form of direct real estate equity investment.
Commercial mortgage backed securities (CMBS) provides investors with indirect, debt investment
Answer = A
“Introduction to Alternative Investments,” Terri Duhon, George Spentzos, CFA, and Scott D.
The incentive fee = ($541,500,000 - $475,000,000) × 0.10 = $6,650,000
Total fees = $14,772,500
Answer = A
"Portfolio Management: An Overview” by Robert M. Conroy, CFA and Alistair Byrne, CFA Modular Level I, Vol. 4, Reading 42, Section 3 (Exhibit 14)
The 2012 return needed to achieve a trailing five year geometric mean annualized return of 5.0% when calculated at the end of 2012 is closest to:
Holding period total return (cumulative) factor calculation through 2011:
(1-0.348)×(1+0.322)×(1+0.111)×(1-0.014) = 0.652 × 1.322 × 1.111 × 0.986 = 0.9442 Compound total return (cumulative) factor at 5% per year of five percent for five years: 1.055 = 1.2763
Return needed in 2012 to achieve a compound annualized return of 5%
1.2763/.9442 = 1.3517 = 35.2 percent
Check: 0.944 × 1.352 = 1.276(1/5) = 1.050 = 5 percent annualized117. Consider a portfolio with two assets. Asset A comprises 25% of the portfolio and has a standard deviation of 17.9%. Asset B comprises 75% of the portfolio and has a standard deviation of 6.2%. If the correlation of these two investments is 0.5, the portfolio standard deviation is closest to:
|
2 + w2 2σ2 |
|
|---|
A. 1.02.
B. 1.05.
C. 1.16Answer = B
A. M-squared
B. Sharpe ratio
C. Treynor ratioAnswer = C
A. low ability to take risk, but a high willingness to take risk B. high ability to take risk, but a low willingness to take risk C. high ability to take risk and a high willingness to take risk
Answer = C
2013 Level I Mock Exam: Morning Session
The morning session of the 2013 Level I Chartered Financial Analyst
(CFA®) Mock Examination has 120 questions. To best simulate the exam day
experience, candidates are advised to allocate an average of 1.5 minutes
per question for a total of 180 minutes (3 hours) for this session of
the exam.
A. reducing each pension fund’s allocation proportionately.
B. distributing them equally amongst all the pension fund portfolios.
2.Dilshan Kumar, CFA, is a world-renowned mining analyst based in London. Recently, he received an invitation from Cerberus Mining, a London Stock Exchange listed company with headquarters in Johannesburg, South Africa. Cerberus asked Kumar to join a group of prominent analysts from around the world on a tour of its mines in South Africa, some of which are in remote locations, not easily accessible. The invitation also includes an arranged wildlife safari to Krueger National Park for the analysts. Kumar accepts the invitation, planning to visit other mining companies he covers in Namibia and Botswana after the safari. To prevent violating any CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct, it is most appropriate for Kumar to only accept which type of paid travel arrangements from Cerberus?
A. Ground transportation to Krueger National Park
B. Economy class round trip ticket from London to Johannesburg
C. Flights on a private airplane to the remote mining sites in South AfricaA. No
B. Yes, with regard to Misconduct
C. Yes, with regard to Reference to the CFA DesignationAnswer = B
A. Equity research reports
B. Investment conference attendance
C. Database services for offshore investmentsAnswer = C
Answer = C
“Guidance for Standards I–VII”, CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard IV (A) Loyalty, Standard V (A) Diligence and Reasonable Basis
Study Session 1–2–bAnswer = B
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard VI (B) Priority of Transactions
Study Session 1–2–b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.Answer = A
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard I (D) Misconduct
Study Session 1–2–a
Demonstrate the application of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct to situations involving issues of professional integrity.Answer = C
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard I (A) Knowledge of the Law, Standard I (B) Independence and Objectivity, Standard III (C) Suitability
Study Session 1–2–c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.Answer = B
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 2, Standard I (A) Knowledge of the Law
Study Session 1–2–c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.B. asset management clients first.
C. newsletter recipients and asset management clients simultaneously.
A. the stock portfolio’s performance history.
B. her contribution to the portfolio’s returns.
C. providing details of the institutional clients.Answer = C
Younis has never told his employer about any of these activities. To comply with the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct with regards to his business activities over the past two years, Younis would least likely be required to disclose which of the following to his employer?
A. Board activities
B. Family investment pool management
C. Non-family member management feesA.firm policies.
B.legal restrictions.
C.industry standards.14.Sheila Schleif, CFA, is an equity analyst at an investment banking division of Mokara Financial Group, a full service financial group. Schleif uses a multi-factor computer model to make stock recommendations for all clients of Mokara. Schleif discovers the model contains an error. If the error were corrected, her most recent buy recommendation communicated to all clients would change to a sell. Schleif corrects the error, changing the buy to a sell recommendation, and then simultaneously distributes via e-mail the revision to all investment banking clients who received the initial recommendation. A week later, Schleif sells the same shares she held in her personal portfolio. Concerning her actions, Schleif most likely violated which of the following CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
A. Fair Dealing
B. Priority of Transactions
C. Diligence and Reasonable BasisA. adherence to strategy.
B. performance measures.
16.Jackson Barnes, CFA, works for an insurance company providing financial planning services to clients for a fee. Barnes has developed a network of specialists, including accountants, lawyers, and brokers who contribute their expertise to the financial planning process. Each of the specialists is an independent contractor. Each contractor bills Barnes separately for the work he or she performs, providing a discount based upon the number of clients Barnes has referred. What steps should Barnes take to be consistent with the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
A. Have his independent contractors approved by the insurance company
B. List the consideration he receives from the specialists on monthly client invoices
C. Inform potential clients about his arrangement with the contractors before they agree to hire himmuch harder than they had expected and they were not able to complete all questions as a result. The candidates go on to tell Plain about broad topic areas that were tested and complain about specific formulas they had memorized what did not appear on the exam. The Level III candidates least likely violated the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct by
discussing:
A. specific formulas.B. broad topic areas.
18.On a flight to Europe, Romy Haas, CFA, strikes up a conversation with a fellow passenger, Vincent Trujillo. When Trujillo learns Haas is in the investment profession, he asks about the CFA designation. Haas tells him the following about the CFA designation:
Statement 1: Individuals who have completed the CFA Program have the right to use the CFA designation.Statement 2: The CFA designation is globally recognized which is why I use it as part of my firm’s name
Statement 3: CFA charterholders must satisfy membership requirements to continue using the designation.Study Session 1–2–b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.C is correct because according to Standard VII (B) Reference to CFA Institute, the CFA
Designation, and the CFA Program this is an accurate statement concerning the CFA designation.
Answer = B
“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. DeFusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 5, Section 3.3
Study Session 2–5–c, d20.Equity return series are best described as, for the most part:
A.platykurtotic (less peaked than a normal distribution).
Study Session 2–7–l
Explain measures of sample skewness and kurtosis.B is correct. Most equity return series have been found to be leptokurtotic.
| Observation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | –3 | –11 | 3 | –18 | 18 | 20 | –6 | 9 | 2 | –16 |
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. DeFusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 7, Section 7.3.2, Example 12
Study Session 2–7–g
Calculate and interpret 1) a range and a mean absolute deviation and 2) the variance and standard deviation of a population and of a sample.C is correct. The sample mean is:
̅ ∑ / n = (– 3 – 11 + 3 – 18 + 18 + 20 – 6 + 9 + 2 –16) / 10 = –2.00 / 10 = –0.20.
Sum of squared
differences 1563.6
Divided by n –1 173.7333333
Square root 13.18079411A is correct. Given that X and Y are independent, their joint probability is equal to the product of their individual probabilities. In this problem, we calculate 0.2 × 0.5 = 0.1.
23.Assume that a stock’s price over the next two periods is as shown below.
|
|
|
| Sud,du = 79.2 | ||
B. 37.50%.
C. 56.25%.Answer = B
The probability of an up move followed by a down move is 0.75 × 0.25 = 0.1875.
The probability of a down move followed by an up move is 0.25 × 0.75 also = 0.1875. Both of these sequences result in an end value of $79.2.
“Hypothesis Testing,” Richard A. DeFusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 11, Section 2
Study Session 3– 11– a
Define a hypothesis, describe the steps of hypothesis testing, describe and interpret the choice of the null and alternative hypotheses, and distinguish between one-tailed and two-tailed tests of hypotheses.A is correct. When the null and alternative hypotheses are of the form: H0: θ = θ0 versus Ha: θ ≠θ0, the correct approach is to use a two-tailed test.
Answer = A
“Technical Analysis,” Barry M. Sine, CFA and Robert A. Strong, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 12, Section 3.2
Study Session 3– 12– c
Explain the uses of trend, support, resistance lines, and change in polarity.
The probability of a profit greater than or equal to $1 and less than or equal to $4 is closest to:
A. 0.4.
B. 0.6.
C. 0.8.In this case, F(4) = P( X ≤ 4) = 1.0 and F(1) = P(X ≤ 1) = 0.2.
Therefore, P(1 ≤ X ≤ 4) = 1.0 – 0.2 = 0.8.
Study Session 3– 10– f
Calculate and interpret the standard error of the sample mean.C is correct.
| Here, | ||
|---|---|---|
“Sampling and Estimation,” Richard A. DeFusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 10, Section 4.2
Study Session 3–10–j
Calculate and interpret a confidence interval for a population mean, given a normal distribution with (1) a known population variance, (2) an unknown population variance, or (3) an unknown variance and a large sample size.B is correct. The reliability factor for a 95% confidence interval with unknown population variance and sample size greater than 30 is .
B. increased sensitivity of the market value of debt to a change in market interest rates as maturity is extended.
C. possibility that the borrower will fail to make a promised payment at the contracted time and in the contracted amount.
|
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.81 | 13.99 | |||
| 10.12 | 14.47 | |||
|
10.84 |
|
14.85 | |
| 11.33 | 15.00 | |||
| 12.25 | 17.36 | |||
|
13.39 |
|
17.98 | |
| 13.42 |
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. DeFusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 7, Section 6.1
Study Session 2–7–f
Calculate and interpret quartiles, quintiles, deciles, and percentiles.A is correct. First, find the position of the first quintile with the following formula:
Ly = (n + 1) × (y / 100),
where
y is the percentage point at which we are dividing the distribution. In our case we have y = 20, which corresponds to the 20th percentile (first quintile);
n is the number of observations (funds) in the peer group. In our case we have n = 13;
The mean absolute deviation of returns for the fund is closest to:
A. 9.53%.
B. 11.91%.
C. 13.69%.
| ∑ |
|---|
where
Xiis the return of the fund during year i
̅ is the mean of the returns of the sample
n is the number of returns in the sample
i is the index for the year
In this problem:
Mean: ̅ (–20.60% + 15.00% + 0.50% + 9.80% + 4.60%)/5 = 1.86%
MAD = (|–20.60% – 1.86%| + |15.00% – 1.86%| + |0.50% – 1.86%| + |9.80% – 1.86%| + |4.60% – 1.86%|)/5 = 47.64% / 5=9.53%
| Fund A | ||
|---|---|---|
|
70 | 30 |
|
10 | 16 |
| 7 | 13 | |
| 0.80 | ||
Answer = B
“Probability Concepts,” Richard A. DeFusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, Reading 8, Section 3
Study Session 2–8–k, l
Calculate and interpret covariance and correlation.
where
WA = 70%. This is the weight of Fund A in the portfolio WB = 30%. This is the weight of Fund B in the portfolio.
| . |
|---|
Answer = B
“Demand and Supply Analysis: Introduction,” Richard V. Eastin and Gary L. Arbogast, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, Reading 13, Section 3.2, Example 2.
|
|
A consumer’s indifference curves are strictly convex and he claims that he is indifferent between Baskets 2 and 3. If he is also indifferent between Baskets 1 and 3, the number of units of A in basket 1 is most likely:
A. equal to 60.
Describe the use of indifference curves, opportunity sets, and budget constraints in decision making.
C is correct. Because the consumer is indifferent between all three baskets, they must all fall on the same indifference curve. The MRSBA at Basket 2 is 4, meaning that the slope of the
Answer = B
“Demand and Supply Analysis: The Firm,” Gary L. Arbogast, CFA and Richard V. Eastin
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
36.The following data pertain to the total output in units and average selling prices in an economy that produces only two products, X and Y:
C is correct.
| Nominal GDP | Real GDP | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
|
||
37.Which of the following would be most useful as a leading indicator to signal the start of an economic recovery?
A.An increase in aggregate real personal income (less transfer payments)
B.A decrease in average weekly initial claims for unemployment insurance
C.The narrowing of the spread between the 10-year Treasury yield and the federal funds rate38.
|
 |
|---|
Answer = C
“Demand and Supply Analysis: Introduction,” Richard V. Eastin and Gary L. Arbogast, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, Reading 13, Sections 3.9, 3.10
“International Trade and Capital Flows,” Usha Nair-Reichert, PhD and Daniel Robert Witschi, PhD, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, Reading 20, Sections 3.1, Exhibit 12
Study Session 4–13–i, j, 6–20–e
Calculate and interpret consumer surplus, producer surplus, and total surplus.
Analyze the effects of government regulation and intervention on demand and supply.B. lends foreign currencies on a temporary basis to address balance of payment issues. C. stands ready to lend foreign currencies to member countries during periods of significant external deficits.
Answer = A
If the investor shorts BRL500,000 he will achieve a risk-free arbitrage profit (in BRL) closest to:
| ) | ⁄( ) ( |
|
|---|
Sf/d = Spot rate: number of units of foreign currency (price currency) per one unit of domestic currency
Ff/d = Forward rate: number of units of foreign currency (price currency) per one unit of domestic currency
id = Domestic interest rate
if = Foreign interest rate
The arbitrage profit is the right side of the equation minus the left side.
| Qd sp = 1,000 – 20Psp+ 2I; |
|
|---|
Qd sp = Quantity demanded in number of units
Qs sp = Quantity supplied in number of units
Psp = Price per smart phone in $
I = Household income in $ per year
W = Wage rate in $ per hourB is correct. Market equilibrium occurs when quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied, so set
Qd sp = Qs sp after inserting the given values for I and W. Next, solve for Psp:1,000 – 20Psp+ 2(9,500) = –200 + 50Psp– 80(10)
– 20Psp – 50Psp = – 200 – 800 – 1,000 – 19,000
–70Psp = – 21,000; Psp = – 21,000/–70 = $300.Determine and describe breakeven and shutdown points of production.
C is correct. A firm in a perfectly competitive environment with total costs equal to total revenue and marginal costs greater than marginal revenue is operating at the upper breakeven point. Therefore, it should decrease the level of production to enter profit territory.
Using the consumption basket for August 2011, the Paasche index is closest to:
44.Which of the following is most consistent with real business cycle (RBC) models? The arguments and recommendations of RBC models suggest that:
A. monetary variables have a major impact on GDP growth.
Questions 45 through 68 relate to Financial Statement Analysis
45.The current ratio for an industry is 3.2. Data for a firm in the industry is presented below:
| £ ‘000s | |
|---|---|
| 200 | |
| 350 | |
| 1,250 | |
|
300 |
|
200 |
| 600 |
C. more liquid.
Answer = B
A. increased the prices of its product significantly.
B.decided to make greater use of long-term borrowing capacity.
Explain the effects of barriers to entry, industry concentration, industry capacity, and market share stability on pricing power and return on capital.
A is correct.
“Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol.3, Reading 23, Section 5.1“Understanding Cash Flow Statements,” Elaine Henry, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol.3, Reading 27, Section 3.1, 3.2.5
Study Session 7–23–-e, 8–27–e
Explain the relationships among the income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, and statement of owners’ equity.
|
7,000 |
|
4,200 |
| 500 | |
| 250 | |
| 200 |
A.1,850.
B.2,050.
C.2,300.Answer = B
“Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction,” Elaine Henry, CFA, and Thomas R. Robinson, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Reading 22, Section 4.2, 4.3
Study Session 7–22–f
Describe the steps in the financial statement analysis framework.A is correct. Analyzing the prospects of the industry would be done in the collect data phase of a financial analysis.
B is correct. The annual report is not a requirement of the SEC.
51.An analyst is forecasting gross profit of the three following companies. He uses the five-year average gross margins and forecasts sales using an internal model.
A. 1.
B. 2.C. 3.
| Component | Cost | Useful Life |
|---|---|---|
| A | $500,000 | 10 years |
| B | $500,000 | 5 years |
The depreciation expense for the first year computed under IFRS compared with under U.S. GAAP will most likely be:
A. the same.
C is correct. Dividends received can be classified as either an operating or investing activity under IFRS, but can only be classified as an operating activity under U.S. GAAP.
54.The following selected data are available for a firm:
| $ millions | |
|---|---|
| 90.0 | |
| 15.2 | |
| 28.0 | |
| 34.3 | |
|
13.0 |
If the firm’s tax rate is 40%, the free cash flow to the firm (FCFF) is closest to:
Calculate FCFF:
|
74.7 |
|---|
55.The following financial data is available for a company:
The company’s sustainable growth rate is closest to:
A. 4.00%.
B. 4.40%.
C. 4.78%.
|
|
|---|---|
56.During a period of rising inventory costs, a company decides to change its inventory method from FIFO to the weighted average cost method. Which of the following financial ratios will most likely increase as a result of this change?
A. Current
B. Debt-to-equity
C. Number of days in inventoryA. proxy statement.
B. notes to the financial statements.
C. management discussion and analysis.
Total liabilities at the end of the year are closest to:
Explain the relationships among the income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, and statement of owners’ equity.
B is correct.
| $ 50,000 | ||
|
225,000 | |
|
450,000 | |
| 5,000 | ||
| (402,000) | ||
| 53,000 | ||
| (10,000) | ||
|
43,000 | 43,000 |
|
$318,000 | |
“Financial Reporting Standards,” Elaine Henry, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, and Thomas R. Robinson, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, Reading 24, Section 5.2
Study Session 7-24-d
Describe the International Accounting Standards Board’s conceptual framework, including the objective and qualitative characteristics of financial statements, required reporting elements, and constraints and assumptions in preparing financial statements.C is correct. Relevance and faithful representation are the two fundamental qualitative characteristics that make financial information useful according to the IASB Conceptual Framework.
“Understanding Balance Sheets," Elaine Henry, CFA and Thomas R. Robinson, CFA 2013 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, Reading 26, Section 2.2, 2.3, 4.3,
Study Session: 8-26- c, e
Describe alternative formats of balance sheet presentation.Describe different types of assets and liabilities and the measurement bases of each.
On the 2012 statement of cash flows, the company’s net cash flow from investing activities (in $‘000s) is closest to:
62. Selected information for a company is provided below.
| $ millions | |
|---|---|
|
4,800 |
| 2,880 |
The company’s cash conversion cycle (in days) is closest to:
B is correct.
Cash conversion cycle = Days sales outstanding + Days of inventory on hand – Days of payables
| Accounts receivable | Inventory | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Days in Sales (DSO) | Days on hand (DHO) | ||
| Sales | Purchases | ||
| A/R | Inventory | Payables | |
|
4,800 ÷ 625 | 2,880 ÷ 710 | 2,940 ÷ 145 |
| = 7.68 times | |||
| = 4.06 times | = 20.3 times | ||
| 365 ÷ 7.68 | |||
| 365 ÷ 4.06 | 365 ÷ 20.3 | ||
| = 48 days | = 90 days | = 18 days |
Cash conversion cycle = DSO + DOH – Days in Payables = 48 + 90 – 18 = 120 days
| 300 | 7.70 |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
600 | 12.00 | |
| 400 |
B. higher.
C. the same.
64. A company, which prepares its financial statements according to IFRS, owns several investment properties on which it earns rental income. It values the properties using the fair value model based on prevailing rental markets. After two years of increases the market softened in 2012 and values decreased. A summary of the properties’ valuations is as follows:
Which of the following best describes the impact of the revaluation on the 2012 financial statements?
A.€6.5 million charge to net income
B.€6.5 million charge to revaluation surplus
C.€4.5 million charge to revaluation surplus and €2.0 million charge to net incomeA is correct. For investment properties, when using the fair value model of revaluing assets, all increases and decreases affect net income.
65. Which of the following statements most accurately describes a valuation allowance for deferred taxes? A valuation allowance is required under:
“Income Taxes,” Elbie Antonites, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2013 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, Reading 31, Section 6.1
Study Session, 9-31-g
Describe the valuation allowance for deferred tax assets—when it is required and what impact it has on financial statements.B is correct. A valuation allowance is required under U.S. GAAP if there is doubt about whether a deferred tax asset will be recovered. Under IFRS the deferred tax asset is written down directly.
Answer = B
“Financial Reporting Quality: Red Flags and Accounting Warning Signs,”Thomas R. Robinson, CFA and Paul Munter
2013 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, Reading 33, Section 3
Study Session: 10-33-d
Describe common accounting warning signs and methods for detecting each.
| 2011 December 31 |
||
|---|---|---|
|
2,200 | 2,500 |
|
28% | 30% |
| 1,400 | 1,400 | |
| 25% | 25% | |
| 55 | 60 | |
| 500 | 500 |
The forecasted net income (in ‘000s) for 2012 is closest to:
A. $169.
B. $202.
C. $244.
(25) 0.05 x 500 average debt
A. a lower cash flow per share in that period.
B. a higher earnings per share in future periods. C. the same free cash flow to the firm in that period.
| Example |
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
|
|
A.both projects.
B.Project A only.
C.Project B only.Answer = B
Explain the NPV profile, compare NPV and IRR methods when evaluating independent and mutually-exclusive projects, and describe the problems associated with each of the evaluation methods.
The NPV of project A is €1,780.59
| ) | ) | ) | ) |
|---|
B.decrease.
C.remain unchanged.
| [ ( ) |
|
|---|
If the tax rate increases, then the bracketed term (1 – tax rate) decreases making the equity beta decrease because the asset beta is unchanged.
Answer = B
“Dividends and Share Repurchases: Basics,” George H. Troughton, CFA and Gregory Noronha, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol.4, Reading 39, Section 3.1, 3.2, 3.3.B.decrease.
C.remain unchanged.
73. Which is most likely considered a “pull” on liquidity?
A.Obsolete inventory
B.Reduction in a line of credit
C.Increased difficulty in collecting receivables74. Based on best practices in corporate governance procedures, independent board members most likely:
A.meet only in the presence of management.
B is correct. Under best practices in corporate governance procedures, independent board members should have a “lead” director when the board chair is not independent.
75. The unit contribution margin for a product is $12. Assuming fixed costs of $12,000, interest costs of $3,000, and a tax rate of 40%, the operating breakeven point (in units) is closest to:
B is correct. The operating breakeven point is:
76. The effective annualized cost (%) of a banker’s acceptance that has an all-inclusive annual rate of 5.25% for a one-month loan of $2,000,000 is closest to:
)
77. Which of the following is most consistent with the best practices of corporate governance?
Study Session 11-41-a, b
Define corporate governance.Describe practices related to board and committee independence, experience, compensation, external consultants, and frequency of elections, and determine whether they are supportive of shareowner protection.
C.statements made by the company’s management regarding capital structure policy.
Answer = B
A. act to level the playing field for market participants.
B. help define minimum standards of practice for agents.
80. A company has initiated the process of selling unproductive land representing 5% of its total assets and using the proceeds to buy back its common shares. Holding other factors constant, these actions by the company will most likely result in a:
A. higher return on equity.
B. higher operating margin.
C. lower sustainable growth.Calculate and interpret ratios used in equity analysis, credit analysis, and segment analysis. Describe the elements that should be covered in a thorough company analysis.
A is correct. Selling unproductive land and using the proceeds from the sale to buy back shares reduces the total assets. Holding sales constant the decrease in assets would improve the asset turnover. Buying back shares increases the firm’s financial leverage. Both the increase in asset turnover and financial leverage will lead to a higher return on equity.
“Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools,” John J. Nagorniak, CFA and Stephen E. Wilcox, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 51, Section 4
Study Session 14-51-c
Explain the rationale for using present-value of cash flow models to value equity and describe the dividend discount and free-cash-flow-to-equity models.A is correct. FCFE is a measure of the firm’s dividend paying capacity.
Answer = A
“Introduction to Industry and Company Analysis,” Patrick W. Dorsey, CFA, Anthony M. Fiore, CFA and Ian Rossa O’Reilly, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 50, Section 6.1
“Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools,” John J. Nagorniak, CFA and Stephen E. Wilcox, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 51, Section 4.3, Example 8
Study Session 14-50-k, 14-51-e
Describe the elements that should be covered in a thorough company analysis.
| V3 = | ) = $46.86 | ) + | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V0 = | ) + | ) + | ||
83. A trader buys 500 shares of a stock on margin at $36 a share using an initial leverage ratio of 1.66. The maintenance margin requirement for the position is 30 percent. The stock price at which the margin call will occur is closest to:
A. $20.57.
B. $25.20.
C. $30.86.84. Which of the following financial intermediaries are most likely to provide liquidity service to their clients?
A. Dealers
B. Brokers
C. ExchangesA. $49.49.
B. $49.84.
C. $49.94.Answer = B
A. security prices that reflect fundamental values.
B. the use of resources where they are most valuable.
87. An investor gathers the following information for an index:
“Security Market Indices,” Paul D. Kaplan, CFA, and Dorothy C. Kelly, CFA.
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 47, Section 2
Study Session 13-47-b
Calculate and interpret the value, price return, and total return of an index.Answer = B
“Market Efficiency,” W. Sean Cleary, CFA, Howard J. Atkinson, CFA, and Pamela Peterson Drake, CFA.
| Company A | Company B | |
|---|---|---|
| $20 | $10 | |
|
$22 | $13 |
|
16% | 13% |
| 40% | 60% |
Answer = C
“Overview of Equity Securities” Ryan C. Fuhrmann, CFA, and Asjeet S. Lamba, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 49, Section 7.1
“Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools” John J. Nagorniak, CFA, and Stephen E. Wilcox, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, Reading 51, Section 4.2
Study Session 14-49-g, 14-51-e
Distinguish between the market value and book value of equity securities.
90. An investor gathers the following data about a company:
| $1.47 | |
|---|---|
| $4.00 | |
| Estimate of long-run return on equity (ROE) | 15% |
| 40% | |
| 12% |
The company’s justified forward P/E is closest to:
A. 10.0.
B. 13.3.
C. 20.0.Justified forward P/E: P0/E1 = p / (r – g)
p = payout ratio = 40% (given);
r = required rate of return = 12% (given)
g = (1 – Dividend payout ratio) × ROE = (1- 0.40) × 15 = 9% P0/E1 = p / (r – g) = 0.40 / (0.12 – 0.09) = 13.3xAlternatively:
Justified forward P/E: P0/E1 = (D1 / E1) / (r – g)
g = (1 – Dividend payout ratio) × ROE = (1- 0.40) × 15 = 9%
D1 = $1.47 x 1.09 = 1.60; E1 = $4.00 (given); r = required rate of return = 12% (given) P0/E1 = (D1 / E1) / (r – g) = (1.60 / 4.00) / (0.12 – 0.09) = 13.3x
Answer = A
“Derivative Markets and Instruments,” Don M. Chance, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, Reading 60, Section 2.1
Study Session 17-60-c
Define forward contracts, futures contracts, options (calls and puts), and swaps and compare their basic characteristics.B.receive EUR 4,312,500 from the dealer.
C.receive EUR 5,000,000 from the dealer.Answer = C
Answer = A
“Futures Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, Reading 62, Section 3
Study Session 17-62-d
Describe price limits and the process of marking to market, and calculate and interpret the margin balance, given the previous day’s balance and the change in the futures price.C.Yes, if it pays a high enough dividend.
Answer = C
Answer = B
“Swap Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, Reading 64, Section 3.1
Study Session 17-64-b
Describe, calculate, and interpret the payments of currency swaps, plain vanilla interest rate swaps, and equity swaps.“Risk Management Applications of Option Strategies,” Don M. Chance, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, Reading 65, Section 2.1
Study Session 17-65-a
Determine the value at expiration, profit, maximum profit, maximum loss, breakeven underlying price at expiration, and payoff graph of the strategies of buying and selling calls and puts, and determine the potential outcomes for investors using these strategies.C is correct because buying a call gives the owner the right to buy the stock at the exercise price. The investor predicts that the stock will increase to $95 at the end of two months. He will likely be able to sell his calls for at least $7 and realize a profit.
C.has a sinking fund provision.
Answer = C
B.assumes all the bonds have the same discount rate. C.ignores differences in coupon rates across the bonds.
Answer = A
A.Both investors will choose the taxable bond.
B.Both investors will choose the tax-exempt bond.
100. The yield on a U.S. Treasury STRIPS security is also known as the Treasury:
A.spot rate.
101. Consider a 5-year option-free bond that is priced at a discount to par value. Assuming the discount rate does not change, one year from now the value of the bond will most likely:
A.increase.
A is correct because the bond is priced below its par value but will be worth exactly par value at maturity. Over time, assuming a stable discount rate, the value of the bond must rise so that it is equal to par at maturity.
102. The market value of an 18-year zero-coupon bond with a maturity value of $1,000 discounted at a 12% annual interest rate with semi-annual compounding is closest to:
C.security has a bullet maturity rather than an amortizing structure.
Answer = B
| Notation | Forward Rate |
|---|---|
| 1f0 | 0.50% |
| 1f1 | 0.70% |
| 1f2 | 1.00% |
| 1f3 | 1.50% |
| 1f4 | 2.20% |
| 1f5 | 3.00% |
| 1f6 | 4.00% |
A.0.74%.
B.1.48%.
C.2.06%.Answer = B
A.increases measurement accuracy.
B.is easier to model than scenario analysis.
106. An analyst uses a valuation model to estimate the value of an option-free bond at 92.733 to yield 11%. If the value is 94.474 for a 60 basis point decrease in yield and 91.041 for a 60 basis point increase in yield, the effective duration of the bond is closest to:
A.1.85.
B.3.09.
C.6.17.
A.put the issue.
B.call the issue.
108. The bonds issued by ALS Corp. are currently priced at 108.00 and are option free. Based on a portfolio manager’s valuation model, a 10 basis points rise in interest rates will result in the bond price falling to 106.50 while a 10 basis points fall in interest rates will result in the bond price rising to 110.00. The market value of the portfolio manager’s holdings of ALS bonds is $2 million. The expected change in the market value of this holding for a 100 basis point change in interest rates will be closest to:
A.$124,000.
B.$322,600.
C.$645,200.The approximate percent change in the value of the holdings (the dollar duration) is: 0.1613 × 2,000,000 = $322,600.
Questions 109 through 114 relate to Alternative Investments.
“Introduction to Alternative Investments,” Terri Duhon, George Spentzos, CFA, and Scott D.
Stewart, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, Reading 66, Sections 2.1 Study Session 18-66-b
Describe categories of alternative investments.C. convenience yield.
Answer = B
C. reduce exposure to inflation.
Answer = C
A. assets are not marked to market.
B. data are subject to survivorship bias.
C is correct. Since commodity indices are constructed using commodity futures and not the underlying commodities there can be differences between commodity index returns and the returns of the underlying commodities.
113. Which of the following investments most likely provides an investor with indirect, equity exposure to real estate?
“Introduction to Alternative Investments,” Terri Duhon, George Spentzos, CFA, and Scott D.
Stewart, CFA
2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, Reading 66, Sections 5.1, 5.2 Study Session 18-66-dexposure. Real estate investment partnerships are a form of direct real estate equity investment.
Commercial mortgage backed securities (CMBS) provides investors with indirect, debt investment
Answer = A
“Introduction to Alternative Investments,” Terri Duhon, George Spentzos, CFA, and Scott D.
The incentive fee = ($541,500,000 - $475,000,000) × 0.10 = $6,650,000
Total fees = $14,772,500
Answer = A
"Portfolio Management: An Overview” by Robert M. Conroy, CFA and Alistair Byrne, CFA Modular Level I, Vol. 4, Reading 42, Section 3 (Exhibit 14)
| Year | Net Return (%) |
|---|---|
|
The 2012 return needed to achieve a trailing five year geometric mean annualized return of 5.0% when calculated at the end of 2012 is closest to:
Holding period total return (cumulative) factor calculation through 2011:
(1-0.348)×(1+0.322)×(1+0.111)×(1-0.014) = 0.652 × 1.322 × 1.111 × 0.986 = 0.9442 Compound total return (cumulative) factor at 5% per year of five percent for five years: 1.055 = 1.2763
Return needed in 2012 to achieve a compound annualized return of 5%
1.2763/.9442 = 1.3517 = 35.2 percent
Check: 0.944 × 1.352 = 1.276(1/5) = 1.050 = 5 percent annualized117. Consider a portfolio with two assets. Asset A comprises 25% of the portfolio and has a standard deviation of 17.9%. Asset B comprises 75% of the portfolio and has a standard deviation of 6.2%. If the correlation of these two investments is 0.5, the portfolio standard deviation is closest to:
A. 1.02.
B. 1.05.
C. 1.16Answer = B
A. M-squared
B. Sharpe ratio
C. Treynor ratioAnswer = C
A. low ability to take risk, but a high willingness to take risk B. high ability to take risk, but a low willingness to take risk C. high ability to take risk and a high willingness to take risk
Answer = C
2012 Level I Mock Exam: Morning Session
The morning session of the 2012 Level I Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA®) Mock Examination has 120
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
| 109–114 |
|
|
| 115–120 | ||
|
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct,” CFA Institute
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 8
Study Session 1-1-a
Describe the structure of the CFA Institute Professional Conduct Program and the process for the enforcement of the Code and Standards.C is correct because the two principles of the Rules of Procedure for Proceedings Related to Professional Conduct are confidentiality of proceedings and fair process to the member and candidate.
B is correct because a composite must include all actual, fee-paying, discretionary portfolios managed in accordance with the same investment mandate, objective, or strategy (Standards IV Composites).
By including both value and growth portfolios, the composite is made up of portfolios with different investment mandates or strategies.
Answer = A
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 123–125
Study Session 1-2-c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 78–80
Study Session 1-2-b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.B is correct because the client is the trust/trustees, not the beneficiary. Mawar followed Standard III (C) Suitability by managing the trust assets in a way that would likely result in a
Answer = C
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 46–47, 90–91, 144–146
Study Session 1-2-a, b
Demonstrate and explain the application of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct to situations involving issues of professional integrity.Answer = B
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = A
CFA Institute Standards
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 101–102
Study Session 1-2-c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.
B.disclosure of conflicts.
C.independence and objectivity.
A.Nonpayment of CFA Institute membership dues
B.Attributing her superior returns to participation in the CFA Program
C.Indicating that being a CFA charterholder has enhanced her portfolio management skillsAnswer = B
A.A multi-national financial services holding company
B.An investment management division of a regional commercial bank
C.A locally incorporated subsidiary undertaking investment management servicesAnswer = A
B.fee- and non-fee-paying discretionary accounts.
C.fee- and non-fee-paying discretionary and non-discretionary accounts.
12. In countries where new local laws relating to calculation and presentation of investment performance conflict with GIPS standards, firms who have claimed GIPS compliance should most likely:
A.stop claiming GIPS compliance.
13. Firms claiming GIPS compliance must make every reasonable effort to provide a compliant presentation to which of the following?
A.Existing clients
B.Prospective clients
C.Both existing and prospective clients
14. James Simone, CFA, the CFO of a publicly listed company, seeks to improve the quality of his company’s communication with institutional fund managers. He holds an investor briefing with this group the evening before the company earnings are announced. The company’s quarterly earnings are broadcast in a press release the next day before the market opens. The earnings information in the investor briefing is identical to that in the press release. Did Simone most likely violate the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
A.Yes
B.No, because investor briefing and press release information are identical C.No, because the company releases information while the market is closedA.No
B.Yes, she did not disclose her potential conflicts of interest to either client.C.Yes, she profited on the real estate to the detriment of her financially stressed client.
16. Prudence Charmaine, a CFA charterholder, was recently accused in writing of cheating on a professional accounting exam. She denied cheating and successfully defended herself against the allegation. As part of her defense and as evidence of her character, Charmaine stated she is a CFA charterholder and upholds the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct. On her next annual Professional Conduct Statement, Charmaine does not report this allegation to CFA Institute. Did Charmaine most likely violate the CFA Institute Code of Ethics or Standards of Professional Conduct?
A.No
B.Yes, she improperly used the CFA Institute Code and Standards to defend herself. C.Yes, she did not report the allegation on her annual Professional Conduct Statement.
17. Margie Germainne, CFA, is a risk management consultant who has been asked by a small investment bank to recommend policies to prevent bank employees from front running client orders. These clients generally invest in one or more of the bank’s large cap equity unit trusts.
To ensure compliance with the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct, Germainne should least likely recommend which of the following? Employees should be restricted from trading:
“Guidance for Standards I–VII,” CFA Institute
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 54, 131–134
Study Session 1-2-c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.A is correct because while Standard VI (B) Priority of Transactions is designed to prevent any potential conflict of interest or the appearance of a conflict of interest with respect to personal transactions, it does not ban employees from trading securities. A ban on all equity related securities could be excessively restrictive to employees and unnecessary if appropriate personal transaction policies and procedures are in place.
C is correct because the Standards require the disclosure of conflicts (Standard VI (A)). For Meir to understand what potential conflicts of interest employees may have with the firm and with their clients, he would need to know the outside interests of each staff member. The staff
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = C
“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. DeFusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkle
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 266–267
Study Session 2-5-c
Calculate and interpret the effective annual rate, given the stated annual interest rate and the frequency of compounding.“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. DeFusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E.
Pinto, and David E. Runkle
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 399
Study Session 2-7-j, k
Explain skewness and the meaning of a positively or negatively skewed return distribution. Describe the relative locations of the mean, median, and mode for a unimodal, nonsymmetrical distribution.
|
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
–12,500 | 2,000 | 4,000 | 5,000 | 2,000 | 1,000 | 500 |
Calculate and interpret the results using each of the following methods to evaluate a single capital project: net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), payback period, discounted payback period, and profitability index (PI).
C is correct. Enter the given cash flows into a financial calculator and solve for IRR. CF0 = –12,500, CF1 = 2,000, CF2 = 4,000, CF3 = 5,000, CF4 = 2,000, CF5 = 1,000, and CF6 = 500. Compute i.
|
|---|
return across the period is closest to:
23. The following sample of 10 items is selected from a population. The population variance is unknown.
The standard error of the sample mean is closest to:
“Sampling and Estimation,” Richard A. DeFusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkle
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 557
Study Session 3-10-f
Calculate and interpret the standard error of the sample mean.
A is correct. When the population variance is unknown, the standard error of the sample meanis
| 𝑠 | |
|---|---|
| 𝑠𝑋� = | √𝑛 |
s2 = [(10 – 3.6)2 + (20 – 3.6)2 + (–8 – 3.6)2 + (2 – 3.6)2 + (–9 – 3.6)2 + (5 – 3.6)2 + (0 – 3.6)2 + (–8 – 3.6)2 + (3 – 3.6)2 + (21 – 3.6)2] ÷ 9 = 117.6 and s = 10.844.
The standard error of the sample mean is, therefore, 10.844 ÷ 100.5 = 3.429.
C.conditional distribution.
Answer = A
25. An analyst collects data relating to five commonly used measures of use of debt (leverage) and interest coverage for a randomly chosen sample of 300 firms. The data comes from those firms’ fiscal year 2011 annual reports. This data is best characterized as:
A.time-series data.
C is correct. Data on some characteristics of companies at a single point in time are cross-sectional data.
26. A financial contract offers to pay €1,200 per month for five years with the first payment made today. Assuming an annual discount rate of 6.5%, compounded monthly, the present value of the contract is closest to:
Calculate and interpret the future value (FV) and present value (PV) of a single sum of money, an ordinary annuity, an annuity due, a perpetuity (PV only), and a series of unequal cash flows.
B is correct. Enter the following into a financial calculator:
number of periods (5 × 12), N= 60; the discount rate, I/Y= (6.5/12) = 0.54166667; payment, PMT = 1,200.27. A two-tailed t-test of the null hypothesis that the population mean differs from zero has a p- value of 0.0275. Using a significance level of 5%, the most appropriateconclusion is:
A.reject the null hypothesis.
Runkle
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 599–600
Study Session 3-11-e
Explain and interpret the p-value as it relates to hypothesis testing.A is correct. The p-value is the smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected. In this case, the given p-value is less than the given level of significance and we reject the null hypothesis.
The t-statistic to test the hypothesis that the mean difference is equal to zero is closest to:
A.0.23.
B.0.27.
C.0.52.
𝑑 = 1 𝑛 � 𝑑𝑖
Then, calculate the sample variance and the standard error of the mean difference:
In this case, the mean difference is 1.4. The sample variance is 36.8. The standard error of the mean difference is 2.712932. The t-statistic is 0.51605.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Differences | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 18 | 7 | (7 – 1.4)2 = 31.36 |
| 2 | 12 | 9 | 3 | (3 – 1.4)2 = 2.56 |
| 3 | –5 | –8 | 3 | (3 – 1.4)2 = 2.56 |
| 4 | 6 | 3 | 3 | (3 – 1.4)2 = 2.56 |
| 5 | –8 | 1 | –9 | (–9 – 1.4)2 = 108.16 |
|
|
|||
| Sample variance: | 147.2 ÷ 4 = 36.8 | |||
| Standard error: | 2.712932 = √36.8 ÷ 5 | |||
| t-Statistic: |
A.£2,525.
B.£2,542.
C.£2,854.Answer = B
B is correct. The future value of a given lump sum, calculated using continuous compounding, is FV = PV × ert. In this case, 2000 × e.06×4 = 2,542.
30. A graphic depiction of a continuous distribution that shows the left tail to be longer than the right tail is best described as having:
Answer = C
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. DeFusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkle
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 401
Study Session 2-7-j
Explain skewness and the meaning of a positively or negatively skewed return distribution.“Sampling and Estimation,” Richard A. DeFusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkle
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 562–566
Study Session 3-10-h, i
Distinguish between a point estimate and a confidence interval estimate of a population parameter.Describe the properties of Student’s t-distribution and calculate and interpret its degrees of freedom.
The median value of the items is:
A.3.
B.4.
C.5.
Questions 33 through 44 relate to Economics
33. Demand for a good is most likely to be more elastic when:
C is correct. The longer the time that has elapsed since a price change, the more elastic demand is. For example, if gas prices rise, consumers cannot quickly change their mode of transportation
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 20 |
| 4 | 36 |
| 6 | 50 |
| 8 | 62 |
The marginal revenue product ($ per worker) for hiring the fifth and sixth workers is closest to:
A.14.
B.21.
C.42.B is correct. The marginal product (MP) is the amount of additional output resulting from using one more unit of input: ΔTP/ΔL, where ΔTP is the change in total product and ΔL is the change in total labor. The marginal revenue product (MRP) is the marginal product of an input times the price of the product: MP × Price = ΔTP/ΔL × Price.
In this problem, the marginal product of hiring the 5th and 6th workers (ΔL = 2) is 14 shirts per hour/2 workers = 7 shirts per hour/worker. With each shirt resulting in $3 of revenue, the MRP is 7 shirts per hour/worker × $3/shirt = $21 per worker.
Answer = C
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.Increasing reserve requirements
B.Selling securities on the open market
C.Purchasing securities on the open marketAnswer = C
A.increase.
B.decrease.
A is correct. Aggregate demand rises when the government increases spending by the same amount as it raises taxes because the marginal propensity to spend out of disposable income is less than 1, and hence for every dollar less in disposable income, spending only falls by c (where c is the marginal propensity to consume in dollars). Aggregate spending will fall less than the tax rise by a factor c. This additional output will, in turn, lead to further increases in income and output through the multiplier effect.
38. In early 2011, a New Zealand traveler returned from Singapore with SGD7,500 (Singapore dollars). A foreign exchange dealer provided the traveler with the following quotes:
B is correct. The NZD/SGD cross-rate is NZD/USD × USD/SGD = 0.7670 × 1.26 = 0.9664. The traveler will receive 0.9664 NZD per SGD; 0.9664 NZD/SGD × 7,500 SGD = 7,248 NZD.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
If the real interest rate is 3% and government spending increases to 2,000, the increase in aggregate income will be closest to:
|
|---|
|
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A is correct. Normal profitis the level of accounting profit needed to just cover the implicit opportunity costs ignored in accounting costs. This is all that a firm needs to earn in the long run to remain in business. Failing to earn normal profits over the long run has a debilitating impact on the firm’s ability to access capital and to function properly as a business enterprise.
41. A small country has a comparative advantage in the production of pencils. The government establishes an export subsidy for pencils to promote economic growth. Which of the following will be the most likely result of this policy?
“International Trade and Capital Flows,” Usha Nair-Reichert and Daniel Robert Witschi 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 456–457
Study Session 6-20-d
Compare types of trade and capital restrictions and their economic implications.C is correct. Export subsidies interfere with the functioning of the free market and result in a deadweight loss to society. The deadweight loss arises on the producer side as the higher subsidized price causes inefficient producers to remain in the market; on the consumer side, the higher price causes those that would have purchased at the lower price to be shut out of the market.
Answer = B
“International Trade and Capital Flows,” Usha Nair-Reichert and Daniel Robert Witschi 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 452–456
Study Session 6-20-d
Compare types of trade and capital restrictions and their economic implications.C.adjusting interest rates to stimulate higher domestic savings.
Answer = A
44. In the classification of currency regimes, a currency board system (CBS) most likely differs from a fixed-rate parity system in that:
A.a CBS has a discretionary target level of foreign exchange reserves.
C is correct. In a CBS, the monetary authority has an obligation to maintain 100% foreign currency reserves against the monetary base. It thus cannot lend to troubled financial institutions. As long as the country under a fixed-parity regime maintains its exchange peg, the central bank can serve as a lender of last resort.
Questions 45 through 68 relate to Financial Statement Analysis
“Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction,” Elaine Henry and Thomas R. Robinson 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 28–31
Study Session 7-22-d
Describe the objective of audits of financial statements, the types of audit reports, and the importance of effective internal controls.B is correct. For a publicly traded firm in the United States, the auditor must express an opinion as to whether the company’s internal control system is in accordance with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, under the Sarbanes–Oxley Act. This is done either as a final paragraph in the auditor’s report or as a separate opinion.
“Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 71–73
Study Session 7-23-d
Explain the need for accruals and other adjustments in preparing financial statements.A is correct. The adjusting entry to record the expiry of a prepaid expense is the reduction of an asset (the prepaid) and the recognition of the expense.
Analyze balance sheets and statements of changes in equity.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Shareholders’ Equity (¥) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 200,000 | ||
| (6,000) | ||
| 50,000 | ||
|
42,000 | |
|
(7,000) | |
| 85,000 | 85,000 | |
| (3,000) | ||
| 276,000 | ||
presented below.
| Sales revenue | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| Cost of goods sold | 47,000 | 47,500 |
| Depreciation expense | 4,000 | 3,500 |
| Net income | $ 11,122 |
Current Assets
Current Liabilities
Accounts payable
| 7,000 | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
The cash collected from customers in 2011 is closest to:
A is correct. Cash collected from customers = Revenues – Increase in accounts receivable= $100 – (25 – 13.5) = 88.5.
49. Selected information for a company and the common size data for its industry are provided below.
Which of the following is most likely a contributor to the company’s inferior ROE compared to that of the industry? The company’s:
A.tax burden ratio.
Demonstrate the application of the DuPont analysis of the return on equity, and calculate and interpret the effect of changes in its components.
C is correct.
| Calculation | Company | Industry | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||
|
|
||
financial statements within the IFRS Conceptual Framework?
A.Matching
B.Materiality
C.Accrual basisA is correct. The IFRS Conceptual Framework specifies a number of general features underlying the preparation of financial statements, including materiality and accrual basis. Matching is not one of those general features; it is a general principle of expense recognition.
51. A company suffered a substantial loss when its production facility was destroyed in an earthquake against which it was not insured. Geological scientists were surprised by the earthquake as there was no evidence that one had ever occurred in that area in the past. Which of the following statements is most accurate? The company should report the loss on its income statement:
“Understanding Income Statements,” Elaine Henry and Thomas R. Robinson
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 182–183
Study Session 8-25-e
Describe the financial reporting treatment and analysis of non-recurring items (including discontinued operations, extraordinary items, and unusual or infrequent items) and changes in accounting standards.A is correct. To qualify as an extraordinary item, an item must be both unusual in nature and infrequent in occurrence: The description of the earthquake meets these criteria. Extraordinary items are only allowed under U.S. GAAP and are reported on the income statement net of tax.
A.$1,000.
B.$1,050.
C.$1,250.Answer = B
tax payable [or current income tax expense] and representing an increase in the expense). Therefore, the income tax expense = 1,000 + 50 = 1,050.
53. Which of the following inventory valuation methods best matches the actual historical cost of the inventory items to their physical flow?
54. A company has announced that it is going to distribute a group of long-lived assets to its owners in a spin-off. The most appropriate way to account for the assets until the distribution occurs is to classify them as:
A.held for sale with no depreciation taken.
C is correct. Long-lived assets that will be disposed of other than by sale, such as a spin-off, an exchange for other assets, or abandonment, are classified as held for use until disposal and continue to be depreciated until that time.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| 2011 | 2010 | |
|---|---|---|
| $21,000 | $18,500 | |
|
600 | 425 |
|
1,525 | 1,462 |
| 728 | 620 | |
| 3,233 | 3,080 | |
| $27,086 | $24,087 |
The pension expense (in thousands) reported in 2011 is closest to:
A.$1,525.
B.$2,217.
C.$2,253.56. An analyst is assessing a company’s quality of earnings by looking at the cash flow earnings index (operating cash flow divided by net income). Potential problems would most likely be indicated if the ratio were consistently:
A.equal to 1.0.
“Financial Reporting Quality: Red Flags and Accounting Warning Signs,” Thomas R. Robinson and Paul Munter
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 594
Study Session 10-33-d
Describe common accounting warning signs and methods for detecting each.B is correct. A cash flow earnings index consistently below 1.0 could indicate potential problems in a company’s quality of earnings.
| Year | Millions |
|---|---|
| 2012 | $ 200 |
| 2013 | 200 |
| 2014 | 200 |
| 2015 | 200 |
| 2016 | 200 |
|
$ 1,000 |
After adjustment for the off-balance-sheet financing, the debt-to-total-assets ratio for the company is closest to:
Explain appropriate analyst adjustments to a company’s financial statements to facilitate comparison with another company.
A is correct. The present value of the operating leases should be added to both the total debt and the total assets.
B.financial position.
C.comprehensive income.
A.verifiability.
B.comparability.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A is correct. Under the International Accounting Standards Board’s Conceptual Framework, verifiability is the qualitative characteristic that means that different knowledgeable and independent users would agree that the information presented faithfully represents the economic events that it is intended to represent.
Contrast cash flow statements prepared under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and U.S generally accepted accounting principles (U.S. GAAP).
A is correct. Interest paid must be categorized as an operating cash flow activity under U.S. GAAP, although it can be categorized as either an operating or financing cash flow activity under IFRS.
| Income Statement Items | ($) |
|---|---|
| 421,000 | |
| 315,000 | |
| Balance Sheet Items | |
|
30,000 |
|
40,000 |
| 36,000 | |
| 33,000 |
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = A
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.4.8%.
B.15.2%.
C.22.7%.
|
|
15.2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15.2 | |||
| According to International Financial Reporting Standards, which of the following conditions | |||
B.Costs can be reliably measured.
C.Goods have been delivered to the customer.
64. A company entered into a three-year construction project with a total contract price of $10.6 million and an expected total cost of $8.8 million. The following table provides cash flow information relating to the contract:
“Understanding Income Statements,” Elaine Henry and Thomas R. Robinson
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 162–164
Study Session 8-25-b
Describe the general principles of revenue recognition and accrual accounting, specific revenue recognition applications (including accounting for long-term contracts, installment sales, barter transactions, and gross and net reporting of revenue), and the implications of revenue recognition principles for financial analysis.
• €2.0 million for repairs to the building’s roof and windows
• €0.5 million to modify the interior layout to meet their needs (moving walls and doors, inserting and removing partitions, etc.)
• €0.1 million on an orientation and training session for employees to familiarize them with the facilityThe cost to be capitalized to the building account (in millions) for accounting purposes is closest to:
Initial cost €35.00 Repairs to roof and windows 2.00 Modifications to interiors 0.50 Total cost €37.5 million
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| • | ||
|---|---|---|
| • |
|
|
| • |
|
|
| • | Market rate at issue |
Answer = C
“Non-Current (Long-Term) Liabilities,” Elizabeth A. Gordon and Elaine Henry 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 537, 539–540, 544
Study Session 9-32-c
Explain the derecognition of debt.
The market value of debt at retirement can be determined by discounting the future cash flows at the current market rate (5%) using a financial calculator:
FV = 20,000,000; i = 5%; PMT = 1,200,000; N = 2; Compute PV = 20,371,882
Interest
| 2009 |
|
Coupon 6% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% | ||||
| 21,780,729 | 871,229 | 1,200,000 |
|
|
| 2010 | 21,451,958 | 858,078 | 1,200,000 |
|
| 2011 | 21,110,036 | 844,401 | 1,200,000 |
B.the auditor’s report.
C.financial statement analysis.
68. Which of the following is most likely a reason that a lessor can offer attractive lease terms and lower cost financing to a lessee? Because the:
A.lessor retains the tax benefits of ownership.
A is correct. The lessor often retains the tax benefits of ownership of the leased asset, which allows the lessor to pass those savings along to the lessee in the form of lower financing costs or other attractive terms.
Questions 69 through 78 relate to Corporate Finance
B is correct. Financing costs are not included in a cash flow calculation but are considered in the calculation of the discount rate.
70. A company has an equity beta of 1.4 and is 60% funded with debt. Assuming a tax rate of 35%, the company’s asset beta is closest to:
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
71. A company’s taxable income is 17.1% of sales. Assuming taxes of 42% and a dividend payout of 50%, the net profit margin is closest to:
Net profit margin = Net income ÷ Sales = [Earnings before tax × (1 – Tax rate)] ÷ Sales
(0.171 × Sales) × (1-0.42)
=
Sales
= 0.171 × (1 – 0.42) = 9.92%.
| Year 0 | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| –$75,000 | $21,600 | $23,328 | $37,791 | $40,815 |
Answer = C
“Capital Budgeting,” John D. Stowe and Jacques R. Gagne
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, p. 15
Study Session 11-36-d
Calculate and interpret the results using each of the following methods to evaluate a single capital project: net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), payback period, discounted payback period, and profitability index (PI).
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C is correct.
DOL = (Revenues – Variable operating costs)
(Revenues – Variable operating costs – Fixed operating costs)B.link compensation with long-term objectives.
C.include a representative from the firm’s external auditor.
• Bonds are priced at par and they have an annual coupon rate of 9.2% • Preferred stock is priced at $8.18 and it pays an annual dividend of $1.35 • Common equity has a beta of 1.3
• The risk-free rate is 4% and the market premium is 11%
• Capital structure: Debt = 30%; Preferred stock = 15%; Common equity = 55% • The tax rate is 35%The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) for the company is closest to:
Describe how taxes affect the cost of capital from different capital sources. Calculate and interpret the expected return of an asset using the CAPM.
C is correct.
A.dividends.
B.long-term leases.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| 4 million | |
|---|---|
| 40% | |
| 10% | |
|
$20.00 |
|
$6 million |
Answer = A
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela Peterson Drake
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 40–43
“Dividends and Share Repurchases: Basics,” George Troughton and Gregory Noronha 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 142–143
Study Session 11-37-b, 11-39-d
Describe how taxes affect the cost of capital from different capital sources.𝐶𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑒𝑎𝑟𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔𝑠 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑠ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑒 = $6,000,000 ÷ 4,000,000 = $1.50
𝐸𝑎𝑟𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔𝑠 𝑦𝑖𝑒𝑙𝑑 = $1.50 ÷ $20.00 = 7.5%
If the after-tax cost of debt (10% × [1 – 40%] = 6%) is below the earnings yield, the earnings per share will increase. This can be derived from Example 7 on p. 142.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A is correct. Note: The face value is greater than the purchase price because the T-bill sells at a discount.
| 𝐹𝑎𝑐𝑒 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 − 𝑃𝑢𝑟𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒 | 360 | |
|---|---|---|
| × | 𝐷𝑎𝑦𝑠 𝑡𝑜 𝑚𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑦 |
𝐷𝐵𝑌 = $10,000 − $9,932.40
$10,000
Answer = C
“Market Organization and Structure,” Larry Harris 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 51–53
Study Session 13-47-g, h
80. The type of voting in board elections that is most beneficial to shareholders with a small number of shares is best described as:
A.statutory voting.
B.voting by proxy.C is correct. Cumulative voting allows shareholders to direct their total voting rights to specific candidates, as opposed to having to allocate their voting rights evenly among all candidates. Thus, applying all of the votes to one candidate provides the opportunity for a higher level of representation on the board than would be allowed under statutory voting.
81. An investor gathered the following data in order to estimate the value of the company's preferred stock:
The value of the company's preferred stock is closest to:
A is correct.
|
|---|
Answer = C
“Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools,” John J. Nagorniak and Stephen E. Wilcox 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 276, 281, 289–291
Study Session 14-52-h
Calculate and interpret the following multiples: price to earnings, price to an estimate of operating cash flow, price to sales, and price to book value.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
83. An investor evaluating a company's common stock for investment has gathered the following data.
| $2.50 | |
|---|---|
| 60% | |
| 25% | |
| 5% | |
|
12% |
Using the two-stage dividend discount model, the value per share of this common stock in 2012 is closest to:
= $1.67 + $1.87 + $28.03 = $31.57.
84. Which of the following is least likely to be directly reflected in the returns on a commodity index?
B is correct. Commodity index returns reflect the changes in future prices and the roll yield. Changes in the underlying commodity spot prices are not reflected in a commodity index.
85. A trader who has bought a stock at $30 is concerned about a downside movement in the stock and would like to place an order that guarantees selling it at $25. Which of the following will most likely help the trader achieve her objective? (GTC = Good-till-cancelled)
C is correct. Option contracts can be viewed as limit orders for which execution is guaranteed at the strike price. Therefore, a “put buy” order at a strike price of 25 will guarantee selling the stock at 25.
86. A trader who buys a stock priced at $64 on margin with a leverage ratio of 2.5 and a maintenance margin of 30% will most likely receive a margin call when the stock price is at or falls just below:
C is correct.
| Equity = |
|
|
|---|---|---|
87. Compared to its market-value-weighted counterpart, a fundamentally weighted index will least likely have a:
A.value tilt.
88. A U.S. institutional money manager prefers to invest in depository instruments of non-domestic equity securities that are privately placed in the U.S. and not subject to the foreign ownership and capital flow restrictions. The type of security that is most appropriate for this investor is:
A.global registered shares.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B is correct. Global depository receipts (GDRs) meet the investor preferences. They are not subject to the foreign ownership and capital flow restrictions that may be imposed by the issuing company’s home country because they are sold outside of that country. GDRs cannot be listed on U.S. exchanges, but they can be privately placed with the institutional investors based in the United States.
Based on the above information, the analyst will most appropriately conclude that compared to the firms in Industry 2, those in Industry 1 would potentially have:
A.larger economic profits.
Explain effects of industry concentration, ease of entry, and capacity on return on invested capital and pricing power.
Describe the principles of strategic analysis of an industry.
B.experiencing a higher than the sustainable growth rate.
C.mature and relatively insensitive to the economic fluctuations.
91. Which of the following is least likely one of main purposes of derivative markets?
A.Reveal prices and volatility of the underlying assets
B.Improve market efficiency by lowering transaction costs C.Enable companies to more easily practice risk managementA.$30
B.$60
C.$70
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = C
“Swap Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 144–147
Study Session 17-64-b
Describe, calculate, and interpret the payment of currency swaps, plain vanilla interest rate swaps, and equity swaps.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
94. Epsilon Inc., a U.S. based company, must pay ¥1,000,000,000 to its Japanese component supplier in 3 months. Epsilon approaches a dealer and enters into a USD/JPY currency forward contract, containing a stipulation for physical delivery, to manage the foreign exchange risk associated with the payment to its supplier. Which of these best describes Epsilon’s currency forward contract?
“Forward Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 43–44
Study Session 17-61-h
Describe the characteristics of currency forward contracts.A is correct because this currency forward contract requires physical delivery; therefore, Epsilon receives 1,000,000,000 JPY from the dealer in exchange for paying USD.
A is correct because, for a European put, the exercise price must be adjusted to the present value because the option can only be exercised on expiration.
96. An investor purchases ABC stock at $71 per share and executes a protective put strategy. The put option used in the strategy has a strike price of $66, expires in two months, and is purchased for $1.45. At expiration, the protective put strategy breaks even when the price of ABC is closest to:
C is correct because to break even, the underlying stock must be at least as high as the amount expended up front to establish the position. To establish the protective put, the investor would have spent $71 + $1.45 = $72.45.
Questions 97 through 108 relate to Fixed Income Investments
| Year | Risk Free Rate | Coupon Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.00% | 6.00% |
| 2 | 3.50% | 5.00% |
| 3 | 4.25% | 3.50% |
| 4 | 3.70% | 4.60% |
| 5 | 3.25% | 5.50% |
C.deferred coupon bond.
Answer = B
A.zero.
B.related to the security’s coupon reset frequency. C.similar to an otherwise identical fixed-rate security.
A.arbitrage transaction.
B.balance sheet transaction.
C.capital infusion transaction.A.$92.89
B.$99.07
C.$107.44Answer = A
B is correct because if the discount rate rises to 7.5% from 6.5%, the price of a bond decreases. At a discount rate of 7.5%, the bond sells at a discount to face value. As a discount bond approaches maturity, it will increase in price over time until it reaches par at maturity.
102. A fixed income security’s current price is 101.45. You estimate that the price will rise to 103.28 if interest rates decrease 0.25% and fall to 100.81 if interest rates increase 0.25%. The security’s effective duration is closest to:
Study Session 16-59-d
Calculate and interpret the effective duration of a bond, given information about how the bond’s price will increase and decrease for given changes in interest rates.B is correct because the effective duration equals
(Price if rates fall – Price if rates rise)/(2 × Current price × Change in rates) = (103.28 – 100.81)/(2 × 101.45 × 0.0025) = 4.87.
A.Both are affirmative covenants.
B.Covenant 1 is negative and Covenant 2 is affirmative. C.Covenant 1 is affirmative and Covenant 2 is negative.
A.par value plus accrued interest.
B.accrued interest plus agreed upon bond price. C.agreed upon bond price excluding accrued interest.
105. An investor purchases a 5% coupon bond maturing in 15 years for par value. Immediately after purchase, the yield required by the market increases. The investor would then most likely have to sell the bond at:
A.par.
106. Given two otherwise identical bonds, when interest rates rise, the price of Bond A declines more than the price of Bond B. Compared to Bond B, Bond A most likely:
A.is callable.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
107. A BBB-rated corporation wishes to issue debt to finance its operations at the lowest cost possible. If it decides to sell a pool of receivables into a special purpose vehicle (SPV), its primary motivation is most likely to:
B is correct because a key motivation for a corporation to establish a special purpose vehicle (SPV) is to separate it as a legal entity. In the case of bankruptcy for the corporation, the SPV is unaffected because it is not a subsidiary of the corporation. Given this arrangement, the SPV can achieve a rating as high as AAA and borrow at lower rates than the corporation.
108. Which of the following is least likely a tool used by the U.S. Federal Reserve Bank to directly influence the level of interest rates?
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Questions 109 through 114 relate to Alternative Investments
B is correct because closed-end funds trade in the secondary markets and do not offer a redemption feature.
110. An analyst is evaluating an investment in an apartment complex based on the following annual data:
| 3% | |
|
|
|
300,000 |
| 5% | |
| 80% | |
| 12% | |
| 15% |
Based on the income approach, the value of the investment is closest to:
A.$1,141,667.
B.$3,641,667.
C.$6,242,857.
The property is appraised based on cash flows and is independent of the financing decision. Thus, the market capitalization rate is used rather than the lending rate. Depreciation is also not deducted because it is implicitly assumed that repairs and maintenance allow the investor to keep the building in good condition.
111. Which of the following statements regarding biases in hedge fund performance in hedge fund databases is least likely correct?
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 227–229
Study Session 18-66-m
Describe the performance of hedge funds and the biases present in hedge fund performance measurement, and explain the effect of survivorship bias on the reported return and risk measures for a hedge fund database.C is correct because hedge fund managers themselves, not database administrators, decide whether they want to be included in a database. Managers who have funds with an unimpressive track record will not wish to have that information exposed.
A.–€3,157,000.
B.–€1,140,000.
C. €2,017,000.Answer = B
113. When market participants expect the spot price of a commodity to be higher in the future, the commodity market is most likely said to be in:
A.contango.
A is correct because when a commodity market is in contango, futures prices are higher than the spot price because market participants believe the spot price will be higher in the future. When spot prices are above the futures price, the market is said to be in backwardation.
114. Which of the following is least likely a reason for discounting the value of stock in a closely held company?
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Questions 115 through 120 relate to Portfolio Management
B is correct. Endowments have a long investment time horizon and a high level of risk tolerance. (See Exhibit 14 on pp. 295–296.)
116. An investor’s transactions in a mutual fund and the fund’s returns over a four-year period are provided in the table below:
| Year | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| New investment at the beginning of the year | $2,500 | $1,500 | $1,000 | $0 |
| –20% | 65% | –25% | 10% | |
| Withdrawal by investor at the end of the year | $0 | –$500 | –$500 | $0 |
“Portfolio Risk and Return Part I,” Vijay Singal
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 324–330
Study Session 12-44-a
Calculate and interpret major return measures and describe their appropriate uses.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
|
|---|
CF1 = –1,500 (new investment atbeginning of Year 2).
| Cable Incorporated | 30% | 0.65 | 68% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 32% |
The standard deviation of returns of the portfolio formed with these two stocks is closest to:
A.25.04%.
B.26.80%.
C.32.85%.
118. Risk that can be attributed to factor(s) that impact a company or industry is best described as:
A.market risk.
C is correct. Risk that is due to company-specific or industry-specific factors is referred to as
unsystematic risk.
B is correct.
𝛽 = 𝜌𝑖𝑚𝜎𝑖𝜎𝑚 𝜎𝑚2
“Basics of Portfolio Management and Construction,” Alistair Byrne and Frank E. Smuddle 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, p. 457–458
Study Session 12-46-d
Distinguish between the willingness and the ability (capacity) to take risk in analyzing an investor’s financial risk tolerance.B is correct. An individual’s ability to take risk is impacted by such factors as time horizon and
questions. To best simulate the exam day experience, candidates are advised to allocate an average of
1.5 minutes per question for a total of 180 minutes (3 hours) for this session of the exam.
|
27 | |
|
21 | |
| 18 | ||
|
36 | |
|
15 | |
| 18 | ||
|
9 | |
|
18 | |
| 109–114 | 9 | |
| 115–120 | 9 | |
| 180 |
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Questions 1 through 18 relate to Ethical and Professional Standards
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 19–21, 46–47
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate and explain the application of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct to situations involving issues of professional integrity.A is correct because by failing to adhere to the non-compete clause he agreed to abide by when signing his employment contract, Hasina shows a lack of professional integrity toward his employer. This behavior reflects poorly on the good reputation of members and is a violation of the Code of Ethics, which states that members and candidates must act with integrity, and Standard I (D) Misconduct, which states that members and candidates must not engage in any professional conduct involving dishonesty, fraud, or deceit or commit any act that reflects adversely on their professional reputation, integrity, or competence. The Code of Ethics at times requires a member or candidate to uphold a higher standard than that required by law, rule, or regulation, or in this case the strict application of the employment agreement.
Answer = C
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = B
“Introduction to the Global Investment Performance Standards (GIPS®),” CFA Institute 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 173
Study Session 1-3-c
Explain the requirements for verification.C.both Musa and Kassim.
Answer = C
5. Zhao Xuan, CFA, is a sell side investment analyst. While at a software industry conference, Zhao hears rumors that Green Run Software may have falsified its financial results. When she returns to her office, Zhao conducts a thorough analysis of Green Run. Based on her research, including discussions with some of Green Run’s customers, Zhao is convinced that Green Run’s reported 50% increase in net income during recent quarters is completely fictitious. So far, however, Zhao is the only analyst suspicious about Green Run’s reported earnings. According to the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct, the least appropriateaction for Zhao is to:
A.report her suspicions to Green Run’s management.
B is correct because the analyst has conducted thorough research that indicates the company falsified its financial results, and she should request the company address this issue publicly as recommended by Standard II (A) Material Nonpublic Information. If a member or candidate determines that information is material, the member or candidate should make reasonable efforts to achieve public dissemination of the information. This effort usually entails
encouraging the issuer company to make the information public. If public dissemination is not possible, the member or candidate must communicate the information only to the designated supervisory and compliance personnel within the member’s or candidate’s firm and must not take investment action on the basis of the information.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A is correct because selling stock short is a management strategy and does not necessarily violate any aspect of the Code and Standards.
7. Kirsten Kelso, CFA, is a research analyst at an independent research firm. Kelso is part of a team of analysts who focus on the automobile industry. Recently, Kelso disagreed with two research sell recommendations written by her team even though she felt confident the research process was properly conducted. In a webcast open to all institutional but not retail clients, Kelso states “even though my name is on the sell reports, these stocks are a buy in part because sales and share prices for both auto companies will rise significantly due to strong demand for their vehicles.” Kelso’s actions would least likely violate which of the following CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
C is correct because the recommendation is based on a reasonable and adequate research process, so the analyst could follow the research team’s opinion, as required by Standard V (A) Diligence and Reasonable Basis.
8. Gardner Knight, CFA, is a product development specialist at an investment bank. Knight is responsible for creating and marketing collateralized debt obligations (CDOs) consisting of residential mortgage bonds. In the marketing brochure for his most recent CDO, Knight provided a list of the mortgage bonds that the CDO was created from. The brochure also states “an independent third party, the collateral manager, had sole authority over the selection of all mortgage bonds used as collateral in the CDO.” However, Knight met with the collateral manager and helped her select the bonds for the CDO. Knight is leastlikely to be in violation of which of the following CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
9. Monique Gretta, CFA, is a research analyst at East West Investment Bank. Previously, Gretta worked at a mutual fund management company and has a long-standing client relationship with the managers of the funds and their institutional investors. Gretta often provides fund managers, who work for Gretta’s former employer, with draft copies of her research before disseminating the information to all of the bank’s clients. This practice has helped Gretta avoid several errors in her reports, and she believes it is beneficial to the bank’s clients, even though they are not aware of this practice. Regarding her research, Gretta least likely violated the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct because:
A.her report is a draft.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.
C.investments outside his mandate.
Answer = A
A.Fair Dealing
B.Communication with Clients
C.Diligence and Reasonable BasisAnswer = A
B.intellectual property.
C.prospective client disclosure.
13.Oliver Opdyke, CFA, works for an independent research organization that does not manage any client money. In the course of his analysis of Red Ribbon Mining he hears rumors the president of Red Ribbon, Richard Leisberg, has recently been diagnosed with late stage Alzheimer’s disease, a fact not publicly known. The final stage of Alzheimer’s is when individuals lose the ability to respond to their environment, the ability to speak, and, ultimately, the ability to control movement. Leisberg is the charismatic founder of Red Ribbon, and under his leadership the company grew to become one of the largest in the industry. According to the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct, the most appropriateaction for Opdyke is to:
A.immediately publish a sell recommendation for Red Ribbon Mining.
C is correct because members and candidates should make reasonable efforts to achieve public dissemination of information that is material and nonpublic, as required by Standard II (A) Material Nonpublic Information. This effort usually entails encouraging the issuer company to make the information public. In this case, if the diagnosis is fact and not rumor, then this information is material and should be disclosed.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
C.recommendation.
Answer = B
B.to CFA Institute when the investigation concludes. C.to CFA Institute if the allegations are proven correct.
Answer = A
A.return of capital.
B.promised returns.
17.Jan Loots, CFA, quit his job as a portfolio manager at an investment firm with whom he had a non-solicitation agreement he signed several years ago. Loots received permission to take his investment performance history with him and also took a copy of the firm’s software-trading platform. Subsequently, Loots sent out messages on social media sites announcing he was looking for clients for his new investment management firm. Access to Loots’ social media sites is restricted to friends, family, and former clients. Loots least likely violated the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct concerning his:
A.trading software.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
C is correct because the portfolio manager received permission to use his investment
performance history from his prior employer. The member violated his non-solicitation agreement by indicating his availability to new clients on several social media sites accessible by clients of his former employer, a violation of Standard IV(A) Loyalty, because he did not act for the benefit of his former employer. In this case, the member may cause harm to his former employer if his weekend messages result in clients moving to his new business from his former employer. The member also violated this standard by taking his employer’s property, trading software.Answer = A
CFA Institute Standards
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 19–21, 59, 131
Study Session 1-2-c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.
| P(Cut div│EPS exceed) | 5% |
| P(Cut div│EPS equal) | 10% |
| P(Cut div│EPS below) | 85% |
𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑏𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑒𝑤 𝑖𝑛𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑔𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑛 𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡
= 𝑈𝑛𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑏𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑛𝑒𝑤 𝑖𝑛𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑚𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 × 𝑃𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑟 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑏𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑜𝑓 𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡Using Bayes’ formula (given above), the updated (posterior) probability that the company’s EPS are below the consensus is closest to:
B is correct. First, calculate the unconditional probability for a cut in dividends: P(Cut div) = P(Cut div│EPS exceed) × P(EPS exceed)
+ P(Cut div│EPS equal) × P(EPS equal)
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B.to have a variance equal to that of the entire population.
C.to have a mean smaller than the mean of the entire population.
21.A project offers the following incremental after-tax cash flows:
“Discounted Cash Flow Applications,” Richard A. DeFusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkle
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 312–314
“Capital Budgeting,” John Stowe and Jacques R. Gagne
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 10–11
Study Session 2-6-a, 11-36-d
Calculate and interpret the net present value (NPV) and the internal rate of return (IRR) of an investment.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
|
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 16 | 100 | |
| 25 | 12 | 30 | |
|
30 | 2 | 10 |
A.8.2%.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
23.Given the following information about three portfolios:
A.Portfolio A
B.Portfolio B
C.Portfolio CAnswer = B
A.P(A).
B.P(B).
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
25.Assume that the real risk-free rate of return is 3% and that the expected inflation premium is 5%. If the risk premium incorporates default risk, liquidity risk, and any maturity premium, an observed (nominal) interest rate of 12% implies that the risk premium is closest to:
“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. DeFusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkle
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 256–258
Study Session 2-5-b
Explain an interest rate as the sum of a real risk-free rate, expected inflation, and premiums that compensate investors for distinct types of risk.A is correct. The nominal rate = real risk-free rate of return + an inflation premium + risk premiums (default, liquidity, maturity preference).
In this case, 12 = 3 + 5 + X. Solve for X. X = 4.Answer = B
“Discounted Cash Flow Applications,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkle
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 318
“Capital Budgeting,” John D. Stowe and Jacques R. Gagne
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 13–15
Study Session 2-6-b, 11-36-d, e
Contrast the NPV rule to the IRR rule, and identify problems associated with the IRR rule.
27.A low price range in which buying activity is sufficient to stop a price decline is best described as:
A.support.
A is correct. Support is defined as a low price range in which buying activity is sufficient to stop the decline in price.
28.An investor purchases one share of stock for $85. Exactly one year later, the company pays a dividend of $2.00 per share. This is followed by two more annual dividends of $2.25 and $2.75 in successive years. Upon receiving the third dividend, the investor sells the share for $100. The money-weighted rate of return on this investment is closest to:
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
29.Independent samples drawn from normally distributed populations exhibit the following characteristics:
| Size | Sample mean | Sample standard deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 25 | 200 | 45 |
| B | 18 | 185 | 60 |
“Hypothesis Testing,” Richard A. DeFusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkle 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 608–612
Study Session 3-11-g
Identify the appropriate test statistic and interpret the results for a hypothesis test concerning the equality of the population means of two at least approximately normally distributed
populations, based on independent random samples with (1) equal or (2) unequal assumed variances.B is correct. The t statistic for the given information (normal populations, variances assumed equal) is calculated as:
In this case we have:
C.Divide X by the difference between the standard deviation of X and the standard deviation of the standard normal distribution.
Answer = A
Answer = B
“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. DeFusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E.
32.A technical analyst has detected a price chart pattern with three segments. The left segment shows a decline followed by a reversal to the starting price level. The middle segment shows a more pronounced decline than in the first segment and again a reversal to near the starting price level. The third segment is roughly a mirror image of the first segment. This chart pattern is most accuratelydescribed as:
A.a triple bottom.
C is correct. An inverse head and shoulders pattern consists of a left segment that shows a decline followed by a reversal to the starting price level, a middle segment that shows a more pronounced decline than in the first segment and again a reversal to near the starting price level, and a third segment that is roughly a mirror image of the first segment.
Questions 33 through 44 relate to Economics
Answer = B
“Demand and Supply Analysis: Introduction,” Richard V. Eastin and Gary L. Arbogast 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 31–33
Study Session 4-13-l
Calculate and interpret consumer surplus, producer surplus, and total surplus.
The income effect arising from this change in the price of Y is best described as the distance between:
A.Qb and Qa.
B.Qc and Qb.
C.Qc and Qa.B is correct. When the price of Y falls, the budget constraint shifts outward from BC1 to BC2, indicating an increase in the consumption of Y. Points a and b reflect the change in consumption of Y due solely to a decrease in price because BC3 reduces her income by a sufficient amount to return her to her original indifference curve. Qc – Qb is the income effect (which is negative here) because this is an inferior good.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = B
“The Firm and Market Structures,” Richard G. Fritz and Michele Gambera
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 157–160
Study Session 4-16-a
Describe the characteristics of different market structures: perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and pure monopoly.
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| A. |
|
||
| B. |
|
||
| C. |
|
||
“Aggregate Output, Prices, and Economic Growth,” Paul R. Kutasovic and Richard G. Fritz 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 247–254
Study Session 5-17-h
Describe the causes of shifts in and movements along aggregate demand and supply curves.A is correct. If stock prices rise, the aggregate demand curve will shift to the right (increase in AD) because of higher consumption (wealth effect), not lower investments.
Answer = B
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Labor force participation rate = Labor force ÷ Working age population. Unemployment rate = Unemployed ÷ Labor force.
Answer = B
“International Trade and Capital Flows,” Usha Nair-Reichert and Daniel Robert Witschi 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 444–450
Study Session 6-20-b
Distinguish between comparative advantage and absolute advantage.
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The profit maximizing output for this firm (in units) is closest to:
A.7.
Describe the firm’s supply function under each market structure.
Describe and determine the profit-maximizing price and output for firms under each market structure.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
40.Which of the following government interventions in market forces is most likely to cause overproduction?
41.In an effort to influence the economy, a central bank conducted open market activities by selling government bonds. This implies that the central bank is most likely attempting to:
A.contract the economy by reducing bank reserves.
Determine whether a monetary policy is expansionary or contractionary.
A is correct. Selling government bonds results in a reduction of banks’ reserves and reduces banks’ ability to lend, causing a decline in money growth through the multiplier mechanism and hence leading to a contraction in the economy.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = A
43.Four countries operate within a customs union. One country proposes moving to a common market structure. What additional level of economic integration between the countries would most likely arise if this change took place? They would:
A.establish common trade barriers against non-members.
B is correct. A common market structure incorporates all aspects of the customs union and extends it by allowing free movement of factors of production among members.
44.The current spot rate for the USD/EUR is 0.7500. The forward rate for the EUR/Australian dollar (AUD) is 1.4300, which represents a 400 point forward premium to the spot rate (scaled up by four decimal places). The USD/AUD spot rate is closest to:
Convert forward quotations expressed on a points basis or in percentage terms into an outright forward quotation.
B is correct.
| Spot = 1.4300 − 400 10,000 = 𝟏. 𝟑𝟗𝟎𝟎 | ||
|
||
|
||
“Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction,” Elaine Henry and Thomas R. Robinson 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 27, 31
Study Session: 7-22-c, e
Describe the importance of financial statement notes and supplementary information—including disclosures of accounting policies, methods, and estimates—and management’s commentary.Identify and explain information sources that analysts use in financial statement analysis besides annual financial statements and supplementary information.
The end of year owners’ equity is closest to:
A.$19,400.
B.$19,900.
C.$20,400.
|
$10,000 | |
|---|---|---|
|
1,000 | |
| 6,000 | ||
| 4,000 | ||
| (600) | ||
| 3,400 | 3,400 | |
|
$20,400 | |
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = B
“Understanding Income Statements,” Elaine Henry and Thomas R. Robinson
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 158–159
Study Session: 8-25-b
Describe the general principles of revenue recognition and accrual accounting, specific revenue recognition applications (including accounting for long-term contracts, installment sales, barter transactions, and gross and net reporting of revenue), and the implications of revenue recognition principles for financial analysis.
Sales $2,240,000
Cost of goods sold 1,320,000
Gross profit 920,000
Net Income $316,600Selected Balance Sheet Data
as of December 31st
(Can $ thousands)
2011 2010
Total current assets
Other current liabilities 130,700 182,700
Total current liabilities $260,300$339,900The company operates in an industry in which suppliers offer terms of 2/10, net 30. The payables turnover for the average company in the industry is 8.5 times. Which of the following statements is most accurate? In 2011, the company on average:
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Elaine Henry, Thomas R. Robinson, and Jan Hendrik van Greuning
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 352, 356
“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., Kenneth L. Parkinson, and Pamela Peterson Drake
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, p. 164
Study Session 8-28-b, 11-40-f
Classify, calculate, and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability, and valuation ratios.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
|
|
|
|
49.Which of the following will most likely result in an increase in a company’s sustainable growth rate?
A.Higher tax burden ratio
B.Lower interest burden ratio
C.Higher dividend payout ratioA is correct.
Sustainable growth rate = Retention ratio × ROE.
A higher tax burden ratio (Net income/Earnings before tax) implies that the company can keep a higher percentage of pretax profits; this implies a lower tax rate and a higher ROE. The interest burden ratio is earnings before tax to EBIT, and a lower ratio means that the company has higher borrowing costs (it gets to keep a lower pre-tax income from a given EBIT), implying a lower ROE and sustainable growth.
50.During 2010, the following events occurred at a company. The company:
A is correct. The customer list is the only identifiable intangible asset, and it should be amortized on a straight-line basis over its expected future life: $100,000 ÷ 4 = $25,000/year. Goodwill is an unidentifiable intangible and should be tested for impairment but not amortized. All advertising and promotion costs, such as the media placements, are typically expensed. If the reputation of the company has been enhanced as the CEO suggests, this is an internally generated intangible that is not recorded on the balance sheet and is therefore not amortized.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Description | Amount (£000s) | |
|---|---|---|
| 55,000 | ||
|
|
10,000 |
| 12,000 |
Answer = A
“Understanding Cash Flow Statements,” Elaine Henry, Thomas R. Robinson, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, and Michael A. Broihahn
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 275–285
Study Session 8-27-c, d
Contrast cash flow statements prepared under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (U.S. GAAP).
“Inventories,” Michael A. Broihahn
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 416–418
Study Session: 9-29-f
Describe the measurement of inventory at the lower of cost and net realisable value.A is correct. Under IFRS, the inventory would be written down to its net realizable value ($4.1 million), whereas under U.S. GAAP, market is defined as current replacement cost and hence would be written down to its current replacement cost ($3.8 million). The smaller write down under IFRS will reduce the amount charged to the cost of goods sold, as compared with U.S. GAAP, and result in a lower cost of goods sold of $0.3 million.
Explain the impairment of property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets.
C is correct. Intangible assets with indefinite lives need to be tested for impairment at least annually. PP&E (including land) and intangibles with finite lives are only tested if there has been a significant change or other indication of impairment.
| €50 million | |
|---|---|
| 4% | |
|
10 years (31 December 2020) |
|
92.28 |
B is correct. IFRS requires the effective interest method for the amortization of bond discounts/premiums. The bond is issued for 0.9228 × €50 million = €46.140.
Interest expense = Liability value × Market rate at issuance: 0.05 × €46.140 = €2.307.
A.improved because the debt-to-equity ratio decreased.
B.deteriorated because the debt-to-equity ratio increased. C.improved because the fixed charge coverage ratio increased.
| 2011 | 2010 | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Debt-to-equity ratio (Total debt ÷ Equity) |
= 70% |
||
= 2.81 |
A.days sales payable (DSP).
B.gains on the sale of long-term assets.
• using stock buybacks to offset dilution of earnings.
A is correct. An increase in the days sales payable would indicate the company is stretching out its payables, which would increase the cash from operations.
“Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 76–78
Study Session: 7-23-g
Explain the use of the results of the accounting process in security analysis.A is correct. Understanding the accounting process may assist an analyst in identifying earnings manipulation, but it will not prevent the manipulation of earnings by management. It is important for analysts to understand the accounting process so they can make adjustments for items not reported and to aid in the assessment of management’s judgment of accruals and valuations.
“Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 58
Study Session: 7-23-c
Explain the process of recording business transactions using an accounting system based on the accounting equation.B is correct. There would be no effect on the accounting equation because the company has exchanged one asset for another. Cash has decreased, and office equipment, a capital asset, has increased.
Answer = C
“Financial Reporting Standards,” Elaine Henry, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, and Thomas R.
|
Industry |
|---|---|
| 3.0 | |
| 50.0% | |
| 40.0% |
A.operates in the manufacturing industry.
B.has made significant acquisitions in the past.
C.has higher financial leverage than the industry.
61.Which of the following is least likely a benefit of the direct method for reporting cash flow from operating activities? Compared with the indirect method, the direct method provides:
A.supplementary data under U.S. GAAP.
62.A firm reported the following financial statement items:
“Understanding Cash Flow Statements,”Elaine Henry, Thomas R. Robinson, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, and Michael A. Broihahn
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 312–313
Study Session: 8-27-i
Calculate and interpret free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to equity, and performance and coverage cash flow ratios.B is correct.
| Cash Flow Item | 300 (1 – 0.40) | Amount (€) |
|---|---|---|
| 2,100 | ||
| 400 | ||
| 180 | ||
| (210) | ||
|
0 | |
|
€2,470 |
Answer = C
“Understanding Income Statements,” Elaine Henry and Thomas R. Robinson
250,000 × 7/12 145,833
Total before split 229,166
Including effect of 2:1 split 458,33364.To gain insight into what portion of the company’s assets is liquid, an analyst will most likely use:
“Understanding Balance Sheets,” Elaine Henry and Thomas R. Robinson
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp 252–253
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Elaine Henry, Thomas R. Robinson, and Jan Hendrik van Greuning
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 341–342; 359
Study Session 8-26-h, 8-28-b, c
Convert balance sheets to common-size balance sheets, and interpret common-size balance sheets.Classify, calculate, and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability, and valuations ratios.
| 2011 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Event | Units | NZ$/unit |
| 0 | 0 | |
|
1,000 | $22.50 |
|
800 | $25.00 |
| 400 | $25.50 | |
| 1,700 | $40.00 | |
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = A
B.$2,820.
C.$6,720.Answer = B
|
$35,000 |
|---|
Value for tax purposes:
Carrying amount = Start of year balance × (1 – 0.20)
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
67.An analyst is analyzing two companies in the same industry and believes that they have similar strategies regarding the use of property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). He also thinks that the PP&E assets of the two companies are roughly of the same age and have the same expected useful lives remaining. Company A uses the LIFO method of inventory valuation, and Company B uses the FIFO method. The following additional information is available from the companies’ financial statements:
| Company A | Company B | |
|---|---|---|
| 5,800 | 6,300 | |
| 1,100 | N/A | |
| 4,300 | 4,200 | |
|
2,500 | 3,000 |
|
1,250 | 1,200 |
| 125 | 120 |
C.uses more aggressive accounting estimates related to PP&E.
Answer = C
Current ratio adjusted to FIFO for Company A
(5,800 + 1,100) ÷ 4,300 1.60
Co A is more liquid
| 1,250 | 1,800 |
|---|
The analyst believes the two companies’ PP&E are of the same age; however, the useful life remaining for Company B’s assets is 15 years compared with 10 for Company A, implying B is using a longer useful life or more aggressive accounting policies.
The more aggressive PP&E estimates combined with the use of FIFO indicate that Company B has a lower quality of earnings, not higher. The adjusted current ratio for Company A (adjusted to include the LIFO reserve to convert the balance sheet to FIFO for comparison) is higher than the current ratio for B, indicating that A is more liquid.
“Financial Reporting Quality: Red Flags and Accounting Warning Signs,” Thomas R. Robinson and Paul Munter
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 594–595
Study Session 10-33-b, d
Describe activities that will result in a low quality of earnings.Describe common accounting warning signs and methods for detecting each.
Answer = B
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.Debt-rating approach only
B.Yield-to-maturity approach only
C.Both the yield-to-maturity and the debt-rating approachesAnswer = A
| Year 0 | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| –$606,061 | $2,151,515 | –$2,542,424 | $1,000,000 |
A.15%
B.18%
C.21%Answer = C
72.Based on a need to borrow $2 million for one month, which of the following alternatives has the least expensive effective annual cost?
A.A banker’s acceptance with an all-inclusive annual rate of 6.1%
B.A credit line at 6.0% annually with a $4,000 annual commitment fee
C.Commercial paper at 5.9% annually with a dealer’s annual commission of $1,500 and a backup line annual cost of $3,500
| Method | Formula | Calculation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
$2,000,000 | |||
|
(10,833 × 12) ÷ 2,000,000 | |||
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
73.Using the firm’s income statement presented, its degree of financial leverage is closest to:
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
1.4 |
74.The “per unit contribution margin” for a product is $12. Assuming fixed costs of $12,000, interest costs of $3,000, and taxes of $2,000, the operating breakeven point (in units) is closest to:
A.1,000.
B.1,250.
C.1,417.
75.Which of the following capital budgeting techniques is most directly related to stock price?
A.Net present value
B.Profitability index
C.Discounted payback period76.A company’s data are furnished below:
A.11.5%.
B.13.0%.
C.14.0%.Answer = B
| 𝑤𝑑 = |
|
|
|---|
A.Money market yield
B.Discount-basis yield
C.Bond equivalent yieldAnswer = C
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B is correct. The retained earnings in a pro forma analysis increases by net income less dividends:
𝐷𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑑 = 𝑁𝑒𝑡 𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒 × 𝐷𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑑 𝑝𝑎𝑦𝑜𝑢𝑡 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜 = $1.26 𝑚𝑖𝑙𝑙𝑖𝑜𝑛 × 40% = 0.504 𝑚𝑖𝑙𝑙𝑖𝑜𝑛
79.The index weighting that results in portfolio weights shifting away from securities that have increased in relative value (e.g., decrease in book-to-market) toward securities that have fallen in relative value whenever the portfolio is rebalanced is most accurately described as:
A.equal weighting.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B is correct. Fundamentally weighted indices generally will have a contrarian “effect” in that the portfolio weights will shift away from securities that have increased in relative value and toward securities that have fallen in relative value whenever the portfolio is rebalanced.
Answer = A
“Introduction to Industry and Company Analysis,” Patrick W. Dorsey, Anthony M. Fiore, and Ian Rossa O’Reilly
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 234–235
Study Session 14-51-g
Describe product and industry life-cycle models, classify an industry as to life-cycle phase (e.g., embryonic, growth, shakeout, maturity, or decline) based on a description of it, and discuss the limitations of the life-cycle concept in forecasting industry performance.
| Year | EPS | DPS | ROE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 |
|
|
B is correct. V0 = D1/(r – g).
Dividend growth rate over the period 2006–2011 = 1.25(1 + g)5 = 1.92; g = 8.96% ≈ 9%.
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
Answer = A
“Market Efficiency,” W. Sean Cleary, Howard J. Atkinson, and Pamela Peterson Drake 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 148–149
Study Session 13-49-g
Contrast the behavioral finance view of investor behavior with that of traditional finance.
C.establish strong market research teams to match customer needs with product development.
Answer = A
84.The following data pertain to a margin purchase of a stock by an investor.
If the stock is sold exactly one year after the purchase, the total return on the investor’s investment is closest to:
A.14%.
B.19%.
C.22%.
| $55 x 500 | $27,500 | |
|---|---|---|
|
$50 x 500 x 0.55 |
|
| $13,750 x 0.06 | –$825 | |
| $1.80 x 500 | $900 | |
| $0.05 x 500 | –$25 | |
| $13,800 | ||
|
($50 x 500 x 0.45) + ($0.05 x 500) | $11,275 |
|
22.4% |
A.brokered market.
B.order-driven market.
C.quote-driven market.A.Operational
B.Allocational
C.InformationalAnswer = C
B.with no restrictions on short selling.
C.with high information-acquisition costs.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
88.An analyst collects the following data on the return on equity (ROE) and the payout ratio for two companies, M and N. Using a required return of 12.4% for both companies, she computes the justified forward P/E ratios, which are also given below.
If Company M increases its dividend payout ratio to 40% and Company N decreases its dividend payout ratio to 30%, which of the following will most likely occur? The justified P/E ratio of:
“Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools,” John J. Nagorniak and Stephen E. Wilcox
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 288–291
Study Session 14-52-g, h
Explain the rationale for using price multiples to value equity, and distinguish between multiples based on comparables versus multiples based on fundamentals.Calculate and interpret the following multiples: price to earnings, price to an estimate of operating cash flow, price to sales, and price to book value.
Company N:
New dividend growth rate = (1 – 0.3) x 14% = 9.8%; New Justified forward P/E = 0.3/(0.124 – 0.098) = 11.5x.89.A fund manager gathers the following data in order to assess a stock’s potential for a possible addition to her portfolio:
| $20 million | |
|---|---|
| $140 million | |
| 10.75% | |
| 1.80 | |
|
5.25% |
|
3.50% |
| 13.60% |
Answer = A
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela Peterson Drake
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 52–53
“Overview of Equity Securities,”Ryan C. Fuhrmann and Asjeet S. Lamba
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 194–195
Study Session 11-37-h; 14-50-h
Calculate and interpret the cost of equity capital using the capital asset pricing model approach, the dividend discount model approach, and the bond-yield-plus risk-premium approach. Compare a company’s cost of equity, its (accounting) return on equity, and investors’ required rates of return.
Answer = B
“Market Efficiency,” W. Sean Cleary, Howard J. Atkinson, and Pamela Peterson Drake 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 140–144
Study Session 13-49-d, f
Contrast the weak-form, semi-strong-form, and strong-form market efficiency.
A.minimum account balance required as prices change.
B.performance bond ensuring fulfillment of the obligation.
92.A buyer would face the greatest risk of default with:
A.a farmer making physical delivery on a short soybean futures position.
“Futures Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, p. 53
Study Session 17-62-b
Compare futures contracts and forward contracts.C is correct because in a forward contract, each party assumes the risk that the other party will default.
“Option Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 85–86
Study Session 17-63-c
Define the concept of moneyness of an option.C is correct because only an in-the-money option would be exercised. Moneyness describes the relationship between the price of the underlying and an option’s exercise price.
“Option Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 98–100
Study Session 17-63-i
Define intrinsic value and time value, and explain their relationship.C is correct because an out-of-the-money option will have an intrinsic value of zero at all times.
C.euro dollar time deposit in the United States.
Answer = A
B.pay the market value to the counterparty.
C.sell an offsetting swap listed on an exchange.Answer = C
A.The floor in a floating-rate security
B.An accelerated sinking fund provision
C.The call option in a fixed-rate securityAnswer = A
98.Consider two bonds that are identical except for their coupon rates. The bond that will have the highest interest rate risk most likely has the:
A.lowest coupon rate.
A is correct because a lower coupon rate means that more of the bond’s value comes from repayment of face value, which occurs at the end of the bond’s life.
99.Duration is most accurate as a measure of interest rate risk for a bond portfolio when the slope of the yield curve:
“Risks Associated with Investing in Bonds,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 359–363
Study Session 15-54-g
Describe yield-curve risk, and explain why duration does not account for yield-curve risk.C is correct because duration measures the change in the price of a portfolio of bonds if the yields for all maturities change by the same amount; that is, it assumes the slope of the yield curve stays the same.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = C
Answer = C
“Understanding Yield Spreads,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 456–457
Study Session 15-56-e
Calculate and compare yield spread measures.“Yield Measures, Spot Rates, and Forward Rates,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 538–539
Study Session 16-58-b
Calculate and interpret traditional yield measures for fixed-rate bonds, and explain their limitations and assumptions.C is correct because a security with a present value of 96.47, 19 interest payments of 8, and a 20th payment of principal plus interest (108) has a yield to maturity of 8.37%.
B.higher.
C.the same.
A.$99.75.
B.$105.65.
C.$107.03.Answer = B
| + | 103 | = | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ( 1 | + | .0 0160 | 2 | ) 1 | ( 1 | + | .0 0220 | 2 | ) 2 | ( 1 | + | .0 0270 | 2 | ) 3 | ( 1 | + | .0 0310 | 2 | ) 4 | |||||
105.Consider three bonds that have the same yield to maturity and maturity. The bond with the greatest reinvestment risk is most likely the one selling at:
A.par.
106.Using the U.S. Treasury forward rates provided below, the value of a 2½-year, $100 par value Treasury bond with a 5% coupon rate is closest to:
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.


| ( 1 | + | 2 ) ( 1 + . 012 2 ) ( 1 + . 018 2 ) ( 1 + . 023 2 ) ( 1 + . 027
2 ) ( 1 + . 027 |
2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | ( 1 | |||
| + | ( 1 |
A.putable.
B.callable.
A is correct because when interest rates rise, a putable bond is more likely to be put back to the issuer by the investor, limiting the loss of value and giving the bond more positive convexity than an option-free bond. In contrast, a callable bond is likely to be called from the investor when interest rates fall, limiting the gain in value and giving the bond negative convexity.
108.The table below provides information about a portfolio of three bonds.
“Introduction to the Measurement of Interest Rate Risk,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 612–620
Study Session 16-59-g
Calculate the duration of a portfolio, given the duration of the bonds comprising the portfolio, and explain the limitations of portfolio duration.A is correct because the market values of the bonds (Price × Par amount) are $17,479,376, $4,018,928, and $6,771,416, respectively, for a portfolio value of $28,269,720. Therefore, the duration of the portfolio is
| | 17 , | 479 , 376 | × | .8 56 | | + | | ,4 018 , 928 | × | .9 19 | | + | | × | 11 . 48 | | = | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 28 , | 269 , 720 | | | 28 , | 269 , 720 | | | 28 , | 269 , 720 | | |||||||||||
109.Which of the following least likely describes an advantage of investing in hedge funds through a fund of funds? A fund of funds may provide investors with:
A.lower fees due to economies of scale.
A is correct because the fees on funds of funds are usually higher. The fund of funds manager charges a fee, and there is a fee charged by each hedge fund.
110.Compared with investment in an open-ended index mutual fund, which of these is least likely a benefit to an investor in an index exchange traded fund (ETF) on the same index?
A is correct because open-ended mutual fund shares are created and redeemed at net asset value with no bid–ask spread, whereas ETFs trade like stocks with a bid–ask spread.
111.Which of the following is least likely an aggregation vehicle for real estate ownership?
112.An investor might consider investments in commodities because, historically, commodity returns have had a higher positive correlation with:
A.inflation.
113.Do base management fees most likely get paid to the manager of a hedge fund regardless of the fund’s performance?
A.Yes
B.No, only when the fund’s gross return is positive
C.No, only when the fund’s net asset value exceeds the previous high water mark
114.The three main sources of return for commodities-related investments are:
A.collateral yield, roll yield, and spot price return.
A is correct because the three main sources of return for a commodities investment are collateral yield, roll yield, and spot price return.
Questions 115 through 120 relate to Portfolio Management
Answer = A
“Portfolio Management: An Overview,” Robert M. Conroy and Alistair Byrne 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 296–300
Study Session 12-43-c
Describe the steps in the portfolio management process.
A.A and B.
B.A and C.
C.B and C.Answer = C
B.market risk.
C.diversifiable risk.
118.Last year, a portfolio manager earned a return of 12%. The portfolio’s beta was 1.5. For the same period, the market return was 7.5% and the average risk-free rate was 2.7%. Jensen’s alpha for this portfolio is closest to:
A.0.75%.
B.2.10%.
C.4.50%.
| Stock | Expected Return | Beta |
|---|---|---|
| Booraem Inc. | 12.85% | 1.5 |
|
11.27% | 1.1 |
| Gutmann Inc. | 9.51% | 0.8 |
If the expected market return is 9.5% and the average risk-free rate is 1.2%, according to the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) and the security market line (SML), which of the three stocks is most likely overvalued?
B is correct. Booraem Inc. is overvalued because it lies below the SML. The expected return, 12.85%, is less than the required return. According to the CAPM, the required return for Booraem Inc. is 0.1365 or 13.65%:
0.1365 = 0.012 + 1.5(0.095 – 0.012).
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently registered CFA candidates and copying, posting to any website, e-mailing, distributing, and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = A
“Basics of Portfolio Management and Construction,” Alistair Byrne and Frank E. Smuddle 2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, p. 474
Study Session 12-46-f
Explain the specification of asset classes in relation to asset allocation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 97-108 |
|
|
|
||
|
||
|
A.No.
B.Yes, related to Misconduct.
| 2. |
|
|---|
A.No.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B is correct because Barrett's client base is made up of a small number of large
institutions so stating in the advertisement that his client base is a larger number is a misrepresentation and a violation of Standard I(C). In addition, since the advertisement focuses only on the benefits and does not mention the potential risks of these investments it is also potentially misleading to clients.
B is correct as Miffitt has not violated the confidentiality Standard which involves information about former, current, and prospective clients.
| 4. |
|
|---|
"Guidance for Standards I-VII CFA Institute"
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 49-52
Study Session 1-2-c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.A is correct as the information concerning the qualified opinion is non-public and if it is material she would be in violation of Standard II(A) if she took investment action based on the information. She should also make reasonable efforts to achieve public
dissemination of the information.
Answer = B
"Guidance for Standards I-VII CFA Institute"
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 78-81
Study Session 1-2-b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.
| 6. |
|---|
A.Provide the information and inform her client.
B.Send the requested documents and inform her supervisor.
A.Duties to Clients
B.Duties to Employers
C.Communication with Clients
program. He has also violated a duty to his employer as contradicting employer instructions are not permitted unless the member is acting to protect the integrity of capital markets and the interests of clients.
| 8. |
|
|---|
1. deducts all fees and taxes;
2. uses actual and simulated performance results;
3. bases the performance on a representative individual account.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = C
| 10. |
|---|
B.No, because she has taken steps to ensure the violations will not be repeated by the analyst.
C.No, because she is taking steps to implement compliance procedures that are more than adequate.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
vendor when it applies to her country and would like to use a local vendor on whom she has already conducted due diligence. Which of the following actions concerning the research vendor should La Valle most likely take to avoid violating the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
"Guidance for Standards I-VII CFA Institute
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 107-109
Study Session 1-2-c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.A is correct. When a member has reason to suspect that either secondary or third-party research or information comes from a source that lacks a sound basis, the member must not rely on that information as indicated by Standard V(A) Diligence and Reasonable Basis.
| 12. |
|---|
Answer = B
"Guidance for Standards I-VII CFA Institute"
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 116-118
Study Session 1-2-c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.
B.Sell his stock holdings to eliminate any potential conflict of interest.
C.Refuse to write the report and ask his employer to assign another analyst to complete the analysis.
| 14. |
|---|
A.No.
B.Yes, related to Misconduct.
C is correct as Standard VI (B) requires that investment transactions for clients and employers have priority over transactions in which members have beneficial ownership. By executing her own accounts transactions with those of the hedge fund the analyst has violated this Standard. Micro cap securities can be thinly traded and easily influenced by changes in the volume of activity so that the analyst may benefit when she combines her transactions with the hedge funds and she should let the fund execute its orders before she makes changes to her account.
"Guidance for Standards I-VII CFA Institute"
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 136
Study Session 1-2-b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.B is correct because Standard VI(C) requires disclosure of any compensation,
consideration, or benefit received from or paid to others for the recommendation of products or services. Even without cash changing hands the arrangement provides for a quid pro quo referral of clients and should be disclosed.
| 16. |
|---|
A.CFA Institute.
B.CFA Program.
A.fines for violations.
B is correct as the CFA Institute may revoke membership for violations of the Institute Code of Ethics.
| 18. |
|
|---|
Questions 19 through 32 relate to Quantitative Methods
|
|
|
| Sud,du = 101.20 | ||
Answer = C
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Degrees of freedom | p = 0.10 | p = 0.05 | p = 0.025 | p = 0.01 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 1.383 | 1.833 | 2.262 | 2.821 |
| 10 | 1.372 | 1.812 | 2.228 | 2.764 |
| 11 | 1.363 | 1.796 | 2.201 | 2.718 |
The 95% confidence interval is closest to:
A.a lower bound of -2.33 and an upper bound of 14.83. B.a lower bound of -2.20 and an upper bound of 14.70. C.a lower bound of -0.71 and an upper bound of 13.20.
concept is based on a two-tailed approach. For a 95% confidence interval, 2.5% of the distribution will be in each tail. Thus, the correct t-statistic to use is 2.262. The confidence interval is calculated as:
A.340 and 424.
B.354 and 410.
C.396 and 480.
| 22. |
|
|---|
A.14.00.
B.15.56.
C.17.20.
The sum of the ten numbers is 140. Dividing by 10 gives the mean of 14.
Add one to each of the given returns, then multiply them together, then take the fourth root of the resulting product. 0.92 × 1.04 × 1.17 × 0.88 = 0.985121. 0.985121 raised to the 0.25 power is 0.996259. Subtracting one and multiplying by 100 gives the correct geometric mean return of -0.37%.
| 24. |
|
|---|
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 557
Study Session 3-10-e
Calculate and interpret the standard error of the sample mean.The standard error of the sample mean, when we know the sample standard deviation, is:
Answer = B
“Probability Concepts,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E.
| 26. |
|---|
Answer = A
“Time Value of Money,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 286-290
Study Session 2-5-d, f
Solve time value of money problems when compounding periods are other than annual.
A = 30000 / 49.318433 = 608.291829
| 27. |
|
|---|
Answer = C
“Hypothesis Testing,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
| 29. |
|---|
A.H0: θ = θ0 versus Ha: θ≠ θ0
B.H0: θ≤ θ0 versus Ha: θ > θ0
C.H0: θ≥ θ0 versus Ha: θ < θ0Answer = B
A.Type I error.
B.Type II error.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
When we do not reject a false null hypothesis we have a Type II error.
McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 375-378
Study Session 2-7-f
Describe, calculate, and interpret quartiles, quintiles, deciles, and percentiles.The first quintile is the 20th percentile. The first decile is the 10th percentile, the first quartile is the 25th percentile, and the median is the 50th percentile. While it is possible that these various percentiles or some subsets of them might be equal (for example the 10th percentile possibly could be equal to the 20th percentile), in general the order from smallest to largest would be: first decile, first quintile, first quartile, median.
Answer = B
“Probability Concepts,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E.
| 33. |
|
|---|
A.elastic.
If demand is elastic, a 1 percent price cut increases the quantity sold by more than 1 percent and total revenue increases.
In the short run, a company can vary the quantity of labor but the quantity of capital is fixed. In the long run, a firm can vary both the quantity of labor and the quantity of capital.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| 35. |
|---|
A.21.
B.23.
| 36. |
|
|---|
A.both firms cheat.
The Nash equilibrium of the prisoners’ dilemma game is that both firms cheat.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = B
“Money, the Price Level, and Inflation,” Michael Parkin
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, p. 371
Study Session 6-24-d
Explain the goals of the U.S. Federal Reserve (Fed) in conducting monetary policy and how the Fed uses its policy tools to control the quantity of money, and describe the assets and liabilities on the Fed’s balance sheet.
| 38. |
|---|
Answer = B
“U.S. Inflation, Unemployment, and Business Cycles,” Michael Parkin
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, p. 399
Study Session 6-25-b
Describe and distinguish among the factors resulting in demand-pull and cost-push inflation and describe the evolution of demand-pull and cost-push inflationary processes.
Answer = A
“Elasticity,” Michael Parkin
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 10-11
Study Session 4-13-a
Calculate and interpret the elasticities of demand (price elasticity, cross elasticity, and income elasticity) and the elasticity of supply and discuss the factors that influence each measure.
| 40. |
|---|
C.perfectly elastic.
Answer = A
A.maximize total surplus.
B.generate underproduction.
C.minimize deadweight loss.
42. A minimum wage above the equilibrium wage is best characterized as a:
A.price floor.
When a price floor is applied to labor markets, it is called a minimum wage. Being above the equilibrium wage is irrelevant.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Fiscal Policy,” Michael Parkin
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 440-441
Study Session 6-26-b
Discuss the sources of investment finance and the influence of fiscal policy on capital markets, including the crowding-out effect.The tendency for a government budget deficit to decrease private investment is called the crowding-out effect.
| 44. |
|---|
Answer = C
“Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly,” Michael Parkin
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 228-233
Study Session 5-20-a, d
Describe the characteristics of monopolistic competition and an oligopoly.
A.Collect data
B.Process data
C.Analyze/interpret data
A.Accrued revenue arises when a company receives cash prior to earning the revenue.
B.A valuation adjustment for an asset converts its historical cost to its depreciated value.
The statement about accrued expenses is correct; a valuation adjustment for an asset converts its historical cost to current market value; accrued revenue arises when revenue has been earned but not yet received.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| 47. |
|---|
Explain the general requirements for financial statements.
Based on International Accounting Standard (IAS) general requirements for financial statements, fundamental principles include fair presentation, going concern, accrual basis, consistency and materiality.
Answer = A
"Financial Reporting Standards," Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Karen O'Connor Rubsam, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, pp.110-111
Study Session: 7-31-d
Describe the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) framework, including the qualitative characteristics of financial statements, the required reporting elements, and the constraints and assumptions in preparing financial statements.
| 49. |
|---|
The gross profit recognized in year 2 is closest to:
|
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | |||
|
|---|
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Understanding the Income Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, pp.160-163
“Long-Lived Assets,” Elaine Henry, CFA, and Elizabeth A. Gordon
2011 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, pp 422-426
Study Session: 8-32-d, 9-37-d
Demonstrate the appropriate method of depreciating long-term assets, accounting for inventory, or amortizing intangibles, based on facts that might influence the decision.
| 52. |
|
|---|
If the company reports under IFRS instead of U.S. GAAP, its net income will most likely be:
A.the same.
Demonstrate the appropriate classification and related accounting treatments for marketable and nonmarketable financial instruments held as assets or owned by the company as liabilities.
Identify and explain the major international accounting standards for each asset and liability category on the balance sheet and the key differences from U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
| 53. |
|---|
B.comparing companies using different accounting methods.
C.providing insights into microeconomic relationships within a company that help analysts project earnings and free cash flow.
Evaluate and compare companies using ratio analysis, common-size financial statements, and charts in financial analysis.
Financial ratio analysis is limited by the use of alternative accounting methods.
Answer = A
"Understanding The Cash Flow Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, pp. 252-254
"International Standards Convergence,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, pp. 650-651
Study Session: 8-34-c, 10-43-c
Compare and contrast the key differences in cash flow statements prepared under international financial reporting standards and U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
| 55. |
|---|
A.$89,000.
B.$105,000.
C.$111,000.Answer = B
| 100,000 | |
|---|---|
| 8,000 | |
|
(12,000) |
|
9,000 |
| 105,000 |
| 1. | 1. The company suffered losses from discontinued operations in each of the past three years. |
|---|---|
| 2. | 2. The most recent year’s tax rate was only one half the prior two years’ rate as a result of a fiscal stimulus. |
| 3. | 3. The company experienced gains on the sale of investments in each of the past three years. |
A.use the most recent tax rate because that is the best predictor of future tax rates.
B.exclude the gains on the sale from investments because the company is a manufacturing firm.
The company is a heavy equipment manufacturer - since gains on investments is not a core part of its business, they should not be viewed as an ongoing source of earnings. Discontinued operations are considered to be nonrecurring items (even though they have occurred in the past three years); they are normally treated as random and unsustainable and should not be included in a short-term forecast; the change in the current tax rate is best viewed as temporary (in the absence) of additional information and should not be the basis of the calculation of the average tax rate.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.is more liquid.
B.has more financial risk.
Company A has a higher current ratio and shorter cash conversion cycle and it therefore more liquid. The lower financial leverage ratio indicates that it has less financial risk, not more, and it has less time between cash outlay and cash collection.
Measure Definition Company A Company B Current ratio CA/CL 2.78 2.66 Cash
conversion DOS + DOH – Days payable 28 + 32 – 42 32 + 35 – 40 cycle = 18 = 27 Financial
Leverage Total assets/Sh equity 3.82 3.94
| 58. |
|---|
Answer = A
“Inventories,” Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, p.379-380
Study Session: 9-36-a
Distinguish between costs included in inventories and costs recognized as expenses in the period in which they are incurred.
| Cost | ¥ millions |
|---|---|
| 100,000 | |
| (5,000) | |
| 20,000 | |
| Shipping of raw materials to manufacturing facility | 10,000 |
|
50,000 |
|
175,000 |
"Inventories,” Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, pp. 382-383, 390-391
Study Session: 9-36-e
Compare and contrast cost of sales, ending inventory, and gross profit using different inventory valuation methods.During a period of rising prices, ending inventory under LIFO will be lower than that of FIFO and cost of goods sold higher; therefore, inventory turnover (CGS/average inventory) will be higher.
| 60. |
|---|
"Inventories,” Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, pp.386-388
Study Session: 9-36-f
Discuss the measurement of inventory at the lower of cost and net realisable value.Under IFRS, the recovery of previous write-down is limited to the amount of the original write-down (€20,000) and is reported as a decrease in the cost of sales.
| January 1, 2010 | |
|---|---|
| MXN 2,000,000 | |
|
MXN 200,000 |
|
10 years |
| 5,000,000 units | |
| 800,000 units |
B.140,000 higher using the units-of-production method compared with the straight-line method.
C.112,000 higher using the double-declining method compared with the units-of- production method.
| 62. |
|
|---|
A.increase return on sales.
The increase in the value of the land bypasses the income statement and goes directly to a revaluation surplus account in equity. Equity increases thereby decreasing the debt to equity ratio
Determine the tax base of a company’s assets and liabilities.
Calculate income tax expense, income taxes payable, deferred tax assets, and deferred tax liabilities, and calculate and interpret the adjustment to the financial statements related to a change in the income tax rate.
| 64. |
|---|
A.£4,695,562.
B.£5,301,000.
C.£5,316,000.Answer = C
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Using the effective annual interest (EAI) rate method which is required under IFRS
| Year | Carrying Amount at Start of Year |
Interest Payment @ Coupon Rate |
Amortisation of Premium | Carrying Amount @ End of Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 5,376,881 | 295,728 | 325,000 | 29,272 | 5,347,609 |
| 2011 | 5,347,609 | 294,119 | 325,000 | 30,881 | 5,316,728 |
| Alternatively, take the PV of the cash flows over the remaining 8 years at 5.5% | |||||
| 5,000,000 x 6.5% x PVA(8y, 5.5%) + 5,000,000 x PV(8y, 5.5%) = 5,316,728 | |||||
“Non-Current (Long-term) Liabilities,” Elizabeth A. Gordon and Elaine Henry, CFA 2011 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, p. 521-522, 537
Study Session: 9-39-g, h, l
Distinguish between a finance lease and an operating lease from the perspectives of the lessor and the lessee.Determine the initial recognition and measurement and subsequent measurement of finance leases.
| 66. |
|---|
A.improve its current ratio.
B.improve its relations with its suppliers.
C.manage the timing of operating cash flows.
| Criterion |
|
|---|---|
| 35.0 | |
| 48.2 | |
| 58.6 | |
| 75.0 | |
|
10.8 |
If all the criteria were completely independent of each other, the number of stocks meeting all four criteria would be closest to:
If the criteria are independent of one another, the probability that all will occur is the product of the individual probabilities (Multiplication Rule for Independent Events), i.e., 0.35 x 0.482 x 0.586 x 0.75 = 0.074, or 7.4%, which would produce 371 meeting the criteria, i.e., 7.4% x 5,000.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Financial Statement Analysis: Applications,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, pp. 618-620
“Overview of Equity Securities,” Ryan C. Fuhrmann, CFA and Asjeet S. Lamba, CFA 2011 Modular Level 1, Vol.5 pp. 192-193
“Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools”, John J Nagorniak, CFA and Stephen E.Wilcox, CFA
2011 Modular Level 1, Vol. 5, p. 288
Study Session: 10-42-e; 14-58-h, 14-60-h
Determine and justify appropriate analyst adjustments to a company’s financial statements to facilitate comparison with another company.
Questions 69 through 78 relate to Corporate Finance
| 69. |
|
|---|
Explain the NPV profile, compare and contrast the NPV and IRR methods when evaluating independent and mutually exclusive projects, and describe the problems associated with each of the evaluation methods.
The NPV at 15% is $99.93. The NPV at 10% is -$0.01. The NPV at 8% is -$307.59. Where NPV = -4.662,005 + [22,610,723/(1+i)1] - [41,072,261/(1+i)2] +
[33,116,550/(1+i)3] – [10,000,000/(1+i)4]
| 70. |
|---|
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Describe how taxes affect the cost of capital from different capital sources.
"Financial Analysis Techniques," Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.3, p. 329
“Working Capital Management” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., CFA, Kenneth L. Parkinson, and Pamela Peterson Drake, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.4, pp. 162-167
Study Session 8-35-d; 11-48-c
Calculate, classify, and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability, and valuation ratios.Evaluate overall working capital effectiveness of a company, using the operating and cash conversion cycles, and compare its effectiveness with other peer companies.
| 72. |
|---|
“Cost of Capital” Yves Courtois, CFA, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela Peterson Drake, CFA 2011 Modular Level I, Vol.4, pp. 52-58
Study Session 11-45-h
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B.inventory turnover.
C.cash conversion cycle.
| 74. |
|
|---|
Answer = C
“Financial Statement Analysis” Pamela Peterson Drake, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.4, pp. 219-220, 223-224
Study Session 11-49
The candidate should be able to demonstrate the use of pro forma income and balance sheet statements.
| 75. | ||
|---|---|---|
| 7.0% 2.0% 10.4% 1.0 40.0% |
||
A.0.75.
B.1.05.
C.1.20.Answer = A
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = C
“Measures of Leverage,” Pamela Peterson Drake, CFA, Raj Aggarwal, CFA, Cynthia Harrington, CFA, and Adam Kobor, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 107-108
Study Session 11-46-b
Calculate and interpret the degree or operating leverage, the degree of financial leverage, and the degree of total leverage
| 77. |
|---|
C.purchase of shares on the open market.
Answer = A
A.32.0%.
B.43.3%.
C.44.9%.Answer = C
| 79. |
|
|---|
A.operational.
Economies that use resources in such a way that they are most valuable are allocationally efficient.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Buyer | Seller | Offer Size (# of shares) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500 | 18.50 | 1 | 200 | 20.20 |
| 2 | 300 | 18.90 | 2 | 300 | 20.35 |
| 3 | 400 | 19.20 | 3 | 400 | 20.50 |
| 4 | 200 | 20.10 | 4 | 100 | 20.65 |
| 5 | 100 | 20.15 | 5 | 200 | 20.70 |
If a trader submits an immediate-or-cancel limit buy order for 700 shares at a price of $20.50, the most likely average price the trader would pay is:
A.$20.35.
B.$20.50.
C.$20.58.
A.Equal weighted indices require frequent rebalancing.
Discuss rebalancing and reconstitution.
After an equal weighted index is constructed and the prices of constituent securities change, the index is no longer equally weighted. Therefore, maintaining equal weights requires frequent adjustments (rebalancing) to the index.
| 82. |
|---|
Assuming the beginning value of the float-adjusted market-capitalization-weighted equity index is 100, the ending value is closest to:
A.109.1.
B.110.9.
C.111.3.
| Stock | Shares Outstanding |
% Shares in Market Float |
|
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) |
|
(4) |
|
(6) | (3) x (6) | |
| 5,000 | 90 | 4,500 | 40 | 180,000 | 45 | 202,500 | |
| 2,000 | 100 | 2,000 | 68 | 136,000 | 60 | 120,000 | |
| 6,000 | 70 | 4,200 | 60 | 252,000 | 70 | 294,000 | |
| 4,000 | 40 | 1,600 | 20 | 32,000 | 24 | 38,400 | |
|
600,000 | 654,900 | |||||
| Index Value | 100 | 109.1 |
In an efficient market, prices should be expected to react only to the “unexpected” or “surprise” element of information releases. Investors process the unexpected information and revise expectations accordingly.
| 84. |
|
|---|
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Market Efficiency,” W. Sean Cleary, CFA, Howard J. Atkinson, CFA and Pamela Peterson Drake, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 148-150
Study Session 13-57-g
Compare and contrast the behavioral finance view of investor behavior to that of traditional finance in regards to market efficiency.
“Overview of Equity Securities,” Ryan C. Fuhrmann, CFA and Asjeet S. Lamba, CFA 2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, p. 182
Study Session 14-58-e, f
Discuss the methods for investing in non-domestic equity securities.Compare and contrast the risk and return characteristics of various types of equity securities.
| 86. |
|---|
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Overview of Equity Securities,” Ryan C. Fuhrmann, CFA and Asjeet S. Lamba, CFA 2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 177-178
Study Session 14-58-c
Distinguish between public and private equity securities.
Answer = C
“Introduction to Industry and Company Analysis,” Patrick W. Dorsey, CFA, Anthony M.
A.a top-down investment approach.
B.portfolio performance attribution.
Study Session 14-59-a
Explain the uses of industry analysis and the relation of industry analysis to company analysis.Indexing and passive investing strategies would not engage in over- or underweighting of industries, industry rotation, or timing investments in industries. Therefore, industry analysis is not useful to such investors or portfolio managers.
| 89. |
|---|
Wilcox, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 300-303
Study Session 14-60-j
Explain asset-based valuation models and demonstrate the use of asset-based models to calculate equity value.
|
$137,000 | |
|---|---|---|
| $70,000 | ||
|
$9.57/share |
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Wilcox, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 268-270, 288-295
Study Session 14-60-a, h
Evaluate whether a security, given its current market price and a value estimate, is overvalued, fairly valued, or undervalued by the market.Calculate and interpret the following multiples: price to earnings, price to an estimate of operating cash flow, price to sales, and price to book value.
| 91. |
|---|
Answer = A
“Forward Markets and Contracts”, Don M. Chance, CFA 2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, p. 32
Study Session 17-69-a
A.cap.
B.floor.
C.collar.
A.$0.00.
B.$4.00.
C.$4.30.Answer = C
c0 ≥ Max[ 0, S0 – X / ( 1 + r )T]
Max[0, 29 – 25/(1.05)3/12] = 4.30
94. If the volatility of returns of an underlying security increases, then:
A is correct because higher volatility increases the possible upside value of the
underlying which increases the price of calls and does not hurt puts. Higher volatility also increases the possible downside value of the underlying which increases the price of puts and does not hurt calls.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| 95. |
|---|
C.$210.
Answer = B
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
|
||
|---|---|---|
A.pay the dealer $6,229.
B.pay the dealer $18,564.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
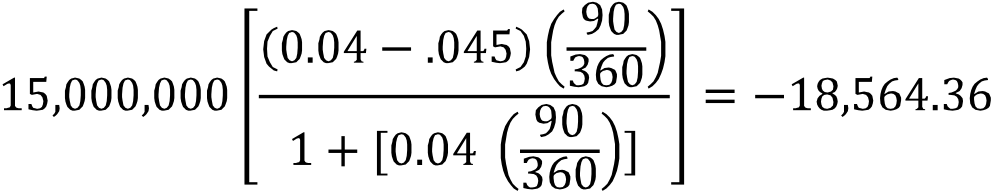
| 97. |
|---|
A.step-up note.
B.floating-rate bond.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| 98. |
|
|---|
“Features of Debt Securities,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, p. 326-328
Study Session 15-61-b
Describe the basic features of a bond, the various coupon rate structures, and the structure of floating-rate securities.B is correct because LIBOR + 300 bps at the reset date equals 1.5% + 3.00% = 4.5%, which is below the floor of 5.00% so the coupon rate will be equal to the floor.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Identify the common options embedded in a bond issue, explain the importance of embedded options, and state whether such options benefit the issuer or the bondholder.
| 100. |
|---|
C.discount or premium, depending on its duration.
Answer = A
Answer = B
“Risks Associated with Investing in Bonds,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, p. 355
Study Session 15-62-d
Identify the relationship among the price of a callable bond, the price of an option-free bond, and the price of the embedded call option.
A.1.78.
B.5.94.
| rise | = | 100 1. | − |
|
= | .5 94 |
|
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| price | if | yields | decline | − | price | if | |||||||||||||||
| 103. | 2 | × | initial | × | change | in | 2 | × | 98 2. | × | .0 003 | ||||||||||
A.increased default risk.
B.lower interest payments.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
C is correct because the when the market is willing to pay less for investing in risky bonds, the spreads on those bonds widens relative to default-free bonds. Thus the investor is concerned about credit spread risk.
105. What type of risk does the bid-ask spread most closely measure?
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| 106. |
|
|---|
A.$660.
B is correct according to the table below showing the remaining principal balance after 3 monthly payments.
| Month |
|
Interest | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 220,000.00 | 1,856.49 | 1,100.00 | 756.49 | 219,243.51 | |
|
219,243.51 | 1,856.49 | 1,096.22 | 760.27 | 218,483.24 |
|
218,483.24 | 1,856.49 | 1,092.42 | 764.07 | 217,719.17 |
Answer = C
“Overview of Bond Sectors and Instruments,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA 2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 406-408
Study Session 15-63-f
State the motivation for creating a collateralized mortgage obligation.
B.they offer greater diversification.
C.they have smaller bid-ask spreads.Answer = A
| 110. |
|---|
A.a hedge fund.
B.a mutual fund.
111. The real estate valuation approach that uses a perpetuity discount type model is the:
A.cost approach.
B is correct. The income approach to real estate valuation values a property using a perpetuity discount type of model.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B is correct. Early-stage financing is capital provided for companies moving into operation and before commercial manufacturing and sales have occurred.
| 113. |
|
|---|
C is correct. Closed-end mutual funds calculate NAV as follows: NAV = (Assets – Liabilities)/Number of shares Outstanding
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B is correct. When a commodity market is in contango, futures prices are higher than the spot price because market participants believe the spot price will be higher in the future.
Questions 115 through 120 relate to Portfolio Management.
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 286-292
Study Session 12-51-b
Discuss the types of investment management clients and the distinctive characteristics and needs of each.A is correct. Banks have a short term horizon and high liquidity needs. See Exhibit 14, page 291.
| 116. |
|---|
“Portfolio Management: An Overview”, by Robert M. Conroy and Alistair Byrne.
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 292-296
Study Session 12-51-c
Describe the steps in the portfolio management process.
|
|
| Correlation coefficient between RTF and KIU |
“Portfolio Risk and Return: Part I”, by Vijay Singal.
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 329-331.
A.a lower level of risk and return.
B.a higher level of risk and return.
C.the same level of risk and return.Answer = B
| 119. |
|
|---|
Based on the capital asset pricing model (CAPM), JKU is most likely:
Illustrate applications of the CAPM and the SML.
B is correct because:
| 120. |
|---|
B.the security market line.
C.a capital allocation line.Answer = C
2011 Level I Mock Exam: Afternoon Session
The afternoon session of the 2011 Level I Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA®) Mock Examination has 120
|
|
27 |
|---|---|---|
| 21 | ||
| 18 | ||
|
|
36 |
| 15 | ||
| 18 | ||
|
|
9 |
| 97-108 | 18 | |
| 109-114 | 9 | |
| 115-120 | 9 | |
| 180 |
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Questions 1 through 18 relate to Ethical and Professional Standards.
Answer = A
“Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct,” CFA Institute
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 8
Study Session 1-1-c
Explain the ethical responsibilities required by the Code and Standards, including the multiple sub-sections of each Standard.
B.Loyalty, Prudence and Care.
C.Additional Compensation Arrangements.
parties involved, therefore Zagoreos is in violation of Standard IV (B) Additional Compensation Arrangements. However, there is no indication that the member has received compensation, consideration, or benefit received from, or paid to, others for the recommendation of products or services and therefore has not violated Standard VI (6) related to referral fees.
3. Christy Pasley, CFA, is the Chief Investment Officer for Risen Investment Funds (RIF) a mutual fund organization. At a meeting between Homeland Builders (HB), a publicly traded company, Pasley learns HB sales are much slower than expected. In fact, HB sales declined more than 20% in the last quarter, but this information has not yet been widely disseminated. Immediately after meeting with HB, Pasley purchases put options on HB stock. Subsequently, HB issues a press release with their most recent sales figures. Has Pasley mostlikely violated the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
"Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 49-55
Study Session 1-2-b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.A is correct, as members and candidates who possess material nonpublic information that could affect the value of an investment must not act or cause others to act on the information. Even though the information is disclosed in a meeting with the mutual fund, this has not made the information public and it should not be used until it is more widely disseminated. It does not matter that the securities purchased are options rather than stocks.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = C
B.Yes, because she failed to detect Longtree’s actions.
C.Yes, because she did not take steps to ensure that the violation will not be repeated.
6. Wang Dazong, CFA, is a sole proprietor investment advisor. Dazong believes in putting his money at risk along with his clients and trades the same securities as his clients. In order to ensure fair treatment of all accounts, he rotates trade allocations so that each account has an equal likelihood of receiving a fill on their orders. This allocation procedure also applies to Dazong's own account. According to the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct, the allocation procedure used by Dazong:
A.complies with the Standards.
7. Tammi Holmberg is enrolled to take the Level I CFA examination. While taking the CFA examination, the candidate on Holmberg's immediate right takes a stretch break and a piece of paper from his pocket falls onto Holmberg's desk. Holmberg glances at the paper and realizes there is information written on the paper, which includes a formula Holmberg needs for the question she is working on. Holmberg had not memorized this formula and could not complete the question without this information. Holmberg pushes the paper off her desk and uses the formula to complete the question. According to the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct, Holmberg most likely:
A.compromised her exam.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 139-140
Study Session 1-2-b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.C.Additional Compensation Arrangements.
Answer = B
B.disclose conflicts related to the real estate he sold to the partnership. C.return all profits earned from his minority interest to the limited partners.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.Yes.
B.No, with regard to Misconduct.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
11. Praful Chandarana, CFA, is starting a new business to offer investment-consulting services to pension fund trustees in response to a new regulation that requires all pension fund Investment Policy Statements (IPS) to be reviewed and approved by an independent CFA Charterholder. Prior to starting the new business, he meets with the pension fund regulator to clarify if the CFA Charterholder undertaking the IPS review should be a licensed financial advisor. A separate regulatory body grants the license to those giving investment advice to clients. The regulator states they do not require the CFA Charterholder to hold a financial advisor’s license, despite financial-related advice being given to the pension funds during any IPS review. Chandarana therefore, starts his new business to undertake IPS reviews without obtaining a financial advisors license. Subsequently when clients of his former employer contact him he informs them of his new company and the services he offers. Does Chandarana most likely violate the CFA Code and Standards?
B is correct because the CFA Code of Ethics requires Chandarana to uphold the rules governing financial advisors. However, he failed to do so because he did not obtain a financial advisors license. The CFA Standards of Professional Conduct (I(A) – Professionalism – Knowledge of the Law) states that when rules or regulations are in conflict, Members must comply with the more strict law, in this case the requirement for financial advisors to be licensed.
12. Mailaka Securities (MS) advertises the use of a “bottom up” investment style in its marketing material. Recently, MS senior management decided to switch to a “top down” approach, citing the fact that it is less labor intensive. All other aspects of the research process are to remain the same. The head of research at MS, Mara Cherogony, CFA, is instructed to supervise the implementation of the new procedures, notify clients of the changes, and revise the text of marketing materials when new material is produced. Which of the following CFA Standards pertaining to Investment Analysis, Recommendations and Actions is Cherogony least likely in danger of violating?
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 116-117
Study Session 1–2–a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.C is correct because research can still be considered diligent and having a reasonable basis if done using a “top down” research methodology as opposed to a “bottom up” methodology. By not communicating to prospective clients the change in the investment process through the delay in the creation of new marketing material however Cherogony violates Standard V (B) – Communication with Clients which requires Members and Candidates to disclose to clients and prospective clients the basic format and general principles of the investment processes they use to analyze investments, select securities and construct portfolios and must promptly disclose any changes that might materially affect those processes. As a supervisor, Cherogony is responsible for ensuring compliance with the Code and Standards.
Answer = A
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 90-91, 99
Study Session 1–2–b
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.
B.Disclosure of Conflicts.
C.Priority of Transactions.Answer = C
B.Yes, with regard to investment statements.
C.Yes, with regard to purchasing venture capital funds.
Bravoria provided his client with investment statements more frequently than that which is required; i.e. quarterly so was not in violation of regular account information.
16. Sato Kashingaki, CFA, is a financial advisor who practices in multiple jurisdictions. In his resident country, Country A, he is not required by law to hold a financial advisors license but he is required to uphold a fiduciary duty to his clients. In Country B, authorities require him to hold a financial advisors license but he is not expected to uphold a fiduciary duty to his clients. In Country C, authorities require both a financial advisors license and an asset management license in addition to upholding a fiduciary responsibility towards clients. In which of the three countries does Kashangaki have the duty to adhere to the CFA Code and Standards over local laws?
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
17. Hezi Cohen, a CFA candidate, is a heavy user of social networking sites on the Internet. His favorite site only allows a limited number of characters for each entry so he has learned to abbreviate everything, including CFA trademarks. Cohen also enjoys professional networking sites and contributes regularly to blogs that discuss the broad topical areas covered within the CFA Exam Program. In addition, he posts to these blogs pieces he has written in his area of expertise: retirement planning. By claiming to be an expert on retirement planning, he believes his stature within the investment community increases and he can gain more clients. Which Internet activity can Cohen most likely continue to be in compliance with the CFA Standards of Professional Conduct?
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 139-148
Study Session 1–2–c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct.B is correct because the CFA Standards do not prevent a person from claiming to be an expert in their area of specialty as long it is not a misrepresentation and/or an exaggeration of their skill and expertise.
Answer = A
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 108,110
Questions 19 through 32 relate to Quantitative Methods
19. Using the sample results given below, drawn as 25 paired observations from their underlying distributions, test if the mean returns of the two portfolios differ from each other at the 1% level of statistical significance. Assume the underlying distributions of returns for each portfolio are normal and that their population variances are not known.
A.reject the hypothesis that the mean difference equals zero as the computed test statistic exceeds 2.807.
B.accept the hypothesis that the mean difference equals zero as the computed test statistic exceeds 2.807.
| – | 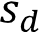 |
|
is the hypothesized difference in the |
|---|---|---|---|
| means, | is the sample standard deviation of differences, and is the sample size. In this case, | ||
the test statistic equals: (
A. 8.0.
B.21.0.
C.24.2.Answer = B
B.less than the arithmetic mean.
C.greater than the arithmetic mean.Answer = B
A.if the population distribution is normal.
B.if the population distribution is symmetric.
normal with mean µ (the population mean) and variance σ2 / n (the population variance divided by n) when the sample size n is large.
23. If the stated annual interest rate is 9% and the frequency of compounding is daily, the effective annual rate is closest to:
EAR = (1 + periodic interest rate)m - 1 = (1 + (.09 / 365))365 – 1 = 0.094162 ~ 9.42%
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
As we increase the degree of confidence, the confidence interval becomes wider. A larger sample size decreases the width of a confidence interval.
25. The belief that trends and patterns tend to repeat themselves and are, therefore, somewhat predictable best describes:
Technical analysts believe that trends and patterns tend to repeat themselves and are, therefore, somewhat predictable
26. An investor purchases 100 shares of stock at a price of $40 per share. The investor holds the stock for exactly one year and then sells the 100 shares at a price of $41.50 per share. On the date of sale, the investor receives dividends totaling $200. The holding period return on the investment is closest to:
HPR = (P1 – P0 + D1) / P0. In this problem: (41.50 – 40 + 2) / 40 = .0875 = 8.75%
27. The number of ways we can choose r objects from a total of n objects, when the order in which the r objects are listed does matter is given by the permutation formula:
C.5,040.
Answer = C
| -2.5 | 5.3 | 6.7 | 8.8 | -4.6 | 9.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3 | 8.2 | 1.4 | 0.8 | -5.3 | 6.9 |
A.16.67%.
B.18.04%.
C.27.59%.Answer = A
29. A sample of 100 observations drawn from a normally distributed population has a sample mean of 12 and a sample standard deviation of 4. Using the extract from the z-distribution given below, find the 95% confidence interval for the population mean.
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x or z | 0 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | .05 | .06 | .07 | .08 | .09 |
| 1.5 | 0.9332 | 0.9345 | 0.9357 | 0.9370 | 0.9382 | 0.9394 | 0.9406 | 0.9418 | 0.9429 | 0.9441 |
| 1.6 | 0.9452 | 0.9463 | 0.9474 | 0.9484 | 0.9495 | 0.9505 | 0.9515 | 0.9525 | 0.9535 | 0.9545 |
| 1.7 | 0.9554 | 0.9564 | 0.9573 | 0.9582 | 0.9591 | 0.9599 | 0.9608 | 0.9616 | 0.9625 | 0.9633 |
| 1.8 | 0.9641 | 0.9649 | 0.9656 | 0.9664 | 0.9671 | 0.9678 | 0.9686 | 0.9693 | 0.9699 | 0.9706 |
| 1.9 | 0.9713 | 0.9719 | 0.9726 | 0.9732 | 0.9738 | 0.9744 | 0.9750 | 0.9756 | 0.9761 | 0.9767 |
| 2.0 | 0.9772 | 0.9778 | 0.9783 | 0.9788 | 0.9793 | 0.9798 | 0.9803 | 0.9808 | 0.9812 | 0.9817 |
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
The 95% confidence interval uses z0.025 as the reliability factor. The cumulative probability value closest to 0.975 provides the appropriate value of z0.025 which is z0.025 = 1.96. The confidence interval is formed as:
B.standard error of the sample statistic.
C.appropriate value from the t-distribution .Answer = B
B.consistency.
C.unbiasedness.
32. Using a discount rate of 5%, compounded monthly, the present value of $5,000 to be received three years from today is closest to:
A.$4,250.
B.$4,305.
C.$4,320.
Questions 33 through 44 relate to Economics
33. If the quantity demanded of pears falls by 4% when the price of apples decreases by 3%, then apples and pears are best described as:
The cross elasticity of demand is defined as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in the price of a substitute or complement. If the cross elasticity of demand is positive, the goods are substitutes. In this case, the 4 % decline in
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
C.partly by the buyer and partly by the seller.
Answer = C
A.increase.
B.decrease.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
36. Assume the U.S. Federal Reserve system (the Fed) has decided to lower interest rates in the economy. To carry out this policy, the Fed will most likely:
“Money, the Price Level, and Inflation,” Michael Parkin
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, p. 376
“Monetary Policy,” Michael Parkin
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 468, 475
Study Session 6-24-d, 6-27-a, b
Explain the goals of the U.S. Federal Reserve (Fed) in conducting monetary policy and how the Fed uses its policy tools to control the quantity of money, and describe the assets and liabilities on the Fed’s balance sheet.Discuss the goals of U.S. monetary policy and the Federal Reserve’s (Fed’s) means for achieving the goals, including how the Fed operationalizes those goals.
Answer = A
“Monitoring Jobs and the Price Level,” Michael Parkin
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 312-313
Study Session 5-22-c
Explain the types of unemployment, full employment, the natural rate of unemployment, and the relation between unemployment and real GDP.
B.Low control over prices is characteristic of oligopolies.
C.An HHI value of 60 indicates that a market is highly competitive.
39. The primary monetary policy goal of most major central banks is best characterized as:
A.containing inflation.
Most major central banks’ primary monetary policy goal is to contain inflation.
40. Externalities, in reference to a particular good, are most likely to impact:
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Efficiency and Equity,” Michael Parkin
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, p. 50
Study Session 4-14-e
Explain 1) how efficient markets ensure optimal resource utilization and 2) the obstacles to efficiency and the resulting underproduction or overproduction, including the concept of deadweight loss.
C.Creation of new money to pay government obligations.
Answer = C
Answer = B
“Monitoring Jobs and the Price Level,” Michael Parkin
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, p. 319
Study Session 5-22- d
Explain and calculate the consumer price index (CPI) and the inflation rate, describe the relation between the CPI and the inflation rate, and explain the main sources of CPI bias.
B.being a nonrenewable natural resource.
C.being priced according to the Hotelling principle.
A.acts as a unit of account.
B.provides a means of payment.
Questions 45 through 68 relate to Financial Statement Analysis
45. At the start of a month, a retailer paid $5,000 in cash for different types of candies. He sold candies costing $2,000 for $3,000 during the month. The most likely effect of these transactions on the retailer’s accounting equation for the month is that assets will:
"Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.3, pp. 39-44, 52, 55
Study Session: 7-30-c
Explain the process of recording business transactions using an accounting system based on the accounting equations.Buying $5,000 of candies will decrease cash by $5,000 and increase inventory by $5,000. Selling $2,000 of candies for $3,000 will decrease inventory by $2,000, and increase either cash (if cash collected in the same accounting period) or accounts receivable (if sold on credit) by $3,000. The combined effect is an increase of $1,000 in assets.
Answer = B
"Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.3, p. 67
Study Session: 7-30-f
Describe the flow of information in an accounting system.
C.Revenues.
Answer = C
48. According to the IFRS framework, which of the following is the least likely qualitative characteristic that makes financial information useful?
A.Materiality.
The four principal qualitative characteristics that make financial information useful are understandability, relevance, reliability and comparability. Materiality relates to the level of detail of the information needed to achieve relevance – whether the omission or misstatement of the information would impact the decision maker's decision.
49. Which of the following statements is most accurate?
“Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.3, p.19
“Understanding the Balance Sheet International,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.3, pp. 201, 226
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
|
$1,000,000 |
|---|---|
| 100,000 | |
| 2,000 | |
| $10 | |
|
|
|
$80,000 |
| 40% | |
A.$7.57.
B.$7.69.
C.$7.72.Answer = C
| 51. |
|
|---|
"Understanding The Income Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.3, pp.150-152
Study Session: 8-32-b
Explain the general principles of revenue recognition and accrual accounting, demonstrate specific revenue recognition applications (including accounting for long-term contracts, installment sales, barter transactions, and gross and net reporting of revenue), and discuss the implications of revenue recognition principles for financial analysis.Under the installment method, the portion of the total profit that is recognized in each period is determined by the percentage of the total sales price for which the seller has received cash. For Company A 2/10 x 4 = $0.8 million. Note, cost recovery method could be used in this case, but the reported profit would be $0.
Current Liabilities
| $ 9,480 |
A.0.4.
B.0.9.
C.1.3.Answer = B
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
If the investment is reclassified as Available-for-sale as of 31 December 2010, the balance sheet carrying value of the company’s investment portfolio would most likely:
A.remain the same.
54. A company reports its interest payments on long-term debt as a financing activity under IFRS. If the company reports under U.S. GAAP, the most likely effect would be:
A.an increase in cash flow from operations.
Study Session: 8-34-c, 10-43-c
Compare and contrast the key differences in cash flow statements prepared under international financial reporting standards and U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.Identify and explain the major differences between international and U.S. GAAP accounting standards concerning the treatment of interest and dividends on the statement of cash flows.
| $ 500 | |
|---|---|
| 250 | |
|
200 |
|
(30) |
| (25) |
"Understanding The Cash Flow Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van
Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.3, pp. 268-269
Study Session: 8-34-f
Describe the process of converting a cash flow statement from the indirect to the direct method of presentation.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
56. Which of the following statements is most accurate regarding cash flow ratios?
Calculate, classify, and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability, and valuation ratios.
Debt payment ratio (CFO ÷ Cash paid for long-term debt repayment) shows the firm’s ability to pay debts with operating cash flows.
| Measurement Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Fair Value | Income Statement | |
|
Amortized Cost | Income Statement | |
| Fair Value | Equity |
“International Standards Convergence,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 637-639
Study Session: 10-43-a, b
Identify and explain the major international accounting standards for each asset and liability category on the balance sheet and the key differences from U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).Identify and explain the major international accounting standards for major revenue and expense categories on the income statement and the key differences from U.S. GAAP.
The cost of sales (in ‘000s) is closest to:
"Inventories,” Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.3, pp.382-386
Study Session: 9-36-c, e
Calculate cost of sales and ending inventory using different inventory valuation methods and explain the impact of the inventory valuation method choice on gross profit.Compare and contrast cost of sales, ending inventory, and gross profit using different inventory valuation methods.
| Cost of Sales | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weighted Average | CGS FIFO | CGS LIFO | ||||
| Available for sale | ||||||
| Cost $ | Units sold | Units sold |
|
|||
| 1 | 600 | 600 | 1 x 600 | 600 | 3 x 680 | 2,040 |
| 5 | 650 | 3,250 | 5 x 650 | 3,250 | 3 x 650 | 1,950 |
| 3 | 680 | 2,040 | ||||
| 9 | CGAS | $5,890 |
|
$3,850 | $3,990 | |
| $654.44 x 6 = $3,926 | ||||||
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| 59. |
|---|
A.$800,000.
B.$825,000.
C.$855,000.Answer = B
B.inventory turnover.
C.debt-to-equity ratio.Answer = A
61. A company, which prepares its financial statements in accordance with IFRS is in the process of developing a more efficient production process for one of its primary products. The most appropriate accounting treatment for those costs incurred in the project is to:
A.expense them as incurred.
Study Session: 9-37-a
Distinguish between costs that are capitalized and costs that are expended in the period in which they are incurred.Under IFRS research and development costs are expensed until certain criteria are met, including that technical feasibility has been established and the company intends to use it.
Answer = B
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.liabilities when calculating the company’s current ratio.
B.equity when calculating the company’s return on equity ratio. C.liabilities when calculating the company’s debt-to-equity ratio.
A.$60,000.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| $2,060,000 |
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
1,961,000 | |
| $99,000 |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| £8,000 | £8,000 | |
| 20 years | 8 years | |
| £1,200 | £3,000 | |
|
£6,800 | £5,000 |
|
||
| £10,000 | ||
| 20 years | ||
A.£690.
B.£960.
Calculate income tax expense, income tax payable, deferred tax assets, and deferred tax liabilities, and calculate and interpret the adjustment to the financial statements related to a change in the income tax rate.
Compare and contrast a company’s deferred tax items.
| 66. |
|---|
“Financial Reporting Quality: Red Flags and Accounting Warning Signs,”Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, and Paul Munter
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 562-563
Study Session: 10-40-b, e
Describe activities that will result in a low quality of earnings.Describe common accounting warning signs and methods for detecting each.
B.cash from operations.
C.cash from financing activities.
The securitization of accounts receivables for less than book value would result in a loss on the income statement, but an increase in the cash from operations, reflecting the proceeds received.
68. An analyst uses a stock screener and selects the following metrics: a global equity index, P/E ratio lower than the median P/E ratio, and a price-book value ratio lower than the median price- book value ratio. The stocks so selected would be most appropriate for portfolios of which type of investors?
“Financial Statement Analysis: Applications,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 608-611
“Security Market Indices,” Paul D. Kaplan, CFA, and Dorothy C. Kelly, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 105
Study Session: 10-42-d; 13-56-k
Discuss the use of financial statement analysis in screening for potential equity investments.Compare and contrast the types of security market indices
A.net present value and internal rate of return profiles.
B.marginal cost of capital and net present value profiles.
The point where the marginal cost of capital (MCC) intersects the investment opportunity schedule (IOS) is the optimal capital budget (see Figure 1 p.46).
70. Which of the following is most likely a sign of a good corporate governance structure?
“The Corporate Governance of Listed Companies: A Manual for Investors”
2011 Modular Level I, Vol.4, p. 241
Study Session 11-50-b, c
Discuss and critique characteristics and practices related to board and committee
independence, experience, compensation, external consultants, and frequency of elections, and determine whether they are supportive of shareholder protection.Describe board independence and explain the importance of independent board members in corporate governance.
Answer = A
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, CFA, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela Peterson Drake, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 50-51
“Equity valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools,” John J. Nagorniak, CFA, and Stephen E. Wilcox, CFA 2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 276-279
Study Session 11-45-g, 14-60-d
Calculate and interpret the cost of noncallable, nonconvertible preferred stock.
B.Liquidating long-term assets.
C.Centralized cash management system.
A.stable.
B.unreliable.
The debt-rating approach is used when the market prices for debt are unreliable or non-existent.
74. A twenty-year $1,000 fixed rate non-callable bond with 8% annual coupons currently sells for $1,105.94. Assuming a 30% marginal tax rate and an additional risk premium for equity relative to debt of 5%, the cost of equity using the bond-yield-plus-risk-premium approach is closest to:
Calculate and interpret the cost of equity capital using the capital asset pricing model approach, the dividend discount model approach, and the bond-yield-plus-risk-premium approach.
First, you need to determine the yield-to-maturity, which is the discount rate that sets the bond price to $1,105.94 and is equal to 7%. This can be done with a financial calculator:
FV = -1,000, PV = 1,105.94, N = 20, PMT = -80, solve for I, which will equal 7%.
C.interest rate risk.
Answer = A
76. If the degree of financial leverage (DFL) is 1.00, the operating breakeven point compared to the breakeven point, is most likely:
A.lower.
Calculate and interpret the operating breakeven quantity of sales.
When DFL (= operating income ÷ net income) = 1.00, operating income = net income, meaning the fixed cost of debt is zero. The breakeven point is: (fixed costs + fixed cost of debt) ÷ contribution margin. Because the fixed cost of debt is zero, the company’s breakeven point becomes: fixed costs ÷ contribution margin, which is the same as the operating breakeven point.
“Dividends and Share Repurchases: Basics,” George H. Troughton, CFA, and Gregory Noronha, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 141-143
Study Session 11-47-d
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B.previous retained earnings plus forecasted financing surplus or deficiency. C.previous retained earnings plus forecasted net income less forecasted dividends.
Answer = C
79. An investor buys a stock on margin. Assume that the interest on the loan and the dividend are both paid at the end of the holding period. The data related to the transaction are as follows:
|
500 |
|---|---|
| $28 | |
| 3.33 | |
|
6 months |
|
$30 |
The investor’s total return on this investment over the margin holding period is closest to:
A.15.6%.
B.16.7%.
C.21.4%.
| 80. |
|
|---|
“Market Organization and Structure,” Larry E. Harris
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 23-24, 30, 38
Study Session 13-55-d
Describe the types of financial intermediaries and the services that they provide.Clearing houses arrange for financial settlement of trades. In futures markets, they guarantee contract performance.
B.Fundamental.
C.Float-adjusted market-capitalization.
A.relate to long-term price patterns.
B.relate to short-term price patterns.
Momentum anomalies relate to short-term price patterns, typically resulting from investor overreaction in response to the release of unexpected public information.
83. The advantages to an investor owning convertible preference shares of a company most likely include:
Compare and contrast the risk and return characteristics of various types of equity securities.
Convertible preference shares tend to exhibit less price volatility than the underlying common shares because the dividend payments are known and more stable
“Overview of Equity Securities,” Ryan C. Fuhrmann, CFA, and Asjeet S. Lamba, CFA 2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 175, 187
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.mature stage.
B.shakeout stage.
C.embryonic stage.
A.Restaurants.
B.Proprietary drugs.
Explain the effects of industry concentration, ease of entry, and capacity on return on invested capital and pricing power.
Restaurants industry is characterized by low barriers to entry because anyone with a modest amount of capital and some culinary skill can open a restaurant. The industry, however, is fragmented which can lead to fierce competition and weak pricing power.
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 342-343
“Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools,” John J. Nagorniak, CFA, and Stephen E. Wilcox, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 290-291
Study Session 8-35-f, 14-60-h
Demonstrate the application of and interpret changes in the component parts of the DuPont analysis (the decomposition of return on equity).Calculate and interpret the following multiples: price to earnings, price to an estimate of operating cash flow, price to sales, and price to book value.
| Company A | Company B | |
|---|---|---|
| 14.3 (1-0.30) = 10.0% | ||
|
|
|
| 15.4 / 10.9 = 1.4x | 14.3 / 9.0 = 1.6x |
Further, the investor focuses on the firm’s capacity to pay dividends rather than expected dividends. Considering the above, the investor will most likely use which of the following valuation models?
A.Asset-based valuation model.
B.Free-cash-flow-to-equity model.
C.Gordon dividend growth model.Free-cash-flow-to-equity (FCFE) is a measure of the firm’s dividend-paying capacity which should be reflected in the cash flow estimates rather than expected dividends. Analysts must make projections of financials to forecast future FCFE and thus the constant growth assumption as in the Gordon growth model is not an issue. An asset-based valuation model is not appropriate considering the high proportion of intangibles (goodwill and patents) in the firm’s assets.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30% |
| 6x |
“Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools,” John J. Nagorniak, CFA, and Stephen E. Wilcox, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 297-299
Study Session 14-60-i
Explain the use of enterprise value multiples in equity valuation and demonstrate the use of enterprise value multiples to estimate equity value.First, compute the enterprise value (EV) from EBIDTA x EV/EBITDA multiple.
| 90. |
|---|
Answer = C
“Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools,” John J. Nagorniak, CFA, and Stephen E. Wilcox, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 279-281
Study Session 14-60-e
Calculate and interpret the intrinsic value of an equity security based on the Gordon (constant) growth dividend discount model or a two-stage dividend discount model, as appropriate.
B.are private, customized transactions.
C.represent a right rather than a commitment.
Differentiate among the basic characteristics of forward contracts, futures contracts, options (calls and puts), and swaps.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Derivative Markets and Instruments,” Don M. Chance
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp 55-59
Study Session 17-70-d
Describe price limits and the process of marking to market, and calculate and interpret the margin balance, given the previous day’s balance and the change in the futures price.B is correct. $110 of variation margin is required since the $90 margin balance after Day 3 is below the $100 maintenance margin. The $110 variation margin will re-establish the $200 initial margin.
Derivative Markets and Instruments,” Don M. Chance 2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp 110-113
Study Session 17-71-m
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = B
Derivative Markets and Instruments,” Don M. Chance
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp 99-100
Study Session 17-71-i
Define intrinsic value and time value, and explain their relationship.
Answer = A
“Derivative Markets and Instruments,” Don M. Chance
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp 117-118
Study Session 17-71-p
Indicate the directional effect of an interest rate change or volatility change on an option’s price.
| Notional | FX Rate | Swap Rate | # Days Period | # Days Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company | USD130,000,000 | USD 1.30 | 4.00% | 180 | 360 |
| EUR100,000,000 | EUR 1.00 | 2.00% | 180 | 360 |
Which of these interest payments will most likely be made by one of the parties in the transaction?
A.Bank will make a payment of USD 1,000,000.
B is correct because the company pays USD 130,000.000 × 0.04 × 180/360 = USD 2,600,000
Questions 97 through 108 relate to Fixed Income Investments.
Answer = B
“Overview of Bond Sectors and Instruments,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 427-428
Study Session 15-63-k
Describe the mechanisms available for placing bonds in the primary market and differentiate the primary and secondary markets in bonds.
B.Liquidity preference theory.
C.Market segmentation theory.Answer = A
Answer = B
“Understanding Yield Spreads,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 464-465
Study Session 15-64-i
Calculate the after-tax yield of a taxable security and the tax-equivalent yield of a tax-exempt security.
100. A bond portfolio manager is considering three Bonds – A, B, and C – for his portfolio. Bond A allows the issuer to call the bond before stated maturity, Bond B allows the investor to put the bond back to the issuer before stated maturity, and Bond C contains no embedded options. The bonds are otherwise identical. The manager tells his assistant, “Bond A and Bond B should have larger nominal yield spreads to a U.S. Treasury than Bond C to compensate for their embedded options.” Is the manager most likely correct?
A.Yes.
101. If the appropriate annual discount rate is 6%, the value of a 3-year bond that has a 7% coupon rate, has a maturity (par) value of $1,000, and pays interest annually is closest to:
A.$973.76.
| 70 | + | 70 | + | ,1 070 | = | 66 . 04 | + | 62 . 30 | + | 898 . 39 | = | ,1 026 . 73 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 102. | .1 06 1 | .1 06 | 2 | .1 06 | 3 |
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = B
| Period | Years | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 1.20% |
| 2 | 1.0 | 2.10% |
| 3 | 1.5 | 2.80% |
| 4 | 2.0 | 3.30% |
On a BEY basis, the 6-month forward rate one year from now is closest to:
A.2.10%.
B.3.64%.
C.4.21%.
B.a discount.
C.a premium.Answer = C
Answer = B
“Yield Measures, Spot Rates, and Forward Rates,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 538-539
Study Session 15-66-b
Calculate and interpret the traditional yield measures for fixed-rate bonds and explain their limitations and assumptions.
| $ 850 | = | $ 30 | + | $ 30 | + | + | $ 30 | + | $ ,1 030 | . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1( | + | ytm | / | 2 ) | 1 | 1( | + | ytm | / | 2 ) | 2 | | 1( | + | ytm | / | 2 ) | 49 | 1( | + | ytm | / | 2 ) | 50 | ||||||||
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
106. Which of these definitions of duration is most relevant to a bond investor? A bond’s duration is its:
“Introduction to the Measurement of Interest Rate Risk,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA 2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 630-631.
Study Session 15-67-f
Distinguish among the alternative definitions of duration and explain why effective duration is the most appropriate measure of interest rate risk for bonds with embedded options.
“Introduction to the Measurement of Interest Rate Risk,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 622, 633-635
Study Session 16-67-h
Describe the convexity measure of a bond and estimate a bond’s percentage price change, given the bond’s duration and convexity and a specified change in interest rates.A is correct because when convexity is known the percentage change in a bond’s price = (-duration × ∆y × 100) + (C × (∆y)2 × 100) = (-4.50×0.005×100)+(-39.20×0.0052×100) = -2.35.
| Bond | Market Value | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| A | $1.2 million | 3.2 |
| B | $3.4 million | 7.6 |
| C | $2.9 million | 12.4 |
| D | $1.6 million | 1.5 |
Answer = C
“Introduction to the Measurement of Interest Rate Risk,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 632-633
Study Session 16-67-g
Calculate the duration of a portfolio, given the duration of the bonds comprising the portfolio, and explain the limitations of portfolio duration.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.$2,825,000.
B.$2,975,000.
C.$3,228,500.
|
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Failure Probability: | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
If the cost of capital for the project is 18%, the project’s expected NPV is closest to:
(1-.20)=.2688. Then calculate the NPV from success
Subtracting the NPV of failure, -1,000*(1-.2688 or .7312) = -731,200. The difference between the NPVs is the expected NPV of the project, 906,150-731,200=174,950.
C.lower capital gains tax liability relative to mutual funds.
Answer = C
B.expertise in selecting funds and conducting due diligence.
C.access to successful funds that may otherwise be closed to new investors.
A.Control premium.
B.Marketability discount.
B is correct because to estimate a marketability discount for a closely held company, the analyst identifies a publicly traded comparable company with a liquid market. The comparable’s market value of equity is the base to which the marketability discount is applied.
114. An index provider has created a new investable index that tracks the hedge fund industry. Any fund that follows a long/short equity strategy can enter the index. The index provider places new constituents in the index at the end of each year and incorporates the new funds’ track record in the database. Which of the following is least likely a bias that might distort the historical performance of the index?
C is correct because this is not a bias that is associated with distorting the performance of a hedge fund index. Tracking error is a risk more commonly associated with mutual funds and ETFs when their investments deviate significantly from those in the index it is benchmarked against. Many hedge funds pursue absolute returns and may deviate materially from indices.
Questions 115 through 120 relate to Portfolio Management.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, p. 292
Study Session 12-51-c
Describe the steps in the portfolio management process.
C.have assets that are owned directly by the individual.
Answer = C
Answer = B
“Portfolio Risk and Return: Part I,” Vijay Singal, CFA
2011 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, p. 327
Study Session 12-52-a
Calculate and interpret major return measures and describe their applicability.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer = B
| 40% | |
|---|---|
|
20% |
|
85% |
B correct. 0.85*0.40/0.20=1.70
120. A portfolio manager decides to temporarily invest more of a portfolio in equities than the investment policy statement prescribes, because he expects equities will generate a higher return than other asset classes. This decision is most likely an example of:
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Discuss the principles of portfolio construction and the role of asset allocation in relation to the IPS.
1.According to the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct, trading on material nonpublic information is least likelyto be prevented by establishing:
A.fire-walls.
C is correct as selective disclosure occurs when companies discriminate in making material nonpublic information public. Corporations that disclose information on a limited basis create the potential for insider-trading violations. Standard II (A).
2.William Wong, CFA, is an equity analyst with Hayswick Securities. Based on his fundamental analysis, Wong concludes the stock of a company he follows, Nolvec Inc., is substantially undervalued and will experience a large price
Answer: B
“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 48-50, 80-81, 94-95Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Stargazer, Inc. discussing the company’s tender offer to purchase Dynamica Enterprises, a retailer of Stargazer products.
According to the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct, Ward most likely can not use the information because:A.it relates to a tender offer.
A is correct because trading on the information is restricted as it relates to a tender offer; it is clearly material, nonpublic information. Standard II (A).
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
C.both the press release and the research report.
Answer: C
A.Conflicts of Interest
B.Additional Compensation.C.Both Additional Compensation and Conflicts of Interest.
C is correct because members should disclose all potential conflicts of interest, the substantial time involved in managing family accounts, and when engaging in independent practice for compensation should not render services until receiving written consent from all parties. Standard IV (B), Standard VI (A).
6.The eight major provisions of the Global Investment Performance Standards (GIPS) include all of the following except:
C is correct becauseAlternative Assets is not among the eight major provisions or sections of the Global Investment Performance Standards which include:
Fundamentals of Compliance, Input Data, Calculation Methodology, Composite Construction, Disclosures, Presentation and Reporting, Real Estate, and Private Equity. Standard II, Provisions of The Global Investment Performance Standards.7.Hui Chen, CFA, develops marketing materials for an investment fund he founded three years ago. The materials show the 3-, 2- and 1-year returns for the fund. He
Answer: A
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.No.
B.Yes, with regard to Fair Dealing.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
9.Ron Dunder, CFA, is the CIO for Bling Trust (BT), an investment advisor. Dunder recently assigned one of his portfolio managers, Doug Chetch, to manage several accounts that primarily invest in thinly traded micro-cap stocks. Dunder soon notices that Chetch places many stock trades for these accounts on the last
Answer: C
“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 76-78
Study Sessions 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.other client accounts have their orders filled. The fee for managing his family’s
account is based on his firm’s normal fee structure. According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, Nelson’s best course of action with regard to management of his family’s account would be to:
A is correct as Nelson has breached his duty to his family by treating them differently from other clients. They are entitled to the same treatment as any other client of the firm. Nelson should treat his family’s account like any other client account. Standard VI (B) related to Priority of Transactions.
11.Several years ago, Leo Peek, CFA, co-founded an investment club. The club is fully invested but has not actively traded its account for at least a year and does not plan to resume active trading of the account. Peek’s employer requires an annual disclosure of employee stock ownership. Peek discloses all of his personal trading accounts, but does not disclose his holdings in the investment club. Peek’s actions are least likely to be a violation of which of the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.B is correct as there is no indication that the investment club is trading ahead of clients. Standard I (C).
C.decline to accept supervisory responsibility until her firm adopts procedures to allow her to adequately exercise such responsibility.
Answer: C
Upon verifying Orca is on SWIFT’s approved stock list, Crux purchases Orca’s common stock and call options for selective SWIFT clients. Two weeks later, CK announces its intention to acquire Orca. The next day, Crux sells all of the Orca securities, giving the fund a profit of $3 million. What action should Crux most likely take to avoid violating any CFA Institute Standards of Professional
Conduct?A.Refuse to trade based on the information.
A is correct as members/candidates who possess material nonpublic information that could affect the value of an investment should not act or cause others to act on the information. Crux traded on the material information that Orca is about to be acquired by Cyber Kinetics. The information is non-public because it is not publicly available, which was verified when Crux researched Orca on the Internet and found nothing about the acquisition. Standard II (A).
14.Justin Blake, CFA, a retired portfolio manager owns 20,000 shares of a small public company that he would like to sell. He posts messages on several Internet bulletin boards. The messages read, "This stock is going up once the pending patents are released so now is the time to buy. You would be crazy to sell anything below $3 in a few months from now. The stock is a buy at anything below $3. I have done some close research on these guys." According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, Blake most likely violated the Standard or Standards associated with:
“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 45, 89-92
Study Sessions 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.A is correct because Blake violated the Standard regarding Conflicts of Interest because he did not disclose his ownership of shares in his message. He also violated the standard relating to Integrity of Capital Markets by engaging in a practice that is likely to artificially inflate trading volume. Standard II (B), Standard VI (A).
Answer: A
Introduction to the Global Investment Performance Standards (GIPS®) CFA Institute, 2006
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 131
Study Sessions 1-3-b
Explain the construction and purpose of composites in performance reporting.
A.No.
B.Yes, relating to diligence and reasonable basis.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
17.Miranda Grafton, CFA, purchased at varying prices during the trading session a large block of stock on behalf of specific accounts she managed. The stock realized a significant gain in value before the close of the trading day, so Grafton reviewed her purchase prices to determine what prices should be assigned to each specific account. According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, Grafton’s most appropriate action is to allocate the execution prices:
Members have a responsibility to deal with all clients fairly according to Standard III (B). All clients participating in the block trade should receive the same execution price and be charged the same commission.
18.Jiro Sato, CFA, deputy treasurer for May College, manages the Student
Scholarship Trust. Sato issued a Request for Proposal (RFP) for domestic equity managers. Pamela Peters, CFA, a good friend of Sato, introduces him to representatives from Capital Investments, who submitted a proposal. Sato selected Capital as a manager based on the firm’s excellent performance record. Shortly after the selection, Peters, who had outstanding performance as an equity manager with another firm, accepted a lucrative job with Capital. Which of the CFA Charterholders violated CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.
Members should use reasonable care and judgment to maintain independence and objectivity (Standard I (B)). There is no indication of inappropriate behavior in selection of the equity manager or in the acceptance of employment with that manager; both decisions were based on the excellent performance records of the manager and the member, respectively.
B.discrete uniform distribution.
C.continuous uniform distribution.Answer: B
A.equal to the effective annual yield.
B.more than the effective annual yield.
The bond equivalent yield for a semi-annual pay bond is equal to double the semiannual yield to maturity (page 257).
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| $2.4 million | |
|---|---|
| Standard deviation of net income for all companies in the index | $3.2 million |
Answer: C
“Sampling and Estimation,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 483
Study Session 3-10-e
Calculate and interpret the standard error of the sample mean.
A. 9.62.
B.10.80.
C.10.89.Answer: B
The geometric mean return is calculated as the nth root of the product of n terms, where the terms are one plus the returns and n is the number of returns. After taking the nth root, subtract one (refer to Equation 6, p. 297). In this case, ([1+2.2%]*[1+6.2%]*… [1+15.3%]*[1+18.4%])0.10 – 1 = 10.80%.
23.An investor currently has a portfolio valued at $700,000. The investor’s objective is long-term growth, but the investor will need $30,000 by the end of the year to pay her son’s college tuition and another $10,000 by year-end for her annual vacation. The investor is considering three alternative portfolios:
| Portfolio | Expected Return | Standard Deviation of Returns |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8% | 10% |
| 2 | 10% | 13% |
| 3 | 14% | 22% |
“Common Probability Distributions,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W.
McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 445-446
Study Session 3-9-l
Define shortfall risk, calculate the safety-first ratio, and select an optimal portfolio using Roy’s safety-first criterion.B.mean return per unit of risk.
C.mean excess return per unit of risk.
25.A fundamental analyst studying 100 potential companies for inclusion in her stock portfolio uses the following three screening criteria:
A. 2.0.
B. 8.5.
C.20.0.Answer: A
26.When using stock return data, a geometric mean return calculation is most likely preferred over a geometric mean calculation because:
A.return data can be negative.
McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 296-299
Study Session 2-7-e
Define, calculate, and interpret measures of central tendency, including the population mean, sample mean, arithmetic mean, weighted average or mean (including a portfolio return viewed as a weighted mean), geometric mean, harmonic mean, median, and mode.Taking the nth root of a negative number when n is an even number cannot be done (unless one uses imaginary numbers). As returns can be negative, it might not be possible to find their geometric mean. However, returns cannot be lower than -100%. By adding one to each return, as is done in the geometric mean return calculation, we create a series of numbers greater than or equal to zero. The product of such terms must therefore also be positive and the nth root can always be found.
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W.
McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 283-299
Study Session 2-7-e
Define, calculate, and interpret measures of central tendency, including the population mean, sample mean, arithmetic mean, weighted average or mean (including a portfolio return viewed as a weighted mean), geometric mean, harmonic mean, median, and mode.“Discounted Cash Flow Applications,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W.
McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 253-257
Study Session 2-6-d, e
Calculate and interpret the bank discount yield, holding period yield, effective annual yield, and money market yield for a U.S. Treasury bill.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: B
Answer: C
“Hypothesis Testing,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 523-524
Study Session 3-11-c
Define and interpret a decision rule and the power of a test, and explain the relation between confidence intervals and hypothesis tests.
“Technical Analysis,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA and Keith Brown, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 576-582
Study Session 3-12-cBy accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B.skewed to the right.
C.useful in describing the distribution of stock prices.
Explain the relationship between normal and lognormal distributions and why the lognormal distribution is used to model asset prices.
The lognormal distribution is bounded by zero and thus skewed to the right. The lognormal distribution is a good fit to stock prices as stock prices can not fall below zero.
Answer: A
“Output and Costs,” Michael Parkin
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 141-142
“Perfect Competition,” Michael Parkin
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 166
Study Session 4-17-d, 5-18-b
Explain the company’s production function, its properties of diminishing returns and diminishing marginal product of capital, the relation between short-run and long-run costs, and how economies and diseconomies of scale affect long-run costs.B.entirely opportunity cost.
C.part economic rent and part opportunity cost.
35.The most likely initial (short-run) effect of demand-pull inflation is an increase in:
A.the price level and a decrease in real GDP.
The initial effect of demand-pull inflation is an increase in the aggregate demand which, in turn, leads to an increase in the real GDP (Figure 2 (a), pp. 399).
36.According to the short-run Phillips curve, when inflation is less than expected, the most likely initial effect is that:
“U.S. Inflation, Unemployment, and Business Cycles,” Michael Parkin
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 406-408
Study Session 6-25-e
Explain the impact of inflation on unemployment, and describe the short-run and long-run Phillips curve, including the effect of changes in the natural rate of unemployment.The difference between actual and expected rates of inflation influences unemployment. When inflation falls below its expected rate, unemployment rises above the natural rate.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: A
Answer: C
“Organizing Production,” Michael Parkin
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 108-109
Study Session 4-16-d
Explain command systems and incentive systems to organize production, the principal-agent problem, and measures a firm uses to reduce the principal-agent problem.C.the supply of loanable funds.
Answer: B
40.The view that the money wage rates are sticky in the short-run is least likely held by which of the following schools of thought?
A.Classical
B.Keynesian
C. MonetaristA.both firms earn economic profits.
B.neither firm earns an economic profit.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
42.Limited liability is most likely to be an advantage of which type of business organization?
43.In a simple economy containing only two goods – apples and shirts – the prices and quantities in the base period and the current period are:
|
Quantity | Price ($) |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 1.00 | |
| 5 | ||
| Current period | Quantity | Price ($) |
| 25 | 1.25 | |
|
5 |
|
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
The cost of the CPI basket at base period prices is: (25 × $1.00) + (5 × $20.00) = $125. The cost of the CPI basket at current period prices is: (25 × $1.25) + (5 × $20.50) = $133.75. The CPI for the period is ($133.75 / $125) × 100 = 107.
The elasticity of supply is closest to:
A.0.60
B.0.64
C.0.67Questions 45 through 68 relate to Financial Statement Analysis
45.A firm reports sales of €50,000,000 for the year ended December 31, 2009. Its
“Understanding The Cash Flow Statement”, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, pp. 267-268
Study Session 8-34-e
Demonstrate the steps in the preparation of direct and indirect cash flow statements, including how cash flows can be computed using income statement and balance sheet data.The cash collections from sales is equal to sales less the change in receivables: €50,000,000 - (€7,500,000-€6,000,000) = €48,500,000.
|
|
|
|
A.215,000.
B.420,000.
C.430,000.Answer: C
The weighted average number of shares outstanding is time weighted: 5/12 of the year there were 180,000 shares, and 7/12 of the year there were 240,000
(180,000+60,000) on a pre-split basis; the stock split is treated retroactively to the start of the year.[(180,000 x 5/12) + (240,000 x 7/12)] x 2 = 430,000
“Understanding the Cash Flow Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, p. 254
“International Standards Convergence”, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA 2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, p. 665
Study Session 8-34-c, 10-43-c
Compare and contrast the key differences in cash flow statements prepared under international financial reporting standards and U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.Identify and explain the major differences between international and U.S.GAAP accounting standards concerning the treatment of interest and dividends on the statement of cash flows.
The revenue reported is equal to the percentage of the contract that is completed in that period, where percentage completion is based on costs. In Year 2, the percent completed is $3,000,000/$4,400,000 = 68.2%, resulting in 68.2% x 5,300,000 = 3,616,636 revenue being recognized.
49.An analyst’s examination of the performance of a company is least likely to include an assessment of a company’s:
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, pp.7-9
Study Session 7-29-a
Discuss the roles of financial reporting and financial statement analysis.“Financial Reporting Standards,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, pp. 106-108
Study Session 7-31-d
Describe the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) framework, including the qualitative characteristics of financial statements, the required reporting elements, and the constraints and assumptions in preparing financial statements.Timeliness is a constraint in the IFRS Framework. Neutrality is a factor that contributes to reliability and going concern is an assumption of the Framework.
“Understanding The Income Statement”, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA 2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, pp. 141, 166
Study Session 8-32-a, f
Describe the components of the income statement and construct an income statement using the alternative presentation formats of that statement.Discuss the financial reporting treatment and analysis of nonrecurring items (including discontinued operations, extraordinary items, and unusual or infrequent items), and changes in accounting standards.
“Understanding the Balance Sheet,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, pp. 201-203
Study Session 8-33-b
Describe the various formats of balance sheet presentation.Under IAS No. 1 liquidity-based presentation is recommended when it provides information that is more relevant and reliable than the current/noncurrent format, such as in the case of banks and financial institutions.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Understanding the Cash Flow Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, p. 254
Study Session 8-34-b
Describe how noncash investing and financing activities are reported.
|
||
|
$4,000 | |
| $0 | ||
|
$92,000 | |
|
$3,000 | |
“Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van
Greuning, CFA, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, pp. 43
Study Session: 7-30-b, c
Explain the accounting equation in its basic and expanded forms.
55.A company reported net income of $400,000 for the year. At the end of the year, the company had an unrealized gain of $50,000 on its available-for-sale securities, an unrealized gain of $40,000 on held-to-maturity securities and an unrealized loss of $100,000 on its portfolio of held-for-trading securities. The company’s comprehensive income (in $) for the year is closest to:
Demonstrate the appropriate classifications and related accounting treatments for marketable and nonmarketable financial instruments held as assets or owed by the company as liabilities;
List and explain the components of owners’ equity;By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| % of Total Assets | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Industry 1 | Industry 2 | Industry 3 | |
| 6.9 | 2.6 | 19.4 | |
|
1.9 | 57.5 | 25.4 |
|
18.2 | 31.9 | 19.1 |
| 19.5 = Property, plan |
23.2 t and equipment |
42.3 | |
C.Industry 1 is the consumer discretionary products industry and Industry 3 is the financial industry.
Answer: B
57.Due to global oversupply in the micro-chip industry a company wrote down its
2009 inventory by €4.0 million from €12.0 million. The following year, due to a change in competitive forces in the industry the market price of these chips rose sharply to 10% above their original 2009 value. If the company prepares its financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), its 2010 inventory (in €-millions) will most likely be reported as:
Identify and explain the major international accounting standards for each asset and liability category on the balance sheet and the key differences from U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
Although IFRS does require write-downs, it also allows revaluations, but not to exceed the original value, i.e., 12. The exception to this, where gains are allowed, is in producers of agricultural, forest and resource products.
A.6.4.
B.7.0.
Alternatively, ROE = Return on Total Assets x Total Assets/Equity = 11.2 x 1/0.625 = 17.9%
59.A capital lease requires annual lease payments of $2,000 at the start of each year.
“Long-term Liabilities and Leases,” Elizabeth A. Gordon and R. Elaine Henry, CFA
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, pp. 537-539
Study Session 9-39-gBy accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Year | Starting Balance |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10,000 | 0 | 2,000 | 2,000 | 8,000 |
| 2 | 8,000 | 960 |
60.Two software companies that report their financial statements under U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) are identical except as to how soon they judge a project to be technologically feasible. One firm does so very early in the development cycle while the other usually waits until just before the project is released to manufacturing. Compared to the company that judges technological feasibility early, the one that waits until closer to manufacturing will most likely report lower:
“Long-Lived Assets,” R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Elizabeth Gordon
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, pp. 418-422, 427-431
Study Session 9-37-b, c
Compute and describe the effects of capitalizing versus expensing on net income, shareholders’ equity, cash flow from operations, and financial ratios including the effect on the interest coverage ratio of capitalizing interest costs.Explain the circumstances in which software development costs and research and development costs are capitalized.
Answer: A
“Inventories,” Elbie Antonites, CFA and Michael Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, pp. 379-380
Study Session 9-36-a
Explain IFRS and U.S. GAAP rules for determining inventory cost including which costs are capitalized and methods of allocating costs between costs of goods sold and inventory.
| $ millions | |
|---|---|
| 2.25 | |
| 6.00 | |
| 4.00 | |
|
1.00 |
|
13.25 |
B.13.8 impairment loss in the income statement
C.7.4 reduction in the balance sheet carrying amount.Answer: B
A.reduction in tax rates.
B.decrease in interest rates.
Discuss the valuation allowance for deferred tax assets - when it is required and what impact it has on financial statements.
Under U.S. GAAP, deferred tax assets must be assessed at each balance sheet date. If there is any doubt whether the deferral will be recovered, the carrying amount should be reduced to the expected recoverable amount. The asset is reduced by increasing the valuation allowance. Should circumstances change, so that it is more probable that the deferred tax benefits will be recovered, the deferred asset account will be increased (and the valuation allowance decreased). An increase in the carry forward period for tax losses extends the possibility that benefits will be realized from the deferred tax asset and would likely result in a decrease in the valuation allowance and an increase in the deferred tax asset.
“Understanding the Balance Sheet,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level 1 Vol. 3 p.226
"Long-term Liabilities and Leases,” Elizabeth Gordon and R. Elaine Henry, CFA 2010 Modular Level 1 Vol. 3 pp. 532-535
Study Session 8-33-g, 9-39-c,List and explain the components of owners’ equity.
65.A pharmaceutical company has been very successful for the past several years, increasing its sales many-fold over that of its competition. It has been able to meet or beat analysts’ optimistic quarterly earnings estimates and consistently registers
very high sales towards the end of each quarter. Most of the company’s sales are to two of its major wholesalers. The firm covers the carrying costs for these two wholesalers and guarantees them a return on investment until the wholesalers sell the products.
“Financial Reporting Quality: Red Flags and Accounting Warning Signs,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA and Paul Munter
2010 Modular Level 1, Vol. 3, pp. 574-580
Study Session 8-32-b, 10-40-e
Explain the general principles of revenue recognition and accrual accounting, demonstrate specific revenue recognition applications (including accounting for long-term contracts, installment sales, barter transactions, and gross and net reporting of revenue), and discuss the implications of revenue recognition principles for financial analysis.Describe common accounting warning signs and methods of detecting each.
Answer: A
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.No effect
B.A decrease
C.An increaseAnswer: C
B.Accelerating sales from later periods into the present quarter.
C.Classifying financing cash flows as operating cash flows to increase operating cash flows.
Enron classified financing cash flows as operating cash flows.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: A
“Capital Budgeting,” John D. Stowe, CFA and Jacques R. Gagné, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, p. 9
Study Session 11-44-b
Discuss the basic principles of capital budgeting, including the choice of the proper cash flows.
A.and cash conversion cycle are both longer.
B.is longer, but its cash conversion cycle is shorter. C.is shorter, but its cash conversion cycle is longer.
Parkinson, and
Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 95-101
Study Session 8-35-d, 11-46-b, c
Calculate, classify, and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability and valuation ratios.Compare a company’s liquidity measures with those of peer companies.
| Company | Industry | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| 65 + 87 = 152 Longer |
|
|
|
152-28 = 124 Longer |
| $426 | |
|
$0 |
|
-$185 |
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, CFA, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 40-41
Study Session 11-44-d, 11-45-a
Calculate and interpret the results using each of the following methods to evaluate a single capital project: net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), payback period, discounted payback period, and profitability index (PI).Calculate and interpret the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of a company.
B.lower for Project 1 than for Project 2.
C.greater for Project 1 than for Project 2.Answer: B
Using the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) approach, the cost of equity (%) for the company is closest to:
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, CFA, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, p. 52
Study Session 11-45-h
Calculate and interpret the cost of equity capital using the capital asset pricing model approach, the dividend discount model approach, and the bond-yield-plus risk-premium approach.The cost of equity using the CAPM = Risk Free Rate + Beta x Market Equity Risk Premium= 3.5 + 1.6 x (6.0) = 13.1%.
Parkinson, and
Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, p. 102-104
Study Session 11-46-d
Identify and evaluate the necessary tools to use in managing a company’s net daily cash position.Simple projections are used to forecast short-term needs. Projection models and averages are normally used to forecast medium term cash flow needs. Statistical models are normally used to forecast long term needs, not short term cash flow needs.
Answer: B
“Capital Budgeting,” John D. Stowe, CFA and Jacques R Gagné, CFA
76.An investment fund owns 8 percent of the outstanding voting shares of a public company. There are several larger voting blocks of shares such that the
investment fund is not assured of being able to elect representation on the board of directors. Which type of shareholder voting right would be most beneficial in allowing the investment fund to ensure their interests are represented on the board?A.Proxy
B.Cumulative
C.ConfidentialBy accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
77.Information about the 2009 actual results for a company and its projected sales, cost of goods sold and assets for 2010 are presented below:
| All figures in ₤-000s | ||
|---|---|---|
| 2009 actual | 2010 projected | |
| 9,000 | 9,900 | |
| Cost of goods sold | 3,000 | 3,450 |
| 4,500 | 4,725 | |
| 1,800 | ||
| Current liabilities | 1,200 | |
A.1,890.
B.1,980.
C.2,070.Answer: B
B.44.6.
C.109.0.
Cost of trade credit = {[ 1 + Discount/(1 – Discount)] (365/Days beyond discount period) } -1
= {1 + (0.02 ÷ (1 – 0.02)}(365 ÷ (30 -10)) – 1 = 44.6%By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
C.use trading rules for detecting the price movements that lead to new equilibrium prices.
Answer: B
B.cyclical company.
C.speculative company.
Differentiate between 1) a growth company and a growth stock, 2) a defensive company and a defensive stock, 3) a cyclical company and a cyclical stock, 4) a speculative company and a speculative stock and 5) a value stock and a growth stock.
Growth companies are characterized by above-average investment opportunities that yield rates of return greater than the firm’s required rate of return. They also retain a large portion of their earnings to fund the superior investment projects and hence they tend to have low dividend payout ratios.
Answer: C
“Organization and Functioning of Securities Markets,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA and Keith C. Brown, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 6-7
Study Session 13-52-a
Describe the characteristics of a well-functioning securities market.
“Introduction to Price Multiples,” John D. Stowe, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 200-202
Study Session 14-59-b
Calculate and interpret P/E, P/BV, P/S, and P/CF.To normalize the EPS, multiply the current book value per share with the average ROE for the most recent full cycle. Normalized P/E = current market price / normalized EPS.
“Security-Market Indexes,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA and Keith C. Brown, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 54-60
Study Session 13-53-bBy accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| $2.00 | |
|---|---|
|
5.10% |
|
60% |
| 1.50 | |
| 5.60% | |
| 4.20% | |
|
Using the dividend discount model the company’s price per share (in $) is closest to:
Brown, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 142-143
Study Session 12-51-e, 14-56-c
Calculate, using the SML, the expected return on a security and evaluate whether the security is overvalued, undervalued, or properly valued.Calculate and interpret the value of both a preferred stock and a common stock using the dividend discount model (DDM).
85.All else equal, a decrease in the expected rate of inflation will most likely result in a decrease in:
A.the real risk-free rate.
Brown, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 153-155
Study Session 14-56-e
Explain the components of an investor’s required rate of return (i.e., the real risk-free rate, the expected rate of inflation, and a risk premium) and discuss the risk factors to be assessed in determining an equity risk premium for use in estimating the required return for the investment in each country.The nominal risk-free rate of return includes both the real risk-free rate of return and the expected rate of inflation. A decrease in inflation expectations would decrease the nominal risk-free rate of return, but would have no effect on the real risk-free rate of return.
“Organization and Functioning of Securities Markets,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA and Keith C. Brown, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 13-15
Study Session 13-52-c
Distinguish between call and continuous markets.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
C.adjust rapidly to the release of all public information; that is, security prices fully reflect all public information.
Answer: B
A.less than the company’s trailing P/E ratio. B.the same as the company’s trailing P/E ratio. C.greater than the company’s trailing P/E ratio.
Answer: A
The trailing P/E ratio is computed as the current stock price divided by the current or trailing 12-months’ EPS. On the other hand, the P/E ratio based on the infinite period dividend discount model is computed as (D/E) / (k – g).
If markets are in equilibrium, the price per share reflects the value determined by the constant growth dividend. Using the constant growth model the stock's value is ($2.40)(1.08) / 0.07 = $37.03;
The trailing P/E = 37.03 / 6 = 6.17. The DDM P/E is the dividend payout ratio divided by k-g = 0.4 / 0.07 = 5.71. Another way of computing DDM P/E is: Current Market Price/Expected 12-month earnings: 37.03/(6.00 x 1.08) = 5.71.“Organization and Functioning of Securities Markets,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA and Keith C. Brown, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 26-28
Study Session 13-52-g
Describe the process of buying a stock on margin, compute the rate of return on a margin transaction, define maintenance margin, and determine the stock price at which the investor would receive a margin call.Investor’s return = (Market value of the stock – Loan) / Investor’s Equity. Equity = 100 x 60 x 0.4 = $2,400; Loan = 100 x 60 x 0.6 = $3,600
Market value of the stock = (70 x 100) = $7,000;
| Company 1 | Company 2 | |
|---|---|---|
|
37.5% | 40.0% |
|
12% | 10.0% |
| 1.6 | 2.0 |
C.the same.
Answer: C
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Questions 91 through 96 relate to Derivative Investments.
Answer: B
“Swap Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 133-134
Study Session 17-71-a
Describe the characteristics of swap contracts and explain how swaps are terminated.“Option Markets and Contracts”, Don M. Chance
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 103-107
Study Session 17-70-i
Calculate and interpret the lowest prices of European and American calls and puts based on the rules for minimum values and lower bounds.The lower bound on a European call is either zero or the underlying asset’s price minus the present value of the exercise price, whichever is greater.
$1200 – ($1160 / 1.04 0.25) = $51.32.2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 7-10
Study Session 17-67-b
Define a forward commitment and a contingent claimA swap agreement is equivalent to a series of forward agreements, which are described as forward commitments.
“Swap Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp.140-144
Study Session 17-71-b
Define, calculate, and interpret the payment of currency swaps, plain vanilla interest rate swaps, and equity swaps.The company pays the swap dealer the fixed rate of 5.25%, pays the bank Libor of 4.75% (as set at the beginning of the period) plus .50% and receives Libor of 4.75% from the swap dealer.
B.$1.48.
C.$1.50.Answer: C
If no funds are withdrawn and margin calls are met at the beginning of the next day, the ending margin account balance on Day 3 for an investor with a short position of 10 contracts is closest to:
A.$70.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
At the end of Day 1, the balance in the investor’s account would be $20. At the beginning of Day 2, the investor would deposit $30.
A.Call protection.
B.Refunding protection.
C.Sinking fund protection.A.A conversion privilege.
B.A floor on a floating rate bond.
99.The most relevant definition for duration is:
A.a security’s price sensitivity to changes in yield.
“Introduction to the measurement of interest rate risk,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 542-543
Study Session 16-66-e
Distinguish among the alternative definitions of duration and explain why effective duration is the most appropriate measure of interest rate risk for bonds with embedded options.This is the most relevant definition because users of duration are interested in a
| Bond 1 | Bond 2 | Bond 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| $500,000 | $1,200,000 | $300,000 | |
| $580,000 | $1,100,000 | $320,000 | |
|
11.0% | 6.0% | 9.0% |
|
6.2 | 8.1 | 2.9 |
Study Session 16-66-f
Compute the duration of a portfolio, given the duration of the bonds comprising the portfolio, and explain the limitations of portfolio duration.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
101.Jasper Corporation sold its receivables to a special purpose vehicle, JTL
Corporation, created by Jasper for that purpose. If JTL sells securities backed by the receivables, the credit rating associated with those securities will most likely be based on the:“Overview of Bond Sectors and Instruments,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 336-338
Study Session 15-62-i
Define an asset-backed security, describe the role of a special purpose vehicle in an asset-backed security’s transaction, state the motivation for a corporation to issue an asset-backed security, and describe the types of external credit
enhancements for asset-backed securities.The rating of asset-backed securities typically is independent of the issuer or
“Introduction to the measurement of interest rate risk,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 545-547.
Study Session 16-66-g
103.An investor is considering the purchase of two bonds. One is a 5% coupon tax-exempt bond that yields 4.5% while the other is a 7% coupon bond that is taxable and yields 6.0%. If the two bonds are alike in all other characteristics, the marginal tax rate that would make the investor indifferent between the two bonds is closest to:
A.25.0%.
B.28.6%.
C.33.3%.A.putable bond and a callable bond.
B.zero-coupon bond and a Treasury strip.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
105.An analyst has gathered the following information:
| Year | 3-Year Treasury Rate | Treasury Spot Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.75% | 3.00% |
| 2 | 3.75% | 3.50% |
| 3 | 3.75% | 4.00% |
Explain the arbitrage-free valuation approach and the market process that forces the price of a bond toward its arbitrage-free value and explain how a dealer can generate an arbitrage profit if a bond is mispriced.
A.zero-coupon securities.
B.issued directly by the U.S. Treasury.
Describe how stripped Treasury securities are created and distinguish between coupon strips and principal strips.
Although the U.S. Treasury does not issue zero-coupon securities, it has created the STRIPS program through which securities that are stripped from the principal or interest payments of U.S. Treasury securities become direct obligations of the U.S. government.
Answer: C
“Overview of Bond Sectors and Instruments,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 321-323
Study Session 15-62-g
Describe the types of securities issued by municipalities in the United States and distinguish between tax-backed debt and revenue bonds.Answer: C
“Overview of Bond Sectors and Instruments,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 330-332
Study Session 15-62-h
Describe the characteristics and motivation for the various types of debt issued by corporations (including corporate bonds, medium-term notes, structured notes, commercial paper, negotiable CDs, and bankers acceptances.)109.Which classification of hedge funds is least likely to use a short position in stock as a part of its strategy?
A.Market-neutral funds.
110.When comparing investing in exchanged traded funds (ETFs) to investing in open-end mutual funds, which of these is most likelynot an advantage of ETFs?
ETFs:
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 195-197
Study Session 18-73-b,c
Distinguish among style, sector, index, global, and stable value strategies in equity investment and among exchange traded funds (ETFs), traditional mutual funds, and closed end funds.Explain the advantages and risks of ETFs.
| $1,800,000 | |
|---|---|
|
$1,200,000 |
|
6% |
| 90% | |
| 15% | |
| 5 years | |
| 25% |
Based on the income approach, the value of the investment is closest to:
A.$4,000,000.
B.$5,455,000.
C.$6,133,000.A.first-stage financing.
B.mezzanine financing.
C.second-stage financing.113.An analyst compared the performance of a hedge fund index with the
performance of a major stock index over the past eight years. She noted that the hedge fund index (created from a database) had a higher average return, higher standard deviation, and higher Sharpe ratio than the stock index. All the successful funds that have been in the hedge fund database continued to accept new money over the eight-year period. What biases do the risk and return measures in the database most likely have? Average return:A.and standard deviation are both overstated.
114.An analyst estimates that an initial investment of £500,000 in a venture capital project will pay £6 million at the end of five years if the project succeeds and that the probability the project survives to the end of the fifth year is 25 percent. The required rate of return for the project is 19 percent. The expected net present value of the venture capital investment is closest to:
A.£128,000.
The probability that the venture will pay 6 million at the end of five years is 25%.
The probability of failure is 75%. The expected NPV if the project succeeds is 2,014,296 using FV = 6,000,000, I = 19%, n = 5 for a present value of 2,514,296 – 500,000 = 2,014,296.
A.investing a portion of his capital in the risk-free asset and the balance in a fully diversified portfolio of all equities.
B.investing a portion of his capital in the risk-free asset and the balance in a fully diversified portfolio of all risky assets.
116.The least likely reason for constructing an investment policy statement is that it:
A.minimizes the costs of portfolio construction.
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 215-217
Study Session 12-49-a
Describe the steps in the portfolio management process and explain the reasons for a policy statement.A is correct. This is not a reason for constructing an investment policy statement. The two reasons are: 1) it helps investors create realistic investment goals, and 2) it identifies a benchmark portfolio that will be used to judge the performance of the portfolio manager.
The correlation coefficient between returns for the two common stocks is closest to:
A.0.025.
B.0.388.
C.0.465.
| r ij | j |
|
|||||
| 22 3. | = 4.722 | ||||||
|
.8 65 |
|
|||||
| .3 937 |  .4 722 .4 722 |
||||||
Answer: B
“An Introduction to Asset Pricing Models,” Frank K. Reilly and Keith C. Brown 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 272-276
Study Session 12-51-bA.total return.
B.current income.
120.The standard deviation of returns for shares of Oakmont Corporation and Sunrise Corporation are 14% and 12% respectively. If the correlation between the two stocks is 0.25, a portfolio consisting of 35% invested in Oakmont and 65% in Sunrise has a standard deviation closest to:
A.10.2%
B.12.7%
C.35.0%
Questions 1 through 18 relate to Ethical and Professional Standards.
1.Alexander Newton, CFA, is the chief compliance officer for Mills Investment Limited. Newton institutes a new policy requiring the pro rata distribution of new security issues to all established discretionary accounts for which the new issues are appropriate. The policy also provides for the distribution of new issues to newly established discretionary accounts where appropriate after their one-month anniversary date. This policy is disclosed to all existing and potential clients. Did Newton violate any CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 53-58
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.Standard III (B) Fair Dealing requires when making investments in new offerings, advance indications of interest should be obtained as well as, providing for a method for calculating allocations. Additionally, disclosure of inequitable allocation methods does not relieve a member from this obligation.
Answer: A
“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 69-71
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.A.No.
B.Yes, with respect to misrepresentation.
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 29-31, 80-82
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.Members are in compliance with CFA Institute’s Standard V (A) Diligence and Reasonable Basis, if they rely on the research of another party who exercised diligence and thoroughness. Because Bishop’s opinion did not agree with the final report, disassociating her from the report is one way to handle this difference between the analysts.
Introduction to the Global Investment Performance Standards (GIPS®) CFA Institute, 2006
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 131
Study Sessions 1-3-c
Explain the requirements for verification of compliance with GIPS standards.Verification tests (Standard V) whether the investment firm has complied with all the composite construction requirements of GIPS on a firm-wide basis, and whether the firm’s processes and procedures are designed to calculate and present performance results in compliance with the GIPS Standards. Verification must be performed by an independent third party. A firm cannot perform its own
verification.C.Additional Compensation Arrangements.
Answer: A
B.Professional misconduct.
C.Referencing Candidacy in the CFA Program.
7.Jeffrey Jones passed the Level I CFA examination in 1997 and the Level II examination in 2009. He is not currently enrolled for the Level III examination. According to the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct, which of the following is the most appropriate way for Jones to refer to his participation in the CFA Program?
A.Jeffrey Jones, CFA (expected 2011).
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
8.Rebecca Wong is enrolled to take the Level I CFA examination. Her friend William Leung had purchased Level I study materials from a well-known CFA review program the previous year. Leung made a photocopy of the previous year’s copyrighted materials and sold it to Wong to help her study. Who violated the CFA Institute Code of Ethics or any Standards of Professional Conduct?
“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 15-18
Study Session 1–2–a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.Photocopying copyrighted material, regardless of the year of publication, is a violation of the CFA Institute Standards (Standard I (A)) as copyrighted materials are protected by law. Candidates and members must comply with all applicable laws, rules, and regulations and must not knowingly participate or assist in a violation of laws.
C.violated both Misconduct and Integrity of Capital Markets Standards.
Answer: B
professional reputation, integrity, or competence. Bennett’s actions violated the Code of Ethics and the Standard relating to Professionalism but not the Standard relating to Integrity of Capital Markets.
10.Albert Nyakenda, CFA, was driving to a client’s office where he was expected to close a multi-million dollar deal, when he was pulled over by a traffic policeman When Nyakenda, realized the policeman planned to wrongly ticket him for speeding, he offered to buy him “lunch” so that he could quickly get to his client’s office. The alternative was to go to the police station and file a complaint of being wrongly accused that would also involve going to court the next day to present his case. The lunch would cost significantly more than the ticket. Did Nyakenda violate the CFA Code of Ethics?
“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 11
Study Session 1–2–a, b
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.
A.a sampling of the suitability of North America for clients.
B.a due diligence exercise on Mark Carlson and Carlson Consulting. C.the due diligence exercise on the top ten asset managers herself.
12.Reiko Kimisaki, CFA, is an investment advisor for a national social security fund in a frontier market with a very limited and illiquid capital market and a very young labor force with an investment time horizon of 25 – 30 years. She has been asked to suggest ways to increase the investment return of the overall portfolio.
After careful assessment of the Fund’s previous investment history, and available
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 60 - 62
Study Session 1–2–c
Recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional ConductB.If she does not breach the confidentiality of names of staff.
C.If the discussed changes are unlikely to affect the public perception of the bank.
The information overheard would not be considered material only if the staff likely to be terminated were not considered to be in influential positions such that any public announcement of their removal would be unlikely to move the share
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: B
“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 48 – 50, 75, 80 - 81
Study Session 1–2–a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.A.Yes.
B.No, because her responsibilities do not apply.
Distinguish between conduct that conforms to the Code and Standards and conduct that violates the Code and Standards.
A supervisor’s responsibilities relate to detecting and preventing violations by anyone subject to their supervision or authority regarding activities they
supervise. Ndenda had no way of detecting and/or preventing Rutabingwa from cheating during the CFA exam, an event she did not attend.Answer: C
“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 30
Study Session 1–2–a, b
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.A.No.
B.Yes, because returns are lower than expected by the Partners. C.Yes, because he did not disclose the increased costs to his Partners.
18.A Central Bank fines a commercial bank for not following statutory regulations with regard to making specific non-performing loan provisions on three loans. Louis Marie Buffet, CFA, sits on the Board of Directors of the Commercial Bank as a non-executive director, representing minority shareholders. He also chairs the internal audit committee of the bank that determines the provisioning policy of
the bank. Mercy Gatabaki, CFA is the bank’s external auditor and follows international auditing standards whereby she tests the loan portfolio by randomly selecting loans to check for compliance in all aspects of Central Bank regulations.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: B
19.An increase in which of the following items is most likely to result in a wider confidence interval for the population mean?
A.Sample size
B.Reliability factor
C.Degrees of freedom
| Joint Probability Function of Security A and Security B Returns |
|---|
| (Entries are joint probabilities) |
|---|
|
A. 3.
B.12.
C.24.Answer: B
= 0.6(2 × 4) + 0.4(−3 × −6) = 0.6(8) +0.4(18) = 4.8 + 7.2 = 12.
21.An analyst determines that approximately 99 percent of the observations of daily sales for a company are within the interval from $230,000 to $480,000 and that daily sales for the company are normally distributed. The standard deviation of daily sales (in $) for the company is closest to:
Given that sales are normally distributed, the mean is centered in the interval. Mean = ($230,000 + 480,000) / 2 = $355,000. 99 percent of observations under a normal distribution will be plus/minus three standard deviations. Thus, ($355,000 - $230,000)/3.0 = $41,667. It is also the case that ($480,000 - $355,000)/3.0 = $41,667.
22.The least accurate statement about measures of dispersion for a distribution is that the:
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W.
McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 307-308
Study Session 2-7-g
Define, calculate, and interpret 1) a range and mean absolute deviation, and 2) the variance and standard deviation of a population and of a sample.
Answer: C
“Discounted Cash Flow Applications,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W.
of the subpopulations she has created. For the manager’s sample, which of the following best describes the sampling approach?
A.Systematic
B.Simple random
C.Stratified random
|
2.8092 |
|---|---|
| Critical value at the 0.05 significance level | 1.96 |
| Critical value at the 0.01 significance level | 2.58 |
The analyst most likely conducted a:
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Study Session 3-11-a, c
Define a hypothesis, describe the steps of hypothesis testing, interpret and discuss the choice of the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis, and distinguish between one-tailed and two-tailed tests of hypotheses.B.close to one.
C.close to zero.Answer: C
Answer: B
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 270
Study Session 2-7-aA.geometric mean return.
B.time-weighted rate of return.
C.money-weighted rate of return.29.A 180-day U.S. Treasury bill has a holding period yield (HPY) of 2.375%. The bank discount yield (in %) is closest to:
A.4.640.
B.4.750.
C.4.875.Convert among holding period yields, money market yields, effective annual yields, and bond equivalent yields.
First, use the HPY to find money market yield: rMM = (HPY) ×(360/t) = .02375 × (360 / 180) = 0.0475. Then use the money market yield to find the bond discount yield: rMM= (360 rBD) / ((360 – (t)( rBD)). In this case: 0.0475 = (360 rBD) / ((360 – (180)( rBD)). Now solve for rBD.
A.0.000360.
B.0.003855.
C.0.005140.Answer: C
Using the binomial probability function,
, the
probability (in %) that exactly 6 of the 10 firms in the sample hold hedge funds is closest to:
McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 428
Study Session 3-9-f
Calculate and interpret probabilities given the discrete uniform and the binomial distribution functions.The number of trials is 10, the number of success is 6, and the probability of success is 0.60.
McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 435-439
Study Session 3-9-h
Describe the continuous uniform distribution, and calculate and interpret probabilities, given a continuous uniform probability distribution.
|
|---|
Questions 33 through 44 relate to Economics
33.For a firm in perfect competition, as the quantity of labor increases, the marginal revenue product most likely diminishes because of a decline in:
“Markets for Factors of Production,” Michael Parkin
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, p. 268
Study Session 5-21-a
Explain why demand for the factors of production is called derived demand, differentiate between marginal revenue and marginal revenue product (MRP), and describe how the MRP determines the demand for labor and the wage rate.For a firm in perfect competition, as quantity of labor increases, marginal revenue product diminishes because marginal product diminishes.
Answer: A
“Elasticity,” Michael Parkin
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, p.14
Study Session 4-13-b
Calculate elasticities on a straight-line demand curve, differentiate among elastic, inelastic, and unit elastic demand, and describe the relation between price elasticity of demand and total revenue.Answer: C
“Monitoring Jobs and the Price Level,” Michael Parkin
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, p. 313
Study Session 5-22-c
Explain the types of unemployment, full employment, the natural rate of unemployment, and the relation between unemployment and real GDP.C.subsidies and quotas.
Answer: B
B.government borrowing.
C.government expenditures.Answer: A
A.a price increase and the seller pays the entire tax. B.a price increase and the buyer pays the entire tax. C.no change in price and the seller pays the entire tax.
Answer: B
B.inelastic.
C.perfectly elastic.
40.In perfectly competitive industries what is the most likely final long-run effect of a permanent decrease in demand?
A.Price decreases.
A permanent decrease in demand in a perfectly competitive industry will, in the short-run, cause the demand curve to shift to the left causing prices to fall and creating losses for producers. As the fall in demand is permanent, eventually firms will leave the industry due to these economic losses. As firms leave the industry the supply curve moves to the right thus increasing prices back to an equilibrium where economic profit is zero.
41.If a regulatory agency sets prices equal to a monopoly’s long-run average cost (LRAC), the monopoly will most likely have economic profit that is:
If regulators set the price to equal long-run average cost, the monopolist will earn zero economic profits (Figure 11, p. 210).
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: B
"Markets in Action” Michael Parkin
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, p. 71-72
Study Session 4-15-a
Explain market equilibrium, distinguish between long-term and short-term effects of outside shocks, and describe the effects of rent ceilings on the existence of black markets in the housing sector and on the market’s efficiency.
The inflation rate (in %) for the period is closest to:
A.2.35.
B.2.38.
C.2.41.44.The quantity theory of money is best described as the proposition that, in the long run, an increase in the quantity of money brings a percentage increase in the price level that is:
A.equal.
B.lower.
C.higher.Questions 45 through 68 relate to Financial Statement Analysis
45.According to the International Financial Reporting Standards framework, which of the following qualities of financial information is least likely to improve its reliability?
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 107-108
Study Session 7-31-d
Describe the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) framework, including the qualitative characteristics of financial statements, the required reporting elements, and the constraints and assumptions in preparing financial statements.The IFRS framework identifies five factors that contribute to reliability: faithful representation, substance over form, neutrality, prudence and completeness. Consistency is not one of them.
| Year ended 31 December | 2009 | 2008 |
|---|---|---|
| 322.8 | 320.1 | |
| 27.2 | 26.8 | |
| Cash flow from operations | 15.3 | 38.1 |
A. proportion of sales made on a cash basis.
B. inventory, anticipating lower demand for its products in 2010. C. proportion of interest-bearing debt relative to trade accounts payable.
47.According to International Financial Reporting Standards which of the following is one of the conditions that must be met for revenue recognition to occur?
A.Costs can be reliably measured
B.Payment has been partially received
C.Goods have been delivered to the customerBy accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
48.A company accrued wages of $2,000 and collected accounts receivable of $10,000. Which of the following best describes the effect of these two transactions on the company?
“Financial Analysis Techniques”, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 328-329
Study Session 8-34-g, 8-35-d
Analyze and interpret a cash flow statement using both total currency amounts and common-size cash flow statements.B.200,000 for the stock split and 150,000 for the stock dividend. C.150,000 for the stock split and 200,000 for the stock dividend.
Answer: A
50.Under International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) the preparation of a complete set of financial statements is best described as a(n):
A.objective of financial reporting.
51.Which of the following transactions will mostlikely result in a decrease in a company’s current ratio? The:
A.recording of a warranty expense.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 160
The recording of a warranty expense will create a warranty liability and the resulting increase in current liabilities will decrease the current ratio.
52.A company issued bonds in 2009 that mature in 2019. The measurement basis that will most likely be used on the 2009 balance sheet for the bonds is:
Demonstrate the appropriate classifications and related accounting treatments for marketable and non-marketable financial instruments held as assets or owed by the company as liabilities.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Accounting Shenanigans on the Cash Flow Statement,” Marc A. Siegel 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 592-595
Study Session 10-41
The candidate should be able to analyze and discuss the following ways to manipulate the cash flow statement:
stretching out payables
B.the discounted value of the future cash flows that are required to satisfy the obligation.
C.the undiscounted amount of cash or cash equivalents expected to be paid to satisfy the obligation.
The settlement value for a liability is the undiscounted amount of cash or cash equivalents expected to be paid to satisfy the liabilities in the normal course of business.
55.A company has just completed the sale of a tract of land for €3.5 million which was originally acquired at a cost of €2.0 million. The purchaser made a down-
“Understanding the Income Statement”, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp.150-152
Study Session: 8-32-b
Explain the general principles of revenue recognition and accrual accounting, demonstrate specific revenue recognition applications (including accounting for long-term contracts, installment sales, barter transactions, and gross and net reporting of revenue), and discuss the implications of revenue recognition principles for financial analysis;Under the installment method, the portion of the total profit of the sale (3.5 – 2.0 = 1.5) that is recognized in each period is determined by the percentage of the total sales price for which the seller has received cash, which is €1.5/€3.5 x
Which of the companies most likely prepares their financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles)?
A.Both
B.Company A only
C.Company B onlyCompany A prepares its financial statements under IFRS while company B uses U.S. GAAP. The common practice under IFRS presentation is to present noncurrent assets before current assets and long term liabilities before current ones. Minority interest must be shown as a component of equity under IFRS.
Under U.S. GAAP, current assets are presented before long term assets and current liabilities before long term ones; under U.S. GAAP, minority interest is often shown “in-between” liabilities and equity (although it could also be shown as an equity component).
The adjustments to convert operating leases into capital leases would increase the amount of total debt in the debt-equity ratio thus increasing the ratio; the portion of the lease payment estimated to be lease interest expense would lower the interest coverage ratio.
58.To gain insight into what portion of a company’s assets is liquid, an analyst will most likely use:
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Financial Analysis Techniques”, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
59.An analyst gathers the following information ($ millions) about three companies operating in the same industry:
| Company 1 |
|
Accumulated Depreciation |
|---|---|---|
| 58.9 | ||
| 2 | 27.8 | 80.3 |
| 3 | 33.6 | 128.8 |
Discuss the use of fixed asset disclosures to compare companies’ average age of depreciable assets, and calculate, using such disclosures, the average age and average depreciable life of fixed assets.
| 2 | |
|---|---|
| 3 | |
|
|
60.The following information (U.S. $ millions) for two companies operating in the same industry during the same time period is available:
B.higher total asset turnover.
C.lower financial leverage multiplier.
| The DuPont system can be used to break down the ROE into three components: ROE = Profit margin x total asset turnover x financial leverage multiplier. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Company A | Company B | ||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|||
“Inventories,” Elbie Antonites, CFA and Michael Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 380-381
“International Standards Convergence,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 653-654
Discuss how inventories are reported in the financial statements and how the lower of cost or net realizable value is used and applied.Study Session 9-36-b, 10-43-a
Discuss how inventories are reported in the financial statements and how the lower of cost or net realizable value is used and applied.
| First Year | Second Year | |
|---|---|---|
|
80,000 | 100,000 |
|
$8.43 | $12.25 |
| 73,000 | 78,000 | |
| Unit Selling Price | $15.00 | $16.00 |
“Inventories,” Elbie Antonites, CFA and Michael Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 382-384
Study Session 9-36-c
Compute ending inventory balances and cost of goods sold using the FIFO, weighted average cost, and LIFO methods to account for product inventory and explain the relationship among and the usefulness of inventory and cost of goods sold data provided by the FIFO, weighted average cost, and LIFO methods when prices are 1) stable, 2) decreasing, or 3) increasing.The company is accounting for its inventory using the weighted average cost method.
B.348.
C.2,178.
| (£ millions) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 2008 | |
| 2,801 | 2,885 | |
| 1,969 | 2,071 | |
|
123 | 110 |
| Cash & Marketable Securities | 108 | 105 |
|
318 | 286 |
| 248 | 285 | |
| 361 | 346 | |
| 50 | 99 | |
A.23.
B.26.
C.28.Answer: A
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| 365/Receivables Turnover | 365/9.27 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| COGS/Average Payables 365/Payables Turnover |
|
||
|
DOH + DSO – Days In Pay | 49.4 + 39.4 – 65.5 |
C.higher five year average of its coefficient of variation of its operating margin.
Answer: B
Describe the role of financial statement analysis in assessing the credit quality of a potential debt investment.
A lower dividend means more retention and increased equity: higher retained cash flow will result in a higher credit rating
On January 15, 2010 the government lowered the corporate tax rate to 25 percent for 2010 and beyond. The deferred tax liability (€) as at 31 December 2010 is closest to:
67.Which of the following is least likely a condition present in a “fraud triangle”?
A.Constraining debt covenants.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Describe the “fraud triangle”.
B.cash from operating activities.
C.cash from financing activities.Answer: C
financing of payables, securitization of receivables, and using stock buybacks to offset dilution of earnings
The amount spent to buy back stocks to offset dilution is classified as a financing activity on the cash flow statement and therefore cash from financing decreases.
A.2.6.
B.3.9.
C.5.2.Answer: C
70.The post-audit performed as part of the capital budgeting process is least likely to:
“Capital Budgeting,” John D. Stowe, CFA and Jacques R. Gagné, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 6-7
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.$400,000.
B.$600,000.
C.$800,000.Answer: C
B.has the more appropriate reinvestment rate assumption. C.uses more accurate estimates of the project’s cash flows.
Answer: A
|
3.0% |
|---|---|
|
3.5% |
| 6.0% | |
| 8.0% | |
|
4.0% |
|
35% |
The cost of equity using bond-yield-plus-risk-premium approach is to take the before-tax cost of debt plus the risk premium of equity over debt. The before-tax cost of debt is the after-tax cost of debt divided by (1- tax rate). 8.0/(1 – 0.35) = 12.3%.
Adding the risk premium results in a cost of equity of 12.3% + 4% = 16.3%.
Each member is elected for a two-year term and one-half of the positions stand for election every year. The three members of the Audit Committee are all outside directors and have relevant financial experience. The Remuneration Committee is composed of the Chairman and two outside directors. Which of the following actions would provide the greatest improvement in the corporate governance of this company?
A.The Chairman of the Board should be an independent director.
75.Which of the following methods would be least likely to improve the cash collections of a retail organization?
A.Lockbox
B.Debit cards
C.Electronic checksIdentify and evaluate the necessary tools to use in managing a company’s net daily cash position.
A lockbox is a deposit system coordinated with a bank and is useful when the customer is not paying at the time of sale. In retail organizations, the customer normally pays at the time of sale and the best ways to improve cash collections are to ensure the payments made at that time have no credit risk for the seller. Debit cards, credit cards and electronic checks eliminate the credit risk for the seller.
Answer: C
“Financial Statement Analysis,” Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol.4, pp. 151-159
Study Session 11-47
The candidate should be able to demonstrate the use of pro forma income and balance sheet statements.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, CFA, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol.4, pp. 65-66
Study Session 11-45-j
Explain the country equity risk premium in the estimation of the cost of equity for a company located in a developing market.B.decrease in their operating cycle.
C.decrease in their net operating cycle.Answer: C
A four day increase in payables will reduce the cash conversion cycle (net operating cycle) by four days.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Introduction to Price Multiples,” John D. Stowe, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 215-217
Study Session 14-59-a
Discuss the rationales for, and the possible drawbacks to, the use of price-to-earnings (P/E), price-to-book value (P/BV), price-to-sales (P/S), and price-to-cash flow (P/CF) in equity valuation.Using price-to-cash flow rather than price-to-earnings addresses the issue of differences in accounting conservatism between companies (differences in quality of earnings).
Answer: C
“Organization and Functioning of Securities Markets,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA and Keith C. Brown, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 14-15
Study Session 13-52-c
Distinguish between call and continuous markets.Answer: A
“Market Efficiency and Anomalies,” Vijay Singal, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 107-109
Study Session 13-55-a
Explain the three limitations to achieving fully efficient markets.
If stock Z completes a three-for-one stock split at the end of Day 1, the value of the index after the split (at the end of Day 3) is closest to:
A.29.9.
B.31.7.
C.32.3.Index before the split = (10 + 20 + 60) / 3 = 30; New divisor: [(10 + 20 + 20) / X] = 30; X = 1.67
Index after the split = (12 + 19 + 22) / 1.67 = 31.7
| 8.0% | |
|---|---|
| 10.0% | |
| 2.5 | |
|
1.5 |
|
10.0% |
| 5.0% |
Answer: B
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 342-347By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
ROE = ROA x Financial leverage; Retention ratio = growth rate / ROE; Payout ratio = 1 – Retention ratio
ROE = (10.0%)(2.5) = 25%; Retention ratio = 0.15/0.25 = 0.60;
Payout ratio = 1 – 0.60 = 40.0%
B.cyclical stock.
C.speculative stock.
Brown, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 176-178
Study Session 14-56-c, f; 14-58-a
Calculate and interpret the value of both a preferred stock and a common stock using the dividend discount model (DDM).Estimate the dividend growth rate, given the components of the required rate of return incorporating the earnings retention rate and current stock price.
85.An investor opens a margin account with an initial deposit of $5,000. He then purchases 300 shares of a stock at $30. His margin account has a maintenance margin requirement of 30%. Ignoring commissions and interest, the price (in $) at which the investor receives a margin call is closest to:
A.19.05.
B.23.08.
C.23.81.86.The following information is from a company’s most recent financial statements:
| U.S. $ in millions except for shares outstanding and tax rate | |
|---|---|
|
40 |
| 120 | |
| 30 | |
| 190 | |
| (55) | |
|
325 |
|
|
| 40% | |
Answer: C
“Inventories,” Elbie Antonites, CFA and Michael Broihahn, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 396-402
Adj. price to book value ratio = $59 / $31.20 = 1.89.
87.An investor gathers the following data for a company:
The company’s estimated dividend growth rate (in %) is closest to:
“An Introduction to Security Valuation,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA and Keith C.
Brown, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 158-159
Study Session 10-35-e, f; 14-56-f
Demonstrate how ratios are related and how to evaluate a company using a combination of different ratios.ROE = 2 x 2.5 x 2.5 = 12.5%
Retention rate = 1 – ($2 million / $10 million) = 80%; Growth rate = 12.5% x 80% = 10%.88.A company’s $100 par perpetual preferred stock has a dividend rate of 7 percent and a required rate of return of 11 percent. The company’s earnings are expected to grow at a constant rate of 3 percent per year. If the market price per share for the preferred stock is $75, the preferred stock is most appropriately described as being:
Value of perpetual preferred stock = Dividend / Investor’s required rate of return $7/ 0.11 = $63.64. The stock is overvalued by $75.00 – 63.64 = $11.36.
89.An equity analyst working for a growth oriented mutual fund has a tendency to misvalue the stocks of popular companies that she has previously recommended and the fund already owns. Her behavior is most likely consistent with which of the following biases?
Confirmation bias refers to the bias of looking for information that supports prior opinions and decisions, which leads to a tendency to misvalue the stocks of generally popular companies.
90.A company earned $3 a share last year and just paid a dividend of $2 a share. The
Brown, CFA
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 138-141
Study Session 14-56-c
Calculate and interpret the value of both a preferred stock, and a common stock, using the dividend discount model (DDM).V = D1 / (1 + k) + D2 / (1 + k)2 + SP2 / (1 + k)2
The value of the stock:
| 2 ($ .1 08 ) | 2 | $ 75 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .1( 11 ) | .1( 11 ) 2 | .1( 11 ) | 2 |
91.When the underlying stock price is $95, an investor pays $2 for a call option with an exercise price of $95. If the stock price moves to $96, the intrinsic value of the call option would be closest to:
A.-$1.
B.$0.
C.$1.A.loan to the futures trader.
B.requirement set by federal regulators.
C.down payment from the futures trader.93.A derivative is most accurately defined as a financial instrument that provides:
A.a return based on the return of another asset.
This is the definition directly out of the readings. Its return is derived from another underlying asset.
94.An investor enters into a 1 X 3 forward rate agreement (FRA) at a LIBOR rate of 1.5 percent. At expiration, the 60-day LIBOR rate is 1.7 percent and the 90-day LIBOR rate is 1.6 percent. Assuming the contract covers a $1 million notional principal, what payment will the investor most likely receive?
A is incorrect because it uses a 90-
day term: $1 million [(.016-.015)(90/360)/1+.016(90/360)] = $249.00
B.publicized.
C.customized.Answer: C
B.It is based on a notional principal amount.
C.It is paid immediately when the contract expires.
Questions 97 through 108 relate to Fixed Income Investments.
97.An analyst determines that a 5.50 percent coupon option-free bond, maturing in 7 years, would experience a 3 percent decrease in price if market interest rates rise by 50 basis points. If market interest rates instead fall by 50 basis points, the bond’s price would increase by:
The bond is option-free and will therefore exhibit positive convexity. An equal change in rates will produce a greater percentage gain when rates decrease than the percentage loss produced when rates increase.
98.Holding all other factors constant, an increase in expected yield volatility will cause the price of a:
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
99.The table below summarizes the yields and corresponding prices for a hypothetical 15-year option-free bond that is initially priced to yield 7%:
“Introduction to the Measurement of Interest Rate Risk,” Frank J. Fabozzi 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 532-533
Study Session 16-66-d
Compute and interpret the effective duration of a bond, given information about how the bond's price will increase and decrease for given changes in interest rates, and compute the approximate percentage price change for a bond, given the bond's effective duration and a specified change in yield.
|
100 . 9254 |  99 . 0861 99 . 0861 |
2.9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 ( 100 )( .0 001 ) | ||||
“Understanding Yield Spreads,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, p. 367
Study Session 15-63-c
Explain the basic theories of the term structure of interest rates and describe the implications of each theory for the shape of the yield curve.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Introduction to the Valuation of Debt Securities,” Frank J. Fabozzi 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 404-406.
Study Session 16-64-c, d
Compute the value of a bond and the change in value that is attributable to a change in the discount rate;
Explain how the price of a bond changes as the bond approaches its maturity date, and compute the change in value that is attributable to the passage of time.A.$280,000.
B.$287,000.
C.$700,000.Answer: B
A.a zero-coupon bond.
B.a coupon bond selling at a discount to par.
104.If investors expect stable rates of inflation in the future, the pure expectations theory suggests that the yield curve is currently:
A.flat.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
The pure expectations theory explains the term structure in terms of expected future short-term interest rates. Assuming that interest rates reflect a relatively stable real rate of interest plus a premium for expected inflation, stability in inflation expectations would mean unchanged future short-term interest rates and a flat yield curve.
“Risks Associated with Investing in Bonds,” Frank J. Fabozzi 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, p. 271-277,
Study Session 15-61-a
Explain the risks associated with investing in bonds.Volatility risk is the risk that the price of a bond with an embedded option will decline when expected yield volatility changes. By definition, option-free bonds are not affected by volatility risk.
B is correct since the yield-to-maturity measure assumes that the coupon payments can be reinvested at an interest rate equal to the yield-to-maturity, in this case 4%.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B is correct because the yield on an annual-pay basis is calculated as:
“Yield Measures, Spot Rates, and Forward Rates,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 468473
Study Session 16-65-e
Describe the methodology for computing the theoretical Treasury spot rate curve and compute the value of a bond using spot rates.A is correct because the cash flows should be discounted using the appropriate spot rate plus spread :
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Questions 109 through 114 relate to Alternative Investments.
Answer: C
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 202-206
Study Session 18-73-e
Describe the various approaches to the valuation of real estate.
The annual net operating income (NOI) for the apartment complex is closest to:
A.$116,000.
B.$121,000.
C.$137,000.NOI = $180,000 - $15,000 - $10,000 - $18,000 = $137,000.
111.Hedge funds that contain infrequently traded assets would most likely exhibit a downward bias with respect to:
112.When the spot price of a commodity is above the futures price, the commodity market is said to be in:
A.contango.
C is correct because when a commodity market is in backwardation, the futures prices is below the spot price as market participants believe the spot price will be
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: C
“Investing in Commodities,” Ronald G. Layard-Liesching
2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 268-269
Study Session 18-74-b
Describe the sources of return and risk for a commodity investment and the effect on a portfolio of adding an allocation to commodities.C.negative incentive fee.
Answer: C
Questions 115 through 120 relate to Portfolio Management.
115.Factors such as fluctuations in interest rates and changes in industrial production contribute to:
“An Introduction to Asset Pricing Models,” Frank K. Reilly and Keith C. Brown 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 273-275
Study Session 12-51-c
Define systematic and unsystematic risk and explain why an investor should not expect to receive additional return for assuming unsystematic risk.A is correct. Systematic (market-related) risk is caused by macroeconomic variables such as interest rate volatility and variability in industrial production. Unsystematic risk is caused by company-specific attributes.
Answer: B
“The Asset Allocation Decision”, Frank K. Reilly and Keith C. Brown 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 230-232
Study Session 12-49-eA.plot on a flatter line.
B.plot on a steeper line.
118.Which of the following is not an assumption of the Markowitz model? Investors:
A.have homogeneous expectations.
A is correct. This is not an assumption of the Markowitz model, it is an assumption of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM).
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Probability | Rate of Return (%) |
|---|---|
| 0.15 | -12 |
| 0.60 | 11 |
| 0.25 | 18 |
“An Introduction to Portfolio Management,” Frank K. Reilly and Keith C. Brown 2010 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp.242-244
Study Session 12-50-c
Compute and interpret the expected return, variance, and standard deviation for an individual investment and the expected return and standard deviation for a portfolio.C is correct. The table below provides the calculation of the variance
| Bonds | Stocks | |
|---|---|---|
|
55-65% | 35-45% |
|
30-40% | 60-70% |
| 15-50% | 50-85% |
Describe the investment constraints of liquidity, time horizon, tax concerns, legal and regulatory factors, and unique needs and preferences.
A is correct. A moderately risk tolerant retired 65-year-old can structure his or her portfolio so that it provides income and some principal growth. The principal growth is needed because the time horizon is still fairly long. Such a portfolio could have an allocation of 55-65% in bonds and 35-45% in stocks.
A.rely on the integrity of input data.
B.consist of required provisions for firms to follow to achieve best practice.
2.According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, a member who is an investment manager is least likely to breach his duty to clients by:
A.disclosing confidential client information to the CFA Institute Professional Conduct Program.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
According to Standard III(A), members are allowed to use client brokerage to purchase goods or services that are used in the investment decision-making process as the manager is not collecting undisclosed soft commissions and hence the purchase of goods or services used in the investment decision-making process does not present a potential conflict of interest.
Answer: B
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 50-55, 94-95, 98 (Example 3)
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.B.increase supervision of Marshall.
C.initiate an investigation to determine the extent of the wrongdoing.
A.Underwriting relationships.
B.Service on a publicly-traded company’s board of directors.
The Standards do not require members to disclose to clients and prospective clients their obligation to abide by the Code and Standards.
6.A CFA charterholder is the Fund Manager for a non-profit organization. During a presentation regarding the restructuring of their investment portfolio’s asset allocation, the Head of the Finance Committee questions the manager. As part of his response, the manager states, “I am a CFA charterholder, I know what I’m talking about, you should do what I say”. According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, has the charterholder violated any of the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 103-105
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.Standard VII-B Reference to CFA Institute, the CFA Designation, and the CFA Program under Responsibilities as a CFA Institute Member or CFA Candidate holds that individuals may reference their CFA designation, CFA Institute membership or candidacy in the CFA Program but must not exaggerate the meaning or implications of membership in the Institute, holding the CFA
designation, or candidacy in the CFA Program. By inferring that since he is a CFA Charterholder his recommendations are correct exaggerates the implications of holding the CFA designation.C.Communication with Clients and Prospective Clients.
Answer: C
A.Disclosure of Conflicts.
B.Priority of Transactions.
9.In order to comply with the GIPS Standards, a firm must initially show GIPS- compliant history for a minimum of:
A.five years, or since inception if the firm has been in existence for less than five years.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A firm must initially show GIPS-compliant history for a minimum of five years, or since inception if the firm has been in existence for less than five years.
C.Additional Compensation Agreements.
Answer: B
B.No, because he had purchased his own copy. C.No, because both had purchased their own copies.
Answer: A
A.No.
B.Yes, because he has a duty of loyalty to his employer.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
13.Sallie Lewis, CFA, is a research analyst covering the mining industry. Along with other analysts, Lewis visits the primary mine of Gold Rush Mines (GR).
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 36-39
Study Session 1–2–a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.Lewis must investigate the reliability of the information before making an investment recommendation based on the information.
Answer: B
Guidance for Standards I-VII, Standards of Practice Handbook,
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 53-55
Study Session 1–2–a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.B.Yes, with respect to suitability.
C.Yes, with respect to diligence and a reasonable basis.
A.alert CFA Institute.
B.consult outside counsel.
Study Session 1–2–a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.Members must keep client information confidential and must comply with applicable law. If applicable law requires disclosure of client information in certain circumstances, members and candidates must comply with the law. If applicable law requires members to maintain confidentiality, even if the information concerns illegal activities on the part of the client, members should not disclose such information. Lee’s best course of action would be to consult with outside counsel to determine applicable law.
Answer: A
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 69-71
Study Session 1–2–a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.B.Yes, with respect to conflict of interest.
C.Yes, with respect to responsibilities of supervisors.
19.The yield to maturity on otherwise identical option-free bonds issued by the U.S.
Treasury and a large industrial corporation is 6 percent and 8 percent,
respectively. If annual inflation is expected to remain steady at 2.5 percent over the life of the bonds, the most likely explanation for the difference in yields is a premium due to:“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 172-174
Study Session 2-5-bBy accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.$928,000.
B.$1,176,000.
C.$1,552,000.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
21.A project has the following expected cash flows:
Answer: B
“Discounted Cash Flow Applications,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W.
22.An analyst gathers the following information about a common stock investment:
“Discounted Cash Flow Applications,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 221-222
Study Session 2-6-b
Define, calculate, and interpret a holding period return (total return).The holding period return (HPR) is calculated as follows:
HPR = ( – + ) / , where is the initial investment, is the price received at the end of the holding period, and is the cash paid by the investment at the end of the holding period. In this case: HPR = (54 –48 + 4) / 48 = 20.8%. The HPR is not annualized for holding periods shorter than a year.McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 229-233
Study Session 2-6-d
Calculate and interpret the bank discount yield, holding period yield, effective annual yield, and money market yield for a U.S. Treasury bill; and convert amongBy accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Year | Portfolio return |
|---|---|
|
The portfolio’s mean absolute deviation for the five-year period is closest to:
Compute the mean: (8.6 + 11.2 + 12.9 + 15.1 – 9.4) / 5 = 7.68% and compute MAD, (|8.6 – 7.68| + |11.2 – 7.68| + |12.9 – 7.68| + |15.1 – 7.68| + |–9.4 – 7.68|) / 5 = 6.83%.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
If the risk-free rate of return is 4.25 percent, then the coefficient of variation is closest to:
The coefficient of variation is: .5 / 14.3 = 19.49 / 14.3 = 1.36.
26.If an analyst estimates the probability of an event for which there is no historical record, this probability is best described as:
An empirical probability cannot be calculated for an event not in the historical record. In this case, the analyst can make a personal assessment of the probability of the event without reference to any particular data. This is a subjective
probability.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: B
“Probability Concepts,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 344-349
Study Session 2-8-j
Calculate and interpret covariance and correlation.C.has an infinite number of unspecified outcomes.
Answer: A
29.According to the central limit theorem, a sampling distribution of the sample mean will be approximately normal only if the:
A.sample size is large.
30.Which of the following is least likely to be a desirable property of an estimator?
A.Efficiency
B.Reliability
C.Consistency31.An analyst gathers the following information about the price-earnings (P/E) ratios for the common stocks held in a portfolio:
| Interval | P/E range | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
|
Answer: A
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W.
A.$8,133.
B.$8,173.
C.$8,833.Answer: B
$8,173.92 = (1 + 0.5%)*($700.00 / 0.5%)*( 1 – 1/(1 +0.5%)12 ), the rent calculation is an annuity due. Using a financial calculator: PMT = 700, I=0.5, n=12 Compute annuity due PV, PV = 8,173.92.
Questions 33 through 44 relate to Economics
The elasticity of supply equals the percent change in quantity relative to the average quantity divided by the percent change in demand relative to the average demand: The average quantity = (100 + 150)/2 = 125, the % change in quantity = 50/125 = 40%; The average price = (150 + 200)/2 = 175, the % change in price = 50/175 = 28.6% Elasticity of supply = 40%/28.6% = 1.40
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: B
“Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand,” Michael Parkin
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 2, pp. 331-332
Study Session 5-23-c
Differentiate between short-run and long-run macroeconomic equilibrium, and explain how economic growth, inflation, and changes in aggregate demand and supply influence the macroeconomic equilibrium.C.Buyers and sellers share the tax burden.
Answer: A
The company’s economic profit is closest to:
37.In the short run, an increase in output at low levels of production will most likely cause:
A.an increase in the marginal cost due to the rising total fixed cost.
The marginal cost decreases at low levels of output due to economies from greater specialization. However, at higher levels of production, it eventually increases because of the law of diminishing returns.
38.In regulating a natural monopoly, the most commonly adopted compromise pricing rule by a regulator is the:
The average cost pricing rule allows the natural monopoly to cover its costs and to break even (make zero economic profit).
39.Which of the following statements provides the best description of Nash equilibrium of two firms in the game of prisoners’ dilemma?
“Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly,” Michael Parkin
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 2, pp. 229-237
Study Session 5-20-d
Explain the kinked demand curve model and the dominant firm model, and describe oligopoly games including the Prisoners’ Dilemma.Both firms realize that compliance results in an economic loss whereas cheating results in zero economic profit (p. 236). Since zero economic profit is better than an economic loss, both firms cheat.
C.supply of a renewable natural resource is perfectly elastic and the price is equal to the present value of the next period's expected price.
Answer: B
B.decrease the full-employment quantity of labor. C.increase potential Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Answer: B
A.the short-run but not the long-run Phillips curves. B.both the short-run and the long-run Phillips curves. C.neither the short-run nor the long-run Phillips curves.
Answer: B
B.Full employment.
C.Moderating long-term interest rates.
44.The least likely reason why a firm in perfect competition is a price taker is because:
A.buyers are well informed about prices of other firms.
A price taker is a firm that cannot influence the market price and consequently sets its own price at the market place price, not above it. The key reason why a firm in perfect competition is a price taker is because buyers are well informed about prices of other firms and it produces a tiny portion of the total market output.
Questions 45 through 68 relate to Financial Statement Analysis
“Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hennie van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, p.18
Study Session 7-29-c
Discuss the importance of financial statement notes and supplementary
information, (including disclosures of accounting methods, estimates and
assumptions) and management’s discussion and analysis.Management must highlight any favorable and unfavorable trends and identify significant events and uncertainties that affect the company’s liquidity, capital
A.Asset.
B.Revenue.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
47.An analyst prepares common-size balance sheets for two companies operating in the same industry. The analyst notes that both companies had the same
proportion of current liabilities, long-term liabilities, and shareholders’ equity and the following ratios:
| Company 1 | Company 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Current ratio | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| 0.5 | 0.8 |
B.higher percentage of assets associated with accounts receivable. C.lower percentage of assets associated with marketable securities.
Answer: A
The current ratio includes inventory but the quick ratio does not. (Current ratio is higher than quick ratio and quick ratio is higher than cash ratio.) The quick ratio includes accounts receivable but the cash ratio does not. The denominator for all three ratios is current liabilities, which are the same proportion for both
companies. The difference in ratios is therefore created by inventory and
accounts receivable. Company 1 has the higher percentage of inventory because the difference between the current ratio and quick ratio is greater for that
company. Company 2 had the higher percentage of accounts receivable because the difference between the quick ratio and the cash ratio is greater for Company 2.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Understanding the Cash Flow Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp. 243-244
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, p. 507
Study Session 8-34-a, 10-39-c
Compare and contrast cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities, and classify cash flow items as relating to one of these three categories, given a description of the items.Calculate, classify, and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability, and valuation ratios.
At the end of the year, a company sold equipment for $30,000 cash. The company paid $110,000 for the equipment several years ago and had recorded accumulated depreciation of $70,000 at the time of its sale. All else equal, the equipment sale will result in the company’s cash flow from:
A.investing activities increasing by $30,000.
Demonstrate the steps in the preparation of direct and indirect cash flow statements, including how cash flows can be computed using income statement and balance sheet data.
The book value of the equipment at the time of sale is $110,000 - $70,000 = $40,000. The proceeds are $30,000; therefore a loss of $10,000 is reported on the income statement. The loss reduces net income, but it is a non-cash amount, so is added back to net income in the calculation of the cash from operations.
“Income Taxes,” Elbie Antonites, CFA, and Michael Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I,Volume 3, pp. 393-395, 399
Study Session 9-37-d
Calculate income tax expense, income taxes payable, deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities, and calculate and interpret the adjustment to the financial statements related to a change in the income tax rate.
|
$800,000 |
|---|---|
| 70,000 | |
| (90,000) | |
| (120,000) | |
| 100,000 | |
|
50,000 |
|
(20,000) |
| 790,000 | |
51.An analyst gathers the following annual information ($ millions) about a company that pays no dividends and has no debt:
Answer: C
“Understanding The Cash Flow Statement”, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Hennie van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn CFA 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp.267 - 270, 279-280
Study Session 8-34-i
Explain and calculate free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to equity, and other cash flow ratios.A.fully assured to be free of material errors.
B.reasonable assured to be free of all errors.
53.Making any necessary adjustments to the financial statements to facilitate comparison with respect to accounting choices is done in which step of the financial statement analysis framework?
A.Collect data.
Broihahn., CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp.24-27
Study Session 7-29-f
Describe the steps in the financial statement analysis framework.Making any adjustments is part of the processing data step. Commonly used data bases (part of the collection phase) do not make adjustments for differences in accounting choices.
|
|---|
Which of the items is classified as an operating item in the company’s income statement?
“Understanding the Income Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp.163-165
Study Session 8-32-f
Distinguish between the operating and nonoperating components of the income statement.The loss on the disposal of fixed assets is an unusual or infrequent item but it is still part of normal operating activities. The interest expense is the result of financing activities and would be classified as a nonoperating expense by nonfinancial service companies. The realized gain on sale of available for sale securities is an investing activity and would also be classified as a nonoperating gain by a manufacturing company.
C.176.
Answer: A
| 12 | |
|
82 |
|
47 |
| 141 | |
| 44 | |
| 20 | |
| 5 | |
|
8 |
| 77 | |
|
64.0 |
During late December 2008 Company A acquires a small competitor, Company B. During the evaluation of the acquisition it is determined that the customer lists of Company B have a fair value of $50,000. Company A has spent $15,000 during the year updating and maintaining its own customer lists. What will be the value of the customer list intangible asset on Company A’s 31 December 2008 consolidated financial statements?
A.$15,000.
B.$50,000.
C.$65,000.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
57.Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
“Long-Lived Assets,” R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Elizabeth Gordon
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp.368-371
Study Session 9-36-i
Define impairment of long-lived tangible and intangible assets and explain what effect such impairment has on a company’s financial statements and ratios.The equipment is impaired. NBV = $550,000 which is greater than the sum of the undiscounted cash flows 5 yrs x $80,000 = $400,000. The company’s future ROA will increase. Once the asset is written down, there will be lower depreciation charges, which will increase net income, and a lower carrying value of assets, which decreases total assets. Both factors would increase any future ROA.
| $50,000 | |
|---|---|
|
5 years |
|
6 years |
| $0 | |
| $160,000 | |
| 8% | |
Which of the following best describes the classification of the lease on the company’s financial statements for 2008?
A.Operating lease.
It is a sales type lease: the lease period covers more than 75% of its useful life (5/6=83.3%) and the asset is on its books at less than the present value of the lease payments ($199,635) (PMT = $50,000, N=5, i=8%). The firm must have acquired or manufactured the asset if it is recorded at less than the present value of the lease payments.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Financial Statement Analysis: Applications,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp.591-593
Study Session 10-42-c
Describe the role of financial statement analysis in assessing the credit quality of a potential debt investment.Credit analysis is concerned with a company’s debt-paying ability. Returns to creditors are normally paid in cash, so the company’s ability to generate cash internally is the most important factor in credit analysis.
“Long-Lived Assets,” R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Elizabeth Gordon
2009 Modular Level I,Volume 3, 348-352
Study Session 9-36-d
Identify the different depreciation methods for long-lived tangible assets and discuss how the choice of method, useful lives, and salvage values affect a company’s financial statements, ratios, and taxes.A high salvage value estimate reduces the depreciable base and thus depreciation expense; long average lives reduce the annual depreciation expense for any given
“Inventories,” Elbie Antonites, CFA and Michael Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp. 315-318
“Financial Statement Analysis: Applications,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp. 599-601
Study Session 9-35-e, f, 10-42-e
Analyze the financial statements of companies using different inventory
accounting methods to compare and describe the effect of the different methods on cost of goods sold, inventory balances, and other financial statement items; and compute and describe the effects of the choice of inventory method on
profitability, liquidity, activity and solvency ratios.Calculate adjustments to reported financial statements related to inventory assumptions in order to aid in comparing and evaluating companies.
|
|
|
Management is most likely to try and report lower earnings when negotiating concessions from a union.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
C.increased by the change in its LIFO reserve for that period.
Answer: A
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
64.Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
| Average market price per share of common stock during the year | $40 |
|---|---|
| $50 | |
| $30 |
A.5,000.
B.15,000.
C.20,000.65.Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
At the beginning of the year, a lessee company enters into a new lease agreement that is correctly classified as a finance lease, with the following terms:
With respect to the effect of the lease on the company’s financial statements in the first year of the lease, which of the following is most accurate? The reduction in the company’s:
The present value of the lease is $360,477.62. (n = 5, I = 12%, PMT = $100,000) 12% of the original PV is $43,257.31 and represents the interest component of the payment in the first year. The difference between the annual payment and the interest is the amortization of the lease obligation included in cash flow from financing. $100,000 – 43,257.31 = $56,742.69.
Depreciation is $360,477.62 / 5 or $72,095.52 so the total reduction in pretax income would be interest plus depreciation or $115,352.83. Cash flow from operations would be reduced by the amount of the interest only because the depreciation would be added back to determine cash flow from operations.
|
|
|---|---|
|
Answer: A
“Income Taxes,” Elbie Antonites, CFA and Michael Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp. 393-395, 399
Study Session 9-37-d
Calculate income tax expense, income taxes payable, deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities, and calculate and interpret the adjustment to the financial statements related to a change in the income tax rateA.$771.
B.$774.
68.Financial reporting standards are most likely enforced by:
A.both standard-setting bodies and regulatory bodies.
Generally, standard setting bodies make the rules and regulatory authorities enforce the rules.
Questions 69 through 78 relate to Corporate Finance
Answer: C
“Capital Budgeting,” John D. Stowe, CFA, and Jacques R. Gagné, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 6-8
Study Session 11-44-a
Explain the capital budgeting process, including the typical steps of the process, and distinguish among the various categories of capital projects.B.project sequencing.
C.an example of investment synergy.
The required rate of return for the project is 13 percent. The net present value (NPV) of the project is closest to:
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
30, = 40, = 40, = 30, = 20, I = 13, solve for NPV).
| Capital component | Book Value (000) | Market Value (000) | Component cost |
|---|---|---|---|
|
The company’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is closest to:
Because the target capital weights are not given, market value weights are used to compute the WACC. The market value weights for debt, preferred stock and equity are 0.2667, 0.0667, and 0.6667 respectively.
WACC = × × (1 – t) + × + ×
= 0.2667 × 8% × (1 – 0.4) + 0.0667 × 10% + 0.6667 × 12% = 9.95%“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, CFA, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 43-45
Study Session 11-45-f
Calculate and interpret the cost of fixed rate debt capital using the yield-to-maturity approach and the debt-rating approach.Using a financial calculator: N = 20, PMT = 45, PV = –950, FV = 1000; solve for I/Y = 4.90%. The annual yield is twice the semiannual yield = 4.90% × 2 = 9.80%. The after-tax cost of debt = annual yield × (1 – t) = 9.80% × (1 – 0.30) = 6.86%
The cost of a perpetuity is the annual cash flow divided by the selling price. In this case, the cost of preferred ( ) = 6.00 / 40 = 15.0%. Because the preferred stock dividend is not tax deductible to the issuing company, there is no after-tax adjustment.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: C
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, CFA, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 52-53
Study Session 11-45-h
Calculate and interpret the cost of equity capital using the capital asset pricing model approach, the dividend discount model approach, and the bond yield plus risk premium approach.“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., CFA, Kenneth L.
Parkinson, and Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 99-100
Study Session 11-46-e
Compute and interpret comparable yields on various securities, compare portfolio returns against a standard benchmark, and evaluate a company’s short-term investment policy guidelines.Answer: A
“The Corporate Governance of Listed Companies: A Manual for Investors” 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 169-171
Study Session 11-48-f
State the key areas of responsibility for which board committees are typically created, and explain the criteria for assessing whether each committee is able to adequately represent shareowner interests.Answer: B
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.specialist.
B.registered trader.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
80.An analyst gathers the following data for a company to estimate the expected growth rate of dividends and use it as an input for valuing the company’s common stock.
| 10% | |
|---|---|
| 5 % | |
| 1.67 | |
| 25% |
The company’s expected growth rate is closest to:
A.4.2%.
Brown, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 146-147
Study Session 14-56-f, g
Estimate the dividend growth rate, given the components of the required return on equity and incorporating the earnings retention rate and current stock price.Describe a process for developing estimated inputs to be used in the DDM, including the required rate of return and expected growth rate of dividends.
Answer: C
“Organization and Functioning of Securities Markets,” Frank K. Reilly CFA, and Keith C. Brown, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 25-26
Study Session13-52-f
Using the constant growth dividend discount model, the stock’s intrinsic value is closest to:
A.$12.82.
B.$18.29.
C.$19.57.Calculate, using the SML, the expected return on a security, and evaluate whether the security is overvalued, undervalued, or properly valued.
Calculate and interpret the value both of a preferred stock and a common stock using the dividend discount model (DDM).
B.Arithmetic mean.
C.Value-weighted mean.
A.escalation bias.
B.confirmation bias.
C.overconfidence bias.85.An analyst gathers the following data about a company:
|
$40 |
|---|---|
| 12% | |
| $2.00 | |
| 10% |
A.5%.
B.30%.
C.70%.86.Which of the following attributes is least likely to be associated with the characteristics of a well functioning securities market?
A.Market depth.
Wide bid-ask spreads is not a characteristic of a well functioning market.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: B
“Understanding the Cash Flow Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp. 279-280
“An Introduction to Security Valuation,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA, and Keith C.A.Data mining.
B.Arbitrage activity.
Arbitrage activity is not a source of unreliability of an anomaly. Arbitrageurs attempt to take advantage of an anomaly and are not a source of its unreliability.
89.The best characterization of the strong-form of efficient market hypothesis (EMH) with respect to the information set is that it encompasses:
The difference among the three forms of the EMH revolves around the
information set included in each. The weak form includes public market information, the semistrong form includes all public information, and the strong form includes all public and private information. The strong form EMH
encompasses both the weak-from and the semistrong form EMH.90.Among a company’s price to earnings (P/E), price to sales (P/S), and price to cash flow (P/CF) ratios, it is most accurate to state that P/E ratios are generally more stable from period to period than:
“Introduction to Price Multiples,” John D. Stowe, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 182-188, 196-201
Study Session 14-59-a, b
Discuss the rationales for, and the possible drawbacks to, the use of price to earnings (P/E), price to book value (P/BV), price to sales (P/S), and price to cash flow (P/CF) in equity valuation.Calculate and interpret P/E, P/BV, P/S, and P/CF.
A.interest rate cap.
B.interest rate floor.
C.interest rate collar.Answer: B
B.currency swap.
C.interest rate swap.
93.An investor establishes a short position in a futures contract on Day 0 when the price per contract is $100. The investor deposits $5 per contract to meet the initial margin requirement. The maintenance margin requirement per contract is $3.
The Day 1 settlement price that would require the investor deposit additional funds on Day 2 equal to $4 per contract is closest to:
The investor has a short position and will experience a margin call only if the price increases. Additional margin must be deposited to bring the ending balance up to the initial margin requirement. The investor must deposit $4 therefore, the margin balance on Day 1 is -$4 which would result if the price of the contract was $104.
94.Two parties agree to a forward contract to deliver the S&P 500 Index at a price of $375,000 in 2 months time. When the forward contract expires, the price of the S&P 500 Index is $350,000 but the long party is unable to pay the cash
settlement. The short party is most likely obligated to:Given a forward contract cash settlement, only the net payment is required. The long owes the short $25,000.
95.A European bank wants to short a 1x3 forward rate agreement on Euribor. A dealer provides the bank with a quote of 1.75 percent. The bank agrees to enter the FRA with the dealer. At contract maturity, what Euribor rate would most likely result in the European bank receiving a payment from the dealer?
96.According to put-call parity, a synthetic put contains a:
A.long position in the call.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Questions 97 through 108 relate to Fixed Income Investments.
“Understanding Yield Spreads,” Frank J. Fabozzi 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 333-334
Study Session 15-63-g
Identify how embedded options affect yield spreads.Mortgage-backed securities expose an investor to prepayment risk.
Answer: B
“Features of debt securities,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA, 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 223-228
Study Session 15-60-d,e
Explain the provisions for redemption and retirement of bonds;
Identify the common options embedded in a bond issue, explain the importance of embedded options, and state whether such options benefit the issuer or
bondholder.Answer: A
“Yield Measures, Spot Rates, and Forward Rates,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, p. 399
Study Session 16-65-d
Compute and interpret the bond equivalent yield of an annual-pay bond and the annual-pay yield of a semiannual-pay bond
“Yield Measures, Spot Rates, and Forward Rates,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 408
Study Session 16-65-e
Describe the methodology for computing the theoretical Treasury spot rate curve, and compute the value of a bond using spot ratesBy accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: A
“Yield Measures, Spot Rates, and Forward Rates,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 414
Study Session 16-65-f
Differentiate between the nominal spread, the zero-volatility spread, and the option-adjusted spread.“Features of debt securities,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 230-231
Study Session 15-60-f
Describe methods used by institutional investors in the bond market to finance the purchase of a security (i.e., margin buying and repurchase agreements).For institutional investors the term repo rate is less than the cost of bank financing (i.e., broker loan rate or call money rate.)
C.value of the security’s embedded option.
Answer: A
B.inverse floater.
C.floater with a floor.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
105.The duration of a fixed-income portfolio is best interpreted as the:
“Introduction to the Measurement of the Interest Rate Risk,” Frank J. Fabozzi 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 466-467
Study Session 16-66-e
Distinguish among the alternative definitions of duration, and explain why effective duration is the most appropriate measure of interest rate risk for bonds with embedded options.Users of this interest rate risk measure are interested in what it tells them about the price sensitivity of a bond or a portfolio to change in interest rates, therefore B is correct.
Answer: A
“Introduction to the measurement of interest rate risk,” Frank J. Fabozzi, CFA, 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 444-448
Study Session 16-66-a
Distinguish between the full valuation approach (the scenario analysis approach) and the duration/convexity approach for measuring interest rate risk, and explain the advantage of using the full valuation approach.B.7.38.
C.14.77.
( V − y ) , where is the current value, V+ is the
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | = | 127 . 723 | − | 122 . 164 | = | ||||||
| 2 | × | 125 . 482 | × | .0 003 | |||||||
A.0.0439.
B.0.0521.
C.0.0538.Answer: B
Questions 109 through 114 relate to Alternative Investments.
109.Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) are affected by trading risk, which is most likely to:
Answer: B
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik, and Denis McLeavy 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 6, pp 184-185
Study Session 18-73-c
Explain the advantages and risks of ETFs.B.decrease.
C.remain unchanged.
Inflation could make NOI grow at the inflation rate over time. As long as inflation is passed through, it will not affect valuation because the market cap rate also incorporates the inflation rate.
111.An investor evaluates an apartment complex using the income approach. Recent sales in the area consist of an apartment complex and an office building. The data on the apartment complex and the recently sold properties are provided below. All income and expenses are annual.
Answer: C
“Alternative Investments”, Bruno Solnik, and Denis McLeavy
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 6, pp 191-192
Study Session 18-73-f
Calculate the net operating income (NOI) from a real estate investment, the value of the property using the sales comparison and income approaches, and the after-tax cash flows, net present value, and yield of real estate investment.
| Apartment Complex Under Consideration |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Net Operating Income (NOI) | $250,000 | $91,000 | $480,000 |
| $700,000 | $3,000,000 |
C.$1,923,077.
Answer: C
B.positive.
C.negative.
The roll yield when the market is in contango is negative.
114.For a commodity if futures prices prices are above the spot price then the market, then the market is most likely to be:
“Investing in Commodities,” Ronald G. Layard-Liesching
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 6, pp 242-243
Study Session 18-74-a
Explain the relationship between spot prices and expected futures prices in terms of contango and backwardation.When a commodity is in contango, futures prices are higher than the spot price because market participant believe that that the spot price will be higher in the future.
Answer: A
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
If the correlation of returns for the two assets equals 0.75, and the risk-free interest rate 1 percent, then the expected standard deviation of the portfolio is closest to:
A.3.07%.
B.4.23%.
C.4.55%.117.An analyst has gathered monthly returns for two stock indexes A and B:
| Month | Returns for Index A | Returns for Index B |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -6.4% | -6.2% |
| 2 | 6.6% | 19.0% |
| 3 | 12.9% | -7.7% |
| 4 | 3.2% | 4.0% |
The covariance between Index A and Index B is closest to:
118.A completely diversified portfolio will most likely result in the elimination of:
A.systematic variance.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Study Session 12-51-c
The candidate should be able to define systematic and unsystematic risk, and explain why an investor should not expect to receive additional return for assuming unsystematic risk;Answer: B
“Managing Investment Portfolio: A Dynamic Process,” John Maginn, Donald Tuttle, Denis McLeavy, Jerald Pinto
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 259-260
Study Session 12-51-d;
Explain the capital asset pricing model, including the security market line (SML) and beta, and describe the effect of relaxing its underlying assumptions;C.remain unchanged.
Answer: A
2009 Level I Mock Exam: Afternoon Session ANSWERS AND REFERENCES
Questions 1 through 18 relate to Ethical and Professional Standards.
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 53-58
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.The Standard related to fair dealing states that all clients cannot be treated equally because it is impossible to reach everyone simultaneously and each client has unique needs and objectives.
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B.disclosures of beneficial ownerships.
C.duplicate confirmations of employee transactions.
Sandridge recently retired from the investment management profession. As he is retired, Sandridge no longer attends CFA Institute society meetings and has stopped paying his CFA Institute dues. According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, how should Sandridge refer to his affiliation with the CFA Program?
A.David Sandridge, CFA.
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 103-108
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.If a charterholder fails to pay dues for any year, the right to use the CFA designation is suspended. However, stating he was awarded the CFA charter in 1968 is a matter of fact.
Answer: C
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 21-25, 75, 89-91
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.A.service as directors.
B.firm’s market-making activities.
7.According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, a member with supervisory responsibilities violates the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct if the member fails to:
A.prevent violations of the law.
Members with supervisory responsibility must make reasonable efforts to detect violations of laws, rules, regulations, and the Code and Standards. They exercise reasonable supervision by establishing and implementing written compliance procedures.
8.For the past decade, Rachel Pederson, CFA, has managed the account of Olga Stefansson and in that time developed a close relationship with her client. Stefansson has a beach house in the Bahamas which she offers to Pederson and her family free use of for two weeks as a reward for the excellent returns generated in her account. Pederson is so busy at work she does not tell anyone where she is going for vacation. When accepting Stefansson’s offer, Pederson leastlikely violates the CFA Institute Standard relating to:
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 21-22, 69, 75, 89
Study Session 1–2–a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.The Standards require that members not accept gifts or compensation that might reasonably compete with their employer’s interest unless they obtain written consent from all parties involved. Arrangements such as that offered to Pederson may cause a conflict of interest or result in partiality that could impede Pederson’s independence and objectivity.
Answer: C
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, p. 88
Study Sessions 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.C.Diligence and Reasonable Basis.
Answer: A
A.The Standards do not apply to the charterholder’s conduct.
B.The Standards require the charterholder to comply with the agreement with his former employer.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
12.A CFA charterholder is asked to review her firm’s soft dollar practices. As part of the review, she notes that her firm has failed to disclose the practices to the firm’s clients in writing as required by law. The charterholder quickly prepares and distributes the appropriate disclosures. She does not report the firm’s violation to the appropriate regulatory authority. According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, by not reporting the violation to the regulatory authority, has the charterholder violated any CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 15-18, 48-50
Study Session 1-2-a
Demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to situations involving issues of professional integrity.Although disclosure may be prudent in certain circumstances and required if mandated by applicable law, the Code and Standards do not require that members report legal violations to the appropriate governmental or regulatory organizations.
Answer: A
“Guidance for Standards I-VII,” CFA Institute 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 48-50, 89-91 Study Session 1–2–a
A.Loyalty to Employer.
B.Priority of Transactions.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
15.Fred Brubacher, CFA, is an analyst at Van City Bank (VCB). Brubacher receives compensation for referrals to the bank’s brokerage and personal financial-planning divisions. His recent referrals are long-time clients from his previous employer, and Brubacher does not mention VCB’s referral arrangement. Does Brubacher violate any CFA Institute Standards?
Compensation or other benefits received for the recommendation of products or services represents a conflict of interest. According to the Standards, Brubacher must disclose the referral fee arrangement.
16.A CFA charterholder has decided to revise her firm’s written compliance manual. She checks with counsel regarding changes to applicable laws, rules, and regulations. She incorporates these changes as well as changes to the Code and Standards in the new version and distributes copies to her staff along with a memorandum. The
memorandum states that the updated manual includes compliance procedures designed to meet industry standards, regulatory requirements, requirements of the Code and Standards, and circumstances of the firm. According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, did the charterholder violate any Standard of Professional Conduct?“Guidance for Standards I-VII”, CFA Institute
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 76-78By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B.Yes, because she distributed plagiarized material. C.Yes, because she misrepresented her firm’s services.
Answer: A
B.provide a composite list and description to any prospective client on request. C.document their policies and procedures used in establishing and maintaining compliance.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
19.A money manager has $1,000,000 to invest for one year. She has identified three alternative one-year certificates of deposit (CD) shown below:
Answer: C
“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E.
| Investment |
|---|
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 190-208
Study Session 2-5-d, e
Calculate and interpret the future value (FV) and present value (PV) of a single sum of money, an ordinary annuity, an annuity due, a perpetuity (PV only), and a series of unequal cash flows.Draw a time line, and solve time value of money applications (for example, mortgages and savings for college tuition or retirement).
| Date | Amount € | |
|---|---|---|
|
86.00 | |
|
94.00 | |
| 212.00 |
A.11.02%.
B.11.60%.
C.11.89%.Answer: B
A.ordinal.
B.interval.
C.nominal.Answer: A
23.Using Chebyshev’s inequality, what is the minimum proportion of observations from a population of 500 that must lie within two standard deviations of the mean, regardless of the shape of the distribution?
A.75%
B.89%
C.99%
24.If a distribution exhibits positive skewness, then the mean most likely is located to the:
A.left of both the median and mode.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Define and interpret skewness, explain the meaning of a positively or negatively skewed return distribution, and describe the relative locations of the mean, median, and mode for a nonsymmetrical distribution.
“Probability Concepts,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 327-328
Study Session 2-8-e
Calculate and interpret 1) the joint probability of two events, 2) the probability that at least one of two events will occur, given the probability of each and the joint
probability of the two events, and 3) a joint probability of any number of independent events.The probability that at least one of two events will occur is the sum of the probabilities of the separate events less the joint probability of the two events.
C.can be the linear combination of two or more normal random variables.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
27.A portfolio manager gathers the following information about three possible asset allocations:
The manager’s client has stated that her minimum acceptable return is 8 percent. Based on Roy’s safety-first criterion, the most appropriate allocation is:
A.I.
McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 397-399
Study Session 3-9-i
Define shortfall risk, calculate the safety-first ratio, and select an optimal portfolio using Roy’s safety-first criterion.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Allocation | Safety-first ratio |
|---|---|
The standard error of the sample mean is the sample standard deviation (or the population standard deviation if known) divided by the square root of the sample size. In this case, the standard error of the sample mean = 320.5 / 500.5 = 0.80.
29.Compared to the normal distribution, the Student’s t-distribution most likely:
“Sampling and Estimation,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and David E. Runkle, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 1, pp. 436-438By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
B.Making the statistical decision.
C.Specifying the significance level.Answer: B
5)Collecting the data and calculating the test statistic.
6)Making the statistical decision.
Answer: C
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. Defusco, CFA, Dennis W.
| Investment |
|
Frequency: |
|---|---|---|
|
C.III.
Answer: B
B.60.
C.120.
A.experiences constant returns to scale.
B.produces a given output at the least possible cost.
The long-run average cost curve tells the firm the plant size and the quantity of labor to use at each output to minimize cost. Once the plant size is chosen, the firm operates on the short-run cost curves that apply to that plant size. Therefore, the firm is said to be operating on its long-run average cost curve when it is producing a given output at the least possible cost.
35.As the quantity of labor increases, which of the following is the mostlikely outcome with respect to the marginal revenue product (MRP) of labor?
“Markets for Factors of Production”, Michael Parkin
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 2, pp. 255-257
Study Session 5-21-a
Explain why demand for the factors of production is called derived demand, differentiate between marginal revenue and marginal revenue product (MRP), and describe how the MRP determines the demand for labor and the wage rate.MRP decreases for a firm in perfect competition, due to a decline in marginal product.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Elasticity”, Michael Parkin
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 2, pp. 19-20, 27
Study Session 4-13-a
Calculate and interpret the elasticities of demand (price elasticity, cross elasticity, income elasticity) and the elasticity of supply, and discuss the factors that influence each measure.C.greater than normal.
Answer: C
Answer: A
“Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand,” Michael Parkin
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 2, pp. 334-337
Study Session 5-23-d
Compare and contrast the classical, Keynesian, and monetarist schools of macroeconomics.B.decrease.
C.remain constant.
A.resell a product.
B.capture a producer surplus.
C.capture a consumer surplus.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
41.Which of the following will most likely lead to cost-push inflation?
Increased material costs cause firms to manufacture less. Less manufacturing decreases short-run supply making prices rise (see page 388).
42.Which of the following is least likely to be a tool available to central banks for implementing monetary policy?
“An Overview of Central Banks” Anne Dolganos Picker
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 2, pp. 477-485
Study Session 6-28-b
Discuss monetary policy and the tools utilized by central banks to carry out monetary policy.Adjusting taxation is not a tool available to central banks. Only the government can adjust taxation as it is a fiscal policy tool.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: C
A.107.81.
B.114.58.
C.117.97.Answer: A
45.An analyst gathers the following information about a company:
|
$18.4 million |
|---|---|
| 24 times | |
| Number of days of payables | 25 days |
A.40.
B.59.
C.65.Answer: A
“Financial Analysis Techniques”, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Hennie van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp. 506-509
“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., CFA, Kenneth L. Parkinson, and Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 87-90,
Study Session 10-39-c, 11-46-a, b
Calculate, classify and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability, and valuation ratios.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
46.Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
Answer: B
“Financial Analysis Techniques”, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Hennie van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp. 520-525
“Financial Statement Analysis,” Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2009 Modular Level I Volume 4, pp. 132-136
Study Session 10-39-e, 11-47-a
Demonstrate the application of and interpret changes in the component parts of the DuPont analysis (the decomposition of return on equity).A.sales.
B.total liabilities.
Interest expense is an income statement account and the common-size percentage should be computed as a percentage of sales for that company.
48.Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
| Original Cost | Accumulated Depreciation at Date of Sale | Sales Proceeds |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $200,000 | $150,000 | $70,000 |
| 2 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $30,000 |
| 3 | $300,000 | $250,000 | $40,000 |
Answer: B
“Understanding the Cash Flow Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp.263 - 265, 267-270
“Long-Lived Assets,” R. Elaine Henry, CFA, and Elizabeth Gordon
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp.361-366
Study Session 8-34-f, 9-36-h
Demonstrate the steps in the preparation of direct and indirect cash flow statements, including how cash flows can be computed using income statement and balance sheet data.49.Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
The following information is from a company’s 2008 financial statements ($ millions):
In 2008 the company declared and paid cash dividends of $5 million and recorded depreciation expense in the amount of $25 million. The company’s 2008 cash flow from operations ($ millions) is closest to:
A.25.
B.30.
C.35.By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
during 2008. Depreciation expense is added to net income and the changes in balance sheet accounts are also considered to determine cash flow from operations.
B.a higher cost of goods sold, but a lower inventory balance. C.both a higher cost of goods sold and a higher inventory balance.
Answer: C
The negative change in the LIFO reserve would increase the cost of goods sold under FIFO compared to LIFO. FIFO COGS = LIFO COGS – Change in LIFO reserve.
The LIFO reserve has a positive balance so that FIFO inventory would be higher than LIFO inventory. FIFO inventory = LIFO inventory + LIFO reserve.
B.gross profit margin.
C.amount of working capital.
The LIFO reserve did not change from 2007 to 2008. Without a change in the LIFO reserve, cost of goods sold would be the same under both methods. Sales are always the same for both; so gross profit margin would be the same in 2008. The FIFO inventory would be higher because the LIFO inventory and LIFO reserve are added to compute FIFO inventory. Because the inventory balances would be different under FIFO, inventory turnover, and net working capital would also be different under FIFO.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
|
|
| $10,000,000 | |
| Par value of cumulative preferred stock with a 7 percent dividend rate | |
| 30% |
A.$1.05.
B.$1.26.
C.$1.36.Answer: B
At the beginning of the year, two companies issued debt with the same market rate, maturity date, and total face value. One company issued coupon-bearing bonds at par and the other company issued zero-coupon bonds. All other factors being equal for that year, compared with the company that issued par bonds, the company that issued zero-coupon debt will most likely report:
A.higher cash flow from operations but not higher interest expense. B.both higher cash flow from operations and higher interest expense. C.neither higher cash flow from operations nor higher interest expense.
Which of the following is the simplest way for a company to increase its reported operating cash flow?
A.Record sales on a bill-and-hold basis.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
stretching out payables
financing of payables
securitization of receivables
using stock buybacks to offset dilution of earnings.C.disclaimer of opinion.
Answer: A
B.proxy statement.
C.management statement of responsibility.
57.Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
A company acquires a manufacturing facility in which it will produce toxic
chemicals. The cost of the facility (exclusive of the underlying land) is $25 million and it is expected to provide a 10-year useful life, after which time the company will demolish the building and restore the underlying land. The cost of this restoration and cleanup is estimated to be $3 million at that time. The facility will be amortized on a straight-line basis. The company’s discount rate associated with this obligation is 6.25 percent. The total expense that will be recorded in the first year associated with the asset retirement obligation on this property is closest to:The asset retirement costs will be amortized at the same rate as the property (10 years, straight-line) and an accretion expense representing the change in the ARO liability will also arise.
A.Assets are overstated by $5,000 and Liabilities are overstated by $5,000
B.Assets are overstated by $5,000 and Owner’s equity is overstated by $5,000 C.Liabilities are overstated by $5,000 and Owners’ equity is understated by $5,000Answer: C
An analyst gathers the following information from a company’s accounting records (all figures in thousands):
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
A.650.
B.850.
Total assets = liabilities + owner’s equity.
Owner’s equity = $5,250– 2,200= 3,050.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
60.Which of the following is least likely to be a characteristic of an effective financial reporting framework?
“Financial Reporting Standards,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Hennie van Greuning, CFA, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, p.115, 118
Study Session: 7-31-g
Identify the characteristics of a coherent financial reporting framework and barriers to creating a coherent financial reporting network.The characteristics of a coherent financial reporting network are transparency, comprehensiveness and consistency. Comparability is a qualitative characteristic of financial statements.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Understanding the Income Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hennie van Greuning, CFA, Elaine Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp.175-177
Study Session: 8-32-j
Evaluate a company’s financial performance using common-size income statements and financial ratios based on the income statement.
| Company | Industry | Conclusion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Profit Margin |
|
||
|
An analyst would like to compare the European company to a similar U.S. based company and has decided to adjust their financial statements to U.S. GAAP. Under U.S. GAAP, and ignoring tax effects, the cash flow from operations (€ millions) for the company would be closest to:
Compute and describe the effects of capitalizing versus expensing on net income, shareholders’ equity, cash flow from operations, and financial ratios including the effect on the interest coverage ratio of capitalizing interest costs.
Explain the circumstances in which software development costs and research and development costs are capitalized
B.Tax return liability resulting from current period taxable income.
C.Actual cash outflow for income taxes including payments (refunds) for other years.
64.Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
A company is considering issuing either a straight coupon bond or a coupon bond with warrants attached. The proceeds from either issue would be the same. If the firm issues the bond with warrants attached instead of the straight coupon bond, which of the following ratios will mostlikely belowerfor the bond with warrants?
The portion of the proceeds attributable to the warrants would be classified as equity, thus the portion classified as a liability would be smaller (lower). Therefore the debt-to-equity ratio will be lower, for the bonds with warrants.
EBIT would be the same regardless of financing method; the coupon on the bond with warrants attached would be lower if the two issues provided the same proceeds, so the interest coverage would be higher for a bond with warrants attached.
| 2009 forecast | 2008 actual | 2007 actual | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
2,250.0 | 2,150.0 | 1,990.0 |
|
100.00% | 100.00% | |
| 45.00% | 45.00% | ||
| 40.00% | 40.00% | ||
| 3.72% | 4.02% | ||
| Restructuring expense | 7.20% | ||
| 11.28% | 3.78% | ||
|
3.95% | 1.32% | |
|
7.33% | 2.46% |
Prepare a basic projection of a company’s future net income and cash flow.
The cost of goods sold and operating expenses are constant over the two-year period and they can reasonably be used to forecast 2009. Interest expense is declining as a percent of sales, implying it is a fixed cost. Conversion into dollars for each year shows what interest expense has been; 2008 =$80 (3.72% x 2,150); 2007=$80 (4.02 x 1,990) and that would be a reasonable projected amount to use. The restructuring charge should not be included as it is a non-recurring item. The tax rate, 35%, is given.
66.The unrealized gains and losses arising from changes in the market value of available-for-sale securities are reported under U.S. GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) in the:
A.equity section for both.
Under both U.S. GAAP and IFRS the unrealized gains and losses arising from carrying available-for-sale securities at market value are reported in equity as part of accumulated other comprehensive income.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| I. | |
|---|---|
| II. | II. €500,000 of installment sales. No payments are required for one year after which collections will be made on an equal basis over 12 months and taxed on a cash basis. The entire sale and related profit will be recognized for financial reporting purposes in the year of sale. |
A.I only.
B.II only.
II represents a deferred tax liability: The accounts receivable for financial statement purposes has a carrying value of €500,000 but with a tax base of €0. The temporary difference creates a deferred tax liability. Alternatively, accounting income tax expense exceeded taxes payable and the firm expects to eliminate this difference over the course of future operations.
Item I represents a deferred tax asset: Rent received in advance creates a liability on the financial statements with a carrying value of €300,000 but with a tax base of €0. The temporary difference creates a deferred tax asset. Alternatively an excess amount has been paid for income taxes based on the cash received (taxable income exceeded accounting income) and the company expects to recover this difference during the course of future operations.
The total affect on 2008 pre-tax income for the lessor from this lease is closest to:
A.$32,143.
B.$75,000.
C.$82,519.The income in the first year will therefore consist of the gross profit on the sale (357,490-300,000)=57,490 plus interest revenue from financing the lease = 25,024(see below)
| Year | Start Balance |
|
Payment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7%x357,490=25,024 | 357,490-(75,000-25,024)=307,514 |
Total income = 57,490 + 25,024 = 82,514
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Capital Budgeting,” John D. Stowe, CFA, and Jacques R. Gagné, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 8-10
Study Session 11-44-b
Discuss the basic principles of capital budgeting, including the choice of the proper cash flows and determining the proper discount rate.The cash savings related to adopting a new production process is an incremental cash flow, not an opportunity cost.
Answer: C
“Capital Budgeting,” John D. Stowe, CFA, and Jacques R. Gagné, CFA
2008 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 12-19
Study Session 11-44-d
Calculate and interpret the results using each of the following methods to evaluate a single capital project: net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), payback period, discounted payback period, average accounting rate of return (AAR), and profitability index (PI).A.Reinvestment rate assumption.
B.Size of the projects’ initial investments.
72.An analyst gathers the following information about the cost and availability of raising various amounts of new debt and equity capital for a company:
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Answer: B
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Calculate and interpret liquidity measures using selected financial ratios for a company and compare it with peer companies.
Evaluate overall working capital effectiveness of a company, using the operating and cash conversion cycles, and compare its effectiveness with other peer companies.
A.21.28%.
B.23.10%.
C.23.45%.
Answer: C“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., CFA, Kenneth L. Parkinson, and Pamela P. Peterson, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 118-119
Study Session 11-46-f
Assess the performance of a company’s accounts receivable, inventory management, and accounts payable functions against historical figures and comparable peer company values.A.6.03%.
B.6.16%.
C.6.29%.Answer: C
76.Regarding corporate governance, which of the following most likely would be a reason for concern when evaluating an independent board member’s qualifications?
The board member:
“The Corporate Governance of Listed Companies: A Manual for Investors”
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 4, pp. 162-163
Study Session 11-48-d
Identify factors that indicate a board and its members possess the experience required to govern the company for the benefit of its shareowners.Such long-term participation may enhance the individual board member’s knowledge of the company, but it also may cause the board member to develop a cooperative relationship with management that could impair his/her willingness to act in the best interests of shareowners.
Answer: A
“The Corporate Governance of Listed Companies: A Manual for Investors”
A.marginal cost of capital.
B.cost of new debt capital.
Questions 79 through 90 relate to Equity Investments
79.Which of the following is the least accuraterationale to justify the use of price-to-book value (P/B) ratio as a measure of relative valuation of companies or common stocks?
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
“Introduction to Price Multiples,” John D. Stowe, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 188-190
Study Session 14-59-a
Discuss the rationales for, and the possible drawbacks to, the use of price to earnings (P/E), price to book value (P/BV), price to sales (P/S), and price to cash flow (P/CF) in equity valuation.Answer: B
“Security-Market Indexes,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA, and Keith C. Brown, CFA 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 42-46
Study Session 13-53-a
Compare and contrast the characteristics of, and discuss the source and direction of bias exhibited by, each of the three predominant weighting schemes used in constructing stock market indexes, and compute a price-weighted, value-weighted and un-weighted index series for three stocks.
| 5,000,000 shares | |
|---|---|
| -- Issued | 4,000,000 shares |
|
$20,000,000 |
|
$5,000,000 |
| $10,000,000 | |
| $21 |
Answer: B
“Introduction to Price Multiples,” John D. Stowe, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 191-193
Study Session 14-59-b
Calculate and interpret P/E, P/BV, P/S, and P/CF.Answer: A
“Organizing and Functioning of Securities Markets,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA, and Keith C. Brown, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 14-15
Study Session 13-52-c
Distinguish between call and continuous markets.
“Introduction to Price Multiples,” John D. Stowe, CFA, Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jerald E. Pinto, CFA, and Dennis W. McLeavey, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 194-196
Study Session 14-59-b
Calculate and interpret P/E, P/BV, P/S, and P/CF.Inventory Adjustment = $400,000 x 0.70 = $280,000: (FIFO – LIFO values) x (1-Tax rate)
BV per share = $1 m + $10 m + $4 m + $0.28 m = $15.28 / 2 m sh. = $7.64.
| €2.00 | |
|---|---|
| Growth rate in dividend during the next three years |
|
|
8% |
| 12% | |
| 15% |
Answer: A
“An Introduction to Security Valuation,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA, and Keith C. Brown, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 132-135
Study Session 14-56-c
Calculate and interpret the value both of a preferred stock and a common stock using the dividend discount model (DDM).
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Company | ||
|---|---|---|
| Weighted average cost of capital (WACC) | 14% | 12% |
| 20% | 15% | |
| 0 % | 1.2% | |
|
$53 | N/A |
|
$50 | N/A |
The company is a growth company since the spread between ROA and WACC is larger than the industry average and its dividend yield is 0% compared to the industry average of 1.2%. The company’s stock is a growth stock considering its under-valuation. A speculative stock, on the other hand, would be overvalued.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Answer: B
“Understanding the Cash Flow Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp. 279-280
“An Introduction to Security Valuation,” Frank K. Reilly, CFA, and Keith C. Brown, CFA
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, p. 135
Study Session 8-34-i, 14-56-g
Explain and calculate free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to equity, and other cash flow ratios.B.Diversifying completely on a global basis.
C.Paying close attention to the monetary policy environment.
portfolio management is appropriate for portfolio managers with access to superior analysts.
88.An analyst gathers the following data about a company in order to estimate its price/earnings (P/E) ratio.
The P/E ratio is closest to:
A.6.7 x.
Describe a process for developing estimated inputs to be used in the DDM, including the required rate of return and expected growth rate of dividends.
Growth rate = g = RR x ROE = (1 - 0.40) x 15 = 9%; P/E1 = D1/E1 ÷ (k - g) = 0.40 ÷ (0.12 - 0.09) = 13.33
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, R. Elaine Henry, CFA and Michael A. Broihahn
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 3, pp. 520-525By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
A.A large number of profit-maximizing participants analyze and value securities.
B.New information regarding securities comes to the market in a predictable manner.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Questions 91 through 96 relate to Derivative Investments.
Answer: C
“Futures Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 6, pp. 53-57
Study Session 17-69-c
Describe price limits and the process of marking to market, and compute and interpret the margin balance, given the previous day’s balance and the change in the futures price.
|
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
Answer: C
“Option Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 6, pp. 98-101
Study Session 17-70-h
Calculate and interpret the lowest prices of European and American calls and puts based on the rules for minimum values and lower bounds.B.A put is equivalent to a long call, a long position in the underlying asset, and a long position in the risk-free asset.
C.A call is equivalent to a long put, a long position in the underlying asset, and a short position in the risk-free asset.
The payment made at expiration is closest to:
A.$ 12,376 from the investor to the dealer
B.$ 12,376 from the dealer to the investor
C.$ 16,570 from the investor to the dealer
“Risk Management Applications of Option Strategies”, Don M. Chance
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 6, pp. 152-156
Study Session 17-72-a
Determine the value at expiration, profit, maximum profit, maximum loss, breakeven underlying price at expiration, and general shape of the graph of the strategies of buying and selling calls and puts, and indicate the market outlook of investors using these strategies.Profit = max (0, -value of put at expiration + premium) = max (0, -(X-S) +premium) = -1+2.25 = $1.25
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
strategy and a protective put strategy, and explain the risk management application of each strategy.
B.more than the option-free bond.
C.the same amount as the option-free bond.
A.volatility risk and credit risk.
B.event risk and interest rate risk.
C.volatility risk and yield curve risk.The investor faces event risk in a corporate bond and interest rate risk in a long-dated, fixed coupon bond.
99.All else equal, an increase in expected yield volatility is most likely to result in an increase in the price of a(n):
“Risks Associated with Investing in Bonds,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, p. 260
Study Session 15-61-n
Explain how yield volatility affects the price of a bond with an embedded option and how changes in volatility affect the value of a callable bond and a putable bond.An increase in expected yield volatility increases the price of an embedded option. The price of a putable bond will increase because the price of the putable bond is equal to the price of an option-free bond plus the value of the put option.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
“Risks Associated with Investing in Bonds,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 242, 252-253
Study Session 15-61-c, i
Explain how features of a bond (e.g., maturity, coupon, and embedded options) and the level of a bond’s yield affect the bond’s interest rate risk;
Identify the factors that affect the reinvestment risk of a security and explain why prepayable amortizing securities expose investors to greater reinvestment risk than nonamortizing securities.Since both securities have essentially the same maturity, all else the same, the bond with the lower coupon rate will have a higher sensitivity to changes in interest rates. The higher the yield on the bond, the more the reinvestment risk, because the investor must be able to reinvest at the same yield.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
102.For an A- rated corporate bond that has deteriorating fundamentals, but is expected to remain investment grade, the greatest risk is most likely:
103.The difference between nominal spread and zero-volatility spread will most likely be greatest for a mortgage-backed security:
A.in an inverted yield curve environment.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
104.A fixed income portfolio manager is evaluating investments in the mortgage market but is concerned about prepayment risk. The security that will most likely minimize prepayment risk is:
“Overview of Bond Sectors and Instruments,” Frank J. Fabozzi 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 281-288
Study Session 15-62-f
State the motivation for creating a collateralized mortgage obligation.A collateralized mortgage obligation or CMO, is structured to distribute
prepayment risk among different classes or tranches of bonds. Tranche A would be repaid first, followed by tranche B, then C, etc.“Overview of Bond Sectors and Instruments,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 294-296
Study Session 15-62-h
Describe the characteristics and motivation for the various types of debt issued by corporations (including corporate bonds, medium-term notes, structured notes, commercial paper, negotiable CDs, and bankers acceptances).A debenture bond is unsecured and would be expected to recover less should the company file for bankruptcy, while mortgage and collateral trust bonds are secured by real property.
“Understanding Yield Spread,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 335-336
Study Session 16-63-e, i
Compute, compare, and contrast the various yield spread measures.Compute the after-tax yield of a taxable security and the tax-equivalent yield of a tax-exempt security.
| Period | Years | Credit Spread (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
“Introduction to the Valuation of Debt Securities,” Frank J. Fabozzi 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 366-371
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
| Bond | Price ($) | Par Amount Owned | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 102.000 | $7 million | 1.89 |
| B | 94.356 | $5 million | 7.70 |
| C | 88.688 | $3 million | 11.55 |
“Introduction to the Measurement of the Interest Rate Risk,” Frank J. Fabozzi 2009 Modular Level I, Volume 5, pp. 468
Study Session 16-66-f
Compute the duration of a portfolio, given the duration of the bonds comprising the portfolio, and explain the limitations of portfolio duration.Portfolio value = (1.02 × 7 mil) + (0.94356 × 5 mil) + (0.88688 × 3 mil) = 14,518,440
Weight, Bond A = 7,140,000 / 14,518,440 = 0.492
Weight, Bond B = 4,717,800 / 14,518,440 = 0.325
Weight, Bond C = 2,660,640 / 14,518,440 = 0.183
Portfolio duration = (0.492 × 1.89) + (0.325 × 7.70) + (0.183 × 11.55) = 5.55Answer: C
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 6, pp. 214-215
Study Session 18-73-l
Discuss the performance of hedge funds, the biases present in hedge fund performance measurement, and explain the effect of survivorship bias on the reported return and risk measures for a hedge fund database.Answer: B
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 6, p. 200
Study Session 18-73-g
Explain the stages of venture capital investing, venture capital investment characteristics and challenges to venture capital valuation and performance measurement.B.Emerging-market funds.
C.Distressed securities funds.Answer: B
B.returns being understated.
C.correlations with other assets being overstated.
113.Which of the following is the least accurate approach used to value closely held companies? Basing the value of company on the:
A.present value of future economic income.
This is not a method used to value closely held companies. The correct method is to base it on the replacement cost of the company’s assets.
114.The primary motivation for investing in commodity-linked bonds is that they most likely provide:
“Alternative Investments”, Bruno Solnik, and Denis McLeavy
2009 Modular Level I, Volume 6, pp. 225-226
Study Session 18-73-q
Explain the motivation for investing in commodities, commodities derivatives, and commodity-linked securities.The primary reason for investing in commodity-linked bonds is that they provide the investor with an income stream.
B.prohibited from investing in tobacco companies.
C.prohibited from holding less than 5% in cash instruments.
A.stock selection.
B.asset allocation.
C.risk management.117.The risk-free interest rate is 5 percent, and the return on market portfolio is 8 percent. A stock with a beta of 0.5 that has an estimated rate of return of 7 percent is most likely:
A.overvalued.
The required return = E(Ri)= RFR + i (E(Rm)- RFR) = 5 +0.5(8-5) = 6.5. But the estimated return is 7%. Therefore the stock is undervalued because its estimated return, given the risk, lies above the SML, i.e. 7% > 6.5%.
118.The minimum variance zero-beta portfolio most likely has some:
Specifically within the set of feasible alternative portfolios, several portfolios exist where the returns are completely uncorrelated with the market portfolio; the beta of these portfolios with the market portfolio is zero. From among the several zero-beta portfolios, you would select one with minimum variance. This portfolio does not have any systematic risk (beta = 0), but it does have some unsystematic risk.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
Investors maximize one-period expected utility, and their utility curves demonstrate diminishing marginal utility of wealth.
120.Compared to the traditional Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), where lending and borrowing are carried out at the risk-free rate, a zero-beta CAPM would most likely result in a security market line (SML) with:
Compared to the traditional CAPM, where lending and borrowing takes place at the risk-free rate, a zero beta CAPM will result in a SML that has a higher intercept and a flatter slope.
By accessing this mock exam, you agree to the following terms of use: This mock exam is provided to currently-registered CFA candidates. Candidates may view and print the exam for personal exam preparation only. The following activities are strictly prohibited and may result in disciplinary and/or legal action: accessing or permitting access by anyone other than currently-registered CFA candidates; copying, posting to any website, emailing, distributing and/or reprinting the mock exam for any purpose.
C. consist of required provisions for firms to follow to achieve best practice.
D. must be applied with the goal of achieving excellence in performance presentation.
D. using client brokerage to purchase goods or services that are used in the investment decision-making process.
2Correct answer is B
Guidance for Standards I-VII, Standards of Practice Handbook
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 50 Study Session 1-2-a demonstrate a
thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional
Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to specifi c situations
presenting multiple issues of questionable professional conduct A fi
duciary who votes blindly with management on non-routine governance
issues may breach their duty to clients by violating the standard that
relates to loyalty, prudence, and care.
D. Yes, because her allocation procedures contribute to market manipulation of initial public offerings.
3Correct answer is B
Guidance for Standards I-VII, Standards of Practice Handbook
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 50-55, 94-95, 98, Example 3 Study
Session 1-2-a demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and
Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to
specifi c situations presenting multiple issues of questionable
professional conduct B is correct because Scott’s method of allocating
oversubscribed IPOs discriminates against her uncle, who is a fee-paying
client; she violates the Standard related to Fair Dealing. Family
accounts that are fee-paying client accounts should be treated like any
other fi rm account. They should neither receive special treatment nor
be disadvantaged because of an existing family relationship.
C. initiate an investigation to determine the extent of the wrongdoing.
D. demand that the employee involved provide assurances that the activity will not be repeated.
6、David Gunard, CFA, is an equity analyst at Curry Securities. He receives an assignment to analyze Enterloch Corporation, a stock owned by several of Curry's clients. Gunard completes a thorough, fundamental analysis of Enterloch. Given his analysis and the sharp rise in the company's stock price during the past year, Gunard concludes that the shares are substantially overvalued. After the report is approved by Gunard's supervisor, but prior to the release

| reasonable basis? | ||
| A. | No | |
| B. | Yes | |
| C. | No | |
| D. | Yes | |
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.
Guidance for Standards I-VII, Standards of Practice
Handbook
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 36-39
Study Sessions 1-1-c, 1-2-b
explain the ethical responsibilities required by the Code and Standards,
including the multiple subsections of each Standard;

| any other examination? | ||
| A. | No | |
| B. | Yes | |
| C. | No | |
| D. | Yes | |
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
C. his reputation.
D. the employer's reputation.
9 Correct answer is A
B. Yes, because he failed to obtain consent from his employer.
C. Yes, because he failed to disclose his new employment to his existing clients.
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. No.B. Yes, because the performance should be stated net of fees.
12、Crandall Temasek, CFA, filed for personal bankruptcy two years ago after incurring large medical expenses. He was hired recently as a portfolio manager. According to the CFA Institute Standards, must Temasek disclose his bankruptcy filing to his new employer?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. No.
Standards of Practice Handbook, 9th edition (CFA Institute,
2005), p. 33
Standards I-VII
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 35
Study Session 1-2-a
demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of
Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to specific
situations presenting multiple issues of questionable professional
conduct
Members who are involved in a personal bankruptcy filing are not
automatically assumed to be in violation of the standards because
bankruptcy may not reflect poorly on the integrity or trustworthiness of
the person involved.
13、Sallie Lewis, CFA, is a research analyst covering the mining industry. Along with other analysts, Lewis visits the primary mine of Gold Rush Mines (GR). During the visit, a major piece of equipment fails and Lewis overhears an
D. Yes, with respect to material nonpublic information.
13 Correct answer is C
Standards of Practice Handbook, 9th edition (CFA Institute,
2005), pp. 37-40
Standards I-VII
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 36-39
Study Session 1-2-a
demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of
Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to specific
situations presenting multiple issues of questionable professional
conduct
Lewis must investigate the reliability of the information before making
an investment recommendation based on the information.
B. Yes, with respect to suitability.
C. Yes, with respect to fair dealing.
15、Narupa Rhasta, CFA, is manager of the fast-growing individual account division of a bank and treats all clients equally. When the bank's research department issues a buy or sell recommendation on a security, she ensures that the recommended action is implemented in all accounts. Do Rhasta's investment actions violate any CFA Institute Standards?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. No.
Standards of Practice Handbook, 9th edition (CFA Institute,
2005), pp. 69-71
Standards I-VII
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 60-62
Study Session 1-2-a
demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of
Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to specific
situations presenting multiple issues of questionable professional
conduct
Members must consider the needs, circumstances and objectives of clients
when taking investment action for their accounts. By treating all
accounts as if they were the same, Rhasta failed to consider the
uniqueness of each client’s circumstances.
16、Jimmy Lee, CFA, is an investment banker in a country with strict confidentiality laws. He is working on an acquisition for Panda Mining Co. (PMC). While performing due diligence, Lee notices that PMC has a number of questionable offshore partnerships. He investigates the legality of the partnerships and finds evidence of illegal activity.
16 Correct answer is C
Standards of Practice Handbook, 9th edition (CFA Institute,
2005), pp. 79-80
Standards I-VII
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 67-68
Study Session 1-2-a
demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of
Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to specific
situations presenting multiple issues of questionable professional
conduct
Members must keep client information confidential and must comply with
applicable law. If applicable law requires disclosure of client
information in certain circumstances, members and candidates must comply
with the law. If applicable law requires members to maintain
confidentiality, even if the information concerns illegal activities on
the part of the client, members should not disclose such information.
Lee’s best course of action would be to consult with outside counsel to
determine applicable law.
C. Yes, with respect to disclosure of conflicts.
D. Yes, with respect to additional compensation.
B. Yes, with respect to conflict of interest.
C. Yes, with respect to additional compensation.
B. maturity.
C. default risk.
Runkel
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 172-174
Study Session 2-5-b
explain an interest rate as the sum of a real risk-free rate, expected
inflation, and premiums that compensate investors for distinct types of
risk
The difference in yield on otherwise identical U.S Treasury and
corporate bonds is attributed to default risk.
20、Rachel Kelly, age 24, is planning for
retirement. Kelly's annual consumption expenditures are currently
$30,000. She assumes her consumption expenditures will increase with the
rate of inflation, which she expects to average 3% until she retires at
age 68. Given a life expectancy of 83 years and constant expenditures in
retirement, the amount Kelly must accumulate by her retirement date,
assuming an 8% rate of return on her retirement account, is closest
to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. $320,000.
“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W. McLeavey,
Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp.
190-208
Study Session 2-5-d, e
calculate and interpret the future value (FV) and present value (PV) of
a single sum of money, an ordinary annuity, an annuity due, a perpetuity
(PV only), and a series of unequal cash flows;
draw a time line, specify a time index, and solve time value of money
applications (for example, mortgages and savings for college tuition or
retirement)
Kelly expects her consumption spending (currently $30,000 annually) to
increase with the rate of inflation (3%) over the next 44 years until
she retires. Her annual consumption spending at the time she retires
will be $110,143.57 (PV = 30,000, %I = 3, N = 44, solve for FV). To
support that level of spending for 25 years of retirement, assuming an
8% return on her retirement account, she must accumulate $1,175,756 by
her retirement date (PMT = 110,143.57, N = 25, %I = 8, solve for
PV).
21、An analyst gathered the following information about a capital investment's cash flows:

“Discounted Cash Flow Applications,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W.
McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 214-216
Study Session 2-6-a
calculate and interpret the net present value (NPV) and the internal
rate of return (IRR) of an investment, contrast the NPV rule to the IRR
rule, and identify problems associated with the IRR rule
The NPV equals the present value (at time = 0) of the future cash flows
discounted at the opportunity cost of capital (12%) minus the initial
investment, or $10,558 (CF0 = -500,000, CF1 = 100,000, CF2 = 200,000,
CF3 = 100,000, CF4 = 300,000, I = 12, solve for NPV = 10,557.94 ≈
10,558).
The holding period return on the common stock investment is
closest to: Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the
following:
A. 12.5%.
B. 20.8%.
23、A 270-day U.S. Treasury bill with a face value of $100,000 sells for $96,500 when issued. Assuming an investor holds the bill to maturity, the investor's money market yield and effective annual yield, respectively, are closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
24、An analyst gathered the following information about the price-earnings (P/E) ratios for the common stocks held in a
foundation's portfolio:
D. Answer D.
24 Correct answer is B
25、An analyst gathered the following annual return information about a portfolio since its inception on 1 January 2003:
The portfolio's mean absolute deviation and variance of annual returns, respectively, for the five-year period are closest to:
| Variance | ||
| A. | 77.5 | |
| B. | 96.8 | |
| C. | 77.5 | |
| D. | 96.8 | |
25 Correct answer is A
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E.
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
27、If an analyst estimates the probability of an
event for which there is no historical record, this probability is best
described as:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. a priori.
B. objective.
28、Which of the following statements regarding
correlation and covariance is most likely correct? The correlation
between two random variables is their covariance standardized by
the:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. product of the variables' variances.
B. variance of the dependent variable.
“Probability Concepts,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W. McLeavey,
Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 342-347
Study Session 2-8-j
calculate and interpret covariance and correlation
The correlation between two random variables is equal to the covariance
between the variables divided by the product of the variables’ standard
deviations.
29、Which of the following best describes the
discrete uniform distribution? The discrete uniform distribution:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. has a finite number of specified outcomes.
30、An analyst determined that the sample mean and
variance for a normal distribution are 42 and 9, respectively. The 99%
confidence interval for this random variable is closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. 15.0 to 69.0.
B. 18.8 to 65.2.
31、According to the central limit theorem, a
sampling distribution of the sample mean will be approximately normal
only if the:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. sample size n is large.
B. underlying distribution is normally distributed.

2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 428-429
Study Session 2-10-d
interpret the central limit theorem and describe its importance
According to the central limit theorem, the sample mean of a population
described by any probability distribution can be determined if
the sample size n is sufficiently large, e.g., equal to or
greater than 30. This process is used to estimate the population mean
and standard deviation, which usually are unknown.
32 Correct answer is B
“Sampling and Estimation,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W. McLeavey,
Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp.
432-433
Study Session 2-10-g
identify and describe the desirable properties of an estimator
The three desirable properties of an estimator are unbiasedness,
efficiency, and consistency.
| Solution from Nash equilibrium | ||
| A. | both prisoners deny | |
| B. | both prisoners confess | |
| C. | both prisoners deny | |
| D. | both prisoners confess | |
D. Answer D.
33 Correct answer is B
| A. | buyers pay the entire tax. | buyers pay the entire tax. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. | sellers pay the entire tax. | |||
| C. | buyers pay the entire tax. | |||
| D. | sellers pay the entire tax. | |||
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.B. Answer B.
35、Venkat Reddy is very fond of mango fruits. If
mangoes cost 10 rupees each, Reddy spends his budget on fruits that he
values more highly than mangoes. However, at 4 rupees each Reddy buys 20
mangoes for devouring over a one-week period. The total consumer surplus
in rupees for Venkat would be closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. 13.
B. 26.
36 、The Laffer curve depicts a relationship between which of the following sets of two economic variables and its proponents belong to which group of economists?
D. Answer D.
36 Correct answer is B
“Organizing Production,” Michael Parkin
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 92-95
Study Session 4-16-a
explain the types of opportunity cost and their relation to economic
profit, and calculate economic profit
38、Which of the following provides the best description of the effect of subsidies on the prices of goods and the relationship between marginal cost and marginal benefit?
| A. | ||
| B. | ||
| C. | ||
| D. |
|
|
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
D. Answer D.
39 Correct answer is B
C. 1.40.
D. 1.50.
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| private saving | ||||
|
|
|||
|
||||
|
|
|||
|
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
41 Correct answer is A
D. Answer D.
42 Correct answer is C
| Inelastic demand | ||
| A. | ||
| B. | ||
| C. |
|
|
| D. |
|
|
43 Correct answer is C
“Elasticity,” Michael Parkin
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 15-16
Study Session 4-13-b
calculate elasticities on a straight-line demand curve, differentiate
among elastic, inelastic, and unit elastic demand and describe the
relation between price elasticity of demand and total revenue
When demand is elastic, a decrease in price by 1% increases the quantity
sold by more than 1% and it results in an increase in total revenue. But
when demand is inelastic, a decrease in price by 1% increases the
quantity sold by less than 1% and it results in a decrease in total
revenue.
D. the employment-to-population ratio.
44 Correct answer is B
“Monitoring Cycles, Jobs, and the Price Level,” Michael Parkin
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 288-289
Study Session 5-22-a
describe the phases of the business cycle, define an unemployed person,
and interpret the main labor market indicators and their relation to the
business cycle
The three indicators of the state of the labor market that the U.S.
Census Bureau calculates are: the unemployment rate, the labor force
participation rate, and the employment-to-population ratio.
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van
Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 590-592
“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., Kenneth L.
Parkinson, and Pamela p. Peterson 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp.
89-92
Study Session 10-41-d, 11-46-a
calculate and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability,
and valuation ratios;
calculate and interpret liquidity measures using selected financial
ratios for a company and compare it with peer companies
An increase in receivables turnover would indicate that receivables were
outstanding for a shorter period of time, decreasing the cash conversion
cycle.
46、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.

“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van
Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 574-575, 590-592
“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., Kenneth L.
Parkinson, and Pamela p. Peterson 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp.
89-90
Study Session 10-41-a, d, 11-46-a
evaluate and compare companies using ratio analysis, common-size
financial statements, and charts in financial analysis;
calculate and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability,
and valuation ratios;
calculate and interpret liquidity measures using selected financial
ratios for a company and compare it with peer companies
The current ratio includes inventory but the quick ratio does not.
(Current ratio is higher than quick ratio and quick ratio is higher than
cash ratio.) The quick ratio includes accounts receivable but the cash
ratio does not. The denominator for all three ratios is current
liabilities, which are the same proportion for both companies. The
difference in ratios is therefore created by inventory and accounts
receivable. Company 1 has the higher percentage of inventory because the
difference between the current ratio and quick ratio is greater for that
company. Company 2 had the higher percentage of accounts receivable
because the difference between the quick ratio and the cash ratio is
greater for Company 2.
47、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted. An analyst gathered the following information for a company:
All other factors being equal, which of the following is the best conclusion with respect to the information above? From
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn

B. the company's cash flow from operations, but not the company's current ratio.
C. both the company's current ratio and the company's cash flow from operations.
several years ago and had accumulated depreciation of $70,000 for the equipment at the time of sale. All else equal, the
equipment sale will result in the company's cash flow from:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. investing activities decreasing by $10,000.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 251-252, 271-272, 275-276
In 2007, a company reported net income of $130 million and cash flow from operations of $120 million. All else equal, the most likely explanation for the difference between net income and cash flow from operations in 2007 is that the company:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. tightened credit policies and increased collection efforts during the year.B. purchased new property, plant, and equipment at the beginning of the year.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 267-271, 276-277
Study Session 8-34-h
analyze and interpret a cash flow statement using both total currency
amounts and common-size cash flow statements The increase in inventory
(working capital investment) would reduce cash flow from operations
relative to net income.
51、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
B. 58.4.
C. 61.6.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 275-278, 287-288
Study Session 8-34-i
explain and calculate free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to
equity, and other cash flow ratios
Free cash flow to equity in a company without any debt is equal to cash
flow from operations (CFO) less capital expenditures. CFO = net income +
depreciation + loss on sale of equipment + decrease in accounts
receivable - increase in inventories + increase in accounts payable.
(The loss on sale of equipment is added back when calculating CFO. It
would have been deducted in the calculation of net income but the loss
is not the cash impact of the transaction (the proceeds received, if
any, would be the cash effect) and cash flows related to equipment
transactions are investing activities, not operating activities.)
CFO = 45.8 + 18.2 + 1.6 + 4.2 - 3.4 + 2.5 = $68.9 million
$68.9 - $7.3 = $61.6 million free cash flow to equity.
52、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted. Which of the following statements best describes the level of accuracy provided by a standard audit report?
52 Correct answer is D
“Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction,” Thomas R. Robinson,
Jan Hennie van Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 21
Study Session 7-29-d
discuss the objective of audits of financial statements, the types of
audit reports, and the importance of effective internal controls
Audits provide reasonable assurance that the financial statements are
fairly presented, meaning that there is a high degree of probability
that they are free of material error, fraud or illegal acts.
54、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
During 2007 Nagano Incorporated, a manufacturing company, reported the following items on their income statement:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.B. Answer B.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 169-171
Study Session 8-32-f
distinguish between the operating and nonoperating components of the
income statement
The loss on the disposal of fixed assets is an unusual or infrequent
item but it is still part of normal operating activities.
The interest expense is the result of financing activities and would be classified as a nonoperating expense by nonfinancial service companies.
The working capital for the company is closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. $14,900.B. $64,900.
“Understanding the Balance Sheet,” Thomas R. Robinson, Jan Hennie van Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 201-207
Study Session 8-33-a, d
illustrate and interpret the components of the assets, liabilities, and
equity sections of the balance sheet, and discuss the uses of the
balance sheet in financial analysis;
compare and contrast current and noncurrent assets and liabilities
Working capital = current assets - current liabilities.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 218-220
“Analysis of Long-Lived Assets: Part I – The Capitalization Decision,”
Gerald I. White, Ashwinpaul C. Sondhi, and Dov Fried
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 354-355
Study Sessions 8-33-e, 9-36-b
explain the measurement bases (e.g., historical cost and fair value) of
assets and liabilities, including current assets, current liabilities,
tangible assets, and intangible assets;
determine which intangible assets, including software development costs
and research and development costs, should be capitalized, according to
U.S. GAAP and international accounting standards
The purchased customer list is an identifiable intangible because it can
be sold separately from the company and it would be recorded at its fair
market value, the amount paid for it in the acquisition, $50,000. The
amount spent by Popular on its own lists, $15,000, would have to be
expensed because internally generated intangibles are not
capitalized.

| A. | Increase | |
| B. | Decrease | |
| C. | Increase | |
| D. | Decrease | |
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
58、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
Which of the following factors is an analyst least likely to consider when determining if a company's deferred tax liabilities should be treated as a liability or equity?
58 Correct answer is B
“Analysis of Income Taxes,” Gerald I. White, Ashwinpaul C. Sondhi,
and Dov Fried
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 439-440
Study Session 9-38-d
explain the factors that determine whether a company’s deferred tax
liabilities should be treated as a liability or as equity
C. consist of required provisions for firms to follow to achieve best practice.
D. must be applied with the goal of achieving excellence in performance presentation.
D. using client brokerage to purchase goods or services that are used in the investment decision-making process.
2Correct answer is B
Guidance for Standards I-VII, Standards of Practice Handbook
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 50 Study Session 1-2-a demonstrate a
thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional
Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to specifi c situations
presenting multiple issues of questionable professional conduct A fi
duciary who votes blindly with management on non-routine governance
issues may breach their duty to clients by violating the standard that
relates to loyalty, prudence, and care.
D. Yes, because her allocation procedures contribute to market manipulation of initial public offerings.
3Correct answer is B
Guidance for Standards I-VII, Standards of Practice Handbook
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 50-55, 94-95, 98, Example 3 Study
Session 1-2-a demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and
Standards of Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to
specifi c situations presenting multiple issues of questionable
professional conduct B is correct because Scott’s method of allocating
oversubscribed IPOs discriminates against her uncle, who is a fee-paying
client; she violates the Standard related to Fair Dealing. Family
accounts that are fee-paying client accounts should be treated like any
other fi rm account. They should neither receive special treatment nor
be disadvantaged because of an existing family relationship.
C. initiate an investigation to determine the extent of the wrongdoing.
D. demand that the employee involved provide assurances that the activity will not be repeated.
6、David Gunard, CFA, is an equity analyst at Curry Securities. He receives an assignment to analyze Enterloch Corporation, a stock owned by several of Curry's clients. Gunard completes a thorough, fundamental analysis of Enterloch. Given his analysis and the sharp rise in the company's stock price during the past year, Gunard concludes that the shares are substantially overvalued. After the report is approved by Gunard's supervisor, but prior to the release

| reasonable basis? | ||
| A. | No | |
| B. | Yes | |
| C. | No | |
| D. | Yes | |
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.
Guidance for Standards I-VII, Standards of Practice
Handbook
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 36-39
Study Sessions 1-1-c, 1-2-b
explain the ethical responsibilities required by the Code and Standards,
including the multiple subsections of each Standard;

| any other examination? | ||
| A. | No | |
| B. | Yes | |
| C. | No | |
| D. | Yes | |
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
C. his reputation.
D. the employer's reputation.
9 Correct answer is A
B. Yes, because he failed to obtain consent from his employer.
C. Yes, because he failed to disclose his new employment to his existing clients.
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. No.B. Yes, because the performance should be stated net of fees.
12、Crandall Temasek, CFA, filed for personal bankruptcy two years ago after incurring large medical expenses. He was hired recently as a portfolio manager. According to the CFA Institute Standards, must Temasek disclose his bankruptcy filing to his new employer?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. No.
Standards of Practice Handbook, 9th edition (CFA Institute,
2005), p. 33
Standards I-VII
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 35
Study Session 1-2-a
demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of
Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to specific
situations presenting multiple issues of questionable professional
conduct
Members who are involved in a personal bankruptcy filing are not
automatically assumed to be in violation of the standards because
bankruptcy may not reflect poorly on the integrity or trustworthiness of
the person involved.
13、Sallie Lewis, CFA, is a research analyst covering the mining industry. Along with other analysts, Lewis visits the primary mine of Gold Rush Mines (GR). During the visit, a major piece of equipment fails and Lewis overhears an
D. Yes, with respect to material nonpublic information.
13 Correct answer is C
Standards of Practice Handbook, 9th edition (CFA Institute,
2005), pp. 37-40
Standards I-VII
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 36-39
Study Session 1-2-a
demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of
Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to specific
situations presenting multiple issues of questionable professional
conduct
Lewis must investigate the reliability of the information before making
an investment recommendation based on the information.
B. Yes, with respect to suitability.
C. Yes, with respect to fair dealing.
15、Narupa Rhasta, CFA, is manager of the fast-growing individual account division of a bank and treats all clients equally. When the bank's research department issues a buy or sell recommendation on a security, she ensures that the recommended action is implemented in all accounts. Do Rhasta's investment actions violate any CFA Institute Standards?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. No.
Standards of Practice Handbook, 9th edition (CFA Institute,
2005), pp. 69-71
Standards I-VII
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 60-62
Study Session 1-2-a
demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of
Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to specific
situations presenting multiple issues of questionable professional
conduct
Members must consider the needs, circumstances and objectives of clients
when taking investment action for their accounts. By treating all
accounts as if they were the same, Rhasta failed to consider the
uniqueness of each client’s circumstances.
16、Jimmy Lee, CFA, is an investment banker in a country with strict confidentiality laws. He is working on an acquisition for Panda Mining Co. (PMC). While performing due diligence, Lee notices that PMC has a number of questionable offshore partnerships. He investigates the legality of the partnerships and finds evidence of illegal activity.
16 Correct answer is C
Standards of Practice Handbook, 9th edition (CFA Institute,
2005), pp. 79-80
Standards I-VII
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 67-68
Study Session 1-2-a
demonstrate a thorough knowledge of the Code of Ethics and Standards of
Professional Conduct by applying the Code and Standards to specific
situations presenting multiple issues of questionable professional
conduct
Members must keep client information confidential and must comply with
applicable law. If applicable law requires disclosure of client
information in certain circumstances, members and candidates must comply
with the law. If applicable law requires members to maintain
confidentiality, even if the information concerns illegal activities on
the part of the client, members should not disclose such information.
Lee’s best course of action would be to consult with outside counsel to
determine applicable law.
C. Yes, with respect to disclosure of conflicts.
D. Yes, with respect to additional compensation.
B. Yes, with respect to conflict of interest.
C. Yes, with respect to additional compensation.
B. maturity.
C. default risk.
Runkel
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 172-174
Study Session 2-5-b
explain an interest rate as the sum of a real risk-free rate, expected
inflation, and premiums that compensate investors for distinct types of
risk
The difference in yield on otherwise identical U.S Treasury and
corporate bonds is attributed to default risk.
20、Rachel Kelly, age 24, is planning for
retirement. Kelly's annual consumption expenditures are currently
$30,000. She assumes her consumption expenditures will increase with the
rate of inflation, which she expects to average 3% until she retires at
age 68. Given a life expectancy of 83 years and constant expenditures in
retirement, the amount Kelly must accumulate by her retirement date,
assuming an 8% rate of return on her retirement account, is closest
to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. $320,000.
“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W. McLeavey,
Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp.
190-208
Study Session 2-5-d, e
calculate and interpret the future value (FV) and present value (PV) of
a single sum of money, an ordinary annuity, an annuity due, a perpetuity
(PV only), and a series of unequal cash flows;
draw a time line, specify a time index, and solve time value of money
applications (for example, mortgages and savings for college tuition or
retirement)
Kelly expects her consumption spending (currently $30,000 annually) to
increase with the rate of inflation (3%) over the next 44 years until
she retires. Her annual consumption spending at the time she retires
will be $110,143.57 (PV = 30,000, %I = 3, N = 44, solve for FV). To
support that level of spending for 25 years of retirement, assuming an
8% return on her retirement account, she must accumulate $1,175,756 by
her retirement date (PMT = 110,143.57, N = 25, %I = 8, solve for
PV).
21、An analyst gathered the following information about a capital investment's cash flows:

“Discounted Cash Flow Applications,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W.
McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 214-216
Study Session 2-6-a
calculate and interpret the net present value (NPV) and the internal
rate of return (IRR) of an investment, contrast the NPV rule to the IRR
rule, and identify problems associated with the IRR rule
The NPV equals the present value (at time = 0) of the future cash flows
discounted at the opportunity cost of capital (12%) minus the initial
investment, or $10,558 (CF0 = -500,000, CF1 = 100,000, CF2 = 200,000,
CF3 = 100,000, CF4 = 300,000, I = 12, solve for NPV = 10,557.94 ≈
10,558).
The holding period return on the common stock investment is
closest to: Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the
following:
A. 12.5%.
B. 20.8%.
23、A 270-day U.S. Treasury bill with a face value of $100,000 sells for $96,500 when issued. Assuming an investor holds the bill to maturity, the investor's money market yield and effective annual yield, respectively, are closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
24、An analyst gathered the following information about the price-earnings (P/E) ratios for the common stocks held in a
foundation's portfolio:
D. Answer D.
24 Correct answer is B
25、An analyst gathered the following annual return information about a portfolio since its inception on 1 January 2003:
The portfolio's mean absolute deviation and variance of annual returns, respectively, for the five-year period are closest to:
| Variance | ||
| A. | 77.5 | |
| B. | 96.8 | |
| C. | 77.5 | |
| D. | 96.8 | |
25 Correct answer is A
“Statistical Concepts and Market Returns,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E.
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
27、If an analyst estimates the probability of an
event for which there is no historical record, this probability is best
described as:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. a priori.
B. objective.
28、Which of the following statements regarding
correlation and covariance is most likely correct? The correlation
between two random variables is their covariance standardized by
the:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. product of the variables' variances.
B. variance of the dependent variable.
“Probability Concepts,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W. McLeavey,
Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 342-347
Study Session 2-8-j
calculate and interpret covariance and correlation
The correlation between two random variables is equal to the covariance
between the variables divided by the product of the variables’ standard
deviations.
29、Which of the following best describes the
discrete uniform distribution? The discrete uniform distribution:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. has a finite number of specified outcomes.
30、An analyst determined that the sample mean and
variance for a normal distribution are 42 and 9, respectively. The 99%
confidence interval for this random variable is closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. 15.0 to 69.0.
B. 18.8 to 65.2.
31、According to the central limit theorem, a
sampling distribution of the sample mean will be approximately normal
only if the:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. sample size n is large.
B. underlying distribution is normally distributed.

2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 428-429
Study Session 2-10-d
interpret the central limit theorem and describe its importance
According to the central limit theorem, the sample mean of a population
described by any probability distribution can be determined if
the sample size n is sufficiently large, e.g., equal to or
greater than 30. This process is used to estimate the population mean
and standard deviation, which usually are unknown.
32 Correct answer is B
“Sampling and Estimation,” Richard A. Defusco, Dennis W. McLeavey,
Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp.
432-433
Study Session 2-10-g
identify and describe the desirable properties of an estimator
The three desirable properties of an estimator are unbiasedness,
efficiency, and consistency.
| Solution from Nash equilibrium | ||
| A. | both prisoners deny | |
| B. | both prisoners confess | |
| C. | both prisoners deny | |
| D. | both prisoners confess | |
D. Answer D.
33 Correct answer is B
| A. | buyers pay the entire tax. | buyers pay the entire tax. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. | sellers pay the entire tax. | |||
| C. | buyers pay the entire tax. | |||
| D. | sellers pay the entire tax. | |||
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.B. Answer B.
35、Venkat Reddy is very fond of mango fruits. If
mangoes cost 10 rupees each, Reddy spends his budget on fruits that he
values more highly than mangoes. However, at 4 rupees each Reddy buys 20
mangoes for devouring over a one-week period. The total consumer surplus
in rupees for Venkat would be closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. 13.
B. 26.
36 、The Laffer curve depicts a relationship between which of the following sets of two economic variables and its proponents belong to which group of economists?
D. Answer D.
36 Correct answer is B
“Organizing Production,” Michael Parkin
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 92-95
Study Session 4-16-a
explain the types of opportunity cost and their relation to economic
profit, and calculate economic profit
38、Which of the following provides the best description of the effect of subsidies on the prices of goods and the relationship between marginal cost and marginal benefit?
| A. | ||
| B. | ||
| C. | ||
| D. |
|
|
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
D. Answer D.
39 Correct answer is B
C. 1.40.
D. 1.50.
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| private saving | ||||
|
|
|||
|
||||
|
|
|||
|
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
41 Correct answer is A
D. Answer D.
42 Correct answer is C
| Inelastic demand | ||
| A. | ||
| B. | ||
| C. |
|
|
| D. |
|
|
43 Correct answer is C
“Elasticity,” Michael Parkin
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 15-16
Study Session 4-13-b
calculate elasticities on a straight-line demand curve, differentiate
among elastic, inelastic, and unit elastic demand and describe the
relation between price elasticity of demand and total revenue
When demand is elastic, a decrease in price by 1% increases the quantity
sold by more than 1% and it results in an increase in total revenue. But
when demand is inelastic, a decrease in price by 1% increases the
quantity sold by less than 1% and it results in a decrease in total
revenue.
D. the employment-to-population ratio.
44 Correct answer is B
“Monitoring Cycles, Jobs, and the Price Level,” Michael Parkin
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 288-289
Study Session 5-22-a
describe the phases of the business cycle, define an unemployed person,
and interpret the main labor market indicators and their relation to the
business cycle
The three indicators of the state of the labor market that the U.S.
Census Bureau calculates are: the unemployment rate, the labor force
participation rate, and the employment-to-population ratio.
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van
Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 590-592
“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., Kenneth L.
Parkinson, and Pamela p. Peterson 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp.
89-92
Study Session 10-41-d, 11-46-a
calculate and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability,
and valuation ratios;
calculate and interpret liquidity measures using selected financial
ratios for a company and compare it with peer companies
An increase in receivables turnover would indicate that receivables were
outstanding for a shorter period of time, decreasing the cash conversion
cycle.
46、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.

“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van
Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 574-575, 590-592
“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., Kenneth L.
Parkinson, and Pamela p. Peterson 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp.
89-90
Study Session 10-41-a, d, 11-46-a
evaluate and compare companies using ratio analysis, common-size
financial statements, and charts in financial analysis;
calculate and interpret activity, liquidity, solvency, profitability,
and valuation ratios;
calculate and interpret liquidity measures using selected financial
ratios for a company and compare it with peer companies
The current ratio includes inventory but the quick ratio does not.
(Current ratio is higher than quick ratio and quick ratio is higher than
cash ratio.) The quick ratio includes accounts receivable but the cash
ratio does not. The denominator for all three ratios is current
liabilities, which are the same proportion for both companies. The
difference in ratios is therefore created by inventory and accounts
receivable. Company 1 has the higher percentage of inventory because the
difference between the current ratio and quick ratio is greater for that
company. Company 2 had the higher percentage of accounts receivable
because the difference between the quick ratio and the cash ratio is
greater for Company 2.
47、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted. An analyst gathered the following information for a company:
All other factors being equal, which of the following is the best conclusion with respect to the information above? From
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn

B. the company's cash flow from operations, but not the company's current ratio.
C. both the company's current ratio and the company's cash flow from operations.
several years ago and had accumulated depreciation of $70,000 for the equipment at the time of sale. All else equal, the
equipment sale will result in the company's cash flow from:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. investing activities decreasing by $10,000.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 251-252, 271-272, 275-276
In 2007, a company reported net income of $130 million and cash flow from operations of $120 million. All else equal, the most likely explanation for the difference between net income and cash flow from operations in 2007 is that the company:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. tightened credit policies and increased collection efforts during the year.B. purchased new property, plant, and equipment at the beginning of the year.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 267-271, 276-277
Study Session 8-34-h
analyze and interpret a cash flow statement using both total currency
amounts and common-size cash flow statements The increase in inventory
(working capital investment) would reduce cash flow from operations
relative to net income.
51、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
B. 58.4.
C. 61.6.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 275-278, 287-288
Study Session 8-34-i
explain and calculate free cash flow to the firm, free cash flow to
equity, and other cash flow ratios
Free cash flow to equity in a company without any debt is equal to cash
flow from operations (CFO) less capital expenditures. CFO = net income +
depreciation + loss on sale of equipment + decrease in accounts
receivable - increase in inventories + increase in accounts payable.
(The loss on sale of equipment is added back when calculating CFO. It
would have been deducted in the calculation of net income but the loss
is not the cash impact of the transaction (the proceeds received, if
any, would be the cash effect) and cash flows related to equipment
transactions are investing activities, not operating activities.)
CFO = 45.8 + 18.2 + 1.6 + 4.2 - 3.4 + 2.5 = $68.9 million
$68.9 - $7.3 = $61.6 million free cash flow to equity.
52、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted. Which of the following statements best describes the level of accuracy provided by a standard audit report?
52 Correct answer is D
“Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction,” Thomas R. Robinson,
Jan Hennie van Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A. Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 21
Study Session 7-29-d
discuss the objective of audits of financial statements, the types of
audit reports, and the importance of effective internal controls
Audits provide reasonable assurance that the financial statements are
fairly presented, meaning that there is a high degree of probability
that they are free of material error, fraud or illegal acts.
54、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
During 2007 Nagano Incorporated, a manufacturing company, reported the following items on their income statement:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.B. Answer B.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 169-171
Study Session 8-32-f
distinguish between the operating and nonoperating components of the
income statement
The loss on the disposal of fixed assets is an unusual or infrequent
item but it is still part of normal operating activities.
The interest expense is the result of financing activities and would be classified as a nonoperating expense by nonfinancial service companies.
The working capital for the company is closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. $14,900.B. $64,900.
“Understanding the Balance Sheet,” Thomas R. Robinson, Jan Hennie van Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 201-207
Study Session 8-33-a, d
illustrate and interpret the components of the assets, liabilities, and
equity sections of the balance sheet, and discuss the uses of the
balance sheet in financial analysis;
compare and contrast current and noncurrent assets and liabilities
Working capital = current assets - current liabilities.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 218-220
“Analysis of Long-Lived Assets: Part I – The Capitalization Decision,”
Gerald I. White, Ashwinpaul C. Sondhi, and Dov Fried
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 354-355
Study Sessions 8-33-e, 9-36-b
explain the measurement bases (e.g., historical cost and fair value) of
assets and liabilities, including current assets, current liabilities,
tangible assets, and intangible assets;
determine which intangible assets, including software development costs
and research and development costs, should be capitalized, according to
U.S. GAAP and international accounting standards
The purchased customer list is an identifiable intangible because it can
be sold separately from the company and it would be recorded at its fair
market value, the amount paid for it in the acquisition, $50,000. The
amount spent by Popular on its own lists, $15,000, would have to be
expensed because internally generated intangibles are not
capitalized.

| A. | Increase | |
| B. | Decrease | |
| C. | Increase | |
| D. | Decrease | |
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
58、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
Which of the following factors is an analyst least likely to consider when determining if a company's deferred tax liabilities should be treated as a liability or equity?
58 Correct answer is B
“Analysis of Income Taxes,” Gerald I. White, Ashwinpaul C. Sondhi,
and Dov Fried
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 439-440
Study Session 9-38-d
explain the factors that determine whether a company’s deferred tax
liabilities should be treated as a liability or as equity
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Operating lease. Rental revenue of $50,000.B. Direct financing lease. Interest income of $15,971.
Study Session 9-40-d
distinguish between sales-type leases and direct financing leases and
explain the effects of these types of leases on the financial statements
of lessors
It is a sales type lease: the lease period covers more than 75% of its
useful life (5/6) and the asset is on their books at less than the
present value of the lease payments ($199,635) (PMT = $50,000, N=5,
i=8%). They must have acquired or manufactured the asset if it is
recorded at less than the present value of the lease payments. As a
sales type lease they will recognize gross profit for the difference of
the present value and the cost (199,635 - 160,000 = 39,635) and then
interest income on the net investment in the lease (0.08 x 199,635 =
15,971).
60、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
D. Information related to operational efficiency of the company's operations.
60 Correct answer is B
B. high salvage value estimates and long average lives.
C. low salvage value estimates and short average lives.
D. high salvage value estimates and short average lives.
61 Correct answer is B
D. 33.2%.
62 Correct answer is D

63 Correct answer is D
“Analysis of Inventories,” Gerald I. White, Ashwinpaul C. Sondhi, and
Dov Fried
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 315-320
Study Session 9-35-c, e
compare and contrast the effect of the different methods on cost of
goods sold and inventory balances, and discuss how a company’s choice of
inventory accounting method affects other financial items such as income
cash flow, and working capital;
indicate the reasons that a LIFO reserve might decline during a given
period and evaluate the implications of such a decline for financial
analysis
The LIFO reserve increased by $30,000. If an increase in the LIFO
reserve occurs, LIFO cost of goods sold will be higher than FIFO by the
amount of the increase and net income would be lower than FIFO by
$30,000(1 - 0.30) = $21,000. After-tax FIFO net income would be $21,000
higher.
D. decreased by the change in Greene's LIFO reserve for that period.
64 Correct answer is A

Using the treasury stock method, the number of incremental shares
that should be used to compute diluted earnings per share is
closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. 5,000.
“Understanding the Income Statement,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van Greuning, Elaine Henry, and Michael A.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 177-178
Study Session 8-32-h
describe the components of earnings per share and calculate a company’s
earnings per share (both basic and diluted earnings per share) for both
a simple and complex capital structure
Diluted EPS is calculated using the treasury stock method that considers
what would be the effect if the options or warrants had been exercised.
Only options or warrants that are in-the-money are included, as
out-of-the-money options would not be exercised. Therefore, only the
warrants are dilutive; the exercise price is below the average market
price of the stock. Using the treasury stock method:
20,000($30) = $600,000 in proceeds. $600,000 / $40 = 15,000 shares
treasury stock. Incremental shares using the treasury stock method =
20,000 - 15,000 = 5,000.
D. cash flow from operations is $115,353.
66 Correct answer is B
67、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
The following information relates to a profitable company that offered a warranty on a new product introduced in 2007:
B. Deferred tax asset of $65,000.
C. Deferred tax liability of $35,000.
At the beginning of the year, a company issued a $1,000 face value bond. Interest on that bond is paid semiannually, the annual coupon rate on the bond is 9%, and the bond matures in ten years. The market rate of interest at the time the bond was issued was 10% on an annual basis. The amount of the initial liability recorded for this bond was closest to: Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. $938.B. $961.
69、An analyst gathered the following information about the cost and availability of raising new capital for a company:
|
Cost of debt | Cost of | ||||
69 Correct answer is C
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela p.
Peterson
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 64-67
Study Session 11-45-j
describe the marginal cost of capital schedule, explain why it may be
upward-sloping with respect to additional capital, and calculate and
interpret its break-points
The breakpoints for debt and equity are €10 million (€4.0 million /
0.40) and €8.33 million (€5.0 million / 0.60), respectively. The cost of
debt and equity if the firm raises €9.5 million in new financing will be
4% and 15%, respectively, because €9.5 million is below the debt
breakpoint and above the equity breakpoint. The marginal cost of capital
= 0.40 x 4% + 0.60 x 15% = 10.6%.
Based only on the data above, the measure that should most
concern the analyst regarding the company's working capital management
is the:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. quick ratio.
“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., Kenneth L.
Parkinson, and Pamela p. Peterson
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 89-95
Study Session 11-46-a
calculate and interpret liquidity measures using selected financial
ratios for a company and compare it with peer companies
The company’s days sales outstanding is considerably higher than the
industry’s, which means the company is slower in collecting its
receivables than the average firm. This is a concern because the longer
receivables are outstanding, the

Based only on the data above, the company's operating cycle is closest to: Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. 19.1 days.
“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., Kenneth L.
Parkinson, and Pamela p. Peterson 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp.
89-95
Study Session 11-46-a, b
calculate and interpret liquidity measures using selected financial
ratios for a company and compare it with peer companies;
evaluate overall working capital effectiveness of a company, using the
operating and cash conversion cycles, and compare its effectiveness with
other peer companies
Operating cycle = days inventory outstanding + days receivables
outstanding
Days inventory outstanding = 365 / inventory turnover = 17.63 days
Days receivables outstanding = 365 / accounts receivable turnover = 29.2
days
Operating cycle = 17.63 days + 29.2 days = 46.8 days
72、Afton Inc. is offered trade credit terms of
2/10, net 45. Afton's implicit cost of failing to take the discount and
instead paying the account in 45 days is closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. 17.10%.
“Working Capital Management,” Edgar A. Norton, Jr., Kenneth L.
Parkinson, and Pamela p. Peterson
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 120-121
Study Session 11-46-f
evaluate the performance of a company’s accounts receivable, inventory
management, and accounts payable functions against historical figures
and comparable peer company values
The cost of trade credit if paid on day 45 = (1 + 2 / 98)365/35 - 1 =
23.45%.
73、The cash manager for Thomas Industries plans to
issue €2,500,000 (face value) of commercial paper for one month. She is
quoted a rate of 5.88% with a dealer's commission of 1/8% and a backup
line cost of 25 basis points, both of which will be assessed on the face
value. The effective cost of the financing is closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
D. 6.29%.
73 Correct answer is D
D. has formerly served on the boards of several successful companies.
74 Correct answer is A
C. Shares held by the founding family have supernormal voting rights.
D. To ensure accuracy, company officials tabulate and verify shareowner voting.
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. The market value of vacant land used for a distribution center.B. The cash savings related to adopting a new production process.
77、An analyst determined the following cash flows for a capital project:
| A. | 2.75 | |
| B. | 3.78 | |
| C. | 2.75 | |
| D. | ||
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.

the discounted payback period is 3.78 years.
D. Risk of the projects as reflected in the required rate of return.
78 Correct answer is D
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.

The Herfindahl Index and the "Equivalent Number" of firms in this industry, respectively, are closest to:
| A. | 4.00 | |
| B. | 2.90 | |
| C. | 2.09 | |
| D. | 4.00 | |
D. Answer D.
80 Correct answer is B
C. 12.50%.
D. 18.75%.
82、Which of the following is the least accurate statement about the short sale of stocks?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. The short seller must pay any dividends due to the lender of shares.
“Organization and Functioning of Securities Markets,” Frank K. Reilly
and Keith C. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 24-26
Study Session 13-52-f
describe the process of selling a stock short and discuss an investor’s
likely motivation for selling short Short sales have no time limits.
However, if the lender of shares decides to sell them, the broker must
find another investor willing to lend the shares.
83、The appropriate measures of free cash flow and discount rate to use when estimating the total value of a firm, respectively, are:
C. Answer C.
D. Answer D.
84、On January 1, 2008, Abel Moreno, CFO of Monterrey Mining & Metals (MMM), gathered the following data to determine the attractiveness of the company's common stock:
Based on the information gathered, MMM stock's intrinsic value and its attractiveness on January 1, 2008, respectively, were:
| Stock's attractiveness | ||
| A. | Over-valued | |
| B. | Under-valued | |
| C. | Over-valued | |
| D. | Under-valued | |
84 Correct answer is D
“The Time Value of Money,” Richard A. DeFusco, Dennis W. McLeavy,
Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkle 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp.
199-200
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, Gene C. Lai, and Pamela p.
Peterson
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, p. 50
“An Introduction to Security Valuation: Part II,” Frank K. Reilly and
Keith C. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, p. 176-181, 198
Study Sessions 2-5-d; 4-45-h; 14-60-b, e
Calculate and interpret the future value (FV) and present value (PV) of
a single sum of money, an ordinary annuity, an annuity due, a perpetuity
(PV only) and a series of unequal cash flows;
calculate and interpret the cost of equity capital using the capital
asset pricing model approach, the dividend discount
B. Answer B.
C. Answer C.
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Escalation bias
B. Confirmation bias
C. Overconfidence bias
D. Fusion investing bias
86 Correct answer is A
“Efficient Capital Markets,” Frank K. Reilly and Keith C. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 83-84
Study Session 14-54-d
define behavioral finance and describe overconfidence bias, confirmation
bias, and escalation bias
Escalation bias refers to the investor behavior of putting more money
into a failure that they feel responsible for rather than into a
success. This leads to the practice of “averaging down” by viewing the
additional purchase as a “bargain” rather than considering the initial
purchase as a mistake and selling the stock.
| A. | 50% | |
| B. | 58% | |
| C. | 30% | |
| D. | 42% | |
D. Answer D.
87 Correct answer is C
Liquidity refers to the ability to buy or sell an asset quickly and at a known price. Price continuity is a component of liquidity which in turn requires market depth. The distracters in A, B, and D are characteristics of a good market, just as liquidity, but not most closely associated with, or as components of, liquidity.
89、The most accurate characterization of the nature of abnormal returns relating to an anomaly and a source of unreliability of an anomaly, respectively, are:
90、Robert Wu, CFA, gathered the following data on Westminster Property Developers Inc:
90 Correct answer is B
“An Introduction to Asset Pricing Models,” Frank K. Reilly and Keith
C. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 263-265
“An Introduction to Security Valuation: Part II,” Frank K. Reilly and
Keith C. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 180-181
Study Sessions 12-51-e, 14-60-b
calculate, using the SML, the expected return on a security and evaluate
whether the security is overvalued, undervalued, or properly valued;
C. interest rate floor.
D. interest rate collar.
C. interest rate swap.
D. plain vanilla swap.
C. $103.00.
D. $104.00.
B. do nothing until the long makes payment.
C. accept delivery of S&P 500 stocks from the long.
B. spot value.
C. less than par value.
B. $12,376 from the dealer to the investor.
C. $16,570 from the investor to the dealer.
B. the coupon rate.
C. prepayment risk.
|
||
| A. | No | |
| B. | Yes | |
| C. | No | |
| D. | Yes | |
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.

change and investors want to be compensated for this risk. According to the Liquidity Preference Theory, the term structure of interest rates is determined by expectations about future rates and a yield premium for interest rate risk. Because interest rate risk increases with maturity, The Liquidity Preference Theory asserts that the yield premium increases with maturity.
99 Correct answer is B
“Yield Measures, Spot Rates, and Forward Rates,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, p. 431
Study Session 16-68-d
compute and interpret the bond equivalent yield of an annual-pay bond
and the annual-pay yield of a semiannual-pay bond
The bond-equivalent yield of an annual-pay bond = 2 x [(1 + yield on
annual-pay bond)0.5 - 1] = 2 x [(1 + 0.05)0.5 - 1] = 0.0494 = 4.94%
100、An analyst gathered the following information:
B. $46,265.
C. $46,299.
B. one point on the spot curve.
C. all points on the Treasury yield curve.
C. U.S. Treasury security with short maturity in a flat yield curve environment.
D. mortgage-backed security in a steep upward-sloping yield curve environment.
D. effect of changes in interest rates on the value of the security.
103 Correct answer is A
“Yield Measures, Spot Rates, and Forward Rates,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 451-452
Study Session 16-68-g
describe how the option-adjusted spread accounts for the option cost in
a bond with an embedded option The Z-spread is the sum of the OAS and
the option cost.
104 Correct answer is B

D. weighted average number of years to receive the present value of the portfolio's cash flows.
105 Correct answer is C
“Introduction to the Measurement of the Interest Rate Risk,” Frank J.
Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 498-499
Study Session 16-69-e
distinguish among the alternative definitions of duration, and explain
why effective duration is the most appropriate measure of interest rate
risk for bonds with embedded options;
Users of this interest rate risk measure are interested in what it tells
them about the price sensitivity of a bond or a portfolio to change in
interest rates.
The effective durations of Bond A and Bond B are closest to:
| Bond B | ||
| A. | 5.78 | |
| B. | 11.57 | |
| C. | 5.78 | |
| D. | 11.57 | |
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
D. Answer D.
106 Correct answer is D
“Introduction to the Measurement of the Interest Rate Risk,” Frank J.
Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 488-489
Study Session 16-69-d
compute and interpret the effective duration of a bond, given
information about how the bond’s price will increase and decrease for
given changes in interest rates, and compute the approximate percentage
price change for a bond, given the bond’s effective duration and a
specified change in yield
Effective duration = (V_ - V+ ) / (2 × Vo × Δy)
Duration for Bond A = (102.97 - 101.04) / (2 × 102.00 × 0.005) =
1.89Duration for Bond B = (94.07 - 83.81) / (2 × 88.69 × 0.005) =
11.57
D. Answer D.
107 Correct answer is C
“Understanding Yield Spread,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 352-355, 359-361
Study Session 16-65-e, i
compute, compare, and contrast the various yield spread measures;
compute the after-tax yield of a taxable security and the tax-equivalent
yield of a tax-exempt security
Taxable equivalent yield = (tax-exempt yield) / (1 - marginal tax rate)
=

108 Correct answer is A
“Introduction to the Measurement of the Interest Rate Risk,” Frank J.
Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 500-501
Study Session 16-69-f
compute the duration of a portfolio, given the duration of the bonds
comprising the portfolio, and explain the limitations of portfolio
duration
Portfolio value = (1.02 x 7 mil) + (0.94356 x 5 mil) + (0.88688 x 3 mil)
= 14,518,440
Weight, Bond A = 7,140,000 / 14,518,440 = 0.492
Weight, Bond B = 4,717,800 / 14,518,440 = 0.325
Weight, Bond C = 2,660,640 / 14,518,440 = 0.183
Portfolio duration = (0.492 x 1.89) + (0.325 x 7.70) + (0.183 x 11.55) =
5.55
109、Which of the following statements is least
accurate with respect to the advantages of open-end exchange traded
funds (ETFs)? Open-end ETFs:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. tend to trade closer to their net asset values than close-end index
funds.
110、A real estate investment has the following characteristics:

D. $8,696,000.
110 Correct answer is A
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 193-194
Study Session 18-76-f
calculate the net operating income (NOI) from a real estate investment,
the value of a property using the sales comparison and income
approaches, and the after-tax cash flows, net present value, and yield
of a real estate investment
Using the income approach:
($1,800,000 - $1,200,000) / 0.15 = $4,000,000
| A. | No | |
| B. | Yes | |
| C. | No | |
| D. | Yes | |

Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Answer A.
113、An analyst compared the performance of a hedge fund index with the performance of a major stock index over the past eight years. She noted that the hedge fund index (created from a database) had a higher average return, higher standard deviation, and higher Sharpe ratio than the stock index. All the successful funds that have been in the hedge fund database continued to accept new money over the eight-year period. Are the average return and the standard deviation, respectively, for the hedge fund index most likely overstated or understated?
113 Correct answer is B
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 220-222
Study Session 18-76-l
discuss the performance of hedge funds, the biases present in hedge fund
performance measurement, and explain the effect of survivorship bias on
the reported return and risk measures for a hedge fund database
Survivorship bias affects both the returns and the risk (standard
deviation) reported for the hedge funds. Hedge funds with low or
negative returns will be excluded from the index as will funds with high
volatility; those funds will not survive for eight years. If only the
successful funds remain in the index, the returns are overstated and the
risk is understated. Overstated returns and understated risk will tend
to overstate the Sharpe ratio.
114、An analyst estimates that an initial investment of £500,000 in a venture capital project will pay £6 million at the end of five years if the project succeeds and that the probability the project survives to the end of the fifth year is 25%. The required rate of return for the project is 19%. The expected net present value of the venture capital investment is closest to:
D. £2,014,000.
114 Correct answer is B
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 205-206
Study Session 18-76-h
calculate the net present value (NPV) of a venture capital project,
given the project’s possible payoff and conditional failure
probabilities
The probability that the venture will pay £6 million at the end of five
years is 25%. The probability of failure is 75%. The expected NPV if the
project succeeds is £2,014,296 using FV = 6,000,000, I = 19%, n = 5 for
a present value of 2,514,296 - 500,000 = 2,014,296
The NPV of the project is 0.25(2,014,296) + 0.75(-500,000) =
128,574
The investment has a positive NPV and should be accepted.
115 Correct answer is A
“An Introduction to Asset Pricing Models,” Frank K. Reilly and Keith C.
Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 259-262
Study Session 12-51-c
define systematic and unsystematic risk, and explain why an investor
should not expect to receive additional return for assuming unsystematic
risk
Unsystematic risk (risk that can be diversified away) is not rewarded.
Systematic risk is the risk for which investors are compensated.
Systematic risk is that part of total risk that is correlated with the
market and related to changes in macroeconomic variables (such as
changes in interest rate volatility). Standard deviation of returns of
the market portfolio is a measurement of systematic risk.
116、As an investor assumes more risk and moves
upward on the efficient frontier, the slope of the efficient frontier
curve most likely:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. increases and expected return per unit of risk increases.

117、Which of the following statements about the
relation between covariance and correlation is least accurate? If the
covariance of returns between two assets is positive, the correlation
coefficient for those two assets:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. must also be positive.
118、The risk-free rate of return is 3%, the market
risk premium is 9%, and the market is in equilibrium. If a common stock
with a beta of 1.2 is properly valued, then the stock's estimated rate
of return is closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. 10.2%.
B. 10.8%.
119、Regarding an individual's investment policy
statement, which of the following is least appropriate as the investment
objective? The portfolio seeks:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. current income in the form of dividends and interest.
B. 12% annual returns with above-average market risk.

The investment objective must be expressed in terms of both risk and return and current income from dividends and interest represents only the investor’s return objective. It does not include any reference to risk tolerance or risk limits as provided in the other alternatives.
C. 14% and 3.9%.
D. 14% and 15.3%.
Level 1 Mock Exam_Part 2 答案详细解答
1、According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, members must keep information about clients confidential unless the
1 Correct answer is D
Guidance for Standards I-VII, Standards of Practice Handbook 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 67 Study Session 1-1-c
deteriorating economic conditions, that as a group, small-cap equities will underperform during the next 12-24 months. To
preserve her client's wealth, Bridgestone sells what she considers to be the most vulnerable small-cap equities. After
C. Yes, relating to loyalty, prudence, and care.
D. Yes, relating to diligence and reasonable basis.
2 Correct answer is B
3、According to the Standards of Practice
Handbook, a supervisor establishing procedures to eliminate
conflicts of interest relating to personal trading would least
likely recommend requiring:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. disclosure of holdings.
B. preclearance procedures.
recommend practices and procedures designed to prevent violations of the Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional
Conduct Banning employee investments is not recommended. According to Standard VI(B), investment transactions for
established to eliminate confl icts of interest relating to personal trading.
4、Which of the following may claim compliance with
the Global Investment Performance Standards (GIPS)? Select
exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Financial planners.
4 Correct answer is D
Introduction to the Global Investment Performance Standards (GIPS)
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, p. 120
Compliance is a
firm-wide process that cannot be achieved on a single product, portfolio, or composite.
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 119-120
Study Session 1-3-a
B. beneficial ownership of stock.
C. firm's market-making activities.
Study Sessions 1-1-c, 1-2-b
explain the ethical responsibilities required by the Code and Standards, including the multiple subsections of each Standard;
ownership of stock are three examples of such matters.
7、According to the Standards of Practice Handbook, a member with supervisory responsibilities violates the CFA Institute
7 Correct answer is D
Guidance for Standards I-VII, Standards of Practice Handbook
C. Independence and Objectivity.
D. Additional Compensation Arrangements.
C. Yes, with respect to responsibilities of supervisors.
D. Yes, with respect to diligence and reasonable basis.
B. Duty to Employer.
C. Loyalty, Prudence, and Care.
B. Yes, with respect to misrepresentation.
C. Yes, with respect to diligence and reasonable basis.
B. Yes, with respect to record retention.
C. Yes, with respect to loyalty to employer.
13、Romar Brockman, CFA, is a sell-side analyst.
Approximately half of Brockman's compensation comes from his firm's
investment-banking division. Brockman is asked to write a report about
Anacortes Concrete (AC), an investment-banking client. Despite concerns
about the slowdown in concrete demand, Brockman issues a very positive
report on AC. When issuing his report, Brockman least likely
violates the CFA Institute Standard relating to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Loyalty to Employer.
B. Disclosure of Conflicts.
B. Loyalty to Employer.
C. Priority of Transactions.

A. No.
16、Hailey Donnelly works long hours as an investment analyst and is studying for Level I of the CFA Examination. She is concerned that she is not adequately prepared for the exam. Desperate to pass, Donnelly writes several formulas on a small piece of paper which she takes into the examination room. During the exam Donnelly realizes that she does not need the formulas. Has Donnelly violated any CFA Institute Standards?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. No.
17、Abigail Unger, CFA, is a portfolio manager at Cascade Investments (CI). After thoroughly researching mortgage-backed securities and checking client investment objectives for appropriateness, Unger purchases two of the bonds for several clients. Following steep declines in the mortgage-backed securities, several clients complain to CI, claiming the bonds were unsuitable investments. Has Unger violated any CFA Institute Standards?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. No.

18、A. L. Guzdar is a portfolio manager at Woodstock
Investments (WI). Guzdar manages a billion-dollar hedge fund and two
large mutual funds. Market declines cause significant losses for all of
the accounts. Unable to find bids for certain thinly-traded stocks,
Guzdar trades the stocks between the accounts to provide liquidity and
pricing. Guzdar least likely violates the CFA Institute
Standard relating to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Misconduct.
19、A money manager has $1,000,000 to invest for one year. She has identified two alternative one-year certificates of deposit (CD) shown below:
|
||
|---|---|---|
Which CD has the highest effective annual rate (EAR) and how much interest will it earn? Highest EAR Interest earned
B. AnswerB.
C. AnswerC.
e0.0795x1 = 1.082746 = 8.2746%
Interest = $1,000,000 x 8.2746% = $82,746
Therefore, the CD paying 7.95% compounded continuously offers the highest effective annual rate. Note that the EAR is the same concept as the effective annual yield (EAY) presented in Reading 6.
20 Correct answer is D
“The Time Value of Money,” RichardA. Defusco, Dennis W.
McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 190-208
Study Session 2-5-d, e
calculate and interpret the future value (FV) and present value (PV) of
a single sum of money, an ordinary annuity, an annuity due, a perpetuity
(PV only), and a series of unequal cash flows;
draw a time line, specify a time index, and solve time value of money
applications (for example, mortgages and savings for college tuition or
retirement)
MacDonald’s budget will support a monthly payment of $1,300. Given a
30-year mortgage at 7.2%, the loan amount will be $191,517.76 (N = 360,
%I = 0.6, PMT = 1,300, solve for PV). If MacDonald makes a 10% down
payment, then the most he can pay for his new home = $191,517.76 / (1 -
0.10) = $212,797.51 ≈ $212,800.
21、It is least appropriate to use the internal rate of return (IRR) rule to differentiate between mutually exclusive projects when either the projects' scale or cash flow timing, respectively, is:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
C. AnswerC.
D. AnswerD.
| Stock sale (2@106) | 15 January 2008 | €212.00 |
|---|
22 Correct answer is D
“Discounted Cash Flow Applications,” RichardA. Defusco,
Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 222-225
€86 occurs at t=0, another outflow of €94 occurs at t=1, and an inflow of €212 occurs at t=2. Using a financial calculator, the
IRR of these cash flows is 11.60%.
lowest P/E. She then assigned the number 1 to the group with the lowest P/E ratios, the number 2 to the group with the
second lowest P/E ratios, and so on. The measurement scale used by the analyst is best described as: Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. ratio.
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 242-243
Study Session 2-7-a
24、Using Chebyshev's inequality, what is the minimum proportion of observations from a population of 500 that must lie
within two standard deviations of the mean, regardless of the shape of the distribution?
B. right of both the median and mode.
C. left of the median and right of the mode.
C. 45%.
D. 55%.
C. is completely described by two parameters.
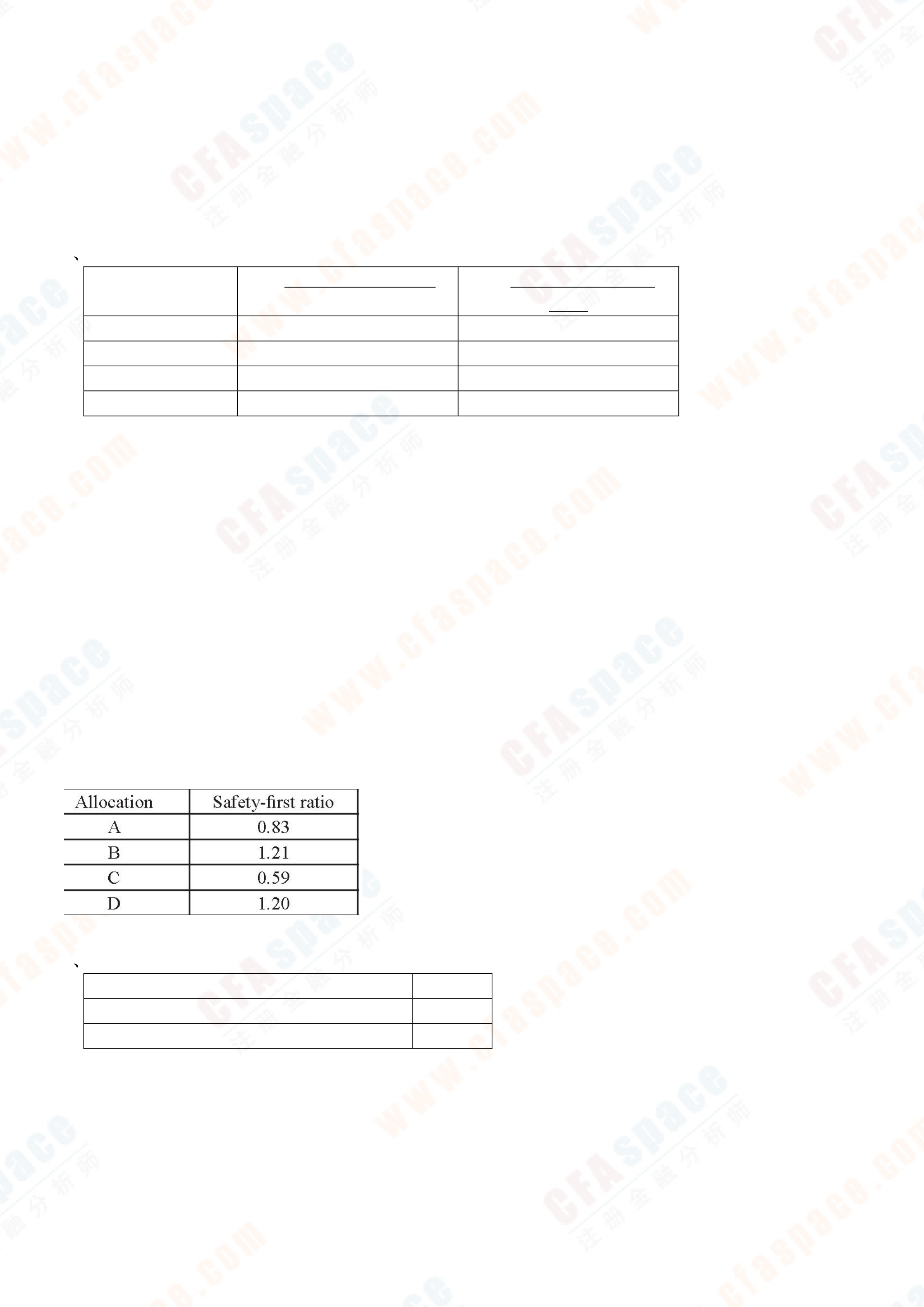
explain the key properties of the normal distribution, distinguish between a univariate and a multivariate distribution, and
explain the role of correlation in the multivariate normal distribution
| Allocation | ||
|---|---|---|
| A | 13% | 6% |
| B | 25% | 14% |
| C | 18% | 17% |
| D | 32% | 20% |
The manager's client has stated that her minimum acceptable return is 8%. Based on Roy's safety-first criterion, the most
appropriate allocation is:
28 Correct answer is B
“Common Probability Distributions,” RichardA. Defusco,
Dennis W. McLeavey, Jerald E. Pinto, and David E. Runkel
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 1, pp. 397-399
the four allocations are:
29、An analyst gathered the following information:
B. 0.64%.
C. 0.80%.
Study Session 2-10-e
calculate and interpret the standard error of the sample mean
C. exhibits skewness.
D. has greater degrees of freedom.
The Student’s t-distribution has fatter tails and is less peeked compared to the normal distribution.
31、The width of a confidence interval most likely will be smaller if the sample variance and number of observations,
| Sample variance | ||
|---|---|---|
| A. | Smaller | Smaller |
| B. | Smaller | Larger |
| C. | Larger | Smaller |
| D. | Larger | Larger |
C. AnswerC.
D. AnswerD.
variance, 2) an unknown population variance, or 3) with an unknown variance and the sample size is large
The width of a confidence interval depends on the size of the standard error. The standard error will be smaller if the sample
C. Making the statistical decision.
D. Specifying the significance level.
alternative hypothesis, and distinguish between one-tailed and two-tailed tests of hypotheses

6) Making the statistical decision.
7) Making the economic or investment decision.
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. AnswerA.B. AnswerB.
B. its long-run average cost curve is horizontal.
C. it produces a given output at the least possible cost.
|
||
|---|---|---|
| A. | changes in technology | changes in technology |
| B. | changes in technology |
|
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. AnswerA.B. AnswerB.
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 297-299
Study Session 5-22-c
36、Which of the following are the most likely effects of an increase in tax on interest income on the investment demand and
interest rates, respectively?
| A. | No effect | No effect |
| B. | No effect | Increase |
| C. | Decrease | No effect |
| D. | Decrease | Increase |
C. AnswerC.
D. AnswerD.
discuss the sources of investment finance and the influence of fiscal policy on capital markets, including the crowding-out
effect
37、The best description of the elasticity of supply of renewable and nonrenewable natural resources, respectively, is:
B. AnswerB.
C. AnswerC.
38、For factors of production that differ in their supply elasticity, perfectly elastic or perfectly inelastic, the factor income is entirely:
|
||
|---|---|---|
| A. | economic rent | economic rent |
| B. | economic rent | opportunity cost |
| C. | opportunity cost | economic rent |
| D. | opportunity cost | opportunity cost |
D. Answer D
38 Correct answer is C
“Demand and Supply in Factor Markets,” Michael Parkin
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 275-277
Study Session 5-21-h
differentiate between economic rent and opportunity costs
When the supply of the factor is perfectly elastic (horizontal supply
curve), the factor’s entire income comprises opportunity cost. When the
supply of the factor is perfectly inelastic (vertical supply curve), the
factor’s entire income comprises economic rent.
39、Which of the following is the most likely effect of changes in inflation and/or unemployment on the Phillips curve?
39 Correct answer is B
“Inflation,” Michael Parkin
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 414-418
Study Session 6-26-e
explain the impact of inflation on unemployment, and describe the
short-run and long-run Phillips curve, including the effect of changes
in the natural rate of unemployment
A change in the natural rate of unemployment shifts both short-run and
long-run Phillips curves. Suppose the natural rate of unemployment
increases from 6 to 9%, but the inflation remains constant at 10%. As a
result, both short-run and long-run Phillips curves move outward
adjusting to the new, higher level of natural unemployment rate. The new
point of intersection between the two lines would be at 9% unemployment
rate and 10% inflation rate (Figure 11, p. 418)
40、According to the feedback rule with productivity shocks, in order to stabilize the price level the most likely action by the Fed and the resulting effect on real GDP, respectively, are:
| A. | the real GDP declines | |
|---|---|---|
| B. | ||
| C. |
|
the real GDP declines |
| D. |
|
D. AnswerD.
40 Correct answer is B
cost-push inflation shock
According to the feedback rule, when the price level rises the Fed decreases the quantity of money in order to reduce aggregate
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. AnswerA.B. AnswerB.
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 253-256
Study Session 5-21-a
and marginal revenue product equals the wage rate. These two conditions are equivalent and the quantity of labor that
maximizes profit produces the output that maximizes profit.
| Pricing rule | Effect on firm’s profit | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | average cost pricing | |
| B. | average cost pricing | |
| C. | marginal cost pricing |
|
| D. | marginal cost pricing |
|
43、Which of the following is the most accurate description of the determination of interest rates?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. The real interest rate is determined in the money market.
44、The short-run effect of an increase in aggregate demand as a result of increases in government purchases on price level and real GDP, respectively, are:
D. AnswerD.
44 Correct answer is A
“Inflation,” Michael Parkin
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 2, pp. 402-405
Study Session 6-26-b
describe and distinguish among the factors resulting in demand-pull and
cost-push inflation, and describe the evolution of demand-pull and
cost-push inflationary processes
An increase in aggregate demand as a result of an increase in government
purchases, an example of demand-pull inflation, leads to an increase in
both price level and the real GDP (Figure 2, p. 402).
| $18.4 million | |
|---|---|
| $2.5 million | |
|
24 times |
|
25 days |
45 Correct answer is A
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van
Greuning, Elaine Henry, and MichaelA. Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 590-593
calculate and interpret liquidity measures usingSelected financial ratios for a company and compare it with peer companies
The cash conversion cycle is equal to inventory processing days + days in accounts receivable - payables payment period.
46、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
Two companies operating in the same industry both achieved the same return on owner's equity with the same net sales,
D. proportion of common equity in the capital structure.
46 Correct answer is C
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van
Greuning, Elaine Henry, and MichaelA. Broihahn
turnover, and financial leverage multiplier.
The first two components can be multiplied to calculate the return on assets (ROA). If the two companies have the same ROE,
way of expressing the interest expense for each company is as a percentage of:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. sales for the industry.
47 Correct answer is B
“Financial Analysis Techniques,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van
Greuning, Elaine Henry, and MichaelA. Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 574-576
48、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
An analyst gathered the following information about three equipment sales that a company made at the end of the year:
C. $10,000 more than net income.
D. $40,000 more than net income.
demonstrate the steps in the preparation of direct and indirect cash flow statements, including how cash flows can be computed
using income statement and balance sheet data
The following information is from a company's 2007 financial statements ($ millions):
| Balances as of the year ended 31 December | 2007 | 2006 |
|---|---|---|
|
140 | 120 |
| 43 | 38 | |
| 48 | 45 | |
| 29 | 36 |
$25 million for 2007. The company's 2007 cash flow from operations ($
millions) was closest to: Select exactly 1 answer(s)
from the following:
A. 10.
B. 25.

2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, pp. 275-278
Study Session 8-34-f
demonstrate the steps in the preparation of direct and indirect cash flow statements, including how cash flows can be computed using income statement and balance sheet data
The change in retained earnings is $20 and dividends are paid from retained earnings. 2007 net income would equal the change in retained earnings plus any dividends paid during 2007. Depreciation expense would be added to net income and the changes in balance sheet accounts would also be considered to determine cash flow from operations.
C. both a lower cost of goods sold and a lower inventory balance.
D. both a higher cost of goods sold and a higher inventory balance.
B. inventory turnover.
C. gross profit margin.
52、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted. An analyst gathered the following information about a company:
The bonds were issued at par and can be converted into 300,000 common shares. All securities were outstanding for the entire year.
Diluted earnings per share for the company are closest
to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. $1.05.
53、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
At the beginning of the year, two companies issued debt with the same
market rate, maturity date, and total face value. One company issued
coupon-bearing bonds at par and the other company issued zero-coupon
bonds. All other factors being equal for that year, compared with the
company that issued par bonds, the company that issued zero-coupon debt
will most likely overstate:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. cash flow from operations but not interest
expense.

54、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
54 Correct answer is D
“Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction,” Thomas R. Robinson,
Hennie van Greuning, Elaine Henry, and MichaelA.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 20
Study Session 7-29-c
discuss the importance of financial statement notes and supplementary information (including disclosures of accounting methods, estimates and assumptions) and management’s discussion and analysis
Management must highlight any favorable and unfavorable trends and identify significant events and uncertainties that affect the company’s liquidity, capital resources and results of operations in the MD&A.
D. disclaimer of opinion.
55 Correct answer is B
“Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction,” Thomas R. Robinson,
Hennie van Greuning, Elaine Henry, and MichaelA.
C. proxy statement.
D. management statement of responsibility.
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Asset
B. Revenue
C. Liability
D. Net income
57 Correct answer is D
“Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van Greuning, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, Elaine Henry, and
elements
Net income is not an element of the financial statements, but the net result of revenues less expenses. The elements are: assets,
adjusting entry related to this payment, ignoring taxes, what would the effect on the financial statements for the year be?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Assets are overstated by $5,000 and Liabilities are overstated by $5,000.
MichaelA. Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 66
liabilities are overstated and owners’ equity is understated.
59、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
| $5,250,000 | |
|---|---|
| $2,200,000 | |
| $1,400,000 | |
|
$800,000 |
|
$200,000 |
59 Correct answer is C
“Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, Hennie van Greuning, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, Elaine Henry, and
Ending retained earnings = 3,050,000 - 1,400,000 = 1,650,000.
Ending retained earnings = beginning retained earnings + net income - dividends.
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. AnswerA.
61、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
Which of the following is least likely to be a characteristic of an effective financial reporting framework?
Comparability is a qualitative characteristic of financial statements.
62、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
| 5,000 | 100% | |
|
2,100 | 45% |
|
1,750 | 32% |
| 475 | 9.5% |
C. is better at controlling product costs, but less effective at controlling operating costs.
D. has a lower gross profit margin than the industry and spends more on its operating costs.
statement
The gross profit for Geneva = 5,000 - 2,100 = 2,900 or 58%. The gross profit for the industry is 1-.45 = 55%. Therefore,
the following revenue events result in the creation of an asset or a liability when the event originally occurs?
D. AnswerD.
63 Correct answer is B
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 197
Study Session 7-30-d, 8-33-a
Lazlo Ltd, a European-based telecommunications provider, follows IASB GAAP and capitalizes new product development costs. During 2007 they spent €25 million on new product development and reported an amortization expense related to a prior year's new product development of €10 million. Other information related to 2007 is as follows:
|
|
|---|---|
| 225 | |
| 1,875 | |
| 290 |
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. AnswerA.65、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted. Which of the following best describes taxes payable?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. Total liability for current and future taxes
B. Expense based on current period pre-tax income
C. Tax return liability resulting from current period taxable income
D. Actual cash outflow for income taxes including payments (refunds) for other years 65 Correct answer is C
“Analysis of Income Taxes,” Gerald I. White, AshwinpaulC. Sondhi, and Dov Fried 2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 423
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| A. | lower | lower |
| B. | lower | higher |
| C. | higher | lower |
| D. | higher | higher |
66 Correct answer is A
“Analysis of Income Taxes,” Gerald I. White,
AshwinpaulC. Sondhi, and Dov Fried
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 486
Study Session 9-39-d
classify a debt security with equity features as a debt or equity
security and demonstrate the effect of issuing debt with equity features
on the financial statements and ratios
The portion of the proceeds attributable to the warrants would be
classified as equity, thus the portion classified as a liability would
be smaller (lower). The lower balance sheet value would lead to a lower
interest expense when it is calculated. The interest expense is based on
the liability at the beginning of the period, not the coupon
payment.
67、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.

D. 167.4.
The tax rate, 35%, is given.
68、Assume U.S. GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles) applies unless otherwise noted.
| A. |
|
|
| B. |
|
|
| C. | ||
| D. |
|
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. AnswerA.
Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 186
“International Standards Convergence,” Thomas R. Robinson, Jan Hennie van Greuning, Elaine Henry, and MichaelA.Broihahn
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 3, p. 682
Study Sessions 8-32-k, 10-43-a
state the accounting classification for items that are excluded from the income statement but affect owners’ equity, and list the major types of items receiving that treatment; identify and explain the major international accounting standards for each asset and liability category on the balance sheet and the key differences from U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) Under both U.S. GAAP and IFRS the unrealized gains and losses arising from carrying available-for-sale securities at market value are reported in equity as part of accumulated other comprehensive income.
B. Replacement project.
C. New product or service.
explain the capital budgeting process, including the typical steps of the process, and distinguish among the various categories
of capital projects
70、Howard Quarries has recently opened a limestone quarry at a location outside their traditional service area. Because
limestone is a major ingredient in concrete, if the quarry is successful Howard plans to build a ready-mix concrete plant at
70 Correct answer is D
“Capital Budgeting,” JohnD. Stowe and Jacques R.
Gagné
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 10-12
71、An analyst determined the following cash flows for a capital project:
| NVP | ||
|---|---|---|
| A. | €14.85 |
|
| B. | €14.85 |
|
| C. | €29.78 | |
| D. | €29.78 |
71 Correct answer is A
“Capital Budgeting,” JohnD. Stowe and Jacques R.
Gagné
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 12-19
Study Session 11-44-d
calculate and interpret the results using each of the following methods
to evaluate a single capital project: net present value (NPV), internal
rate of return (IRR), payback period, discounted payback period, average
accounting rate of return (AAR), and profitability index (PI)
Using a calculator with a 13% discount rate, the NPV is €14.85.
The profitability index = 1 + (NPV / initial investment) = 1 + 14.85 / 100) = 1.15.
D. 10.80%.
72 Correct answer is B
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, GeneC. Lai, and
Pamela p. Peterson
2008 Modular Level I,
Vol. 4, pp. 38-43
Study Session 11-45-a, c
calculate and interpret the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of a
company;
describe alternative methods of
calculating the weights used in the weighted average cost of capital,
including the use of the company’s target capital structure Because the
target capital weights
are not given, you can use market value weights to compute the WACC. The
market value weights for debt, preferred stock and equity are
0.2667, 0.0667, and 0.6667 respectively.
D. weighted average cost of capital.
73 Correct answer is D
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, GeneC. Lai, and
Pamela p. Peterson
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 43-45
Study Session 11-45-d
explain how the marginal cost of capital and the investment opportunity
schedule are used to determine the optimal capital
74、Waynesboro Industries is considering issuing a 10-year, option-free, semiannual coupon bond with a 9% coupon rate. The
bond is expected to sell at 95% of par value. If the company's marginal tax rate is 30%, then the after-tax cost of debt is
74 Correct answer is B
“Cost of Capital,” Yves Courtois, GeneC. Lai, and
Pamela p. Peterson
2008 Modular Level I,
Using a financial calculator: N = 20, PMT = 45, PV = 950, FV = 1000; solve for %I = 4.90%. The annual yield is twice the
semiannual yield = 4.90% x 2 = 9.80%.
B. 6.67%.
C. 10.5%.
calculate and interpret the cost of noncallable, nonconvertible preferred stock
The cost of a perpetuity is the annual cash flow divided by the selling price. In this case: rp = 6.00 / 40 = 15.0%. Because the
| €32.00 | |
|---|---|
| €2.40 | |
|
40% |
|
15% |
| 1.5 | |
| 12% | |
| 4% |
B. 16.0%.

B. 3.13%.
C. 4.12%.
C. purchases shares on the open market to fund stock option commitments.
D. discloses information about compensation paid to executives and board members.
B. Un-weighted Index
C. Price-weighted Index
D. Value-weighted Index
79 Correct answer is A
“Security-Market Indexes,” Frank K. Reilly and KeithC.
Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 42-46
Study Session 13-53-a
compare and contrast the characteristics of, and discuss the source and
direction of bias exhibited by, each of the three predominant weighting
schemes used in constructing stock market indexes, and compute a
price-weighted, value-weighted and un-weighted index series for three
stocks;
A price-weighted index, such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average, is
computed by summing up the prices of individual stocks and dividing by a
divisor that is adjusted for stock splits such that the index value is
the same before and after the split.
80、Two industries, A and B, have the following values for N-firm concentration ratio and Herfindahl Index:
D. Product differentiation strategy would be more appropriate for firms in Industry B than for firms in IndustryA.
80 Correct answer is C
“Equity: Concepts and Techniques,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis
McLeavey
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 138-139
Study Session 14-58-d, e
discuss the specific advantages of both the concentration ratio and the
Herfindahl index;
discuss, with respect to global industry analysis, the elements related
to risk, and describe the basic forces that determine industry
competition
The “equivalent” number of firms is the reciprocal of Herfindahl Index
and it is 10.5 for Industry A and 5.2 for
IndustryB.
| CITC | ||
|---|---|---|
| 14% | 12% | |
| 20% | 15% | |
|
0% | 1.2% |
|
$53 | N/A |
| $50 | N/A |
82、Which of the following is the least accurate rationale to justify the use of price-to-book value (P/BV) ratio as a measure of relative valuation of companies or common stocks?
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. P/BV is helpful in valuing companies experiencing negative earnings per share.
83、Metiu Metev, an analyst with Sofia Equity Researchers, has gathered the following information about Balkan Steel Mills (BSM):
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
D. 82.81 million.
83 Correct answer is D
“An Introduction to Security Valuation: Part II,” Frank K. Reilly and
Keith
C. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 180-181, 184
Study Session 14-60-b, f
calculate and interpret the value both of a preferred stock and a
common stock using the dividend discount model (DDM);
describe a process for developing estimated inputs to be used in the
DDM, including the required rate of return and expected growth rate of
dividends
V = OFCF1 / (WACC - g) = 5 (1.06) / (0.124 - 0.06) =
82.81
Based on the above information, Nenkov's best estimate of the value per share for Geo Telecommunications would be
closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. € 9.72.
“An Introduction to Security Valuation: Part II,” Frank K. Reilly and KeithC. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 182-185
calculate and interpret the value both of a preferred stock and a common stock using the dividend discount model (DDM);
describe a process for developing estimated inputs to be used in the DDM, including the required rate of return and expected
|
|
|
|
C. 3.5.

D. AnswerD.
86 Correct answer is C
“Equity: Concepts and Techniques,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis
McLeavey
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 133-134
Study Session 14-58-a
classify business cycle stages and identify attractive investment
opportunities for each stage
Neoclassical growth theory assumes that marginal productivity of capital
declines as more capital is added. Thus, it predicts that the long-term
level of GDP depends on the country’s savings rate but not the long-term
growth rate because of diminishing marginal returns and reaching a
steady state. This implies increase in dividends, as the new level of
GDP is reached, but not an increase in the dividend growth rate.
87 Correct answer is A
“Organizing and Functioning of Securities Markets,” Frank K. Reilly and
KeithC. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 13-15
Study Session 14-52-b, c
distinguish between primary and secondary capital markets, and explain
how secondary markets support primary markets; distinguish between call
and continuous market
A call market is an exchange (secondary market), not a primary market.
Typically, it is characterized by a few listed stocks or a small number
of active investor-traders. Buy-sell orders are cleared at a single
price (equilibrium price) that satisfies most of the orders.
88、In computing free cash flow to equity, adjustment is needed for payments made to which of the following capital providers?
| Debt holders | ||
|---|---|---|
| A. | No | No |
| B. | No | Yes |
C. AnswerC.
D. AnswerD.
|
||
|---|---|---|
| A. | Low | Low |
| B. | Low | High |
| C. | High | Low |
| D. | High | High |
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. AnswerA.
90、The latest annual report of Waterford Crossing Inc. contains the following data:
| Unadjusted P/BV |
|---|
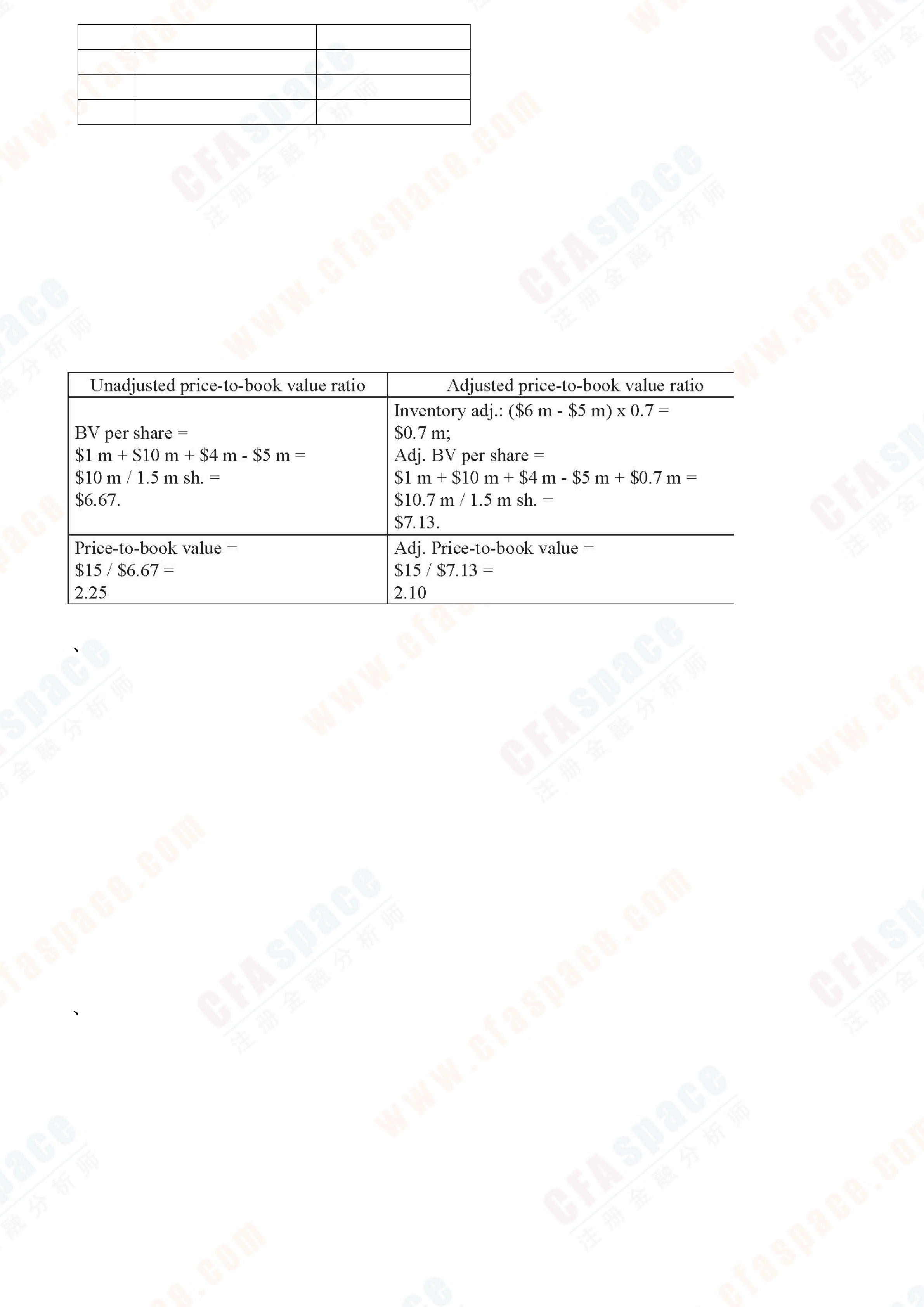
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 216-217
Study Session 14-61-b
B. variation margin requirement.
C. maintenance margin requirement.
Study Session 17-72-b
differentiate between margin in the securities markets and margin in the futures markets, and define initial margin,
B. close out the futures position by selling the futures contract at $505.
C. take delivery of the underlying asset and pay the expiration settlement price to the short.
Study Session 17-72-d

D. a call is equivalent to a long put, a long position in the underlying asset, and a short position in the risk-free asset.
93 Correct answer is C
“Option Markets and Contracts,” Don M. Chance
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 108-110
Study Session 17-73-j
explain put-call parity for European options, and relate put-call parity
to arbitrage and the construction of synthetic options The put requires
a short position in the underlying rather than a long position.
| A. |
|
|
| B. |
|
|
| C. | ||
| D. |
|
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. AnswerA.
95、A market participant has a view regarding the
potential movement of a stock. He sells a customized over-the-counter
put option on the stock when the stock is trading at $38. The put has an
exercise price of $36 and the put seller receives $2.25 in premium. The
price of the stock is $35 at expiration. The profit or loss for the put
seller at expiration is:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. ($1.25).
B. $1.00.
96、An investor purchases a stock at $60 and at the
same time, sells a 3-month call on the stock. The short call has a
strike price of $65 and a premium of $3.60. The risk-free rate is 4%.
The breakeven underlying stock price at expiration is closest
to: Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the
following:
A. $55.85.
B. $56.40.
B. decrease by less than the option-free bond.
C. decrease by more than the option-free bond.
C. volatility risk and yield curve risk.
D. interest risk and exchange-rate risk.
B. callable bond.
C. option-free bond selling at a discount to par.
C. the same reinvestment risk and less interest rate risk.
D. the same interest rate risk and more reinvestment risk.
D. 10.0%.
101 Correct answer is B
“Risks Associated With Investing in Bonds,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 269-271
Study Session 15-63-f
compute and interpret the duration and dollar duration of a bond
The formula for calculating the duration of a bond (estimated percentage
price change for a 100 basis point change in yield) is: Price if yields
decline - price if yields increase / 2(initial price)(change in yield in
decimal) = 99.3 - 89.7 / 2 (95.4)0.0120 = 4.19287.
C. liquidity risk.
D. credit spread risk.
C. $5,000.
D. $7,000.
104 Correct answer is D
“Overview of Bond Sectors and Instruments,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 308-312
Study Session 15-64-f
state the motivation for creating a collateralized mortgage
obligation
Adding Tranche B of the CMO to the portfolio will most likely reduce
prepayment. A passthrough security, such as a Ginnie

| A. |
|
|
| B. | ||
| C. | ||
| D. |
|
|
105 Correct answer is A
“Overview of Bond Sectors and Instruments,” Frank J. Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 318-321
Study Session 15-64-h
describe the characteristics and motivation for the various types of
debt issued by corporations (including corporate bonds, medium-term
notes, structured notes, commercial paper, negotiable CDs, and bankers
acceptances)
Default rates apply to the issuer and would be equal for any security
issued by that issuer while the recovery of the unsecured debenture is
lower than for the first mortgage bond which is secured.
106、Which of the statements is least accurate?
106 Correct answer is A
“Monetary Policy in an Environment of Global Financial Markets,” Otmar
Issing
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5 pp. 379-383
Study Session 15-66-a, b
identify how central bank behavior affects short-term interest rates,
systemic liquidity, and market expectations, thereby affecting financial
markets;
describe the importance of communication between a central bank and the
financial markets
Central banks should guide markets and not follow them. The reason for
this is that financial markets are susceptible to speculative bubbles
that stray from fundamentals. Central bankers must keep their eyes on
fundamentals.
107、An analyst has gathered the following information provided in the table below:
Based on the information provided in the table, the current market price of a $1,000 par value, option-free, 0% coupon corporate bond maturing in 5 years is closest to:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
D. $853.20.
107 Correct answer is A
“Introduction to the Valuation of Debt Securities,” Frank J.
Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 398-399, 410-412
Study Session 15-67-e
compute the value of a zero-coupon bond
Interest rate is 5.6% = 5% + 0.6%. The semiannual interest rate is 2.8%.
The price of the bond, using semiannual discounting is:
108 Correct answer is B
“Introduction to the Valuation of Debt Securities,” Frank J.
Fabozzi
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 5, pp. 392-395
Study Session 15-67-d
explain how the price of a bond changes as the bond approaches its
maturity date, and compute the change in value that is attributable to
the passage of time
The bond’s price should move downward toward par as time passes given
that it trades at a premium and market rates are unchanged.
109、Which real estate valuation approach is most likely to use slope coefficients derived from a statistical analysis to estimate the value of a property?
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
The annual net operating income (NOI) for the apartment complex is closest to: Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. $100,000.B. $116,000.
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| A. | Positive | Positive |
| B. | Positive | Negative |
| C. | Negative | Positive |
| D. | Negative | Negative |
111 Correct answer is C
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 227-228
Study Session 18-76-q
explain the motivation for investing in commodities, commodity
derivatives, and commodity-linked securities
A primary motivation for an investment in commodities, commodity
derivatives, commodity-linked bonds, and
commodity-linked equity are the diversification benefits provided due to
the negative return correlation with other assets and the positive
correlation with inflation.
112、Hedge funds that contain infrequently traded
assets would most likely exhibit a downward bias with respect
to: Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the
following:
A. measured risk but not correlations with conventional
equity investments.

The presence of infrequently traded assets leads to smoothed pricing that induces a significant downward bias to the measured risk of the assets as well as the correlations of returns with conventional equity and fixed income returns.
113 Correct answer is A
“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 220-222
Study Session 18-76-g
explain the stages in venture capital investing, venture capital
investment characteristics and challenges to venture capital valuation
and performance measurement
Venture capital investments provided to initiate commercial
manufacturing and sales is considered a form of first-stage
financing.
114、Which classification of hedge funds is least likely to use a short position in stock as a part of its strategy?
D. prohibited from holding less than 5% in cash instruments.
115 Correct answer is C
“The Asset Allocation Decision,” Frank K. Reilly and
KeithC. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 210-216
Study Session 12-49-d
describe the investment constraints of liquidity, time horizon, tax
concerns, legal and regulatory factors, and unique needs and
preferences
Unique needs and preferences include the prohibition of certain
investments. The investment constraints of liquidity, tax concerns, and
legal and regulatory factors adequately address the portfolio’s other
constraints.
D. evaluation of investor's investment knowledge.
116 Correct answer is C
“The Asset Allocation Decision,” Frank K. Reilly and
KeithC. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 202-203
Study Session 12-49-a
describe the steps in the portfolio management process, and explain the
reasons for a policy statement
The final step in the portfolio management process includes evaluating
portfolio performance. Evaluation of investor’s investment knowledge,
investment research, and portfolio construction are part of the first
three steps in the process.
117 Correct answer is A
“The Asset Allocation Decision,” Frank K. Reilly and
KeithC. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 202-203
Study Session 12-49-a
describe the steps in the portfolio management process, and explain the
reasons for a policy statement
The second step in the portfolio management process includes examining
current and projected financial, economic, political, and social
conditions. Historical trends may be educational, but the focus of the
second phase is determining the short-term and intermediate-term
expected conditions to use in constructing a specific portfolio.
118、Over time, the major source of investment
return and risk is most likely attributed to: Select
exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. market timing.
119、When compared to investors living in a country with high inflation, investors living in a country with generous state pensions will most likely have allocations to equities and fixed income investments, respectively, that are:
Select exactly 1 answer(s) from the following:
A. AnswerA.
119 Correct answer is C
“The Asset Allocation Decision,” Frank K. Reilly and
KeithC. Brown
2008 Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 223-224
Study Session 12-49-e
describe the importance of asset allocation, in terms of the percentage
of a portfolio’s return that can be explained by the target asset
allocation, and explain how political and economic factors result in
differing asset allocations by investors in various countries
The need to invest for portfolio growth is higher in inflationary
environments and lower in countries where workers receive generous state
pensions.
120、An analyst gathered the following information about a portfolio comprised of two assets:
| X | 60 | 11% | 5% |
| Y | 40 | 7% | 4% |
If the covariance of returns for the two assets equals 0.75, then the expected return and expected standard deviation of the portfolio are closest to:
D. AnswerD.
120 Correct answer is C
“An Introduction to Portfolio Management,” Frank K. Reilly and
KeithC. Brown
2008
Modular Level I, Vol. 4, pp. 230-245
Study Session 12-50-c
compute and interpret the expected return, variance, and standard
deviation for an individual investment and the expected return and
standard deviation for a portfolio
The expected return of the portfolio is the weighted average return of
the two
assets = 0.60 x 11 + 0.40 x 7 = 9.4%.

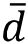
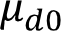
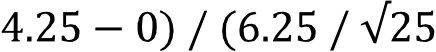
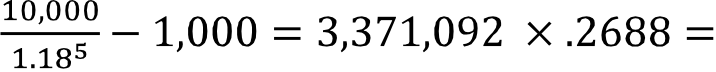
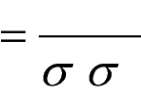 i
j
i
j