Attention individual casesyesno the sampling design processfig
Chapter Eleven
Sampling:
Design and Procedures
iii. iv. |
|---|
11-4 Chapter Outline
| 5. |
|---|
11-5 Sample vs. Census
Table 11.1
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6. Cost of nonsampling errors | ||
|
|
|
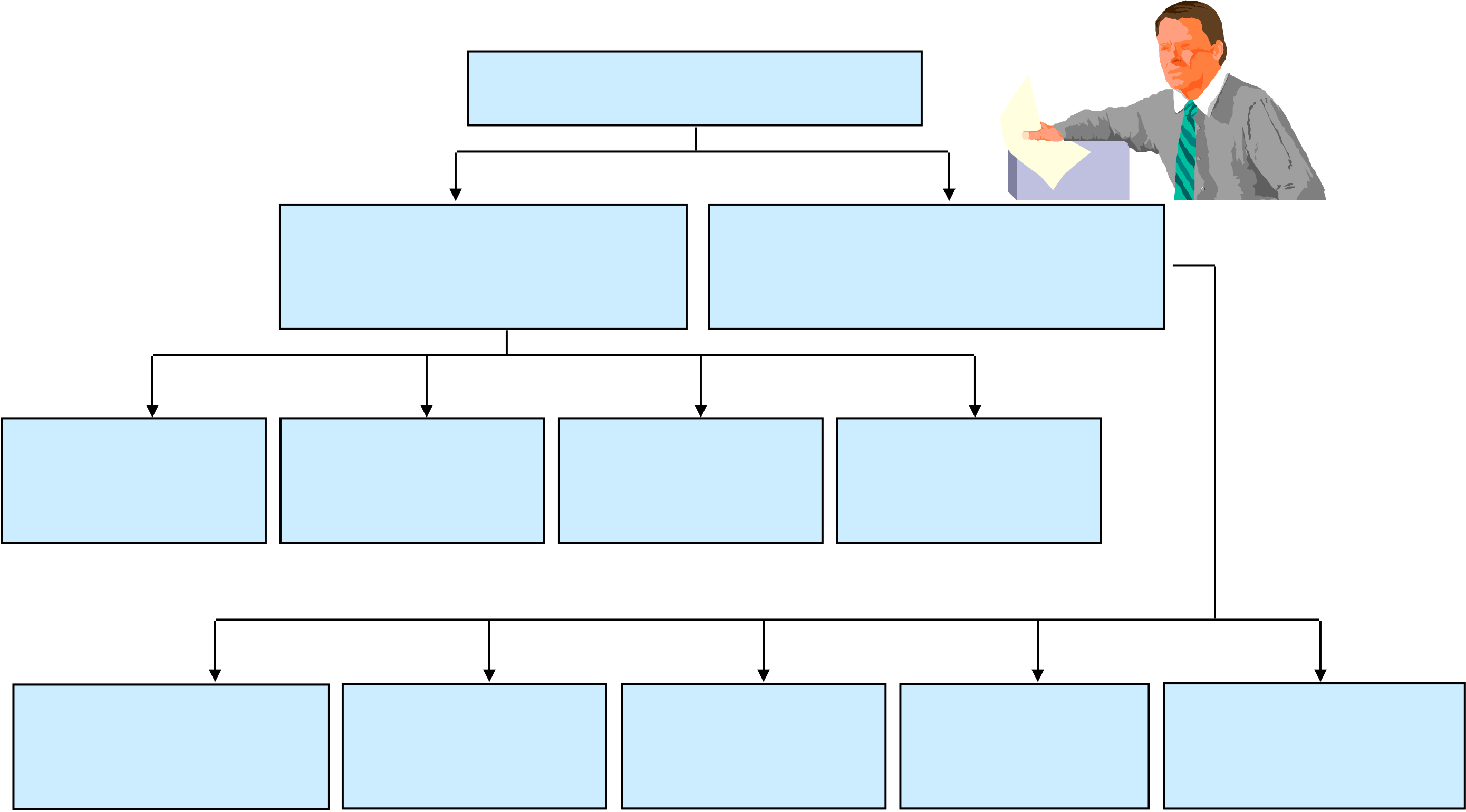
The Sampling Design Process
Fig. 11.1
Execute the Sampling Process
11-7
Time is the time period under consideration.
11-8
Research Studies
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
300-500 |
|---|---|---|
| 300-500 | ||
| 200-300 |
commercial or ad tested)
| 11-10 |
|---|
Techniques
Fig. 11.2
11-11
Judgmental Sampling
Judgmental sampling is a form of
convenience sampling in which the population elements are selected based on the judgment of the researcher.
The first stage consists of developing control categories, or quotas, of population elements.
In the second stage, sample elements are selected based on convenience or judgment.
| Percentage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | ||||||
| Female | 52 | 52 | ||||
| ____ | ____ | |||||
| 100 | 100 | |||||
11-14
Snowball Sampling
Simple Random Sampling
Each element in the population has a known and equal probability of selection.
The strata should be mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive in that every
population element should be assigned to one and only one stratum and no population
elements should be omitted. Next, elements are selected from each
stratum by a random procedure, usually SRS. A major objective of stratified sampling is to increase precision without increasing cost.
| | The elements within a stratum should be as homogeneous |
|---|
Finally, the variables should decrease the cost of the stratification process by being easy to measure and apply.
In proportionate stratified sampling, the size of the sample drawn from each stratum is proportionate to the relative size of that stratum in the total population.
Then a random sample of clusters is selected, based on a probability sampling technique such as SRS.
For each selected cluster, either all the elements are
included in the sample (one-stage) or a sample of elements is drawn probabilistically (two-stage).
|
Cluster Sampling | Multistage |
|---|---|---|
|
Two-Stage |