Called the australian civil engineer dincel construction system
2. Legal regulation of innovative activity of the enterprise.
Legal support of the management system is carried out in the following areas:: 1-Legal issues of the state economy (privatization, business development, tax system, financial and credit policy, foreign economic activity);
2-Laws and regulations on standardization, certification and Metrology, consumer protection, Antimonopoly policy, quality management of goods, safety and labor protection, etc.Liquid thermal insulation. It forms a uniform, smooth, flexible coating after drying that works thermally. The principle of operation of the coating reflects heat and sprays, preventing heat from escaping inside the building. In fact, in the end, the energy supply effect is achieved. The house saves on heating and on electricity spent on its heating.
ЭКЗАМЕНАЦИОННЫЙ БИЛЕТ №2
2. Innovative construction technologies.
Augmented reality (AR) is a digital layer of information that enhances a view of the real world. By using a mobile device with AR capabilities, construction
professionals can look at a job site with additional information laid directly on top of the real world.Australian civil engineer Dincel Construction System. It allows to lift on bearing walls and columns in much smaller terms and is much cheaper, than a usual laying of a brick or pouring (continuous ) concrete. This construction technology is patented and based on a durable solid fire-fighting polymer. These polymer (profile) cells are attached to the material, easily installed manually with the help of
equipment. This construction technology can be used for walls of any length and shape, as well as for pillars of any height. The polymer molds are cut at a specific construction site in the designated challenging plant interruption.
ЭКЗАМЕНАЦИОННЫЙ БИЛЕТ №3
Innovation activity in the Republic of Kazakhstan is regulated by several legislative acts at the national level, the main of which are:
• Constitution of the Republic of Kazakhstan, law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "on innovation" dated 3.07.2002,
Law "on science", decree of the government of the Republic of•
Kazakhstan dated 12.07.2000 № 1059 “on the concept of scientific and technical policy of the Republic of Kazakhstan» ;
• Resolution of the government of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 21.01.1993 № 1090 “on measures to improve the organization of science and development of scientific and technical potential of the Republic»;
Decree of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan “on the Strategy•
of industrial and innovative development for 2003-2015»;
• Order of the Ministry of trade and industry of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 16.04.2004 №93 " on some issues of construction and development of technoparks in the Republic of Kazakhstan»;
• Law of RK on scientific and technical policy;
Convention establishing the world intellectual property organization. Was signed in Stockholm 14.07.1967 year. The world copyright Convention was revised in Paris on 24.07.1971.3. House in 3D.
Innovation activity in the Republic of Kazakhstan is regulated by several legislative acts at the national level, the main of which are:
• Constitution of the Republic of Kazakhstan, law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "on innovation" dated 3.07.2002,
Law "on science", decree of the government of the Republic of•
Kazakhstan dated 12.07.2000 № 1059 “on the concept of scientific and technical policy of the Republic of Kazakhstan» ;
• Resolution of the government of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 21.01.1993 № 1090 “on measures to improve the organization of science and development of scientific and technical potential of the Republic»;
Decree of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan “on the Strategy•
of industrial and innovative development for 2003-2015»;
• Order of the Ministry of trade and industry of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 16.04.2004 №93 “on some issues of construction and development of technoparks in the Republic of Kazakhstan»;
• Law of RK on scientific and technical policy.2. Mechanism of management of investment activity of firms.
1-Legal issues of the state economy (privatization, business development, tax system, financial and credit policy, foreign economic activity);
2-Laws and regulations on standardization, certification and Metrology, consumer protection, Antimonopoly policy, quality management of goods, safety and labor protection, etc.3-Laws and regulations on regulation of commodity safety and
interchangeability, resource saving, production development, social development of the collective, environmental protection;
4-Legal regulation of creation and functioning of the company.
The transition to new technologies poses a number of new special problems for science, based on the parameters and structure of innovative products
( nanotechnology, microelectronics, etc.), measuring the parameters of the
technological process of creating innovative products and ready-to-market products, metrological support of measurement information processing, ensuring the reliability and metrological reliability of measurements.The standards provide consumers and manufacturers of innovative products with accessible sources of necessary information. New standards in the field of protection of the market and the consumer from production will allow audit bodies to carry out control during release and the address of innovative production.
Thanks to the invention of the 3D construction printer, which will print with a special concrete solution, a new production revolution is taking place in the near future. The printer is able to build a house of 250m2 in 24 hours literally. Despite the fact that similar developments are underway in many countries, a feature of the printer, invented by the Americans, is the ability to have on it all the necessary communications in parallel with the pouring of the walls, covering from electricity to the sewer system. In addition, with the help of the printer, you can paint the walls and even repair the roof.
At the heart of the 3D printer for construction is the work of a conventional production printer, only the working scale and material change, instead of plastic, a layer from a special installation, specially designed fast-drying concrete is allocated.
Contour fill dries the concrete layer, so defects are formed, called cold seam, which reduces the strength of the house.
Since the structure of the building uses a special simplified reinforcement cage, laid only when pouring concrete, the strength of the building is significantly reduced and the height of the building is not allowed to build more than four floors.
the approved requirements for the purpose of testing new technologies, organizing industrial, subsequent mass production , entering the market.
Standardization contributes to the creation and implementation of new products from the idea.
2. Innovation of building materials.
Wall blocks "warm"of polystyrene. Manufacturers are wall blocks of
polystyrene with finished facade decoration. Polystyrene concrete is a flammable type of production cells. Its porosity (porization) is achieved by the inclusion of expanded polystyrene granules in a cement mixture with a density of 8-16 kg / M5. Therefore, the walls of the polystyrene block do not require low-weight and additional heating. But the main thing-polystyrene absorbs little moisture due to closed structures in the cavity of concrete, ie has less water-resistant properties than other cellular concretes.3. Example of innovative technologies.
Construction innovative technologies around the world are of great importance for many large construction firms and companies. A serious problem in the
construction industry in many countries, on the one hand, leads to a decrease in the cost of building materials, on the other hand, saving wages involved in the work. This process may reflect the quality of buildings and structures constructed. Therefore, for construction, innovative technologies are an important task in the construction industry today.
For instance, you want to impress your boss with an idea, a new initiative that, according to you, can reduce operational costs and increase business.
It doesn’t matter how great your idea is, you cannot execute it without a plan.
Principle 1: Project Goals and Objectives
Principle 2: Budgeting
Principle 3: Scheduling and Estimating
Principle 4: Team Responsibilities
Principle 5: Defining Milestone
Principle 6: Managing Change
Principle 7: Responsibility and Accountability Principle 8: Measuring Success
2. Evaluation criteria of the innovation project.Evaluation criteria:
There are many different evaluation criteria. In principle, it is a matter of weighing up opportunities and risks.Attractiveness of the target market, e.g. market size, market growth, intensity of competition.
Differentiation potential from the competition - a unique position over the competition and a difficult imitation is important.
Economic feasibility, in principle the be-all and end-all, in particular the cost-benefit calculation.
Legally relevant is that it complies, for example, with laws, available property rights and standards.
Top down communication;
Rigid hierarchical relationships;
Limited information sharing; and
Fixed job duties that rarely change over time.
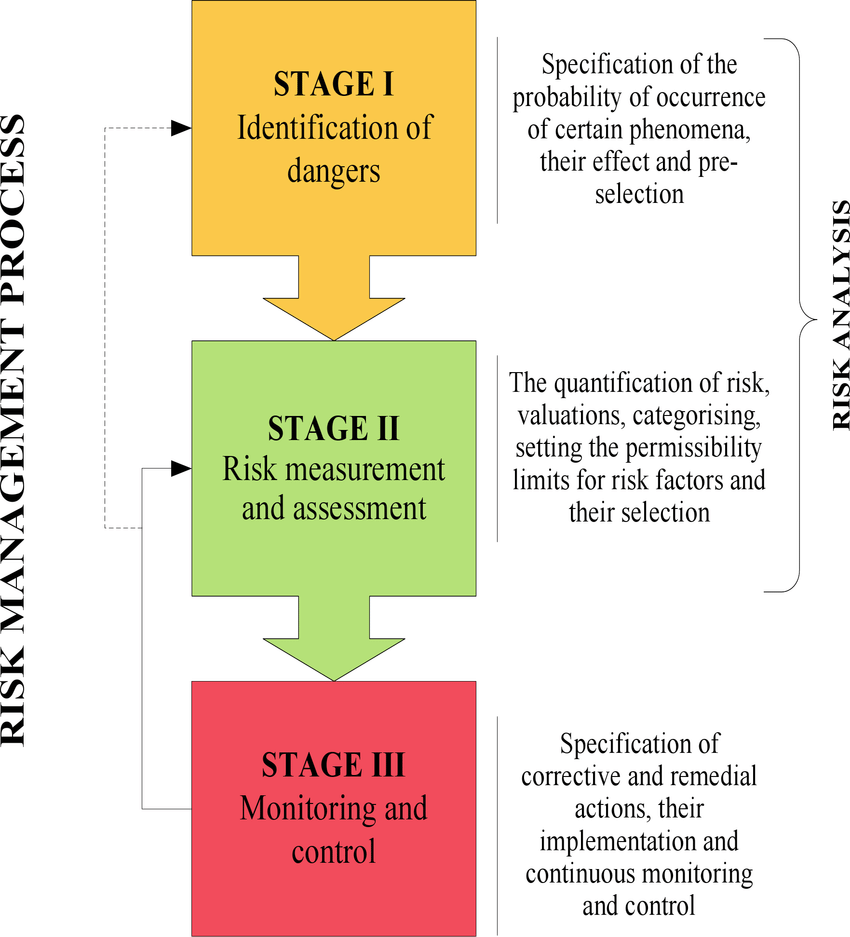
The article presents the issue of risk assessment of innovations. Specificity of technological innovation realized in manufacturing companies has been particularly well described here. An original method of assessing the innovative projects risk has been presented. The elaborated method has been implemented in three enterprises, the business activity of which is not typical for electrical engineering, metal and
mechanical engineering and companies which are going to carry out the innovative project simultaneously with already started innovative projects. Moreover, an example of the risk assessment of a chosen technological innovation has been presented.
Kazakhstan joined the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2015. In June 2017 Kazakhstan joined the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Declaration on International Investment and Multinational Enterprises and became an associated member of the OECD Investment Committee.
Despite institutional and legal reforms, concerns remain about corruption, bureaucracy, arbitrary law enforcement, and limited access to a skilled workforce in certain regions. The government’s tendency to legislate preferences for domestic companies, to favor an import-substitution policy, to challenge contractual rights and the use of foreign labor, and to intervene in companies’ operations continues to concern foreign investors. Foreign firms cite the need for better rule of law, deeper investment in human capital, improved transport and logistics infrastructure, a more open and flexible trade policy, a more favorable work-permit regime and a more customer-friendly tax administration.