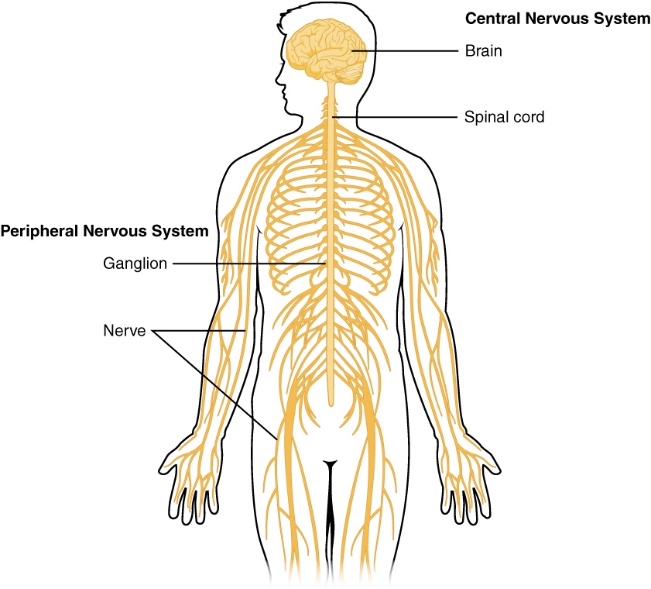
Central nervous system cns and peripheral nervous system pns and derrickson
Introduction
Meninges
Meninges is the connective tissue that covers the CNS. It consists of three layers
 Brain serves as the centre
of nervous system and is in the cranial cavity of the head. It’s the
most complex organ in vertebrates with human cerebral cortex being made
of approximately 14 – 16 billion neurons while cerebellum is said to
contain 55-70 billion. Brain exerts centralised control over other
organs either through electrical impulses or by induction hormone
secretion.
Brain serves as the centre
of nervous system and is in the cranial cavity of the head. It’s the
most complex organ in vertebrates with human cerebral cortex being made
of approximately 14 – 16 billion neurons while cerebellum is said to
contain 55-70 billion. Brain exerts centralised control over other
organs either through electrical impulses or by induction hormone
secretion.
Spinal cord
The nerves that branch out from brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body constitutes the peripheral nervous system. PNS connects CNS to limbs and organs serving as a relay between them. The PNS is not covered by bone or blood brain barrier. Hence, they are prone to damage by mechanical injury and toxins. The peripheral nervous system is divided into two viz. somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
Explain the role of somatic and autonomic nervous system.
Describe the different types of neurons in the Nervous System
Depending upon the nature and direction of impulses neurons in the nervous system are grouped into three types
Depending upon the origin of signals action are classified into voluntary and involuntary (Reflex) actions. In voluntary action the corresponding signal actively originate from brain and is transmitted across CNS via efferent neurons in response to some sensory input. Involuntary responses on the other hand originate from the spinal cord in response to localised stimuli. As the number of neurons involved are less involuntary responses are faster than voluntary responses.
Describe Transmission of nerve impulses
What is the role of neurotransmitters in transmission of nerve impulses?
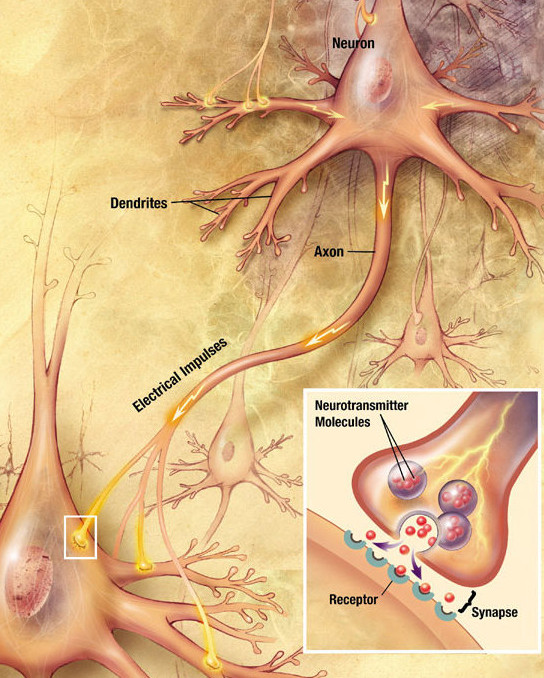 The electrical impulses are
only capable of travelling through the entire length of the neuron. Once
the impulse reaches the end of the neuron the signal is transferred to
the adjacent neuron with help of specialised molecules called
neurotransmitters. This transfer of electrical signal between adjacent
neuron via chemical mediators is called neurotransmission(Bear et al.,
2016).
The electrical impulses are
only capable of travelling through the entire length of the neuron. Once
the impulse reaches the end of the neuron the signal is transferred to
the adjacent neuron with help of specialised molecules called
neurotransmitters. This transfer of electrical signal between adjacent
neuron via chemical mediators is called neurotransmission(Bear et al.,
2016).
Inhibitory drugs: Such as Beta-blockers (mainly used to treat heart disease) "reduce" the process of synaptic transmission
Amphetamine is a CNS stimulant used in treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. Amphetamines causes emotional and cognitive effects such as euphoria, wakefulness, improved cognitive control and libido. However, use of large quantities of the same can cause impair cognitive function and muscle breakdown as well as addiction. Amphetamines act on CNS by enhancing the activity of monoamine neurotransmitters in reward and executive function pathways of the brain. The major neurotransmitters affected by amphetamine are dopamine and norepinephrine. Amphetamine enters the synaptic vesicles causing them to collapse of the vesicle. This releases the neurotransmitters contained in these vesicles into the synaptic cleft triggering the activation of associated receptors(Heal et al., 2013).
