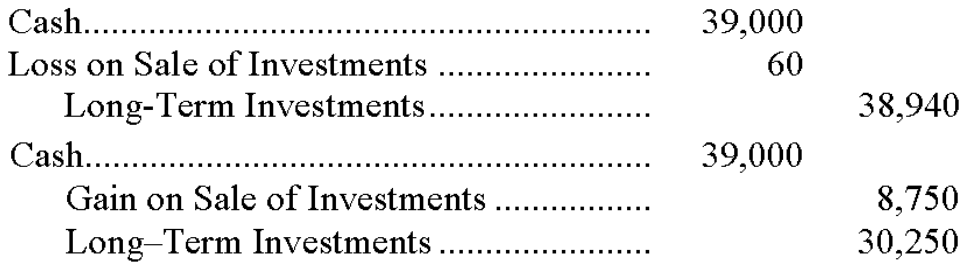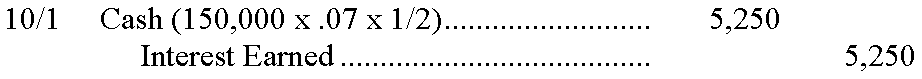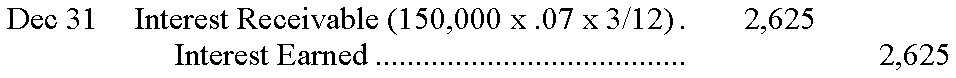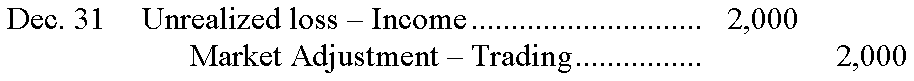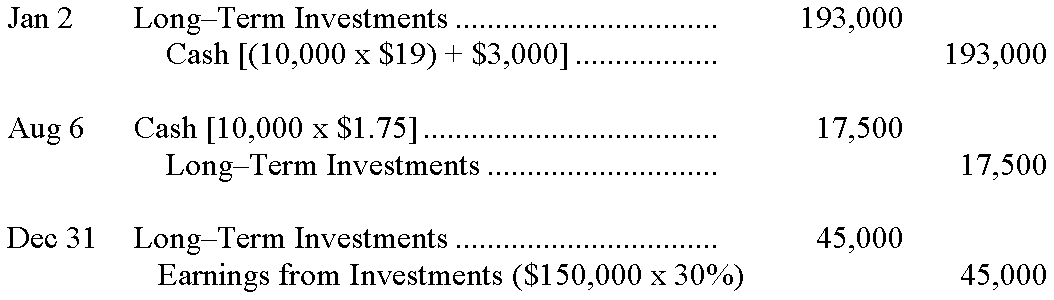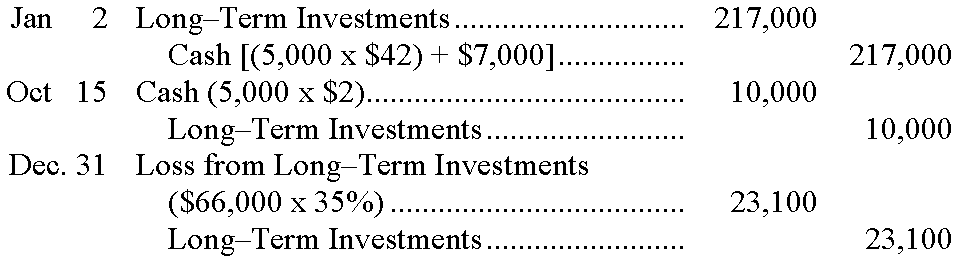Company had profit margin and total asset turnover
|
|||||||
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|---|
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
|
|---|
|
|---|
_
in the short term. _
_
_
_ |
|---|
�
122.Discuss the reasons companies make investments. � �
��
124.What are the accounting basics for debt securities, including recording their acquisition, interest earned, and their disposal? � �
��
126.What is comprehensive income and how is it usually reported in the financial statements? � � �
�
128.Define the foreign exchange rate between two currencies. Explain its effect on business transactions conducted in a foreign currency. � �
��
130.Explain how to record the sale of trading securities. � �
��
132.Explain how available-for-sale debt and equity securities are accounted for at and after acquisition and how they are reported in financial statements. � �
��
134.Explain how transactions (both sales and purchases) in a foreign currency are recorded and reported. � � �
�
�
�
�
|
|---|
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
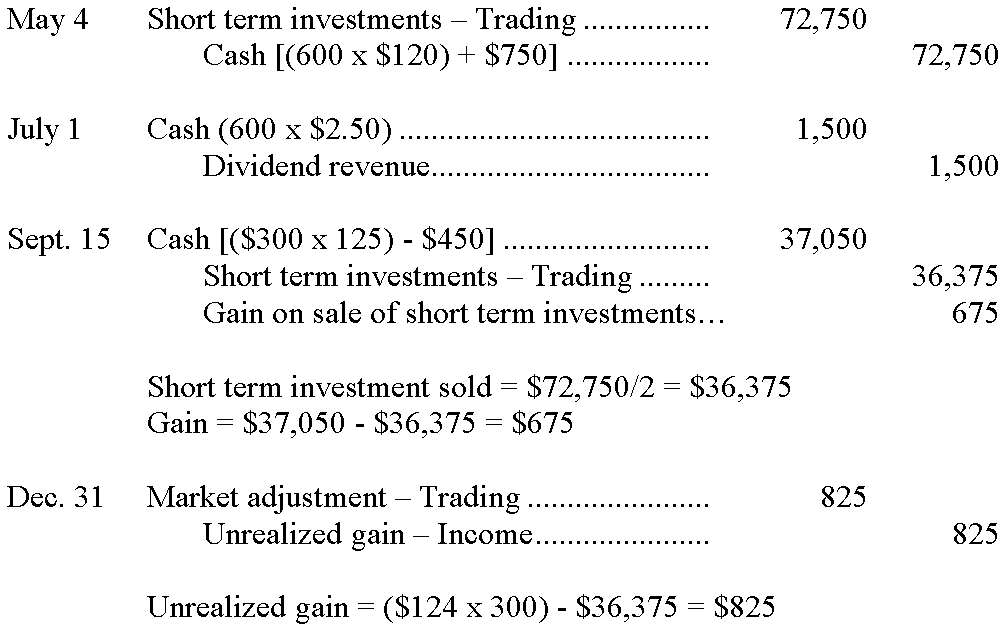
146.Wiffery Company had the following trading securities in its portfolio at December 31. The Market Adjustment – Trading account had balance of zero prior to year-end adjustment. Prepare the appropriate adjusting journal entry. �
�
147.Haladam Company had the following transactions relating to investments in trading securities during the year. Prepare the required general journal entries for these transactions. �
| � | � |
|---|
�
148.Clarity Corporation had the following transactions involving investments in trading securities during the year. Prior to these transactions, Clarity had never had any investments in trading securities. Prepare the required general journal entries to record these transactions. �
�
|
|---|
�
�
�
�
�
�
�
|
|---|
�
�
�
| � | � |
|---|
�
�
�
�
| � | � |
|---|
�
�
�
�
| � | � |
|---|
�
�
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
|
||
37. TRUE
38. FALSE
39. FALSE
40. TRUE
41. FALSE
42. TRUE
43. TRUE
44. TRUE
45. FALSE
46. TRUE
47. FALSE
48. TRUE
49. FALSE
50. FALSE
51. TRUE
52. FALSE
53. TRUE
54. TRUE
55. FALSE
56. FALSE
57. TRUE
58. B
59. A
60. C
61. A
62. C
63. C
64. E
65. C
66. E
67. C
68. C
69. C
70. C
71. C
72. C
73. B
74. C75. E
76. E
77. A
78. E
79. D
80. C
81. A
82. B
83. E
84. D
85. D
86. B
87. C
88. D
89. C
90. C
91. D
92. A
93. E
94. B
95. E
96. C
97. B
98. C
99. C
100. C
101. E
102. E
103. B
104. A
105. E
106. A
107. B
108. A
109. D
110. C
111. D
112. C117. D
118. C
123. Non-influential investments in securities can be classified as: (1) trading, (2) held-to-maturity, and (3) available for sale.
124. At acquisition, debt securities are recorded at cost. If the interest periods do not match up with the investor's accounting period, interest earned and interest receivable must be accrued at year-end. Interest must also be recorded on the interest payment dates. When the debt matures, the cash received is debited, and the debt is credited.
129. The return on total assets is calculated by dividing net income by average total assets. It can be computed from the profit margin ratio and total asset turnover. The return on total assets reflects a company's ability to use its assets to make a profit. It can also be used to assess a company's performance compared to competitors.
130. When trading securities are sold, the difference between the net proceeds (sale price less fees) and the cost of the individual trading securities that are sold is recognized as a gain or loss. Any prior period market adjustment is not used to compute the gain or loss from the sale. Gains and losses are included in net income for the period.
135. 136. |
|---|
(b.) 2010: $620,000 / $3,000,000 = 20.7%
141. (a.) 2009: $450,000 / $2,500,000 = 18.0%
��
154. 155. 160. |
|---|
15 Summary�
|
|---|