Face add bond premium bonds payable
Reporting and Analyzing Liabilities
|
2 |
|---|
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
|
|---|
Liabilities as a Source of Financing
|
|---|
they relate
|
|---|
| Learning Objective | 1 |
|---|
Current Liabilities
Short-term in nature
Due within one year
Categories of current obligations
Current operating liabilities
Accounts payable
Accrued liabilities
Deferred performance liabilities
Current nonoperating liabilities
Short-term interest-bearing debt
Current maturities of long-term debt
Most create a corresponding impact on selling, general and administrative expenses on the income statement
| $ | 3,453 | $ | 2,645 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $ | 21,232 | $ | 19,593 | |
|
$ | 8,352 | $ | 8,102 |
|
$ | 33,037 | $ | 30,340 |
| 7 |
|---|
account.
| (1) | 800 | |
|---|---|---|
|
800 | |
|
Selling Inventory on Account
| 2) |
|
|---|
| (2a) |
|
9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1,500 | |||
| 600 | ||||
|
||||
|
1,500 | |||
| (2b) | ||||
| 600 | ||||
| ©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers |
Recording Payments Received on Account
| (3) |
|
1,100 |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts receivable (–A) | 1,100 | |
Recording a Payment to a Creditor
| 4) |
|---|
| Balance Sheet | Income Statement | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| (4) | 800 | 11 |
|---|
Cash Discounts
Incentives granted to buyers to encourage payment within a specified period of time
Part of credit terms
Stated as a percentage of the purchase priceA buyer purchases $1,000 of merchandise on June 1
with terms of 2/10, n/30. Payment is made on June 9.
 |
$20 extra to pay 20 days later | 13 | |
| $20 ÷ 20 days = $1 per day | |||
| or $365 for one year | |||
| $365 ÷ $980 = 37.2% per year! | |||
| ©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers | |||
n/30.
| (1) | (1) | 156.80 |
|
14 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts payable (+L) | 156.80 | ||||
| Inventory (A) | Accounts Payable (L) | ||||
|
156.80 | ||||
| ©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers | |||||
| Balance Sheet | Income Statement | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| (2a) |
|
156.80 |
|
15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 156.80 | ||||
| ©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers |
period ends.
| (2b) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
3.20 | ||
|
160.00 | ||
| 160.00 |
|
|---|
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
|
©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers 17
Accrued Liabilities
|
18 | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
||
| ©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers |
Accounting for Accruals


| 1) |
|---|
| (1) |
|
300 |
|---|
| 2) |
|
|---|
period.
| Balance Sheet | Income Statement | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
|
| (2) | 300 | 300 | 21 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers | 300 |
Contingent Liabilities
Not all liabilities are certain
Criteria to be met before recognizing:
©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers 22
| 23 |
|---|
What are warranties?
Commitments made by manufacturers to their customers to repair or replace defective products within a specified time period
Estimating Warranty Accruals
| 1) |
|
|---|
| (1) |
|
2,000 |
|---|
Warranty Repairs / Replacement
| 2) |
|
|---|
| Balance Sheet | Income Statement | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
Disclosure for Warranties
Excerpt from Apple’s financial statement notespresented in its 2018 10-K annual report:
©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers
Current Financial Liabilities
| 29 |
|---|
Financing is often permanent and seasonal for seasonal operations
Example of a company with higher seasonal sales in summer
Bank provides a commitment to lend up to a given level with the understanding that the amounts borrowed are repaid in full sometime during the year
Evidenced by an interest-bearing note
|
31 |
|---|
Calculating Interest
Principal x Annual Rate x Portion of Year
Outstanding
| 32 |
|---|
each quarter (April 1, July 1, October 1, and January 1).
| (1) | (1) | 33 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,000 | |||||
| Cash (A) |
|
||||
|
3,000 | ||||
| ©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers | |||||
| Balance Sheet | Income Statement | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||
|
| 3) |
|---|
| Balance Sheet | Income Statement | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
|
|
|---|
©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers 37
Debt Securities
| When a company issues bonds, it is borrowing money. |
|---|

Explain and illustrate the pricing of long-term nonoperating
liabilities.
|
||
|---|---|---|
Also known as the contract |
|
|
41 |
|---|
Valuing Bonds Issued at Par
$400,000 × 8% × 6/12 = $16,000
Interest rate per period:
8% annual rate ÷ 2 payments per year = 4% per period
|
= $270,226 |
|---|
Valuing Bonds Issued at a Discount
$400,000 × 8% × 6/12 = $16,000
|
|---|
Market interest rate per period:
10% annual rate / 2 payments per year = 5% per period

|
= $369,112 |
|---|
Investors wish to value a bond with a face amount of $400,000, an 8% annual coupon rate, 6% market rate, interest payable semiannually, and a maturity of 5 years.
Step 1: Calculate the interest payment.
Step 2: Calculate the present value (PV) of the cash
flows.
PV of interest payments $ $16,000 x 8.53020 = $136,483
PV of annuity for 10 periods @ 3% per period (Table A.3)
| = $434,119 |
|---|
Investors wish to value a bond with a face amount of $400,000, an 8% annual coupon rate, 6% market rate, interest payable semiannually, and a maturity of
PV = unknown, the amount to solve for
PMT = the periodic interest payment: $400,000 × 8% × 6/12 = $16,000
Investors wish to value a bond with a face amount of $400,000, an 8% annual coupon rate, 10% market rate, interest payable semiannually, and a maturity
PMT = the periodic interest payment: $400,000 × 8% × 6/12 = $16,000
FV = the principal amount of the debt: $400,000 given
|
|
Coupon | Equal to | 50 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate | Rate | ||||
|
|
||||
| $400,000 bonds | Less than | ||||
| sold at a discount | |||||
| $400,000 bonds |
|
Greater | |||
| than face | |||||
| sold at a premium | |||||
| value | |||||
|
|||||
|
Interest payments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
= | ||
 $160,000 $160,000 |
|||
|
= $190,887 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
Offers debt
investment to the
public Referred to as a
tombstone
| 52 |
|---|
©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers
Issuing Bonds at Par
$400,000 bonds with 8% coupon rate, issued at par:
|
400,000 |
|---|
Bonds Payable (L) |
|---|
Issuing Bonds at a Premium
$400,000 bonds with 8% coupon rate, issued at a premium, 6%market rate:
|
|
|---|
Reporting Bonds
on the Balance Sheet
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Bonds payable, face $400,000
|
A benefit |
|---|
|
|
|---|
The $16,000 interest payment was made on the $400,000, 8%
bonds, issued at $369,113 (10% market rate).
|
|||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| 60 |
|---|
| 0 | $13,024 | $16,000 | $2,976 |
|
|
61 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 31,145 | 431,145 | ||||
| 2 | 12,934 | 16,000 | 3,066 | 28,079 | 428,079 | |
| 3 | 12,842 | 16,000 | 3,158 | 24,921 | 424,921 | |
| 4 | 12,748 | 16,000 | 3,252 | 21,669 | 421,669 | |
| 5 | 12,650 | 16,000 | 3,350 | 18,319 | 418,319 | |
| 6 | 12,550 | 16,000 | 3,450 | 14,869 | 414,869 | |
| 7 | 12,446 | 16,000 | 3,554 | 11,315 | 411,315 | |
| 8 | 12,339 | 16,000 | 3,661 | 7,654 | 407,654 | |
| 9 | 12,230 | 16,000 | 3,770 | 3,884 | 403,884 | |
| 10 | 12,117 | 16,000 | 3,883 | 0 | 400,000 | |
| 3% |
|
|||||
| $16,000 - |
|
|||||
| $13,024 | ||||||
| ©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers | ||||||
Cash (A) |
|---|
Financial Statement Effects of Bond Repurchase
Bonds trade in secondary markets between
(indenture)
Call provision gives the company the right to repurchase its bonds
| 63 |
|---|
Financial Statement Footnotes
Verizon presented a schedule in its note disclosure of Interest must be excluded from operating activities section of cash flows statement and from net
operating profit when performing a financial
analysis. Interest income
Interest-bearing bonds and notes
|
66 |
|---|
A measure of solvency
Measures the corporation’s financial leverage
| Applying the Debt-to-Equity ratio to Verizon: | |
©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers 68
©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers 69
Verizon in Context
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
©2020 Cambridge Business Publishers 70
Times Interest Earned (TIE)
Measures how many times interest expense is 
| TIE = | ||
|---|---|---|
| Interest expense | ||
| Applying Times Interest Earned ratio to Verizon: | ||
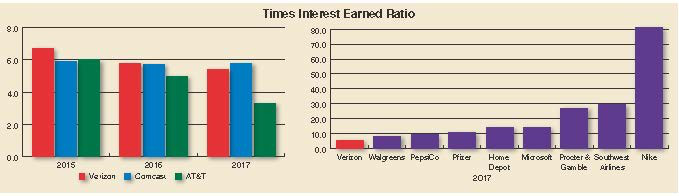
|
|---|
|
73 |
|---|
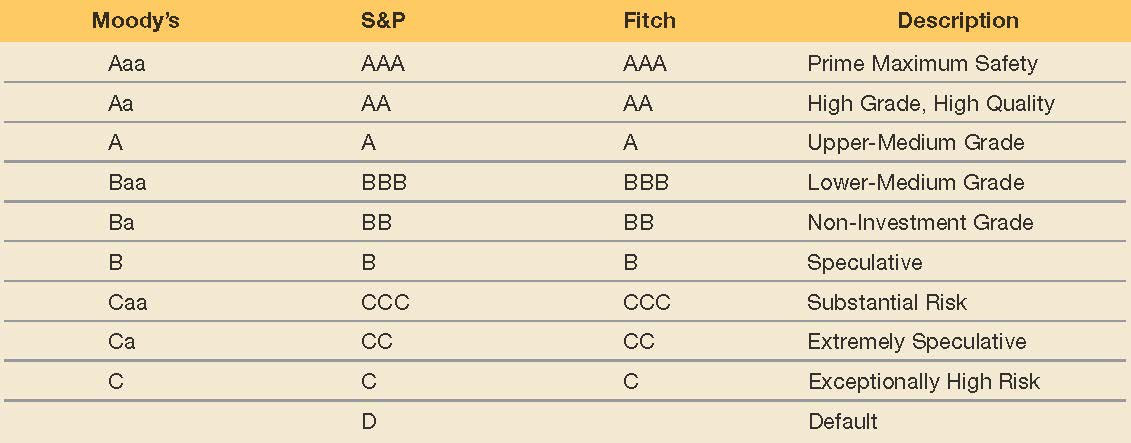
Debt Ratings
Agencies include
Moody’s Investors Service
major bond rating services:
Collateral
Security in the form of assets provided for debt
Debt holder is in a preferred position with secured debtCovenants
Restrictions specified in the debt agreement
Provide debt holder a means of control over the issuer’s operations
Financial Accounting Sixth Edition
Cambridge Business