Ftan mpa mpa mpa mpatmax mpa save mpaproblem solve prob
|
¥ | 10 | -3 | )( 80 | ¥ | 10 | -3 | ) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w | cos | b | |||||||
= 800¥106 |
m2 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tw = F A w s | 6 |
|
|||||||||||
| ¥ | 10 | 6 | = 0.240 | ||||||||||
| ¥ | 10 | 6 |  |
||||||||||
| Fn – 100 cos b = 0 |
|
||||||||||||
| A = 800 | ¥ | 10 | -6 |
|
|||||||||
| s = F n | ¥ | ||||||||||||
| A w | ¥ |  |
|||||||||||
PROBLEM 7.23
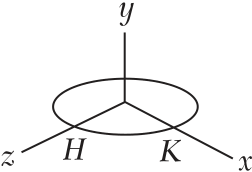
7.23 The steel pipe AB has a 102 mm outer diameter and a 6 mm wall thickness. Knowing that arm CD is rigidly attached to the pipe, determine the principal stresses and the maximum shearing stress at point H.
|
y | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fx = 10 ¥ 103 N | H | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| T = My = 2000 N◊m | z | H | K | ||||||||||||
| c = ro = 51 ¥ 10–3 m | |||||||||||||||
| txy = Tc J = ( | 2000 51 | ¥ | 10 | -3 | ) |  |
|||||||||
| ¥ | 10 | H | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| y | x | ||||||||||||||
| H | |||||||||||||||
| = 27.684 ¥ 10–6 m3 | |||||||||||||||
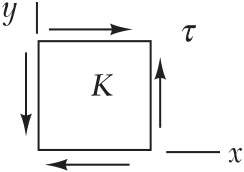
V = Fx = 10 ¥ 103 N
t = (2)(6 mm) = 12 mm = 12 ¥ 10–3 m
| save = 1 2(sx + sy) = 0 | R = | ��� | s | x | - | s | y | ��� | 2 | + | t |  |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
 |
||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T = My = 2000 N◊m | ||||||||||||
| txy = Tc J = ( | 2000 51 | ¥ | 10 | - | 3 | ) | ||||||
|
¥ | 10 | 6 | |||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | ||||
|
||||
|
||||
| D | ||||
| 50 mm | 1.8 kN | |||
Equivalent force-couple system at center of shaft in section at point H.
V = 1.8 kN M = (1.8 ¥ 103)(0.150) = 270 N◊m
| Chapter 7 | 829 | |
|---|---|---|
 |
||
 |
PROBLEM 7.26
7.26 A mechanical uses a crowfoot wrench to loosen at bolt at E. Knowing that the mechanic applies a vertical 100 N force at A, determine the principal stresses and the maximum shearing stress at point Hlocated as shown on top of the 18 mm diameter shaft.
T = (100)(250) = 25000 N◊mm



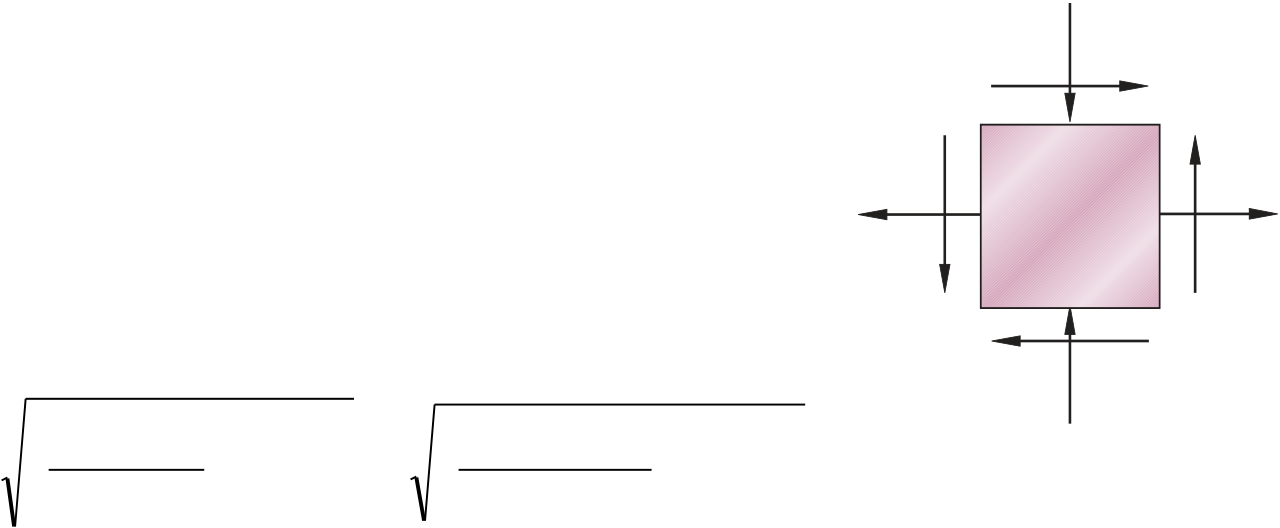



| sx = 82 MPa, |
|
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U = s | x | - | s |
|
||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||||
| R = U | 2 | + t | 2 | |||||||||||
| xy | ||||||||||||||
| 2 | = ± 100 | 2 | - | 28 | 2 | |||||||||
| U = ± R | - t | |||||||||||||
| xy | ||||||||||||||
sy = sx – 2U = 82 ± (2)(96) = – 110 MPa, 274 MPa
| U = ± R | 2 | - t | 2 | = ± 50 | 2 | - | 40 | 2 | Chapter 7 | 831 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xy |
sx = sy + 2U = 75 ± (2)(30) = 135 MPa, 15 MPa
60 MPa |
||
|---|---|---|
| 7.5 through 7.8 | ||
SOLUTION
| 832 | B | b | G | E | C | A |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
| Y: | O | s | ||||||||
| C: |
|
|||||||||
|
||||||||||
| (MPa) | ||||||||||
qA = 1 2a = 52.97º
R = CG 2 + GX 2 = 10 2 + 35 2 = 36.4 MPa
tmax = R = 36.4 MPa
s¢ = save = – 50 MPa
| 48 MPa | 16 MPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 7.5 through 7.8 | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| Points: |
|
y |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y: | ||||
| C: |
|
|||
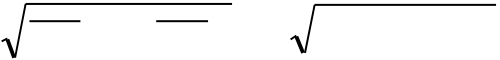
| sx = 120 MPa |
|
t |  |
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s= s | x | + | s | y | ||||||
| ave | 2 | D | ||||||||
| 834 | 70 MPa |  |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||||||||||
| R = CF | 2 | + | FX | 2 | = 105 | 2 | + | 60 | 2 |  |
|||
|
|||||||||||||
|
 |
||||||||||||
| 10 MPa | |||||||||||||
| 7.34 | |||||||||||||
stress, (b) the maximum in-plane shearing stress,
(c) the corresponding normal stress.
|
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R = FC | 2 | + | FX | 2 | = 30 | 2 | + | 20 | 2 | |||
|
||||||||||||
50 MPa
SOLUTION
| sx = 0 | x | + | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s= s | s | y | ||||
| ave | 2 | |||||
been rotated through (a) 25º clockwise, (b) 10º
counterclockwise.
|
y | sy = – 80 MPa | 40 MPa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sx = 55 MPa | |||||||
| s= s | x | + | s | ||||
| ave | 2 | ||||||
j = 50º – 30.65º = 19.35º
| Y | t |  |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sy¢ = save – R cos j = – 86.6 MPa | C | X¢ |
|
||||||
| X | |||||||||
| 20° |
|
||||||||
| j = 30.65 + 20º = 50.65º |
|
||||||||
| sx¢ = save + R cos j = 37.2 MPa | 110 MPa | ||||||||
 |
|||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| sy¢ = save – R cos j = – 62.2 MPa | |||||||||
| Solve Prob. 7.16, using Mohr’s circle. | |||||||||
wise.
SOLUTION
| 838 | X� | t | Y |
|
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| R = FC | 2 | + | FX | 2 | = 55 | 2 | + | 70 | 51.84° | ||||||||||
| 50° | |||||||||||||||||||
| = 89 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||
| O | C | j | |||||||||||||||||
| (a) q = 25º | |||||||||||||||||||
| MPa | |||||||||||||||||||
| j = 51.84º – 50º = 1.84º | X |  |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
j = 51.84º + 20º = 71.84º
sx¢ =save – R cos j = 27.2 MPa tx¢y¢ = R sin j = 84.5 MPa
sy¢ = save + R cos j = 82.7 MPa.
7.17 and 7.18 The grain of a wooden member forms an angle of
|
15° | 3 MPa |
|---|---|---|
|
s (MPa) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y: | X | C |
|
||||
| C: |
|
||||||
| q = – 15º | |||||||
| CX = 0.6 MPa | |||||||