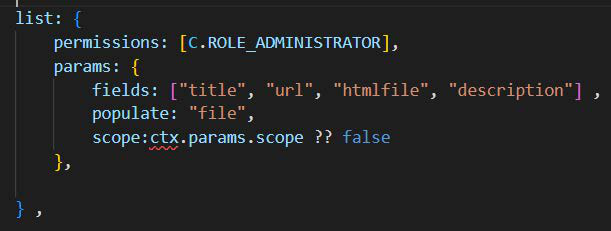
Hidden bydefault list the users const res broker
const check = v.compile(schema);
check({ name: "John", age: 42 }); // Valid
check({ name: "John" }); // Valid
check({ age: 42 }); // Fail because name is required
Nullable
If you want disallow undefined value but allow null value, use nullable
instead of optional .
null is a valid input for nullable fields that has default value.
const schema = {
about: { type: "string", nullable: true, default: "Hi! I'm using javascript" } }
const check = v.compile(schema)
const schema = {
name: { type: "string" }, // required
$$strict: true // no additional properties allowed }const check = v.compile(schema);
It is possible to define more validators for a field. In this case, only one validator needs to succeed for the field to be valid.
const schema = {
cache: [
{ type: "string" },
{ type: "boolean" }
]
}
|
|---|
options available on only method nor on action nor on schema
|
|---|
option available on Fields schema only, there are tonnes beside important listed below
• virtual : true
• hidden : true
• set
• populate
opts.scope is only available on three methods and those are
• updateEntity
Hence below params will not work in action list, thinking we can set the value params for the action list. Becauae as stated earlier params key inside the action here list object can only act as validation schema.
So, from section options only meta and other variable will be set that is given in signature of action pdf.
How to parse query string, Query string parameters. More information: https://github.com/ljharb/qs
like fields:{
username: { type: string ,
| Logger |
|
|---|
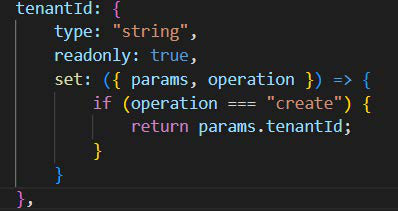
readonly: true => readonly property can be set by the local service only. Any incoming data from api service or any other service can't set it. Only local service can set it by defining a method in the field property itself. In order to set the value we have to define default, set method or other operation hooks for setting the value of read-only fields.
Immutable: true => Immutable fields value can be set only once and once set, it cant be changed in the future. However during the query we can use permissive = true that will ignore the immutable data and still let you change the value.
will be present if it is marked hidden by default, if it is marked as true than it will not be prsent.
})
Scope
Similarly scopes checking doesn't come magically, we have to define method to check scope, If we don't implement scopeAuthrity then anyone one can remove scope.
Fields
The field definition is similar to Fastest Validator schemas. You can define them in the same format and the service uses the Fastest Validator to validate and sanitize the input data. The difference between this schema and FV schema is that here all defined fields are optional (just like the fields in the Database Engines). You should set the property required: true for mandatory fields. i.e for validator , require is true by default, for db, require is false by default
| Example |
|---|
Field properties
type : <string> (no default value, it's a required property)
The type defines the type of the field value. It can be any primitive type ( boolean , number , string , object , array ) or any type from Fastest Validator types. If the type is not a valid database type, you should define the columnType property with a valid database field type as well.
{ id: "abc123",
username: "John Doe",
Example { title: { type: "string", required: true } }
What above means, if you set any field required and if it is not in the context params then it will through error for creating and replace action. Though it has default value or any value doesn't matter.
| Validation error |
|---|
secure
secure:<boolean<(default:false) With the secure property you can encrypt the value of the ID field. This can be useful to prevent users from finding out the IDs of other documents when the database uses incremental ID values. To use it, you should define encodeID(id) and decodeID(id) methods in the service that performs the encoding/decoding operations. The hashids lib can generate Youtube-like alphanumeric IDs from number(s) or from Mongo's ObjectID .Example secure ID using hashids lib`
}}, // ... more fields
methods: {
encodeID(id) {
return id != null ? hashids.encodeHex(id) : id; }, decodeID(id) {
return id != null ? hashids.decodeHex(id) : id; }}}
Please note that the methods should be synchronous.
| Example |
|---|
lastLogin: { type: "date", columnType: "datetime" }, createdAt: { type: "number", columnType: "bigInteger" } } The value of columnType depends on the used adapter and database engine.
default: <string|Function> (Default: null) => For the non-required fields, you can set default values. If the field value is null or undefined in the create and replace actions, the service will set the defined default value. If the default is a Function, the service will call it to get the default value. The function may be asynchronous.
| Property | Type | Callback parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Context | ||||
|
|
|||
| Object | ||||
| Object | ||||
|
|
|||
| String | ||||
| Object |
|
|||
|
Object | |||
| Example | ||||
Immutable: <boolean> (Default: false ) = > The immutable field means that you can set the value once. It cannot be changed in the future. Example {accountType: { type: "string", immutable: true }}
virtual : <boolean> (Default: false ) = >The virtual field returns a value that does not exist in the database. It's mandatory to define the get method that returns the value of the field.{ fullName: {
type: "string",
virtual: true,
get: ({ entity }) => `${entity.firstName} ${entity.lastName}` }}
hidden : <boolean|String> (Default: false ) = > The hidden fields are skipped from the response during transformation.
List the users with createdAt const res = broker.call("users.find", {fields: ["name", "createdAt", "password"]}) The response contains the name and createdAt fields
validate <Function|String> (Default: null ) = >With validate , you can configure your custom validation function. If it is a string, it should be a service method name that will be called. It can be asynchronous. The function should return true if the input value is valid or with a String if not valid. The returned text will be used in the ValidationError as the message of error. Example with validation error.
get is used when we want to transform the result to some other value during fetching, so whatever is stored in db and we want to change before sending it back to caller, we can use get method. However if we dint use get method that doesn't mean we will not get value what is stored in db. By default it returns the value stored in db without using get function in schema.
Callback parameters
| Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Context | ||
| any | ||
| Object |
|
|
| Object |
|
|
| Object | ||
} }
set: <Function> (Default: null) => The set function is called when creating or updating entities. You can change the input value or calculate a new one from other values of the entity. If it is a String , it should be a service method name that will be called. It can be asynchronous.
set: ({ params }) => `${params.firstName} ${params.lastName}` },
email: { type: "string", set: value => value.toLowerCase() }}
It can be asynchronous.
Callback parameters
| Property |
|
Description |
|---|---|---|
| ctx | Context |
|
| value | ||
| params | ||
| field |
|
|
|
||
| id | any | |
| operation | String | |
| entity | Object | |
| root | Object |
Callback parameters
| Property | { |
|
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ctx | |||
| value | |||
| params | |||
|
|
||
| field | |||
| id | |||
| operation | |||
|
|
||
| entity | |||
| root | |||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
Callback parameters
|
|---|
If you want to cherry pick the actions that are auto created, also if you want to set visibility of actions you can set actionVisibility in mixing.
The service generates common CRUD actions if the createActions mixin option is not false . You can finely control which actions should be created.
module.exports = {
mixins: [DbService({
|
Default |
|---|
Description
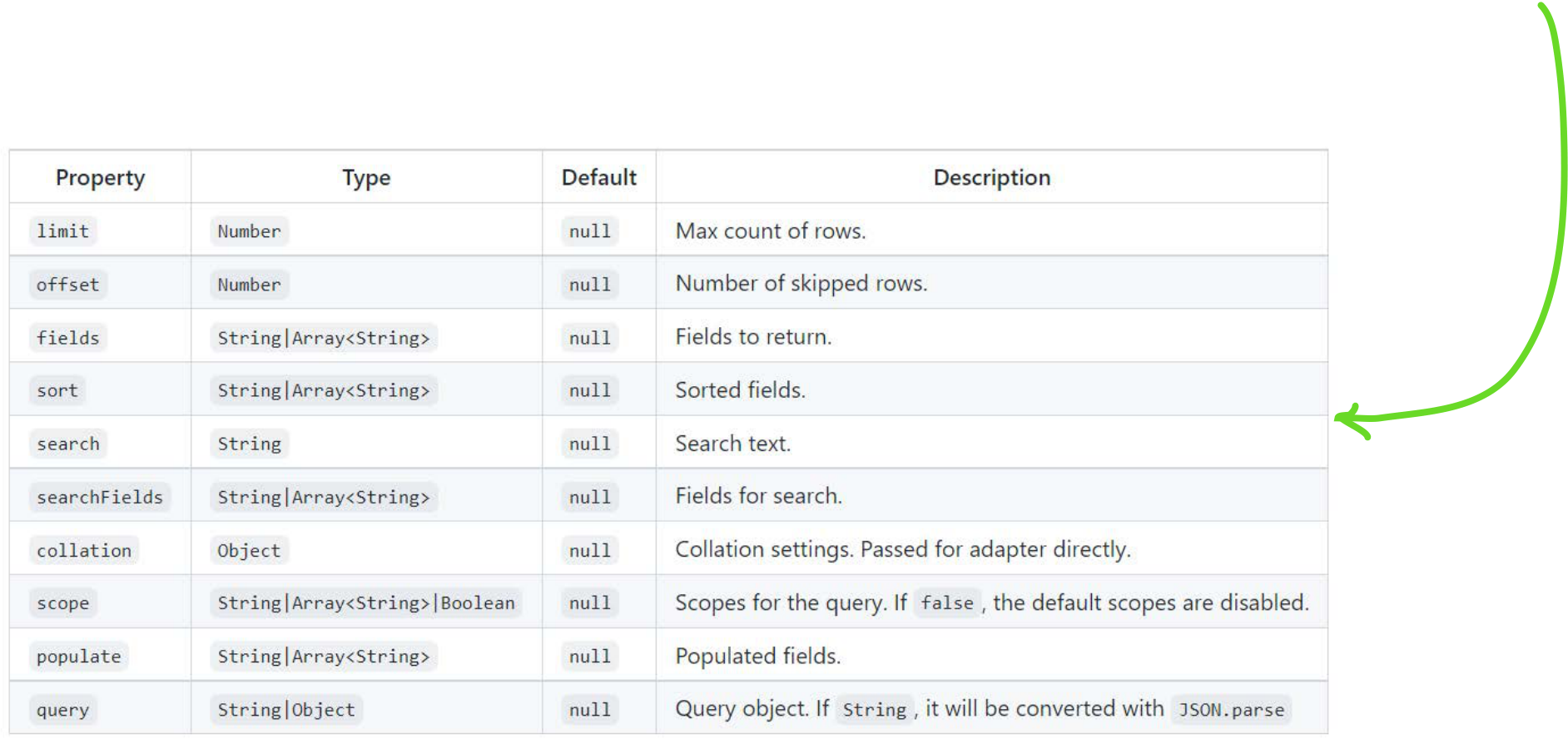
Max count of rows.
Fields for search. see blow for more about search fields are not used in mongoDB
Collation settings. Passed for adapter directly. Scopes for the query. If false, the default scopes are disabled.Populated fields.
While other database might supports search like solr which allow us to search on a specific fields or more than specific fields where are mongo creates one text index for one collection and it automatically look for the text type of data fields and create text index by merging all the text type fields.
For more on full text search watch below
status: true,
votes: {
$gt: 5
}
}} );
[
{
id: "akTRSKTKzGCg9EMz",
title: "Third post",
content: "Content of my 3rd post...", Results votes: 0, status: false,
createdAt: 1618077045354,
},
{
id: "0YZQR0oqyjKILaRn",
title: "My second post",
content: "Content of my second post...", votes: 3,
status: true,
createdAt: 1618077045352,
}
]Examples Limit & offset const posts = await broker.call("posts.find", { limit: 10, offset: 50 });
const posts = await broker.call("posts.find", {
|
|---|
2. listList entities with pagination. It returns also the total number of rows. Parameters
|
Default |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| null | ||||||||||
| null | ||||||||||
|
|
null | ||||||||
| null | ||||||||||
| null | ||||||||||
| searchFields |
|
null | ||||||||
|
null | |||||||||
| null | ||||||||||
|
null | |||||||||
|
null | |||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Results | }, | |||||||||
Examples Pagination The other parameter examples are the same as for the find action.
const posts = await broker.call("posts.list", { page: 3, pageSize: 10 });
| Examples |
|---|
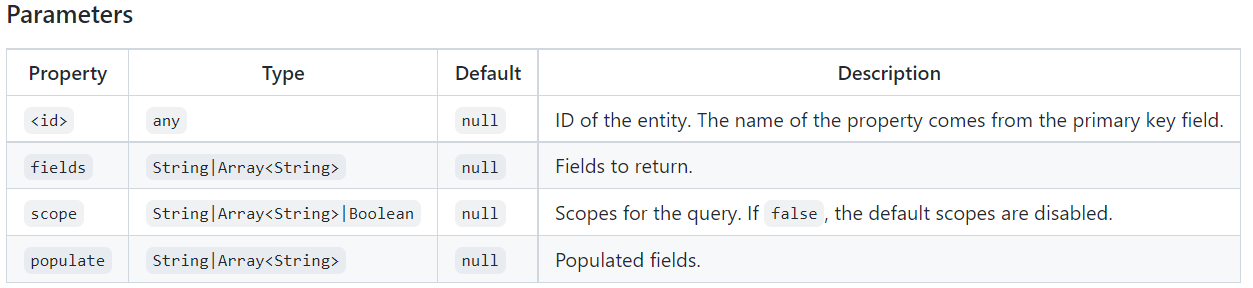
4. getGet an entity by ID, select which fields should be return, pass id.
status: true,
createdAt: 1618077608593 }
Code example
const post = await broker.call("posts.get", { id: "YVdnh5oQCyEIRja0" });Different ID field:
If you want to use another primary key field name instead of id , you should also use it in the action parameters.
| Type | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
null | |||
| null | |||||
|
|
null | |||
| null |
|
||||
|
false | ||||
| throwIfNotExist | false |
|
|||
|
|||||
| reorderResult | false | ||||
|
|||||
|
|||||
const post = await broker.call("posts.resolve", { id: ["YVdnh5oQCyEIRja0", "Di5T8svHC9nT6MTj"] });
});
{
The other parameter examples are the same as for the find action.
6. create Create an entity Create an entity.
|
|
|---|
Parameters There are no special parameters. All fields are used after validation for the entities.
REST endpointNot configured.
},
{
title: "My second post",
content: "Content of my second post..."
}
]);[
{
id: "YVdnh5oQCyEIRja0",
title: "My first post",
|
Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
any | null |
|
|
|---|
9. replace Replace an entity
Replace an existing entity. The difference between replace and update that replace replaces the whole entity. This means that you should specify all required entity fields. This function doesn't merge the new and old entity.
| Parameters | Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| any | null |
ResultsReturn the replaced entity.
| Examples | Result | { | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|||
action name : remove
11. Custom actions To add your own actions, simply create them under actions and call the built-in methods.
sanitizeParams(params: object, opts?: object): Sanitize the input parameters for find , list and count actions.
Options
| Type | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boolean | false | ||
| Boolean | |||
| false If true , the page and pageSize parameters (for list action) are sanitized. | |||
You can not use throwIfNotExist for any method except resolveEntities and one more
findEntity(ctx?: Context, params: object, opts?: object):Find an entity by query & sort. It returns only the first row of the result.
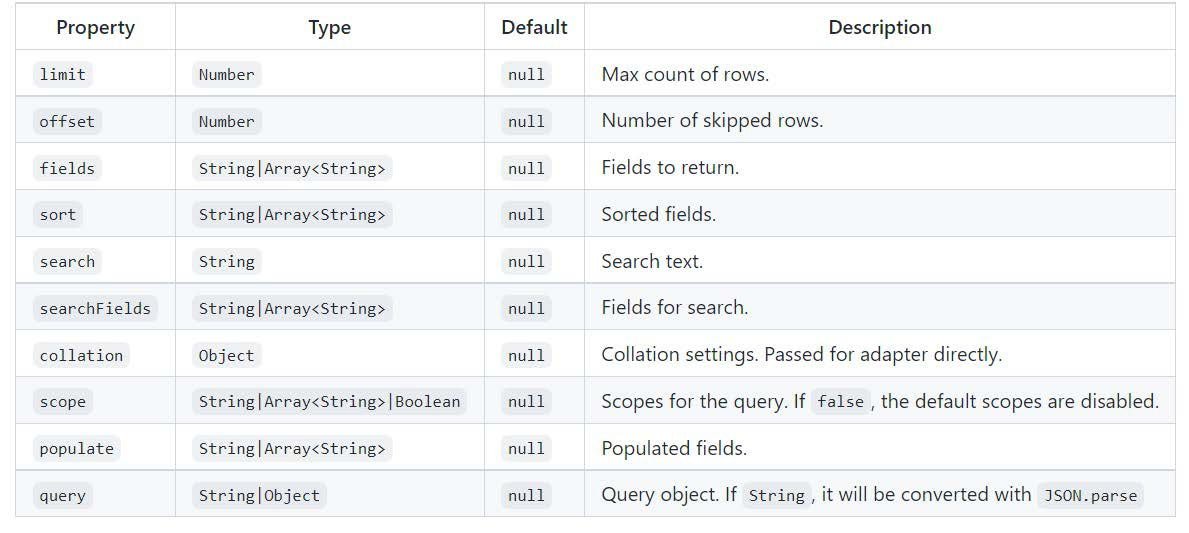
findEntities(ctx?: Context, params: object, opts?: object): Find entities by query. Parameters
| Type | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Context | null | ||
| Object | null |
|
|
| Object | {} | ||
|
|||
| opts.transform | Boolean | true |
| Property | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Context | null | ||
|
|
null | Parameters for search. It's same ascount action parameters, below I have listed the parameter from count function |
resolveEntities(ctx?: Context, params: object, opts?: object) => Return entity(ies) by ID(s).
| Type | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Context | null |
|
|
| null |
|
||
| {} |
|
||
|
Boolean | true | |
| false | |||
| opts.reorderResult | boolean | false | |
Note that there is no singular form of resolveEntities method
const user = await this.resolveEntities(ctx, ctx.params, { transform:
false }); let userd = await this.resolveEntities(ctx, { id: token.owner
});
const usere = await this.resolveEntities(ctx, { id: token.owner
});
let userf = await this.resolveEntities(ctx, { id: token.owner });
const userg = await this.resolveEntities(ctx, { id: ctx.meta.userID });
const userh = await this.resolveEntities(ctx, decoded, { transform:
false });
);
const _userb = await this.resolveEntities(
ctx,
{ id: ctx.meta.userID },
{ transform: false }
);
| Default | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
| false | |||
|
|||
| opts.returnEntities |
|
false | If true , it returns the inserted entities instead of IDs. |
|
Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Context | null | |
| Object | null | ||
| Object | null |
|
|
|
String | Array | |
| Object | null | ||
| Object | {} | ||
|
|||
|
Boolean | false | |
| Boolean | true | ||
| Boolean | false | ||
| If true , readonly and immutable fields can be set and update and field permission is not checked. |
removeEntity(ctx?: Context, params: object, opts?: object)Delete an entity by ID. The method returns only the ID of the deleted entity.
| Type | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Context | null | ||
|
|
null | |
| {} | |||
|
Boolean | true | |
|
|||
| Array | |||
| Boolean | null |
|
|
|
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Context | null |
|
|
| params |
|
null |
transformResult(adapter: Adapter, docs: object|Array<object>, params?: object, ctx?: Context) It transforms the entities coming from the database according to the definitions of the fields .
| Default | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
required |
|
||
| Object|Array<Object> | ||||
| required | ||||
| null |
|
|||
|
null | |||
| Moleculer Context instance. It can be null . |
getAdapterByContext(ctx?: Context, adapterDef?: object) For multi-tenancy, you should define this method which creates an Adapter definition by the Context .
It should return an Array with two values. The first is a cache key, the second is the adapter definition. The service uses the cache key to store the created adapter. Therefore in the next time, if the cache key is present in the cache, the service won't create a new adapter instance but will use the previous one.
encodeID(id: any) => You should define it when you use secure primary key to encrypt the IDs before returning them.
decodeID(id: any) => You should define it when you use secure primary key to decrypt the received IDs.
| ctx |
|
|
||||
| permission | ||||||
| params | ||||||
| field |
|
|
||||
| Property | Type | Description | ||||
| ctx | Context | |||||
| Parameters | name | String | ||||
| operation | String | |||||
| scope | any |
|
||||
Scopes
Scopes
The scopes allow you to add constraints for all query methods, like find , list or count . You can use them with soft-delete feature if you want to list only non-deleted entities. You can define your scopes in the service settings and set the default scopes.
name: "posts",
mixins: [DbService(/*...*/)],
status: true
},
},
// It's a custom Function to modify the query object directly. It can be async, as well.
return q;
}},
| List the active posts without scope definition |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| List all public posts |
|
|||
| List the active & public posts | ||||
| List all posts disabling the default scope(s) | const activePosts = await broker.call("posts.find", { scope: false }); | |||
You can define the indexes in the service settings.indexes property. It has a common format and each adapter will process and create the indexes. Another way, if you call the this.createIndex method directly. see below image Index definition Properties
Streaming The service has a streamEntities method that returns the entities by the query similar to the findEntities . But this method returns a Stream instance instead of all rows.
| Action for streaming |
|
|---|
Nested objects & arrays
The document-based database engines generally handle nested objects & arrays. You can also use them in the field definitions. The definition is similar to Fastest Validator nested object schema.
| Example for nested object field | |
settings: { |
|
module.exports = {
// ...settings: {
fields: {
phones: {
type: "array",
items: {
type: "object",
properties: {
type: { type: "string" },
number: { type: "string", required:true} primary: { type: "boolean", default: false }
}}}}};
Populating: The service allows you to easily populate fields from other services. For example: If you have an author field in the posts entity, you can populate it with users service by the author's ID. If the field is n Array of IDs, it will populate all entities with only one request.
verified: { type: "boolean", permission: "admin" }
}},
methods: {
// If we defined the necessary permissions in the fields, we should write // the permission checking logic into the `checkFieldAuthority` method.async checkFieldAuthority(ctx, permission, params, field) {
const roles = ctx.meta.user.roles || [];
// Returns `true` if the logged in user's role field contains the required role.
scopes: {
notDeleted: {
deletedAt: { $exists: false }
},
},
| List all posts (also deleted entities) | ||
module.exports = {
name: "posts",
mixins: [DbService(/*...*/)],
settings: {/* ... */},
methods: {
/**
* Check the scope authority. Should be implemented in the service.
| Example |
|
|---|
$set : it update the field value, if field is not present then it sets the value i.e. insert a new field with value. $push adds or create single elements to a array fields
Caching: The service has a built-in caching mechanism. If a cacher is configured in the ServiceBroker, the service caches the responses of find , list , get and resolve actions and clears the cache if any entities have been modified. Caching is enabled by default and uses the event name cache.clean.{serviceName} (e.g. cache.clean.posts ) to delete cached entries. To disable it, set cache.enabled = false in Mixin options.
Under the hood To cache the responses, the service uses the built-in action caching mechanism of ServiceBroker. The cache clearing is a bit complicated because if you are running multiple instances of the service with a local Memory cache, you should notify the other instances when an entity has changed. To cover this, the service broadcasts a cache clearing event (e.g. cache.clean.posts ) and also subscribes to this event. In the subscription handler, it calls the
broker.cacher.clean method. So if you have multiple instances of the service, and the first instance updates an entity, then it broadcasts the cache clearing event. Both instances will receive the event and both will clear the cache entries. It's simple but works with any number of instances.
The service will do it for you if you define the dependencies of service and the cacheCleanOnDeps mixin option is true . In this case, the service subscribes to all cache clearing events of the dependencies.
Example with dependencies The service also subscribes to the cache.clean.users and cache.clean.comments events.
"cache.clean.comments",
"my.some.event"
|
Method | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
{serviceName}.created | ||
| createMany | createEntities | {serviceName}.created | |
|
{serviceName}.updated |
|
|
| {serviceName}.replaced | |||
|
{serviceName}.removed | ||
|
|||
| {serviceName}.cleared | |||
Example: Let's say, you have a users service and a posts service. If a user is deleted, we should also delete the user's posts. users.service.js It's just a simple service, you don't have to set anything special.
module.exports = {
name: "users",
mixins: [DbService(/*...*/)],
settings: {
fields: {
id: { type: "string", primaryKey: true, columnName: "_id" },
name: { type: "string" },
email: { type: "email" }}}};adapterConnectedadapterConnected(adapter: Adapter, hash: string, adapterOpts: object)
It is called when a new adapter is created and connected to the database. You can use it to create data tables or execute migrations.
}}}
Entity hooks
{
name: "posts",
// ...
}}}}
3. Set this scope as default scope.
|
|
|---|---|
| Example | |
Steps for configuration : Define the getAdapterByContext method to generate adapter options for |
|
|
|
Adapters
The adapter is a class that performs the database operations with NPM libraries. This project contains many built-in adapters.
There are few common methods for all type of driver such as mongo driver, mysql driver , Knex driver etc.
ods
get hasNestedFieldSupport
It's a getter that returns whether the adapter can handle nested objects & arrays or not.
Disconnect from the database. Don't call directly!
find
find(params: object)Find an entity based on the primary key.
findByIds
findByIds(id: Array<any>)Count entities by params . The params contains the same properties as .
insert
insert(entity: object)Update an entity by ID. The changes contains the changed properties of the entity. It returns the updated entity. If the adapter supports the raw changes, you can enable it with opts.raw = true . In this case,
the changes is not manipulated but passed directly to the database client.updateMany
updateMany(query: object, changes: object, opts: object)removeById
removeById(id: any)Remove an entity by ID. It returns the removed entity ID.
Clear (truncate) the entire table/collection. It returns the number of entities removed.
entityToJSON
entityToJSON(entity: object)Remove an index from the table/collection. .
MongoDB adapter(This section is specific to MongDB)
Usage
Use the default localhost URI
Options
const row = await this.updateEntity(ctx, {
id: "YVdnh5oQCyEIRja0",$set: {
status: false,
height: 192
},
$inc: {
age: 1
},
$unset: {
dob: true
}
}, { raw: true });
objectIDToString
objectIDToString(id: ObjectID): String