Lower level manager 3 response summary (crm)
Table of Contents
Ways to increase organizational effectiveness 26
Middle Level Manager 1 Response Summary (Operations) 36
Middle Level Manager 2 Response Summary (Training) 37
Introduction
All organizations are concerned with what should be done through human resource to achieve a sustained level of performance. This means giving close attention to how individuals can best be motivated through incentives, job satisfaction, higher responsibility and most importantly, the work they do and the organizational context in which they carry out that work
According to David and Andrzej (1997), “the responsibility of the organization is to provide their members with a number of extrinsic and intrinsic rewards, which will enrich their lives and keep them happy. Extrinsic rewards are materials, monetary incentives and associated fringe benefits such as cheap loans, company car, free meals and so on. Intrinsic rewards include work specification, personal responsibility and autonomy. All these can increase the level of worker’s morale, effectiveness and efficiency.
Concept of employee motivation
Concept of Organizational Effectiveness
According to Rajhans, (2012), organizational effectiveness is the efficiency with which organizations are able to meet it set objectives. The prime measures of organizational effectiveness can be expressed through comparing its net profitability with its target profitability. On the other hand, Bogoviz et al., (2013) opined that the measures of organizational effectiveness could also be expressed through organizational growth data and the capability of employees towards satisfying the customers. Highly effective organizations tend to exhibit their strengths by leadership quality, motivation of employees and ability to make innovative decision towards new projects. According to Chiang and Hsieh, (2012), the effectiveness of organization can be determined through its financial development to its capital structure and the relationship between the labour force and productivity.
The productivity of the organization is highly dependent on ability of the employees towards performing as per the standard of the organization. This enhances the concept of employee motivation, where the motivated employees are more likely to perform at their best level. If the employees are getting the support of organizational leaders and the organizations are fulfilling their individual needs, they will positively contribute their effort at their peak to fulfil organizational goals. It has been found that Atlassian Organization of Australia highly take care of employee needs and value their needs so that they can fully concentrate on developing software (Kehoe & Wright, 2013). The organization leaders support the employees in understanding each module of the developing projects. In this way, the organization is highly effective in producing innovative projects and managing the feasibility of those projects.
STATEMENT OF PROBLEM
PURPOSE OF STUDY
The purpose of this study is to attempt to:
provide factors responsible for differences in employee work behaviour and performance
RESEARCH QUESTION
Why is staff motivation necessary for organisation?
How can motivation increase workers’ efficiency and effectiveness in organisation?
OBJECTIVES OF STUDY
To inquire into reasons why motivation is necessary in an organisation
To examine whether the present motivational system adopted by the organisations can increase workers’ efficiency and effectiveness
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY
SCOPE OF WORK
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS
Development: Development is defined as ways of increasing a person skill through trainings necessary for proper job performance.
Training: Training is defined as giving teaching to someone to bring him/her to a desired standard of behaviour and efficiency of physical condition.
Organization: Is defined as the grouping of two or more people with a common goal and aspiration. It is a social system that integrates all the resources to maximize profit and achieve a common goal.
CHAPTER SUMMARY
Motivation is basically concerned with the “what”, “how”, and “why” of human behaviour. A large part of a manager’s task is getting things done through people, he must therefore try to understand people’s motivation. This aspect of getting things done through people is concerned with inducing people to work to the best of their ability. All aspect of motivation of employees cannot be provided by management as other influences occur outside the working environment such as community and family pressures.
Literature Review
Needs Based Theory
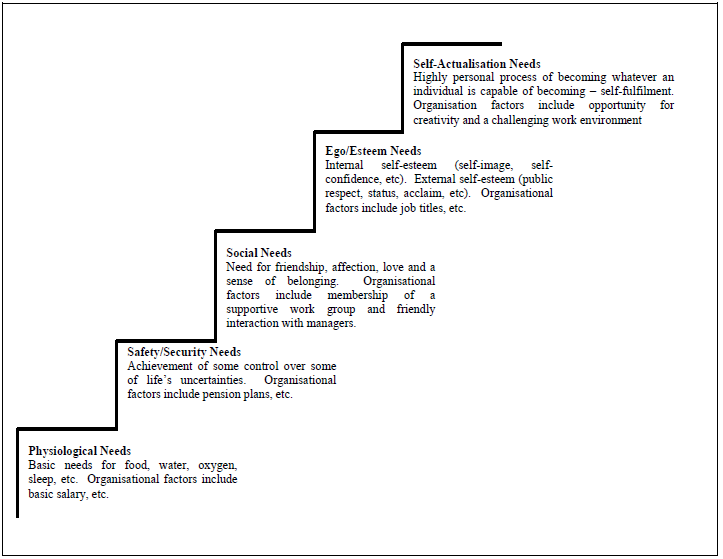
Figure2. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Psychological needs refer to the basic level needs of the employees, which are needed for their survival. According to Breevaart et al., (2014), effective managers should provide comfortable working hours and rational working hours for motivating the employees in their workplace. On the other hand, Imran et al., (2014) opined that employees should also get adequate breaks for getting energy in their work.
Safety Need
Esteem need is defined as the self-esteem and respect which employee gain from others in the organization. According to Hoon Song et al., (2012), effective manager should be highly concerned about the employees and praise them for their contribution in organizational success. On the other hand, Elnaga and Imra, (2013) opined that providing additional responsibility leads to adding value to the employees.
Self-Actualization
Herzberg Theory
Hygiene Factor
According to Gould-Williams, (2016), hygiene factors are highly essential for the existence of satisfaction in the workplace. These factors do not actually lead to positive satisfaction for the employees. However, absence of these factors may lead to job dissatisfaction. On the other hand, Barrick et al., (2013) opined that hygiene factors are extrinsic to the employees and needed for avoiding dissatisfaction in the workplace. These factors are called dissatisfiers and needed to be fulfilled by the organizational managers. The factors which are included under hygiene factor are described below:
Physical Environment
The employees would be interested to work enthusiastically when provided with a hygienic and clean work environment. The equipments related to the work should be well maintained and updated for smooth functionality.
Recognition
Employees are willing to work hard towards achieving organizational goals when they get proper recognition from the management on accomplishing job role. It makes sense that employee’s contribution is highly valued by organization and thus, employees are motivated towards achieving organizational goals.
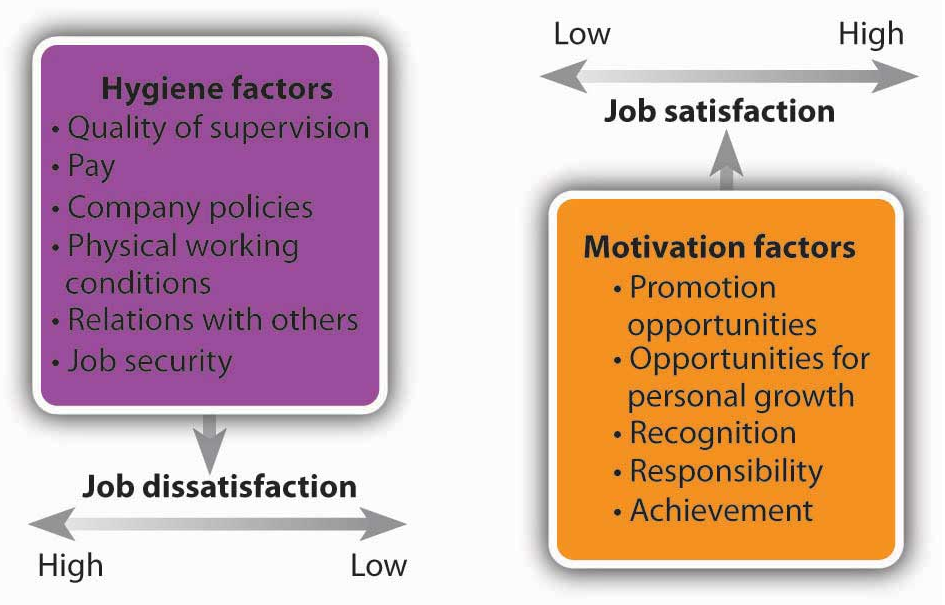
Figure 4: Herzberg Two-Factor Theory
Process-based Theory
Although the organization is able, through job design, to determine the levels of intrinsic rewards available in a job. The perceived levels of intrinsic rewards in the mind of the worker will be highly subjective. The levels of intrinsic rewards are therefore often seen as being beyond the direct control of the organization.
Goal setting theory largely attributed to (Locke, 1968)is a cognitive approach to motivation which proposes that intentions to work towards a goal are a major source of work motivation. Specifically, it suggests that specific goals increase performance. The task difficulty must be easy enough to ensure acceptance from the employee but difficult enough to encourage a high level of effort. Often referred to as stretched target, difficult goals, when accepted, result in higher performance than do easy goals and that feedback leads to higher performance than does non-feedback. Where employees have the opportunity to participate in setting their own goals, their effort exerted in achieving those goals will be greater than when the goals have been assigned to them (Moorhead & Griffin, 1995).
Goal Setting Theory
Realistic and Challenging Goals
According to Kehoe and Wright, (2013), realistic and challenging goals provide a sense of pride and triumph to the employees on achieving those goals. Therefore, these kind of jobs motivate the employees towards achieving the next challenging goals, which enhance the effectiveness of organization. While the organizational goals are challenging in project management, it is expected that the rewards would also be greater. Therefore, the employees become more passionate about achieving those challenging work by enhancing quality of project management.
Ways to increase organizational effectiveness
According to Chiang and Hsieh, (2012), organizational effectiveness is highly dependent on how the organizational leaders behave with their immediate followers. While managing a project of organization, the project managers should clearly communicate the vision and objectives of the projects to the employees. It would assist in making the employees dedicated towards achieving the goals of the projects. On the other hand, Jiang et al., (2012) opined that in case of project management, the project leaders should be supportive to the employees involved in project management. The project leaders should assign right job to right employees and prioritize the work as per the urgency of the project. It would lead effective project management and successful achievement of organizational goals. According to Imran et al., (2014), during project management, employees should get sufficient amount of authority over their job role so that they can feel value in their workplace. Too much of boundaries on the responsibilities of employees would create unwillingness towards their job role. On the other hand, Buller and McEvoy, (2012) opined that productivity of employees actually enhances through putting adequate amount of effort towards organizational success. While organizations initiate succession plan for the employees towards providing promotional opportunity, they become highly motivated towards working hard for organizational goals. Increasing efforts of the employees ultimately leads of better organizational effectiveness in project management.
Integrative Approach to Motivation Modelling
In order to model motivation a complete motivational framework incorporating elements of the motivation theories above needs to be used. Two existing models of motivation, Expectancy Model of Motivation and Job Characteristics Model (JCM) offer an integrative approach to modelling motivation.
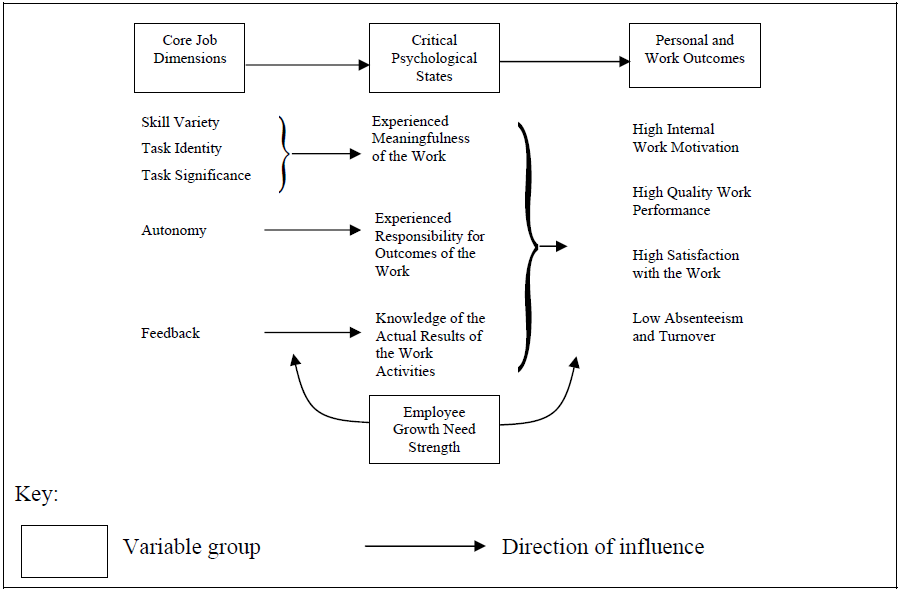
Figure7. Hackman and Oldham’s Job Characteristics Model.
Impact of employee motivation on organizational effectiveness
It has been found that Sausage Software in Australia allows their employees in organizational decision-making process. In this way, the organization gets ample numbers of solutions in case of their critical situation of project management. It becomes easy for the organization to choose the best alternative among the collected decision from the employees. It assists the organization enhance the quality of the project by getting various innovative ideas. According to Buller and McEvoy, (2012), good and generous benefits to the employees assist in encouraging them towards working hard for organizational success. They can easily coordinate their personal benefit with the organization goals. Satisfied and motivated employees their own impressive ways of working towards effective project management.
In concluding this literature review, it can be said that motivation is the internal drive that encourage the employees towards initiating some action. In project management, building effective team and encouraging that team is of highest priority for enhancing the effectiveness of the project. The more employees can associate their self-interest with organizational goal; the more employees will be motivated towards organizational success. Various theories created by famous psychologists highlight the factors of employee motivation and its impact on organizational success. Apart from that, providing great and attractive rewards would be helpful for the managers in increasing the productive of employees and organizational effectiveness.
Methodology
Research Design
This research requires an understanding of factors responsible for differences in employee work behaviour and performances, and explore if monetary incentives are more important to workers than other motivational incentives. This understanding requires an inquiry to be made with the people experiencing this phenomenon and thus, a phenomenology would be the most appropriate ontological foundation.
Sampling
The phenomenological method can be carried out using a minimum of 3 participants but as we are trying to establish an understanding of various sub-components of one phenomenon including performance and motivation, 6 respondents would be interviewed(Englander, 2012). These respondents include:
Mr. Trevor Dainty who is the Sales manager in the organization
Data Collection
This research uses an interview technique for which a questionnaire was prepared and was distributed to the respondents to obtain their views. This questionnaire included demographical data such as gender, age, occupation and experience. Further, open ended questions were prepared based on literature review for the interview. For this, one person from top level, 2 from middle level and 3 from lower levels were selected to take part in the interview process. The open ended questions were divided into six parts which includes:
What are the benefits of rewards and recognition as a method used for enhancing employee productivity?
What strategies do you use for rewarding or giving recognition to your employees?
Do you feel your employees are committed to organizational goals?
How do you get commitment from your employees for the organization?
Data Analysis
All these areas of inquiry would form the complete experience of the respondent and based on the same a thematic analysis would be carried out. As individuals selected reflect the perspective of a specific group. For instance, the middle level manager interviewed would represent all middle level manager views; the analysis would involve identification of collective themes.
The analysis would be carried out in 5 steps beginning with bracketing, delineating units of meaning of data, formation of clusters, and summary of interviews and extraction of a generic theme from all interviews.
Data Analysis
Findings
Top Manager Response Summary (CEO)
Productivity: Organizations use rewards and recognition to enhance the morale of the employees. These methods help improve their performance but they are only one of the strategies that contribute and others include healthy work environment, use of clear instructions on what we want to achieve, what role employees play and how they are vital for our success. Organizations use policies and procedures that include considerations of best principles of human resource management.Motivation affects the way employees behave and they are more confident and professional. Happy employees are 15% more productive.
Rewards & recognition: It empowers employees and reduces competitiveness within company but differential rewards based on personal preferences or position is not effective. Rewards purely based on performance are more effective.
Middle Level Manager 1 Response Summary (Operations)
Rewards & recognition: Reward and recognition can reduce workers’ turnover in an organization. Use of initiative rather than bureaucracy can stimulate employee performance and effectiveness.
Organizational Effectiveness: Elimination of unhealthy rivalry among workers in our company increases organizational effectiveness. Employees have skills but if they lack willingness to make best use of it, efficiency cannot be achieved. Motivation fills this gap. Effectiveness is determined by their ability to achieve desired goals.
Middle Level Manager 2 Response Summary (Training)
Organizational Effectiveness: Focusing on overall performance of the organization rather than individual employees’ performance helps organizational effectiveness. Motivated employees tend to participate more in work and thus, their efficiency is increased. Because of more involvement, their decisions are well thought and thus, they are also more effective.
Employee commitment: Employees are engaged but not committed. External strategies may be used for making them committed such as a proper direction and performance measurement criteria’s based on achievements.
Lower Level Manager 1 response summary (HR)
Employee commitment: Employees are not committed but they show commitment. When properly monitored, their performance is measures and they are given appropriate rewards and recognition
Employee Motivation: Motivation brings benefits like better productivity, job satisfaction, employee satisfaction and better performance. Yes by giving them feeling of worth and trust in the system. Employees can be motivated and de-motivated based on their desired and undesired behavior. Positive reinforcement is used for performing employees. Negative reinforcement, punishment and termination are used for non-performers.
Lower Level Manager 2 response summary (Sales)
Employee Motivation: Motivation provides differentiation to companies which help retain good people. Good motivation like rewards, recognition, support, etc. can keep best of them satisfied but remaining employees may not be satisfied.
Lower Level Manager 3 response Summary (CRM)
Productivity: Productivity parameter is affected by the job profile. Different strategies would work for different profiles.
Discussions
Productivity: Organizations use various productivity improvement strategies like:
rewards and recognition,
Complete delegation with authority
Gender consideration
More confidence and professionalism
Morale boost in employees
Efficient and effective resource usage
Increase retention
Rewards given based on performance
People achieving targets and getting good ratings from team members and seniors get more rewards
Reduction in within company competitiveness
Improved performance
Organizational Effectiveness: Techniques and strategies used for improving organizational effectiveness include
Rewards and recognition
Use of both positive and negative motivation techniques like rewards and punishments
Establishing goals and discipline
More participation from employees at work
Better decision making
Hannan& Freeman's Theories are most prominent theories of organizational effectiveness. They identify constraints, adaptation needs, inertia and selection as important aspects for organizational effectiveness. The interview responses do identify the dimensions of adaptation needs by having profile based approach to rewards, selection efficiencies for differential rewards and organizational constraints such as inability to give rich rewards to everyone. However, the inertia which may be caused by lack of skills in employees or other organizational limitations is not explored in the practical interview. However, this can be a very important dimension as the strategies used would not remain effective if these constraints are not taken care of.
Commitment: Managers at all levels felt that employees are not committed to achieving organization goals unless they are provided an opportunity to achieve their own personal goals by achieving organizational goals. Rewards and recognition gives this opportunity. Strategies that are used by organization to get them committed:
Strategic direction
Benefits achieved with these strategies include:
Theories suggest that commitment levels have different levels of impacts on employees as well as on the organization. Various forms of effects that can be seen include buffering when weak commitment causes more stress in employees, exacerbating when strong commitment causes more stress and pseudo-exacerbating when weak commitment cause more stress as compared to strong commitment. The interview responses only suggest that higher level of commitment has good impact on organization but the impact of the same on employees is not been explored. There has to be a balance between the stress caused to commitment to be able to sustain commitment in employees. Thus, an organization may try to understand how different levels of commitments can cause stress in employees in an organization.
Employee Motivation: Techniques used by organizations for motivating employees include:
Managers guiding their juniors as coach
Brings willingness in employees to work
Besides Mc Gregor, Maslow’s and Herzberg theories of motivation, Urwick’s Theory and Porter and Lawler’s Expectancy Theory are two more popular theories of motivation.Urwick theory is similar to McGregor X & Y theory but has different propositions that include importance of people knowing organizational goals, and relationship between them and the individual needs. The theory is supported in the findings as organizations do understand that employee needs have to be aligned with organizational goals to achieve performance.
Porter’s theory is an improved version of Vroom’s theory which suggests that motivation efforts do not increase performance directly but is mediated by people abilities and traits. Thus, strengthens the finding that suggested use of differential approaches to rewards and recognition for individuals and the role of immediate senior in motivating people. Perception of employees about the value of rewards is thus, important to consider.
Recommendations
Role of immediate senior is important and such a person must act as a coach and guide for juniors to ensure highest level of productivity
Only best performers mostly get rewards and recognition which is why others remain de-motivated and thus, rewards and recognition may not be a sufficient strategy used for motivation and more strategies must be used by organization such as healthy work environment, social communication opportunities, coaching and direction from seniors and so on
Conclusions
References
Allen, M. R., Ericksen, J., & Collins, C. J. (2013). Human resource management, employee exchange relationships, and performance in small businesses. Human Resource Management, 52(2), 153-173.
Barrick, M. R., Mount, M. K., & Li, N. (2013). The theory of purposeful work behavior: The role of personality, higher-order goals, and job characteristics. Academy of Management Review, 38(1), 132-153.
Cherian, J., & Jacob, J. (2013). Impact of self efficacy on motivation and performance of employees. International Journal of Business and Management, 8(14), 80.
Chiang, C. F., & Hsieh, T. S. (2012). The impacts of perceived organizational support and psychological empowerment on job performance: The mediating effects of organizational citizenship behavior. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 31(1), 180-190.
Gallie, D., Zhou, Y., Felstead, A., & Green, F. (2012). Teamwork, skill development and employee welfare. British Journal of Industrial Relations,50(1), 23-46.
Gould-Williams, J. S. (2016). Managers’ motives for investing in HR practices and their implications for public service motivation: a theoretical perspective. International Journal of Manpower, 37(5), 764-776.
Kehoe, R. R., & Wright, P. M. (2013). The impact of high-performance human resource practices on employees’ attitudes and behaviors. Journal of management, 39(2), 366-391.
Manzoor, Q. A. (2012). Impact of employee’s motivation on organizational effectiveness. Business management and strategy, 3(1), 1.
Porter, T. H., Riesenmy, K. D., & Fields, D. (2016). Work environment and employee motivation to lead: Moderating effects of personal characteristics.American Journal of Business, 31(2), 66-84.
Rajhans, K. (2012). Effective organizational communication: A key to employee motivation and performance. Interscience Management Review,2(2), 81-85.
Van De Voorde, K., Paauwe, J., & Van Veldhoven, M. (2012). Employee well‐being and the HRM–organizational performance relationship: a review of quantitative studies. International Journal of Management Reviews, 14(4), 391-407.
Yidong, T., & Xinxin, L. (2013). How ethical leadership influence employees’ innovative work behavior: A perspective of intrinsic motivation. Journal of Business Ethics, 116(2), 441-455.
Kleiber, D., Walker, G., & Mannell, R. (2011). A Social Psychology of Leisure (2 ed.). Venture Pub.
Lester, S. (2000). An introduction to phenomenological research. RGS.
Vroom, V. (1964). Work and Motivation. John Wiley & Sons. inc.
Appendices
QUESTIONNAIRE
The aim of the questionnaire is to sample the opinions of respondents on how to Improve Organizational Effectiveness and Employee Motivation across Sectors. Your feedback is greatly appreciated and is very important as they will help this research in meeting its set objectives.
SECTION I
AGE: 20 - 29 years [ ] 30 – 39 years [ ] 40 – 49 years [ ]
50 – 59 years [ ] 60 years + [ ].
SECTION II
Productivity
How do you boost the productivity of the employees in your organization?
Organizational Effectiveness
What strategies do you use to improve your organizational effectiveness?
Employee Motivation
Is it important to motivate employees in an organization? If yes then why?
Section 2 Responses
Response 1:
How do you boost the productivity of the employees in your organization?
We use rewards and recognition which can enhance the morale of the employees thereby improving their performance at work...What rewards to give and how they are recognized is decided by top management. But this is not sufficient enough to ensure productivity of employees but also creation of a healthy work environment and keeping them motivated is also important. To ensure healthy work environment, we use clear instructions on what we want to achieve, what role employees play and how they are vital for our success. We use policies and procedures that include considerations of best principles of human resource management.
It empowers employees and reduces competitiveness within company. Yes, of course, if differences are there in rewards based on personal preferences or position then it can be dangerous and can lead to internal dislikes but we ensure that our processes are transparent and equal for everyone.
What strategies do you use for rewarding or giving recognition to your employees?
Do you feel that good motivation can enhance workers’ efficiency and effectiveness in organization? Why?
Yes, of course, motivated people tend to achieve goals more easily and thus, are more effective. Efficiency is about the maximum contribution a person can make to the company while working. Well, a motivated employee obviously tries to make the productive use of most of his or her time but the efficiency would depend more on the experience, skills and capabilities of individuals. So, we may say that motivation facilitates best use of skills to achieve efficiency but it does not guarantee it.
Getting commitment is tricky. We try to keep them happy and use retention policies but it depends on them how they value our rewards and recognition systems. What have observed is that employees remain committed to goals to a fair level.
Employee Motivation
What strategies do you use for motivating your employees and if they are sufficient enough to obtain optimum productivity in employees?
We usually have managers acting as examples and they automatically motivate people. Other than that we have strong rewards and recognition system and a healthy work environment.
Response 2:
Yes, employees are motivated when their good work gets recognition so they want to get more rewards for which they either try to do even better in future or at least remain consistence in performance.
Rewards & recognition
Organizational Effectiveness
What strategies do you use to improve your organizational effectiveness?
Do you feel your employees are committed to organizational goals?
They are not by default so we have to attach rewards for being committed.
Yes, as I already mentioned, it fills the gap between skills and willingness to work.
Do you feel that good motivation can enhance job satisfaction of employees? How?
Response 3:
How do you boost the productivity of the employees in your organization?
We use time-bound targets for employees to facilitate performance
Financial rewards motivate people to work more and better.
What strategies do you use for rewarding or giving recognition to your employees?
Do you feel that good motivation can enhance workers’ efficiency and effectiveness in organization? Why?
Motivated employees tend to participate more in work and thus, their efficiency is increased. Because of more involvement, their decisions are well thought and thus, they are also more effective.
We cannot expect internal commitment so we use external factors for getting committed work. For instance, a proper direction and performance measurement criteria’s based on achievements make them committed to organizational goals. For instance, if we say that employees attending training and furnishing good score in assessment will get a better ranking in appraisal then it would motivate employees to participate.
Employee Motivation
What strategies do you use for motivating your employees and if they are sufficient enough to obtain optimum productivity in employees?
Not enough, there is always a scope for improvement but we do use some good strategies like coaching approach from seniors, rewards and good recreational and social relationship building opportunities.
Response 4:
Motivation brings down absenteeism; improve bottom line figures and increases chances of retention. So they work more, better and for longer time. Thus, they are productive.
Rewards & recognition
Organizational Effectiveness
What strategies do you use to improve your organizational effectiveness?
Do you feel your employees are committed to organizational goals?
They are not. They can only be pushed to show commitment.
Yes, motivation brings benefits like better productivity, job satisfaction, employee satisfaction and better performance.
Do you feel that good motivation can enhance job satisfaction of employees? How?
Response 5:
How do you boost the productivity of the employees in your organization?
Gender consideration in apportioning rewards and recognitions to employees stimulates employee performance so we have a gender in all our performance management techniques.
More money or more recognition gives sales people a confidence boost so they talk better and thus, are more productive.
What strategies do you use for rewarding or giving recognition to your employees?
Do you feel that good motivation can enhance workers’ efficiency and effectiveness in organization? Why?
Efficiency means doing things right way and effectiveness means doing right things. A right way gives long term gains while right things ensure gains. So, we need both. Motivation can get right things done but right way is not guaranteed. A motivated sales person may achieve annual target but what if he uses coercive forces on colleagues or others to get those targets achieved? Positive Motivation would not help but may be negative motivation help if they get punishment for using wrong ways.
We just give them what they want without having a negative impact on business. They want a foreign trip; we give them as long as that is within budget and results into a really big deal.
Employee Motivation
What strategies do you use for motivating your employees and if they are sufficient enough to obtain optimum productivity in employees?
Not sufficient, there is always scope for learning and sometimes there are limitations. For instance, we cannot give foreign trips to everyone. But we do have good strategies for the best of best employees. Others may not be well taken care of in reality. Only when you shine, you get the gold.
Response 6:
Motivated employees serve customers better so they are more productive.
Rewards & recognition
Organizational Effectiveness
What strategies do you use to improve your organizational effectiveness?
Do you feel your employees are committed to organizational goals?
Commitment to goals has to be high when they are closely watched but then wherever they can have an opportunity, they can relax and avoid things. For instance, if an employee needs to make a specific number of calls to be measured as productive, he may make sufficient calls but effectiveness of these calls would not be guaranteed. If they are not committed, they may make half hearted attempted that will not convert into organizational benefit.
Yes, it is because motivated employees are easy to manage
Do you feel that good motivation can enhance job satisfaction of employees? How?
