Lqb human cell molecular biologyvirgen workshop answer sheetssemester
https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/guest-blog/body-altering-mutations-in-humans-and-flies/
COPYRIGHT – Dr Sally-Anne Stephenson, QUT
https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/guest-blog/body-altering-mutations-in-humans-and-flies/

http://apps.health.qut.edu.au/scb122/QUT%20VirGen/flies/virgen.htm
INSTRUCTIONS
If the message is "OK" you can proceed to look at the F1 progeny numbers using the "See the results" link. If not, you will have to modify your selection(s).
Click on the link at the bottom to mate the F1 flies and see the F2 progeny numbers. However, if there is more than one phenotype of F1 female, or more than one phenotype of F1 male, you should think about what this means before proceeding.
Mate the parent flies
note down the F1 phenotypes and numbers
outline the segregation of alleles and phenotypes from parents to F2
do a chi-square test of your hypothesis on the F2 data
Wild type female x Radius Incomplete male
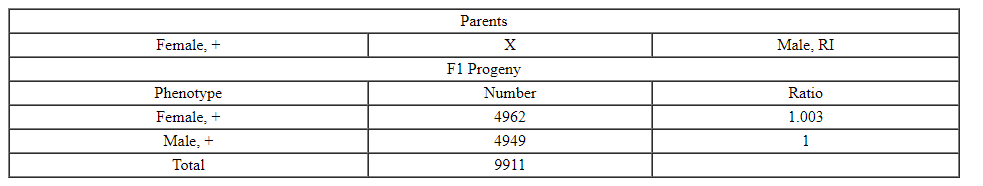
Recessive because F1 (heterozygous) are wild ∴ brown is recessive
4. Model Parents Wild type female x Radius Incomplete male
Gametes + , ri x + , ri
Punnet square
| + ri | ||
|---|---|---|
| + + | + ri | |
| + ri | ri ri | |
7. χ2 is less than 3.84 and F2 ratio is as predicted by model ∴ hypothesis is accepted.
Monohybrid cross number ______2_____
| Parents | F1 cross – Combined sexes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female, ____ | x | Male, __ | Female, ___ | X | Male, ___ | |
| F1 Progeny | F2 progeny | |||||
| Phenotype | Number | Ratio | Phenotype | Number | Ratio | |
| Female, ___ | ___ | |||||
| Male, ___ | ___ | |||||
| Total | Total | |||||
4. Model Parents __Lobe Eyes__ female x __Wild Type___ male
__ __ x __ __
Punnet square
| Phenotype | Observed numbers | Expected ratio |
|---|---|---|
| df = 1 | ||
Because this is less than / more than (circle one) the Chi Square statistic value for 1 degree
freedom (3.84) the F2 ratio is / is not (circle one) as predicted by model
2. Hypothesis __ Curved Wing ___ is _______________and __________________
3. Reasoning ____________ because _________________________________________
F1 __ __
F1 cross __ __ x __ __
| __ __ | ||
|---|---|---|
| __ __ | __ __ | |
| __ __ | __ __ | |
5. Predict F2 phenotype ratio should be __________ : _____________
6. Chi-square test (computer generated)
is accepted / rejected (circle one).
Monohybrid cross number ______4_______
| Parents | F1 cross – Not combined | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female, ____ | x | Male, __ | Female, ___ | X | Male, ___ | |
| F1 Progeny | F2 progeny | |||||
| Phenotype | Number | Ratio | Phenotype | Number | Ratio | |
| Female, ___ | Female, ___ | |||||
| Male, ___ | Male, ___ | |||||
| Total | Male, ___ | |||||
| Total | ||||||
4. Model Parents ___ Wild type ___ female x __ Tan Body __ male
__ __ x __ __
Punnet square
| Phenotype | Observed numbers | Expected ratio |
|---|---|---|
| df = 2 | ||
7. χ2 is ____________ .
Because this is less than / more than (circle one) the Chi Square statistic value for 2 degrees of freedom (5.99) the F2 ratio is / is not (circle one) as predicted by model
Can't cross the F1 flies - F1 ratios are wrong for that option
NB
____________ because _________________________________________
4. Model Parents __________ female x ____________ male
Gametes , x ,
Punnet square
| __ __ | ||
|---|---|---|
| __ __ | __ __ | |
| __ __ | __ __ | |
__________ : _____________:__________ : _____________
6. Chi-square test (computer generated)
Monohybrid cross number ______6_______
1. ___Bar Eyes____ female x __Wild type____ male
| Parents | F1 cross – Not combined | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female, ____ | x | Male, __ | Female, ___ | X | Male, ___ | |
| F1 Progeny | F2 progeny | |||||
| Phenotype | Number | Ratio | Phenotype | Number | Ratio | |
| Female, ___ | Male, ___ | |||||
| Male, ___ | Female, ___ | |||||
| Total | Male, ___ | |||||
| Total | ||||||
__ __ x __ __
Gametes x /
| Phenotype | Observed numbers | Expected ratio |
|---|---|---|
| df = 2 | ||
Because this is less than / more than (circle one) the Chi Square statistic value for 2 degrees of freedom (5.99) the F2 ratio is / is not (circle one) as predicted by model
∴ the hypothesis that Bar Eyes is _________________ and ________________
NB
Dominant OR recessive OR lethal
4. Model Parents _ Wild type__ female x _ Aristapedia Antenna __ male
__ __ x __ __
Punnet square
__ |
__ __ | |
|---|---|---|
| __ __ | __ __ | |
| __ __ | __ __ | |
6. Chi-square test (computer generated)
7. χ2 is ____________ .
For each of the crosses listed below:
mate the parent flies
determine (hypothesise) the mode of inheritance of each mutation (autosomal, sex-linked, dominant, recessive and combinations thereof) and predict the phenotype ratios in the F2
outline the segregation of alleles and phenotypes from parents to F2
The crosses are:
purple eyes female x spineless bristles male
_________________________________ female x _________________________________ male
Insert tables here
| Parents | F1 cross – Combined sexes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female, ____ | x | Male, __ | Female, ___ | X | Male, ___ | |
| F1 Progeny | F2 progeny | |||||
| Phenotype | Number | Ratio | Phenotype | Number | Ratio | |
| Female, ___ | ||||||
| Male, ___ | ||||||
| Total | ||||||
| Total | ||||||
And is ____________ because _________________________________________
Spineless Bristles is ____________ because _________________________________________
F1 __ __ __ __
F1 cross __ __ __ __ x __ __ __ __
_________________ : _________________ : _________________: _____________________
6. Chi-square test (computer generated)
| Phenotype | Observed numbers | Expected ratio |
|---|---|---|
| df = 3 | ||
_________________________________ female x _________________________________ male
2. Hypothesis Phenotype 1 __Lobe eyes __ is ______________ and _________________
Vestigial Wing is ____________ because _________________________________________
And is ____________ because _________________________________________
F1 cross __ __ __ __ x __ __ __ __
Gametes
__ __ __ __ |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
6. Chi-square test (computer generated)
7. χ2 is ____________ .
| Parents | F1 cross – Can’t combine sexes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female, ____ | x | Male, __ | Female, ___ | X | Male, ___ | |
| F1 Progeny | F2 progeny | |||||
| Phenotype | Number | Ratio | Phenotype | Number | Ratio | |
| Female, ___ | ||||||
| Male, ___ | ||||||
| Total | ||||||
| Total | ||||||
2. Hypothesis Phenotype 1 __White eyes_____ is ______________ and _________________
Phenotype 2 ___black body_ is ______________ and _________________
And is ____________ because _________________________________________
4. Model Parents _____________ female x ______________ male
Gametes
__ __ , __ __ , __ __ , __ __ x __ __ , __ __ , __ __ , __ __
6. Chi-square test (computer generated)
| Phenotype | Observed numbers | Expected ratio |
|---|---|---|
| df = 7 | ||
7. χ2 is ____________ .
2. Hypothesis Phenotype 1 ___Lobe Eyes____ is ______________ and _________________
Phenotype 2 ___Sable Body_ is ______________ and _________________
And is ____________ because _________________________________________
4. Model Parents _____________ female x ______________ male
Gametes
__ __ , __ __ , __ __ , __ __ x __ __ , __ __ , __ __ , __ __
__ __ __ __ |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
6. Chi-square test (computer generated)
7. χ2 is ____________ .
mate the parent flies exactly as shown
backcross the F1 females back to the parent male and note down the F2 phenotype numbers
The crosses are:
wild type female x eyeless eyes and shaven bristles male
| Map Distance | Gene location | Linkage | Amount of Crossing over |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 – 5 cM | Very close | Very Tight | Very little |
| 6 – 20 cM | Close | Tight | Little |
| 21 – 30 cM | Somewhat Near | Loose | Some |
| 31 – 50 cM | Far (but still on same chromosome) | Very Loose | A lot |
| 51+ cM | Very far | Not linked |
Linkage cross number ______1_______
1. ________________________________ female x _________________________________ male
4. Ratio produced is _______ : _______ : _______ : _______
Hypothetical ratio if not linked is 1 + : 1 EY : 1 SV : 1 EY, SV
| Phenotype | Observed numbers | Expected ratio |
|---|---|---|
| df = 3 | ||
8. Map distance = ______cM
9. The genes for _______________ and ______________ are located _______________________
_________________ : _________________ : _________________ : _________________
3. Parental phenotypes are ___________________ and _____________________________
| Phenotype | Observed numbers | Expected ratio |
|---|---|---|
| df = 3 | ||
6. _____________ is greater than _______ ∴ does/does not support independent assortment.
Suggests ____________________
Linkage cross number ______3_______
1. ________________________________ female x _________________________________ male
4. Ratio produced is _______ : _______ : _______ : _______
Hypothetical ratio if not linked is 1 + : 1 BW : 1 DP : 1 BW, DP
| Phenotype | Observed numbers | Expected ratio |
|---|---|---|
| df = 3 | ||
8. Map distance = ______cM
9. The genes for _______________ and ______________ are located _______________________
_________________ : _________________ : _________________ : _________________
3. Parental phenotypes are ___________________ and _____________________________
| Phenotype | Observed numbers | Expected ratio |
|---|---|---|
| df = 3 | ||
6. _____________ is greater than _______ ∴ does/does not support independent assortment.
Suggests ____________________
Working with Drosophila fly crosses is a relatively simple way to demonstrate genetic principles. When dealing with human genetics such analyses are not possible. Even if you could tell people with whom to marry & produce offspring, the wait to see the outcome of each cross would be tedious (especially if the trait only manifested itself in mature individuals!). Furthermore, the number of human offspring is not sufficient for any meaningful statistical analysis (as may be done using Drosophila cross data in VirGen).
Pedigree analysis involves the plotting of family relationships back through as many generations as possible (a.k.a. genealogy). The result is a family tree or pedigree. When members of the family inherit a characteristic phenotype this may also be plotted on the pedigree. These phenotypes may simply be examples of commonly seen variation in human features such as eye colour, widow’s peak or attached earlobe OR they may be pathological disease states.
= male showing trait = female showing trait
Problems: For each pedigree determine (where possible) whether the trait is dominant or recessive and whether it is autosomal or sex linked.
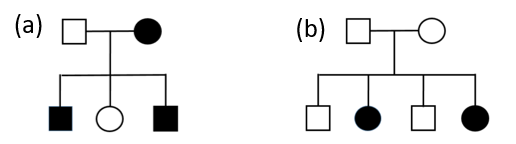
______________________________ _____________________________
______________________________ _____________________________
______________________________ _____________________________
b) III-2 X III-3 ____________________
Problem 3: In this pedigree we know that I-2 is homozygous. With this in mind, is the pedigree displaying a Dominant or recessive trait? a) Is I-1 homozygous or heterozygous? b) What is the probability that the offspring of couple IV-2 and IV-3 will have the trait? c) What is the probability for that the offspring of III-1 and III-2 will have the trait?
c) ______________________________________________
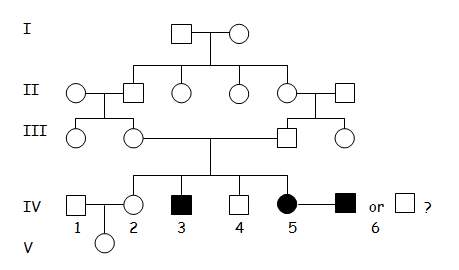 Problem 4: Is
the following pedigree displaying a Dominant or recessive trait? What is
the probability that the offspring of IV5 will show the trait if she
marries a) her boyfriend with the trait OR alternatively b) another
boyfriend who is known to be heterozygous, OR c) these two boyfriends
fight leaving the field clear for her childhood sweetheart who is
homozygous wild type...
Problem 4: Is
the following pedigree displaying a Dominant or recessive trait? What is
the probability that the offspring of IV5 will show the trait if she
marries a) her boyfriend with the trait OR alternatively b) another
boyfriend who is known to be heterozygous, OR c) these two boyfriends
fight leaving the field clear for her childhood sweetheart who is
homozygous wild type...
(20 marks)
