Normalize each peak the intensity the largest peak ihkl ihkl
Problem 2- Reciprocal Lattice and Diffraction – 20
points
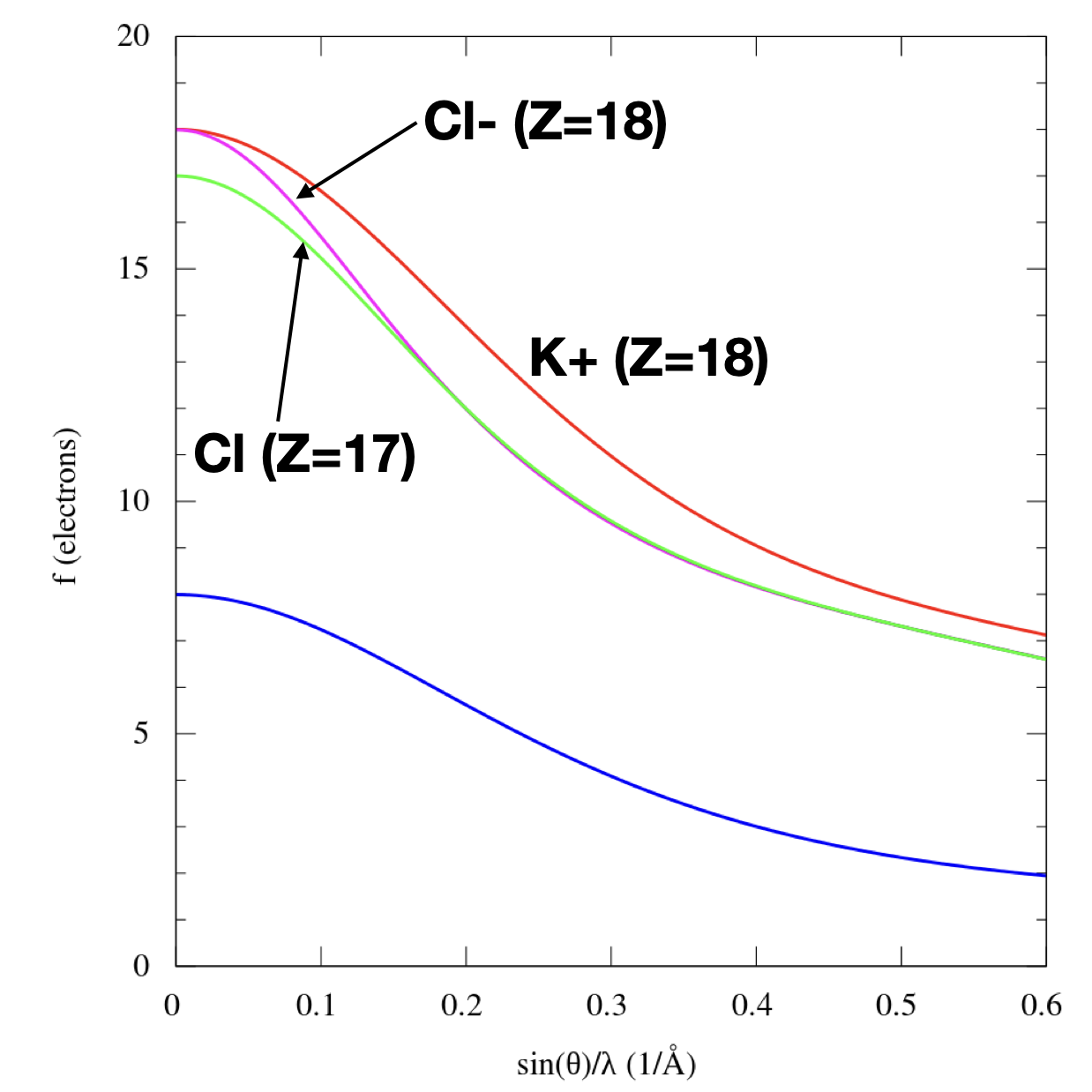
a.Work out the structure factor of KCl, which has the rocksalt crystal
structure. It is advised to use the approach where Shkl = Slattice x
Sbasis.
b.Use your structure factor calculation to draw the corresponding reciprocal lattice for the (h k 0) and (h k 1) plane including lattice points up to (h2+k2+l2)=16 which is the (4 0 0) plane. Note: 7 and 15 are missing in this count, and 9 has two planes.
Problem 4 – Reciprocal Lattice – 10 points
Using the definitions for the reciprocal lattice vectors a*,b*, and c*
obtain expressions for the three basis vectors of the reciprocal lattice
of an orthorhombic C real-space Bravais lattice. Hint: use the primitive
unit cell.
d.Which type of rotation axis is parallel to the [001]? Show this axis in the crystal plan. Also add the mirror plan which is in the third position in the space group symbol.
e.Does this structure include a glide plane? If yes, please indicate the glide plane with its proper notation (dashed, dotted, combined line).
c.Open table 7.1 in Rohrer and explain the following trends: (i) why does the lattice energy decrease going from fluorides to iodides? (ii) why is the lattice binding energy always higher for oxides? Use the underlying physical origin of the ionic bonding for your explanation.
Bonus Questions– 3 points each:
a.Which symmetry elements define an enantiomorphic point group? b.Why do a cube and an octahedron represent the same Bravais lattice?
Reading the table:
|
|---|
4