Quick ratioquick ratio although similar the current ratio
Source: Statista, 2018
This report critically analyses two retail companies Sainsbury and Morrison change management approaches under a five-year financial projection and is supported by literature on their human resource motivation techniques. This is to make a deduction on the profitability and overall performance of both companies. The report concludes by emphasizing that good HR practices alone are not sufficient to improve employee engagement and increase organizational productivity. However, the integration of department, increase productivity and efficiency within the organization better.
Sainsbury's core values lie in the production of products that are health conscious, promote community development and are made with due consideration of the environment and the best ethical practices (J Sainsbury, 2019).
Under fix in the core of Morrison is great customer relationship and experience with a vision to be more competitive and become the best in the retail sector (Morrison, 2022). To achieve this, the brand focuses on human resource development through its different training and meeting customer needs through the provision of a wide range of services and products as its unique selling proposition.
HUMAN RESOURCE PERFORMANCE REVIEW
Illustrated below (fig.3) is the comparison of Sainsbury and Morrison policies and initiatives used for employee motivation and satisfaction within their organization.
2.2.1 Lewin Force Field Theory and Lewis Steps of Change Management (Application on Sainsbury. Fig. 4)
Plate (Picture) 1: Structure flow of a learning environment
On-the-job learning, such as mentoring programmes, job shadowing, master classes and workshops
Apprenticeships in a range of topics such as Data Analysis, HR and Business Management
Source: Fame, annual financial report, 2013-2018
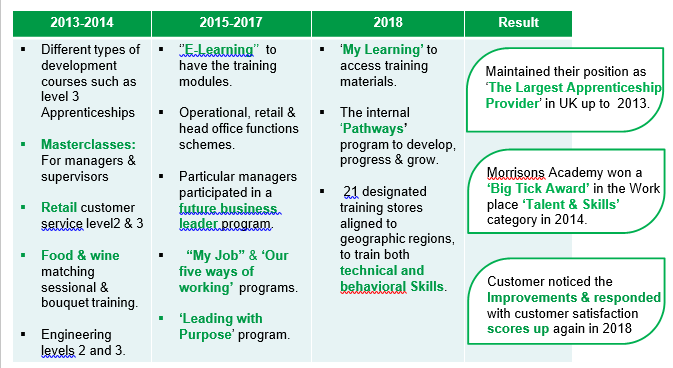
Morrison Learning Organization
Table 2: Morrison training programs from 2013 to 2018
Gross profit margin indices are used to evaluate the company's financial status by comparing gross profit to sales revenue (Tuovila, 2022). A high gross profit margin ratio reflects a higher efficiency of core operations, meaning it can still cover operating expenses, fixed costs, dividends, and depreciation, while also providing net earnings to the business. Formulated from, (Gross profit margin/ Turnover x 100).
Figure 6 (Gross Profit) Result Interpretation
Fig.6 (Net Profit)Interpretation
Fig. (7), shows a revenue decline for both companies from the year 2017 to 2019 and an increase from then forth. The revenue increase can be attributed to the closedown of competitive retailers in lieu of Covid-19 lockdown restrictions.
Fig.8 (Current Ratio) Result Interpretation
Fig. (8), revealed an evaluation current ratio for Sainsbury (0.63) and Morrison (0.39). The analysis reveals Sainsbury has a better ability to pay off its liabilities compared to Morrison.
The fig (9) quick ratio reveals Sainsbury (0.49) still has a better ability to pay its short-term debt using its liquidated assets than Morrison (0.39).
Figure 8: Quick ratio estimates for Sainsbury and Morrison
Figure 10: Gearing Ratio estimates for Sainsbury and Morrison
3.1.6 Return on capital employed (ROCE)
3.1.7. Debt to Equity Ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio is an advantage index that calculates the proportion of total debt and liabilities versus total shareholders’ equity (Fernando, 2019). The ratio shows the comparison of a company's capital structure utilising more debt or equity financing. Simply put, it shows how much Debt the company has relative to Equity.
Table 3: Investor’s Decision summary table from both Sainsbury and Morrison
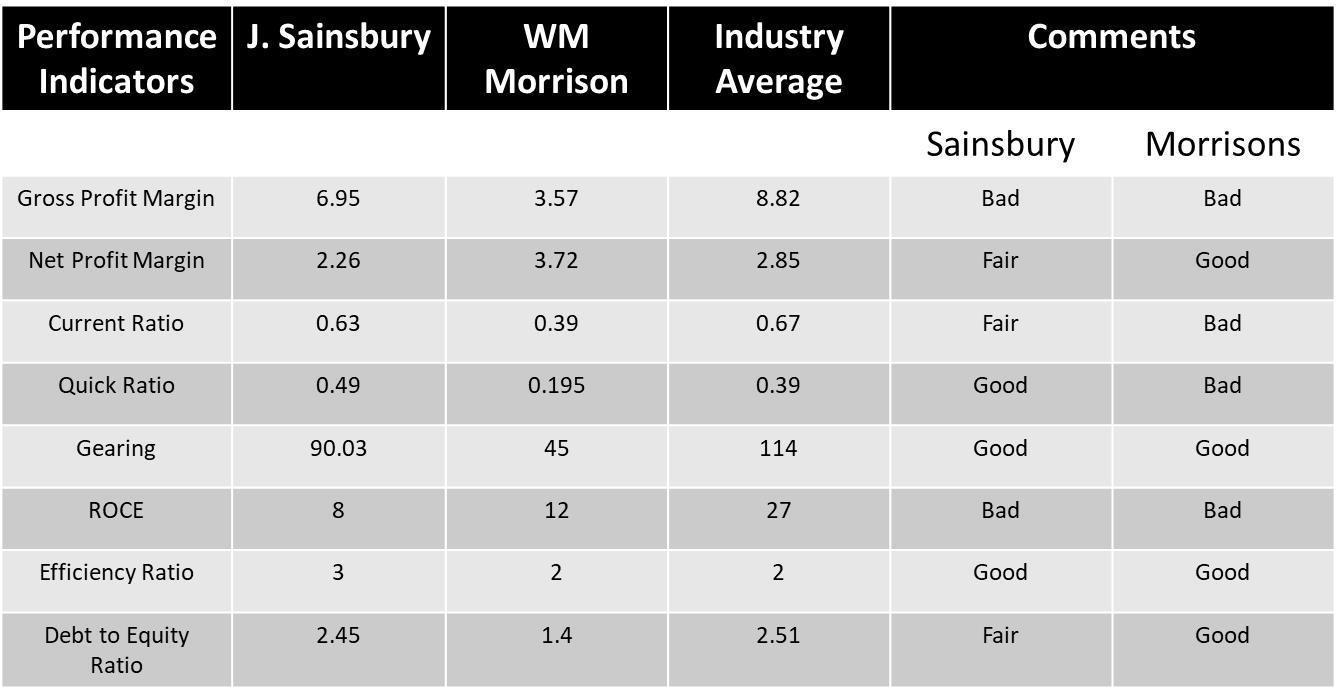
The findings of the HR and FR analyses in comparison with the industry average by Sainsbury and Morrison show steady growth. While this could be propounded to be a great kickback in place of the global COVID-19 pandemic and other challenges (Brexit etc.) that resulted in the financial downturn of major retail companies. The financial position of both companies has proven investment-worthy due to the outlook of industry growth as observed from the TSR graphs. However, based on the analysis, Sainsbury’s capital evaluation looks more promising than Morrison in terms of how they manage and implement changes, both firms employ similar change models. The change management model analysis shows a well established strategic internal and external factors alliance and alignment that are favourable for the advancement and growth of both companies. However, a risk management plan to mitigate future uncertainty is highly encouraged to avoid a decline in the financial outcome.
The culture of employee motivation is of importance as analysed for both companies. Particularly WM Morrison, which has dedicated an entire department to change management and learning development. In addition, Sainsbury's continual distribution of incentives and commission benefits to its staff as a motivational tool for more productivity is highly encouraging.
