Re-added the source and then removed the source
UIN: 325007787
Lab Date: 21 June 2019
Report Due Date: 26 June 2019
Procedure
Task 01: Verify Thévenin's equivalent
1.Construct the circuit shown in Figure 1.0 on a
breadboard, using your AD2 to provide the voltage source and measuring
the exact value of the voltage source before connecting it to the
circuit
2.Use a voltmeter to measure the voltage across the load resistor,
VL, for two different values of RL ≠ 2 kΩ and then
with RL = 2 kΩ
3.Use the voltage measurements to calculate the Thévenin equivalent for
the circuit.
a.First, we measured it with no change to the circuit.
b.Second, we removed the 3V source and measured the resistance.
the 1kΩ and 2kΩ resistors, making sure it is in the correct polarity.
2.With the diode added, we then began to measure the 1kΩ resistance as we did in Task 02,
f.Finally, we re-added the 3V source and then removed the 4V source, then measured its resistance.
| Parameter | Measured | Calculated | % difference | SPICE | % Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VL | -267 mV | -265 mV | -.7519% | -265 mV | .75% |
| VL,1 | 296 mV | 291 mV | 1.704% | 291 mV | 1.7% |
| VL,2 | -560 mV | -556 mV | -.7168% | -556 mV | .72% |
| VL,1 + VL,2 | -267 mV | -265 mV | -.7519% | -265 mV | .75% |
●As expected in our calculations, superposition does indeed apply to this circuit.
Table 3.3: Voltage across 1kΩ resistor with diode in circuit
Conclusion: Being only 3 mV off, this is approximately the same. Superposition indeed applies.
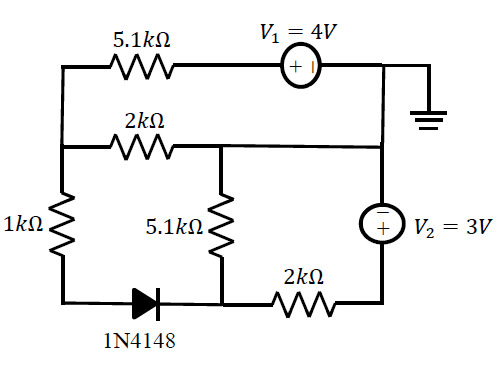
Task 03: Check the superposition principle validity for a
non-linear device Checking for superposition:
Does V1kOhm = VL,1 + VL,2?
Mind voltmeter error.
Task 02: Verify the superposition principle
1.The superposition theorem is a method of finding the total voltage/current of a circuit with all sources active by eliminating all but one source at a time and finding each individual voltage/current using circuit analysis. Then, by adding all individual values, they are “superimposed” and can accurately reflect the voltages/currents with all sources active. Superposition works in Task 2 because there are no non-linear elements in which current can only travel in one direction, therefore current can flow in any direction and does not impede any voltage across any certain pathway.
Task 03: Check the superposition principle validity for a
non-linear device
1.Superposition does not work for a non-linear device such as a diode
because they are polarity-specific - current can only travel in one
direction across a diode, versus current flowing either way through a
resistor depending on outside sources. Since current can only flow one
way, superposition doesn’t hold since the diode blocks currents against
its’ polarity and therefore making the circuit nonlinear. But what does
nonlinear mean?
