Suppose and are running rip for their intra-as routing protocol
c- to determine good routes from senders to receivers through the network
d- to improve individual router performance metrics
c- The path with the least physical distance between hosts
d- None of the above
c- Each node communicates only with its directly connected neighbors
d- Each node routes packet traffic to each of its neighbor nodes
c- each node sends its routing table directly to its neighbors
d- each node sends information about its links to other nodes via broadcast messages
c- so called "fiefdoms"
d- administrative systems
c- must run OSPF
d- run the same routing protocol
c- backed up
d- invisible
c- intra-AS routing protocol
d- transport layer protocol
c- BGP
d- OSPF
c- RIP
d- OSPF
c- EIGRP
d- the network administrator(s)
c- converting to OSPF
d- CIDRized prefixes (eg 192.168.2.12/22)
c- senders in one AS to reach receivers in a different AS
d- the Internet to function as an integrated whole
17) Routers that connect directly between ASs are called
a- Portal Routers
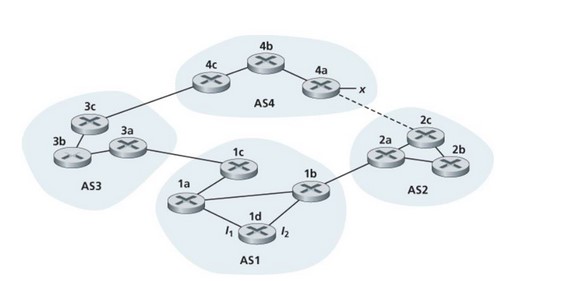
18) Consider the network shown below. Suppose AS3 and AS2 are running OSPF for their intra-AS routing protocol. Suppose AS1 and AS4 are running RIP for their intra-AS routing protocol. Suppose eBGP and iBGP are used for the inter-AS routing protocol. Initially suppose there is no physical link between AS2 and AS4.
Router 3c learns about prefix (subnet) x from which routing protocol: OSPF, RIP, eBGP, or iBGP?
| Matching item | Matching item choices |
|---|---|
| a | |
| b | |
| c | |
| d | |
| e |
19) Consider the network shown below. Suppose AS3 and AS2 are running OSPF for their intra-AS routing protocol. Suppose AS1 and AS4 are running RIP for their intra-AS routing protocol. Suppose eBGP and iBGP are used for the inter-AS routing protocol. Initially suppose there is no physical link between AS2 and AS4.
a
a
True
False
d- flow table
e- None of the above
d- neighboring switches
e- None of the above
d- BGP
e- None of the above
d- All of the above
e- None of the above
