The angle whole sine cos cosine function cos- inverse cosine function
ASSESSMENT GUIDE

workplace.
• Your ability to apply your learning.
The assessment tasks have been designed to enable you to demonstrate the required skills and knowledge and produce the critical evidence to successfully demonstrate competency at the required standard.
Your assessor will ensure that you are ready for assessment and will explain the assessment process. Your assessment tasks will outline the evidence to be collected and how it will be collected, for example; a written activity, case study, or demonstration and observation.
Assessors need to be aware of their responsibilities and carry them out appropriately. To do this they need to:
• Ensure that participants are assessed fairly based on the outcome of the language,
• Ensure that their own qualifications are current.
• When required, request the manager or supervisor to determine that the student is ‘satisfactorily’ demonstrating the requirements for each unit. ‘Satisfactorily’ means consistently meeting the standard expected from an experienced operator.
How long should my answers be?
The length of your answers will be guided by the description in each assessment, for example:
| Type of Answer | Answer Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Short Answer | |
| Long Answer | |
| Brief Report | |
| Mid Report | |
| Long Report |
|
How should I reference the sources of information I use in my assessments?
The following table shows you how to achieve a satisfactory result against the criteria for each type of assessment task. The following is a list of general assessment methods that can be used in assessing a unit of competency. Check your assessment tasks to identify the ones used in this unit of competency.
| Assessment Method | Satisfactory Result | Non-Satisfactory Result |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Questions | ||
| Third Party Report |
|
|
| Written Activity | ||
| All requirements of the written activity are addressed/covered. |
|
|
|
||
|
||
| Case Study |
|
|
| Assessment Method | Satisfactory Result | Non-Satisfactory Result |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| Practical Activity |
|
|
|
||
| Assessment Cover Sheet | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
|
CONSOLATA MATTHEW | Student Number: |
|||
|
Yes | No | |||
|
Yes | No | |||
| Yes | No | ||||
| Yes | No | ||||
| Yes | No | ||||
|
S | NYS | |||
|
S | NYS | |||
| S | NYS | ||||
| Student Signature: |
|
|
|||
| FNSACC313 Perform financial calculations Assessment Guide v1.0 Copyright © Mentor Education Pty Ltd RTO 21683 | 7 |
|---|
Instructions
You will need to research information to assist with your responses for this task.
industry bodies.
You are required to provide information about the following points. You must prepare a written
Your task is to research the following topics then outline your findings in a report. Use the
B.Simple interest: Applying given interest rate on the principal amount for a particular period.
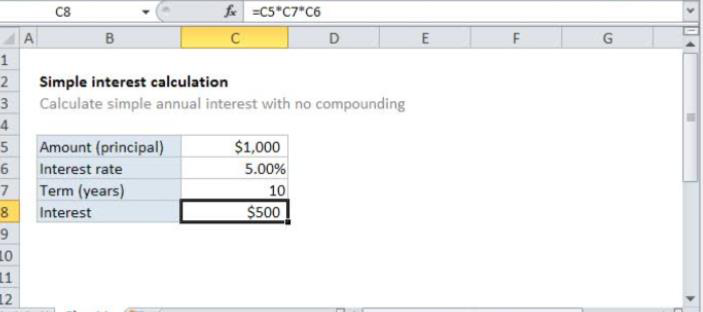
Simple interest is a quickly and easy method of calculating the interest charge ona loan. Simple interest is determined by multiplying the daily interest rate by the principal by the number of days that elapse between payment.Simple interest = P x I x NThis type of interest usually applies to automobile loans or short- term loans, although some mortgages use this calculation method.When you make a payment on simple interest loan, the payment first goes toward the month's interest, and the remainder goes toward the principal. Each month's interest is paid in full, so it never accrues
| 8 |
|---|
Compound interest is different from simple interest. Simple interest is paid at the end of specified term, although if the term is more than 12 months, interest may be paid annually.
Compound interest calculation formula:
A= P x (1 + r) n
A: the end amount of your investment
P: the principal, i.e. the starting amount
r: percentage interest rate converted to a decimal rate (e.g 2% is 0.02) n: number of time periods
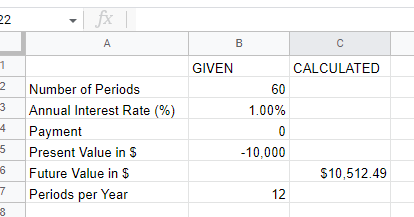
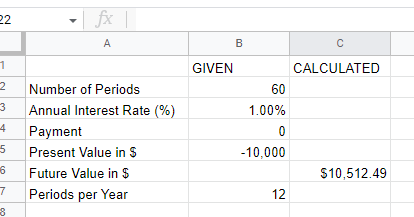
Example: Work out what $2,000 will grow to over 2 years for an investment or savings that grow at 5% annum compounding yearly.

D.Basic loan calculations: EMI = (P X R/12) X [(1+R/12) ^N] / [(1+R/12) ^N-1]. is used where P=Principal, R=rate of interest, N =number of years.
Useful life is the estimated time period that the asset is expected to be used starting from the date it is available for use up to the date of its disposal or termination of use
Rate of depreciation is the percentage of useful life that is consumed in a single accounting period. Rate of depreciation can be calculated as follows:
Rate of depreciation = 1/ Useful Life x 100%
e.g. rate of depreciation an asset having a useful life of 8 year is 12.5% p.a
1/8 x100% =
12.5% per year
|
10 |
|---|
numbers into the formula. Which are
a) Wrong spreadsheets function or formula used: there are some ways to check formulas for accuracy .Check the references Look for mix up s Break it up ¬ Ballpark it Check the arguments Walk through the order of
transcriptions errors can be detected using spell checking programs. However, many transcription errors,
particularly those involving numeric data are difficult or impossible to detect. Transcription errors have been
• Check the references
• Look for mix ups
• Break it up
Ballpark it •
• Check the arguments
• Walk through the order of operation
b) Incorrect order of operation: There are ruling to remember of
operations PEMDAS that is phrase "Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally".
This phrase helps one remember the order of "Parentheses, Exponents,
Multiplication and Division,
Addition and Subtraction.
Computer - Used for higher storage, memory and faster in calculations.
Software-MS - Excel is for performing mathematical calculations using sets of formulas which create fast calculations.
| 12 |
|---|

REPORT CHECKLIST
|
13 |
|---|
| Assessor Signature: | Date: | ||

PORTFOLIO
• Financial services industry documentation and specialist software.
• Information technology systems and databases.
The Goods and Service Tax is a 10% value-added tax levied in Australia on most goods, services, and other items offered for value (GST). Throughout the country, a single unified GST rate is used. The tax is included in the final price and is paid by customers at the point of sale, with the seller claiming the tax from the government. Other GST-registered organizations, firms, and businesses will charge GST on their goods and services to consumers, but they will claim GST on the things and services they acquire for their businesses. GST is a revenue generator for the government.
The GST is used as the common tax in the majority of countries around the world. Multiply the amount by 1.1 to calculate the Goods and Service Tax.
| 15 |
|---|

When you make a payment on a simple interest loan, the money goes first to the interest for that month and then to the principal. Interest is paid in full each month, so it never accumulates.
V = the future value of the investment
P = the principal investment amount
r = the annual interest rate
n = the number of times that interest is compounded per year t = the number of years the money is invested4.Basic loan calculations
Instructions
For each financial calculation, complete the following steps to obtain the required data and
Goods and Services Tax (GST) Formula = P X 0.1 = GST
Simple interest formula = P x I x N
P is the loan amount
I is the interest rate
N is the duration of the loan, using a number of periods You deposit $1000 into a bank account paying 7% simple interest per year. You left the money in for 3 years. Find the interest earned and the amount at the end of those 3 years?$2000 x 7% x 3 years
The interest is $420 and the amount at the end of the 3 years is $2420.
| 17 |
|---|
Compound interest
Compound interest Formula:
V = P(1+r/n)^nt V = the future value of the investment
P = the principal investment amount
r = the annual interest rate
n = the number of times that interest is compounded per year t = the number of years the money is invested forMultiply the amount you borrow (a) by the annual interest rate (r), then divide by the number of payments per year (n). Or multiply the amount you borrow (a) by the monthly interest rate, which is the annual interest rate (r) divided by 12:
a: 500,000 the amount of the loan
r: 0.04 (4% expressed as 0.04)
n: 12 (based on monthly payments)
| 19 |
|---|
Provide evidence of these calculations.
Complete the following steps to check your calculations and to record your outcomes: a.Check your results to ensure that the calculations are accurate and that they meet the required outcomes, including recognising if they contain any routine computational errors, and correcting any identified.
Provide a copy of these calculation worksheets.

Most nations with a GST have a solitary bound together GST framework, which implies that a solitary assessment rate is applied all through the country. A country with a brought together GST stage consolidates focal assessments (e.g., deals charge, extract obligation expense, and administration charge) with state-level duties (e.g., diversion charge, passage charge, move charge, sin duty, and extravagance expense) and gathers them as one single assessment. These nations charge basically everything at a solitary rate.
Just a modest bunch of nations, like Canada and Brazil, have a double GST structure. Contrasted with a brought together GST economy where duty is gathered by the national government and afterward conveyed to the states, in a double framework, the administrative GST is applied notwithstanding the state deals charge. In Canada, for instance, the central government exacts a 5% expense and a few regions/states additionally demand a commonplace state charge (PST), which differs from 7% to 10%. For this situation, a purchaser's receipt will unmistakably have the GST and PST rate that was applied to their buy esteem.
| 21 |
|---|
| Portfolio Report | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
|
|||
|
Has the student satisfactorily completed the
practical activity? |
||
| Yes | No | ||
| | | ||
| | | ||
| | | ||
| | | ||
|
|||
|
| | |
| | | ||
| | | ||
| | | ||
| | | ||

| 23 |
|---|
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Instructions
Answer the questions below by writing in the space provided. If you require more space, use a blank sheet of paper. Alternatively, you may like to use Microsoft Word and print out your answers to each question.What you will need
• Research materials such as books, internet, magazines, workplace documentation etc.
|
|---|
|
|
24 |
|---|
|
|
| 25 |
|---|
7.What do you need to check the results of your calculations?
|
|---|
9.What are 3 of the benefits associated with recording calculation results in accordance with industry standards and enterprise requirements?
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
6th- order-of-operations/a/order-of-operations-review

|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessor name: | |||||
|
|||||
| Yes | No | ||||
| 1 |
|
| | ||
| 2 | | | |||
| 3 | | | |||
| 4 | | | |||
| 5 | | | |||
| 6 |
|
| | ||
| 7 |
|
| | ||
| 29 |
|---|