The higherthe repo margin income markets issuance
2018 LEVEL I MOCK EXAM AM
| 1 |
|
|
|---|---|---|
| A | ||
B is incorrect because providing research coverage in this situation does not consti-tute a violation of the Code and Standards as long as the independence of this research is not compromised.
C is incorrect because providing research coverage in this situation does not consti-tute a violation of the Code and Standards as long as the independence of this research
| 2 | ||
| A |
|
|
B it was overheard and might be considered unreliable.
| A is correct because trading on the information is restricted as it relates to a tender offer; |
|---|
| since it concerns a tender offer. |
|---|
2018 Level I Mock Exam AM 3
|
||
|---|---|---|
| 3 |
|
|
| A | ||
|
|---|
A is incorrect because the two principles of the Rules of Procedure for Proceedings Related to Professional Conduct are confidentiality of proceedings and fair process to the member and candidate.
C is incorrect because the two principles of the Rules of Procedure for Proceedings Related to Professional Conduct are confidentiality of proceedings and fair process to
| C |
|---|
| broadest, most meaningful definition of the firm. |
|---|
|
|---|
| The GIPS Standards |
|---|
| C |
|---|
B is incorrect because placing the integrity of the investment profession and the interests of clients above their own personal interests is one of the six components of the Code of Ethics.
C is incorrect because practicing and encouraging others to practice in a professional and ethical manner that will reflect credit on themselves and the profession is one of
| 7 |
A Both violated Standards.
B Peters violated Standards.
C Neither violated Standards.
|
|---|
LOS a
A is correct because according to Standard VI(A)–Disclosure of Conflicts, Grabbo should disclose to her employer her hedge fund development as this activity could possibly interfere with her responsibilities at Atlantic. In setting up a hedge fund, Grabbo was not acting for the benefit of her employer. She should have informed Atlantic that she wanted to organize the hedge fund and come to some mutual agreement on how this would occur.
|
|---|
| Guidance for Standards I–VII |
|---|
B Analyze the expected returns of private equity in the market.
| C |
|
|---|
| recommendation. |
|---|
| suitability. |
|---|
| Guidance for Standards I–VII |
|---|
10 The Global Investment Performance Standards (GIPS) were developed for the benefit of:
A prospective clients.
B regulators.C broker/dealers.
| A is correct. The GIPS standards benefit two main groups: investment management firms |
|---|
|
|---|
LOS a
C is correct because both Musa and Kassim violated the Standards of Professional Conduct. Musa violated Standard IV(C)–Responsibilities of Supervisors by not ensuring that policies were in place to prevent violations of the Code and Standards (in this case Standard VI(B)–Priority of Transactions) by someone subject to her supervision. As the head of compliance, Musa supervised Kassim and must meet her supervisory responsibilities outlined in the Standards of Professional Conduct. Kassim violated Standard VI(B)–Priority of Transactions in that he did not give sufficient priority to Dunfield’s clients before trading on his recommendation.
A is incorrect because Kassim also violated the Standards (Priority of Transactions) in that he did not give sufficient priority to Dunfield’s clients before trading on his recommendation.
12 Oliver Opdyke, CFA, works for an independent research organization that does not manage any client money. In the course of his analysis of Red Ribbon Mining he hears rumors that the president of Red Ribbon, Richard Leisberg, has recently been diagnosed with late stage Alzheimer’s disease, a fact not publicly known. The final stage of Alzheimer’s is when individuals lose the ability to respond to their environment, the ability to speak, and, ultimately, the ability to control movement. Leisberg is the charismatic founder of Red Ribbon, and under his leadership the company grew to become one of the largest in the industry. According to the CFA Institute Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct, the most appropriate action for Opdyke is to:
| A | 2018 Level I Mock Exam AM | |
|---|---|---|

C is correct because members and candidates should make reasonable efforts to achieve public dissemination of information that is material and nonpublic, as required by Standard II(A)–Material Nonpublic Information. This effort usually entails encouraging the issuer company to make the information public. In this case, if the diagnosis is fact and not rumor, then this information is material and should be disclosed.
|
|---|
13 Based on his superior return history, Vijay Gupta, CFA, is interviewed by the First Faithful Church to manage the church’s voluntary retirement plan’s equity portfolio. Each church staff member chooses whether to opt in or out of the retirement plan according to his or her own investment objectives. The plan trustees tell Gupta that stocks of companies involved in the sale of alcohol, tobacco, gambling, or firearms are not acceptable investments given the objec-tives and constraints of the portfolio. Gupta tells the trustees he cannot reason-ably execute his strategy with these restrictions and that all his other accounts hold shares of companies involved in these businesses because he believes they have the highest alpha. By agreeing to manage the account according to the trustees’ wishes, does Gupta violate the CFA Institute Standards of Professional Conduct?
| A is correct. Standard III(A)–Loyalty, Prudence, and Care, Gupta’s duty of loyalty, prudence, |
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
A revise his research report.
B leave his research report as it is.
| A is correct because Ronde should refuse to follow his supervisor’s request. If Ronde |
|---|
delay information is material and considered nonpublic until it is widely distributed, so
it should not be included in Ronde’s research report or acted on until it becomes public.
C is incorrect because the information Ronde overheard at the industry conference
A Mosaic theory
B Economic theory
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 季更新,永久有效! |
2017-2018年泽稷网校CFA视频音频课程及指南
除CFA资料外赠送金融、财会技能视频包+热门书籍
+1000G考证资料包


免费分享2018年CFA全套备考资料,含最新CFA网课视频,考友交流互助答疑、考试指导、考经分享、

A is correct because the process by which financial analysts combine material public information and nonmaterial nonpublic information as a basis for investment recommen-dations even if those conclusions would have been material inside information had they been communicated directly to the analyst by the company is known as Mosaic Theory.
| nonpublic information. |
|---|
A No.
B Yes, related to referral fees.
| B is correct because Standard VI(C) requires disclosure of any compensation, consider- |
|---|
quo referral of clients and should be disclosed.
A is incorrect because Kawasaki has violated the Standards.
| Guidance for Standards I–VII |
|---|
2018 Level I Mock Exam AM 11
the last year due to negative operating cash flows. Without conducting exten-sive research, Bradovic’s boss puts pressure on him to upgrade the credit rating to an investment grade rating. Bradovic reports this to the firm’s compliance department where he is encouraged to follow his boss’s advice. What course of action is most appropriate for Bradovic to prevent any violation of the CFA Institute Code or Standards?
|
|---|
|
|---|
is in violation of Standard V(A)–Diligence and Reasonable Basis as he is required to undertake due diligence efforts on the third- party research provider on a regular basis to ensure that the quality of this research continues to meet his necessary standards.
B is incorrect because the Code and Standards would not require this action. Tacqueria is in violation of Standard V(A)–Diligence and Reasonable Basis as he is required to undertake due diligence efforts on the third- party research provider on a regular basis
B €61,330.
C €61,663.
B is incorrect. This is the PV of a 60- month ordinary annuity. N = 60, the discount rate
| The Time Value of Money |
|---|
| Cumulative Distribution Function | |
|---|---|
|
|
C is correct. The problem deals with the discrete uniform distribution. This means that the
A is incorrect because 0.4 is the probability of a profit less than or equal to $1.
B required rate of return.
| C |
|
|---|
rate that makes net present value equal to zero
C is incorrect. The required rate of return is the minimum rate of return an investor must receive in order to accept an investment. The expected return is based on the expected value of a random variable and is not the minimum rate of return an investor must receive in order to accept an investment (i.e., the expected return could also be
| Year 1 | Year 2 | |
|---|---|---|
|
Positive | Negative |
Given the information in the table, which of the following is least likely to be an explanation for the difference between the two money- weighted rates of return?
| A |
|
|---|
A is incorrect. If investor A increases the investment in the fund at the end of year 1 and investor B does not make any additions or withdrawals, then the former will have a lower MWR than the latter because in year 2 the fund underperformed with respect to year 1.
B is incorrect. If investor B decreases the investment at the end of year 1 and investor A does not make any additions or withdrawals, then the former will have a higher MWR

|
|---|
|
|---|
C reject the null hypothesis.
| A is correct. Because the p-value (0.0567) exceeds the stated level of significance (0.05), |
|---|
|
|---|
| B is correct. Resistance is defined as a price range in which selling activity is sufficient |
|---|
|
|---|
LOS c
| C |
|
2018 Level I Mock Exam AM |
|---|

| Statistical Concepts and Market Returns |
|---|
LOS m
B mutually exclusive.
| C |
|
|---|
A is incorrect. Events A and B are dependent because if one event occurs, the prob-ability of the other becomes zero.
B is incorrect. Events A and B are mutually exclusive because they cannot occur at
B 7.85%.
C 8.16%.
P ( Event ) |
||||||||
|
P | |||||||
| C | ( Information | | | Event ) | P |
|
|||
| P | ( Event ) | |||||||
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
( Information | | | Event ) | P | ||
| P | |||||
B cross- sectional data.
longitudinal data. C
| B is correct. Data on some characteristics of companies at a single point in time are |
|---|
| A is incorrect. The data are not time- series data. |
|---|
| Sampling and Estimation |
|---|
|
|---|
31 Over a four- year period, a portfolio has returns of 10%, –2%, 18%, and –12%. The geometric mean return across the period is closest to:
A 3.5%.
A is incorrect. It is the arithmetic average and is calculated as: (10 – 2 +18 – 12)/4 = 3.5%. B is incorrect. It is the geometric average of the given numbers, but without adding one, i.e., (10 × –2 × 18 × –12)0.25 = 8.10%.
Statistical Concepts and Market Returns
LOS e
Section 5.4.2
| B is correct. Specification of the mean and variance for a portfolio of four stocks requires |
|---|
| correlations between each of the four stocks. |
|---|
| and variance of a portfolio. |
|---|
| variance of a portfolio. |
|---|
33 Two events A and B are independent if the probability of occurrence of A: A equals the product of the individual probabilities of occurrence of A and B. B is related to the occurrence of B.
| C is correct. When two events are independent, the events are unrelated and the prob- |
|---|
|
|---|
34 If the prices of substitute resources decrease, the demand for a given resource will most likely:
A remain unchanged.
B decrease.
| C |
|
|---|
|
|---|
20 2018 Level I Mock Exam AM
Marginal cost curve: MC = 3 × Q2 – 20 × Q + 73
P indicates price per unit, and Q indicates cost per unit.
C is correct. The profit maximizing output will arise when MR = MC.
MR = 150 – 10 × Q = MC = 3 × Q2 – 20 × Q + 73
| B is incorrect: it arises from setting P = MC |
|---|
Solve for Q = 8.15
II. total income earned by all of the country’s citizens, firms, and the government.
III. total market value produced of resalable and final goods and services.
A is correct. Gross domestic product (GDP) can be defined in terms of either output or
| ■ | ● | |
|---|---|---|
|
|---|
|
|
|---|
|
|---|
38 Three countries produce tables and chairs, and the output per worker per day in each country as follows:

C is correct. A country has a comparative advantage if its opportunity cost for pro-ducing a product is less than the opportunity costs of its trading partners. Notice the
| Tables | Chairs | Advantage (Chairs/ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tables) | |||
| 60 | 80 | 1.33 | |
| 40 | 60 | 1.50 | |
|
40 × 1.1 = 44 | 80 × 0.9 = 72 | 1.64 |
|
|---|

| C is correct. The total hours worked remained unchanged, and accordingly, the growth |
|---|
| Aggregate Output, Prices, and Economic Growth |
|---|
LOS m
| C is correct. The effect of demand–pull inflation is an increase in the aggregate demand, |
|---|
|
|---|
41 In an effort to influence the economy, a central bank conducted open market activities by selling government bonds. This action implies that the central bank is most likely attempting to:
A expand the economy through a lower policy interest rate.B contract the economy through a lower policy interest rate.
|
|---|
42 An investor examines the following rate quotes for the Brazilian real (BRL) and the Australian dollar (AUD) and shorts BRL500,000.
The risk- free arbitrage profit that is available is closest to:
A –BRL6,327.
B BRL1,344.
C BRL6,405.

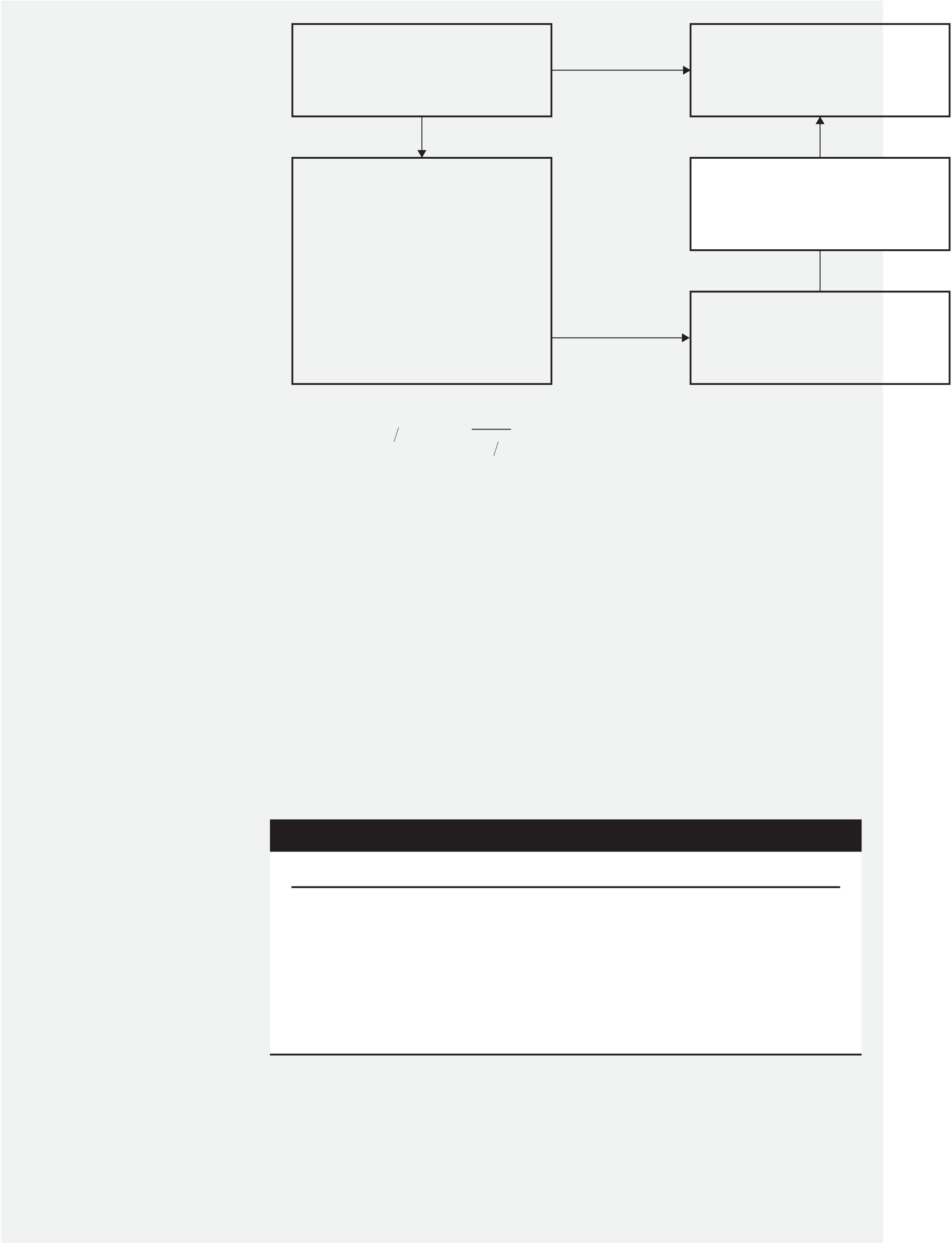
| 24 | ( 1 | Domestic | Invest at |
|
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Future Value of | |||||||||||||||||
| Funds | Invest at | Domestic Funds | |||||||||||||||
| Convert back to | |||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Future Value of | |||||||||||||||||
| Foreign Funds | |||||||||||||||||
| + | i d | ) = | S | f d | ( 1 | + | i | f | ) |
|
F |
|
|||||
| f d | |||||||||||||||||
Left Side of Equation: BRL500,000 × (1 + 0.041) = BRL520,500
Right Side of Equation
Step One: BRL500,000 × (2.1128AUD/BRL) = AUD1,056,400
Step Two: AUD1,056,400 × (1.041) = AUD1,099,712
|
|---|
LOS f, h
|
|---|
|
|---|
B an inelastic demand for money.
C a positive nominal central bank policy rate.
|
|---|
B have no impact on the private sector share of GDP.
C decrease the private sector share of GDP.

| Monetary and Fiscal Policy |
|---|
LOS t
| A is correct. The role of financial reporting is to provide information about the performance |
|---|
of a company, its financial position, and changes in financial position that is useful to a wide range of users in making economic decisions.
B is incorrect. Audit reports express an opinion about the fair presentation of the financial statements.
| Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction |
|---|
47 According to the International Accounting Standards Board’s (IASB)
Conceptual Framework for Financial Reporting, the two fundamental qualita- tive characteristics that make financial information useful are best described as: A understandability and verifiability.
B relevance and faithful representation.
| B is correct. Relevance and faithful representation are the two fundamental qualitative |
|---|
A is incorrect. Verifiability and understandability are two characteristics that enhance the usefulness of relevant and faithfully represented financial information.
C is incorrect. Timeliness enhances the usefulness of relevant and faithfully represented
48 At the end of the year, a company reported an impairment loss on its manufac- turing plant, reducing its carrying amount by 10%. The impairment loss is least likely to cause the company’s:
A debt- to- asset ratio to increase.B cash flow from operations to decline.
| B is correct. The impairment loss is a non- cash charge and will not affect cash flow from |
|---|
|
|---|
49 Obligations arising from past events that are expected to result in an outflow of economic benefits from an entity are most likely known as:
A expenses.B liabilities.
| B is correct. Liabilities are an element of the balance sheet and represent obligations of |
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
| LOS a |
|---|
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| €2,500 | €2,500 | €2,500 | |
| 375 | 250 | 125 | |
|
2,125 | 2,250 | 2,375 |
This company uses the straight- line depreciation method for this capital asset.
A is correct. Based on the annual increase in accumulated depreciation, annual depreciation expense is $125 and the asset was acquired in 2012.
| Remaining useful life three years later = 20 years – 3 years = 17 years |
|---|
| NBV/Depreciation expense = 2,125/125 = 17 years |
|---|
| Long- Lived Assets |
|---|
51 Because of significant changes in the marketplace, the demand for a company’s product has fallen and is not expected to recover to previous levels. The follow-ing information is related to the patent under which the product is produced:
| $ thousands | |
|---|---|
Which of the following statements is most accurate? The patent is impaired under:
A IFRS only.B both IFRS and US GAAP.
C US GAAP only.
The recoverable amount ($32,000) is lower than the carrying value ($36,000). Therefore, the asset is impaired and should be written down to that amount.
LOS i
of the physical flow of the particular items sold and would be most suitable for high- end custom- built motorcycles that are not ordinarily considered interchangeable.
A is incorrect. Although accepted by IFRS, this method is more suitable for inter-changeable inventory.B is incorrect. Although accepted by IFRS, this method is more suitable for inter-
53 Net revenue most likely refers to revenue minus:
A revenues attributable to non- controlling interests.
B estimates of warranty expense.
| C is correct. Net revenue means that the revenue number is reported after adjustments |
|---|
|
|---|
| Understanding Income Statements |
|---|
|
|---|
The average shareholder’s equity is closest to:
A $164,557.
B $123,418.
C $219,409.
| Average shareholders’ equity = $219,409 |
|---|
A is incorrect. It fails to divide by (Revenues/Average total assets):
($300,000/Average shareholders’ equity) = 4.74%/2.6%
| Financial Analysis Techniques |
|---|
LOS d
The company’s cash ratio is closest to:
A 0.46.
B 0.97.
C 0.37.
|
|---|
Which of the companies most likely prepares its financial statements in accor-dance with US GAAP?
A Only Company B
B Both companies
C Only Company A32 2018 Level I Mock Exam AM
|
|---|
LOS c
| lease payments is recognized as a liability. |
|---|
|
|---|
ivity. |
|---|

| Non- Current (Long- Term) Liabilities |
|---|
C is correct. Financial leverage ratio = Average total assets/Average shareholders’
|
|---|
|
|
2,000 |
|---|---|---|
| 2,100 | ||
|
2,050 | |
|
5,000/2,050 | 2.44 |
|
|---|
LOS b
Section 4.4
| ● | ● |
|
|---|---|---|
| ● | ● |
|
| ● | ● | |
| ● | ● |
34 2018 Level I Mock Exam AM
B £371,882.
C £382,556.
The market value of debt at retirement can be determined by discounting the future cash flows at the current market rate (5%) by using a financial calculator:
Face value (FV) = £20,000,000; i = 5%; PMT = £1,200,000; N = 2; Compute present value (PV) = £20,371,882.
| Principal | Interest | Coupon 6% | Premium | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | ||||
| Beginning of | Expense | |||
| year (£) | 4% | |||
|
21,780,729 | 871,229 | 1,200,000 | 328,771 |
|
21,451,958 | 858,078 | 1,200,000 | 341,922 |
| 21,110,036 | 844,401 | 1,200,000 | 355,599 | |
| 20,754,438 |
|
|---|
| value | Interest | Coupon | Premium | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginning of | ||||
| Year | Expense 4% | 6% | Amortization | |
|
21,780,729 | 871,229 | 1,200,000 | 356,146 |
| 21,424,583 | 856,983 | 1,200,000 | 356,146 | |
| 21,068,437 | 842,737 | 1,200,000 | 356,146 |
|
|---|
| Earnings Growth | P/E | |
|---|---|---|
| 5% | 8 | |
|
10% | 15 |
|
8% | 25 |
|
|---|
|
|---|
61 Information about a company’s historical performance for the last two years and additional information are summarized in the following table.
Industry sales are expected to increase 5%, and the company expects to main-tain its current market share and gross profit margin. Operating expenses are not expected to change with the increase in sales.
C $635.

|
|---|
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 Forecast | |||||
| 5,775 | 5,500 |
|
|||
|
$400 | $787.5 | |||
C is incorrect. It takes the average margin of the two previous years without any adjustments for the non- recurring items or change in tax rate. (400/5,500 = 7.3%) and (787.5/5,350 = 14.7%).
½[7.3% + 14.7%] = 11.0%
62 Which of the following companies would most likely be considered to have the lowest financial reporting quality, other things equal?
| A |
|
|---|
A is incorrect. The company’s reports are high quality, but the delay in reporting impairs their usefulness somewhat. The reporting is still better than biased reporting.
B is incorrect. This is an example of decision- useful information about a result that may not be sustainable. Reporting is not of the highest quality, but is better than biased
63 In accrual accounting, if an adjusting entry results in the reduction of an asset and the recording of an expense, the originating entry recorded was most likely a(n):
A deferred revenue.B prepaid expense.
A is incorrect. If the originating entry had been the recording of unearned (deferred revenue), the adjusting entry would be the reduction of the liability and the recording of revenue.
C is incorrect. If the originating entry had been the recording of an accrued expense (a liability and expense), the adjusting entry would be a reduction of the liability and an
| Financial Reporting Mechanics |
|---|
A Develop and communicate conclusions/recommendations
B Articulate the purpose and context of analysis
C Process data

| A is correct. Discussion and presentation of inherent risks in an investment is appropriate |
|---|
| Financial Statement Analysis: An Introduction |
|---|
65 A company purchased equipment for $50,000 on 1 January 2011. It is depreciat- ing the equipment over a period of 10 years on a straight- line basis for account- ing purposes, but for tax purposes it is using the declining balance method at a rate of 20%. Given a tax rate of 30%, the deferred tax liability at the end of 2013 is closest to:
A $6,720.
B $2,820.
| between the carrying amount of the asset and the tax base. | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
LOS c, d
C is correct. If all else is held constant, in a period of rising costs the ending inventory will be lower under the weighted average cost method and the cost of goods sold will be higher (compared to FIFO), resulting in lower net income and retained earnings. There will be no impact on the debt level, current or long- term. Therefore, the debt- to- equity ratio (Total debt/Total shareholders’ equity) will increase because of the decrease in retained earnings (and lower shareholders’ equity).
A is incorrect. In a period of rising costs, the ending inventory would be lower under the weighted average cost method and the cost of sales would be higher, resulting in lower net income and retained earnings. The lower value of inventory would reduce the value of current assets. Current liabilities would remain the same under both FIFO and the weighted average cost method. Therefore, the current ratio will decrease, not increase.
| for inventory turnover). |
|---|
67 Which of the following is most likely to signal manipulation of financial report- ing for a large, diversified company?
A A history of large expense items classified as unusual
B Operating margins out of line with other diversified companies C Changes in accounting policies to reflect new accounting standards
C is incorrect. Accounting policies must be changed to comply with new accounting
| Financial Reporting Quality |
|---|
C $318 million.

A is incorrect because it incorrectly added the decrease in prepaid income tax payable and subtracted the decrease in other accrued liabilities. Therefore, cash paid for operating expenses is incorrectly converted as follows: $324 million – $16 million + $22 million = $330 million.
B is incorrect because it has based the calculation off of the total revenue amount of $359 million instead of the total expense amount of $324 million as follows: $359 +
B recognize expenses in the period that it consumes the associated economic benefits.
C is incorrect because a company recognizes expenses in the period that it loses some previously recognized economic benefit or consumes the economic benefits associated
|
|---|
A Increasing the efficiency of cash flow management
B Renegotiating current debt contracts to lower interest payments C Increasing the availability of bank lines of credit
|
|---|
C Both the yield- to- maturity and the debt- rating approaches.
|
|---|
| Revenues | − |
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOL = | Revenues | − | Variable operati ng costs | − | Fixed operating costs | |||||||
| 9 8 | − | 7 2 | ||||||||||
| = | 9 8 | − | 7 2 | − |
|
|||||||
73 Other factors held constant, the reduction of a company’s average accounts payable because of suppliers offering less trade credit will most likely: A not affect the operating cycle.
B reduce the operating cycle.
| Financial Analysis Techniques |
|---|
74 A firm’s estimated costs of debt, preferred stock, and common stock are 12%, 17%, and 20%, respectively. Assuming equal funding from each source and a marginal tax rate of 40%, the weighted average cost of capital (WAAC) is closest to:
A 13.9%.B 14.7%.
|
|---|
| C is correct. Flotation costs are an additional cost of the project and should be incor- |
|---|
|
|---|
C internal rate of return.
44 2018 Level I Mock Exam AM
| Capital Budgeting |
|---|
LOS e

A is correct. Under appropriate corporate governance procedures, the compensation committee should link compensation with long- term objectives.
|
|---|
78 A company has a fixed $1,100 capital budget and has the opportunity to invest in the four independent projects listed in the table:
C 1 and 2.
|
|---|
allocation line?
A No, because Investor B has a lower risk tolerance
| A is correct. Investor B has a higher risk aversion coefficient, which means a lower risk |
|---|
|
|---|
80 Which of the following institutional investors is most likely to have a low toler-

| A is correct. Insurance companies need to be relatively conservative and liquid, given |
|---|
|
|---|
| Portfolio Management: An Overview |
|---|
81 An analyst uses a multi- factor model to estimate the expected returns of var- ious securities. The model analyzes historical and cross- sectional return data to identify factors that explain the variance or covariance in the securities’ observed returns. This model is most likely a:
A statistical factor model.
B macroeconomic factor model.
| C |
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
82 The slope of the security market line (SML) represents the portion of an asset’s expected return attributable to:
A diversifiable risk.
B market risk.
2018 Level I Mock Exam AM 47
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
84 A factor that most likely measures a client’s ability to bear risk is his or her: A time horizon.
B inclination to independent thinking.
|
|---|
85 An optimal risky portfolio has an expected return of 15% and standard devi-ation of 20%. The risk- free rate is currently 5%. A risk- seeking investor who is considering investing along the capital allocation line (CAL) would most likely:
| A |
|
|---|
B is incorrect because it has lower risks than borrowing and investing more than 100% to the optimal risky portfolio.
C is incorrect because the investor who invests only to the risk- free assets has the
| Portfolio Risk and Return: Part I |
|---|
A Model risk and tail risk
B Liquidity risk and operational risk
C Credit risk and solvency risk

LOS f
|
|---|
2018 Level I Mock Exam AM 49
|
|---|
C is incorrect. A “GTC, stop $25, market sell” order becomes a market order when the price drops to or below $25 and is executed at the best price available in the market. Thus, the selling price of $25 is not guaranteed.
B is incorrect. A “GTC, stop $25, limit $25 sell” order limits the lower boundary to $25 but it does not guarantee execution at $25; in a fast- moving market prices may have
89 Compared with its market- value- weighted counterpart, a fundamental- weighted index is least likely to have a:
A momentum effect.B contrarian effect.
| A is correct. The momentum effect is a characteristic of a market- capitalization- weighted |
|---|
|
|---|
| Security Market Indexes |
|---|
|
|---|
90 Which of the following is least likely to be directly reflected in the returns on a commodity index?
| in the index. |
|---|
| Security Market Indexes |
|---|
|
|---|
B $49.20.
C $52.86.
| Net earnings = Net profit margin × Sales |
|---|
|
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | $ . 2 50 | + | + | ||||||||||||
| V0 = | ( 1 | + | 0 12 ) | ( 1 | + | 0 12 ) | 2 | ( 1 | + | 0 12 ) 3 | ( 1 |
|
|||
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | +( 2 1 25 ) 3 | + | ||||
| ( 0 12 | − | |||||
| 1 12 3 |
|
|||||
= $2.23 + $2.49 + $2.78 + $41.70 = $49.20
|
|---|
|
|---|
The intrinsic value per share is closest to:
A $36.
B $48.
C $72.
52 2018 Level I Mock Exam AM
|
|---|
|
|---|
93 Which of the following statements concerning different valuation approaches is most accurate?
| C |
|---|
| fundamentals and presenting intrinsic value estimations. |
|---|
|
|---|
| Equity Valuation: Concepts and Basic Tools |
|---|
94 When constructing a list of peer companies to be used in equity valuation, which of the following would least likely improve the group? Companies in the same peer group should ideally:
A be exposed to similar stages in the business cycle.
| B is correct. Companies in the same peer group can have different valuations depending |
|---|
on structure and competitiveness.
A is incorrect. Valuations may be of limited value when comparing companies that are exposed to different stages of the business cycle.
95 The type of voting in board elections that is most beneficial to shareholders with a small number of shares is best described as:
A statutory voting.
|
|---|
| C | voting by proxy. |
|---|
|
|---|
| C |
|
|---|
54 2018 Level I Mock Exam AM
|
|---|
| Introduction to Industry and Company Analysis |
|---|
C is correct. In general, a company will utilize share buybacks to satisfy stock compen-sation plans.
A is incorrect. In most cases, the capital that is raised is used to finance the purchase of long- lived assets, capital expansion projects, research and development, the entry into new product or geographic regions, and the acquisition of other companies.
| Overview of Equity Securities |
|---|
98 The value effect market- pricing anomaly most likely occurs when stocks that have below- average price- to- earnings and market- to- book ratios, as well as above- average dividend yields, consistently outperform:
A large- cap stocks.
B growth stocks.
C is incorrect. Value effect does not compare stocks on the basis of earnings surprises. It is the “earnings surprise” anomaly that compares companies on the basis of the unex-
|
|---|
99 Using the following US Treasury spot rates, the arbitrage- free value of a two- year $100 par value Treasury bond with a 6% coupon rate is closest to:
| ( 1 | + | 3 | + | ( 1 | + | 3 | 2 | + | ( 1 | + | 3 | + | ( 1 | + | 4 | = | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 0160 2 ) 1 | 0 0220 2 ) | 0 0270 2 ) 3 | 0 0310 2 ) |
A is incorrect because it treats the spot rates as forward rates.
C is incorrect because it does not divide the annual spot rates by two in the calculation.
|
|---|
101 In a securitization structure, credit tranching allows investors to choose between:
A subordinated bonds and senior bonds.
| A is correct. Credit tranching allows investors to choose between subordinate and |
|---|
senior bond classes as a means of credit enhancement. The purpose of this structure is to redistribute the credit risk associated with the collateral.
B is incorrect because extension and contraction risks refer to the types of prepayment risks in a securitization structure.
| Introduction to Asset- Backed Securities |
|---|
102 A portfolio manager holds the following three bonds, which are option- free and have the indicated durations.
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| $8,000,000 | $12,000,000 | 3 | |
|
$8,000,000 | $6,000,000 | 7 |
|
$4,000,000 | $6,000,000 | 6 |
| as follows: (8/20) × (3.0) + (8/20) × (7.0) + (4/20) × (6.0) = 5.20. |
|---|
|
|---|
C 13.5.

|
|---|
| 25.0 | 35.0 |
|---|
B remained unchanged.
C deteriorated.
is used to calculate the coverage ratios, the same conclusion is reached: for 20X1 the ratio is 3.33, and for 20X2 it is 3.86.
|
|---|
| Fundamentals of Credit Analysis |
|---|
On the basis of these spot rates, the price of the bond today is closest to:
A is correct. The bond price is computed as
|
|---|
years 1 through 6 and the par value is paid at maturity in year six, as follows:
|
|---|
B Shorter supply of the collateral
C Lower credit quality of the counterparty
|
|---|
107 Using the following information and assuming coupons are paid annually, the G- spread of the Steel Co. bond is closest to:
C 100 bps.
| ( 1 | 5 | + | 5 | + | 100 | = | |||||
| + | r | ) | ( 1 | + | r | ) | 2 | ||||
| r | = | ||||||||||
LOS i
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
109 AMK Corp. purchased US government bonds through the Bloomberg fixed- income electronic trading platform. This transaction is most likely known as: A exchange traded.
B private placement.
B is incorrect because private placement is a form of primary markets instead of
|
|---|
C €1.0 billion.

|
|---|
111 A swap in which the investor receives a variable payment in line with market conditions and makes a fixed payment can best be replicated by purchasing a:
| A |
|
|---|
|
|---|
112 During its life, the value of a forward contract is most likely equal to the price of the underlying minus the price of the:
A forward.B forward, discounted over the original term of the contract. C forward, discounted over the remaining term of the contract.
|
|---|

| C is correct. For a deep- in- the- money put option, early exercise may be optimal because |
|---|
| Basics of Derivative Pricing and Valuation |
|---|
114 In a currency swap, the underlying principal amount is exchanged: A only at the start of the swap.
A is incorrect. In a currency swap, the underlying principal is denominated in different currencies and would typically be exchanged not only at the start of the swap but also at the end of the swap.
B is incorrect. In a currency swap, the underlying principal is denominated in different currencies and would typically be exchanged not just at the end of the swap but at the

|
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
LOS e
|
|---|
B 7.4%.
5.8%. C
|
|---|
B is incorrect. It reduces the base of the incentive fee by the hurdle rate. This is only correct in the case of a hard hurdle rate, but not in the case of a soft hurdle rate. Management fee: 2% of $110 million = $2.2 million.
Incorrect subtraction of $8 million (because of the hurdle rate) from the performance of $10 million leaves $2 million.
| Introduction to Alternative Investments |
|---|
118 Relative to traditional investments, alternative investments are best character- ized as having:
A higher correlations with other asset classes.
B unique legal and tax considerations.
tha |
greater liquidity. |
|---|
119 The most likely impact of adding commodities to a portfolio of equities and bonds is to:
A increase risk.B provide higher current income.
C reduce exposure to inflation.
| B is incorrect because commodity investments tend to produce no current income. |
|---|
|
|---|
| A is correct. Real estate limited partnerships are a form of private real estate investment. |
|---|
|
|---|














