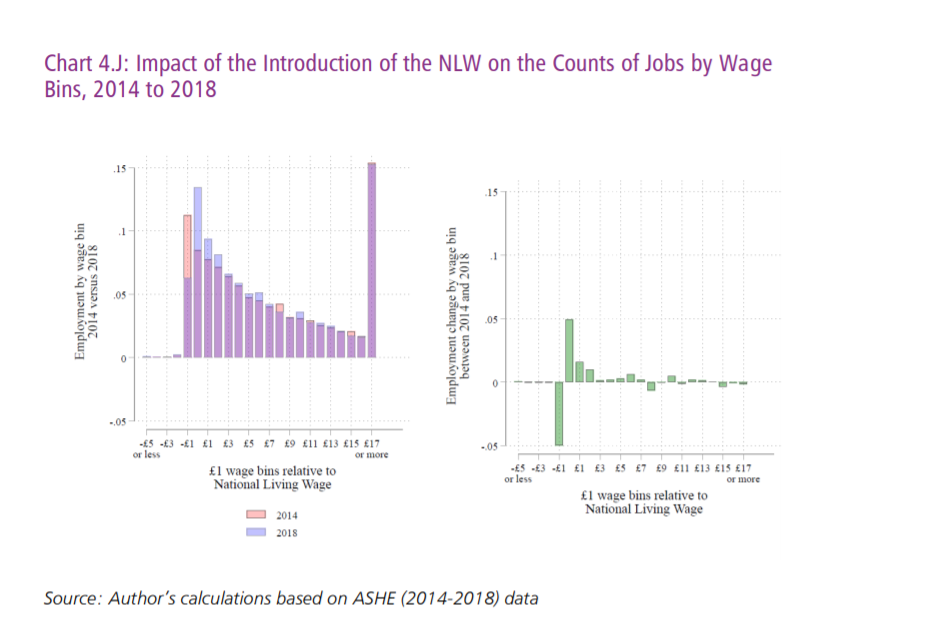
The low wage jobs increased slightly the year
The main rationale behind the introduction of the minimum wage was that the government wanted to increase the support for the workers and also improve these standards of reward when it comes to the work they do. national living wage and national minimum wage together are deferred as minimum wage which aims toward protecting the low-income workers when providing incentives for the work done. Besides that, the minimum wage also aims toward helping the organization by driving fairness in the labor market and make that the competition is based on the quality of goods and services and not according to the low prices driven by low rate of pay. The government believes whoever is entitled for the minimum wage should receive Minimum wage according to the guidelines that are set out. Moreover, through this initiative the government wanted to support the employers to make sure the minimum wage is paid correctly as well as communicated to workers so that they could raise awareness of entitlement as well as route for redressed.
National minimum wage came into effect from first April 1999, where it covered all the worker who were not self-employed, regardless of their occupation, size of the firm, industry and the region. A body was called as low Pay Commission was established in 1999 for advising the UK government so that national minimum wage could be fixed. Each year the LPC commissions and fund research was analyze for impact of minimum wage and then these searches could be used for evidence which could be used by the government for the recommendations. These recommendations are adopted by the government and they are used for setting up the rates. The main aim of the UK government was to make sure that they could effectively raise the minimum wage for workers specially who are above the age of 21. The adult rate was fixed at £3.60 per hour for all those workers who are above the age of 22 whereas workers between 18-21 was £3.00 whereas trainee level of the adults who were working on the new work was given £3.20 whereas the worker under the age of 16-19 were initially exempted. Before the introduction of NMW, the coverage adult rats were fixed at 5.6% whereas youth rate was 8.2%. After the month of the initiative was introduced, the vast majority of the employers were obligated to pay the properly hourly rate.
The neoclassical theory it's quite familiar. mandate minimum wages are considered as any other price floor. It is the mandate wage is considered to exceed the market clearing wage then it represents a downward sloping labor demand curve, that clearly emphasize that form has reduced the quantity of the labor which was demanded. the magnitude of this reduction totally depends upon the wage increase as well as the wage elastic city of Labor demand however when it comes to direction of change then in that case it does unambiguous. Moreover, welfare effects will also have an impact over the wage elasticity of demand, are some of the workers might receive higher wages and they are better off whereas on the other hand adult worker whose product are considered to be worth less than the new minimum will be laid off or they will be restricted to work for fewer hours only. if the quantity of the labor is defined as employment then the wage gain of those people who kept their jobs must be traded off against the wage loss of those who lost their jobs.
Under this approach dis-employment is logically necessary outcome everyone assumes that (1) Form is inclined toward maximizing the profit (2) The low skilled labor market is categorized as competitive and the firms have no monopsony power. according to neoclassical theory which can accommodate a weakening assumption of 2nd factor that is if the labor market is categorized as monopsonistic, firm tend to exercise the market and pay the workers’ lower than the workers’ MRPL (marginal revenue product). Monopsonistic firm tends to offer higher wages so that they could potentially attract new hires which directly leads to costlier labor expenditure as well as inefficiency low employment. in that context, a judiciously chosen minimum wage can potentially increase employment as well as the efficiency. However, when it comes to practice labor economists traditionally address monopsony as an empirical curiosum. The more individual low wage organizations typically tend to employ low percentage of low wage workforce, which clearly demonstrate that monopsony power is limited when it comes to implementation of practice.
Employment search model
Minimal range have been analyzed through theoretical framework that is based on job search model. according to this framework the effect of employment totally depends upon the level of minimum wage is and also depends upon the impact on the job search intensity, accepted wages and Lastly the probability of getting the offer of a job. According to research that was conducted by Swinnerton (1996) clearly present or search equilibrium model in which the organization indicate work demand curve which is a downward sloping, on labor productivity tend to varies from organization to organization. besides that, the unemployed have imperfect information, the job search are sequential as well as random. Through these events in the author have clearly represented an increase in average labor productivity and have a positive welfare effect in case where there is a negative impact employment then also it has the chances that positive welfare would arise.
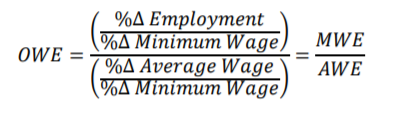
Evaluations of the National Minimum Wages
Compelling evidence for longer run impact of national minimum wage has come from Manning (2016), In his study the author has constructed group based on region, age and gender. Moreover, through his study evaluated how the change in log of average wages and employment rate have varied over the groups between the 1997 to 2007. through his study he has partial out the fixed effect on the age, gender and region group, and have stated differing trends in the region as well as the demographic group hence the below chart is based on residualized outcome and after partialing out the fixed effects.
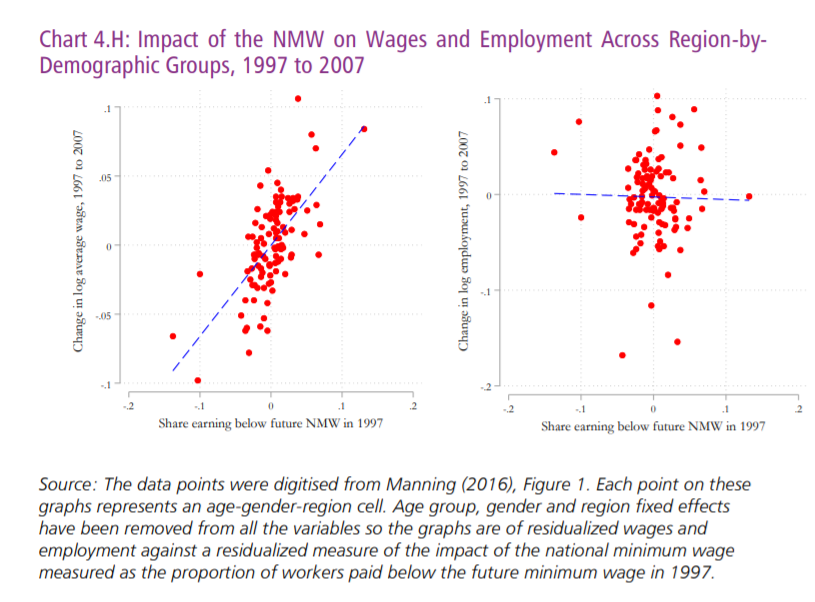
According to the Manning (2016) who have used region and demographic variations, have Evaluated 96 group which was categorized by 12 regions, 2 gender categories Ann food age categories, the affected share was revealed to varied from 6% to 34%. Considering the changes in Group level log employment and log average wages between 2014 to 2018, highlighted in the left panel but the average wage growth was quite much faster after the introduction of NLW in the following groups who have larger share also affected workers, the regulation coefficient was 0.36. however there has been no statistically significant relationship which could be pointed out between the shares and employment. the regression coefficient was -0.05. Together it was implied that OWE is around -0.13 Which clearly indicates a very little impact on the employment after the introduction of national living wages.
Conclusion
From the above discussion and overall evidence that have been presented in the above section provides clear indication that effect of minimum wage effect on the employment is ‘muted’. Moreover, according to the overall OWE median for the 48 estimates that have been drawn through the various countries and effected group is around -0.16 which clearly suggest that Minimum wage have potentially increase the wages compared to the any effect on jobs. According to the set of studies which considered the broad group of workers where their OWE is Estimated to be quantitatively is -0.04 which is close to zero, it clearly suggests that job losses are quite small. According to the recent set of studies which have provided estimate for evaluating the impact of policy and also for rationalizing the divergent estimates in the literature, these literatures have confirmed that impact of minimum wage in increase on job is considerably small.
Another margin of the adjustment has been presented by the scholars such as Coviello, Deserranno and Persico (2019) that is ‘productivity’. Who have used a broader discontinuity design as well as the data from US retailer and to find productivity gains that are concentrated among low-productivity workers, and are particularly high during high unemployment periods - which together are consistent with an efficiency wage model. According to Riley and Bondibene (2017) who have used evidence from UK firms and find evidence of increased Total Factor Productivity (TFP) which they argue is consistent with theories of efficiency wage and training. Finally, as discussed above, there is evidence that higher minimum wages reduce worker turnover. Lower turnover costs (from recruitment and training) also translate into higher productivity per worker; moreover, lower turnover can increase firm incentives to provide general training and raise productivity.
