With probability set and statistical significance set confidence
SAMPLING
• Researchers use samples to infer characteristics of a population
The entire universe or population of
interest. The ‘population of Bond
students’ is easy to define; but what if I am interested in motorsports
fans, how do I define that population? Or something that sounds simple,
like ‘Australian
adults’?
A subset of that population.
DEFINING THE TARGET POPULATION
What is the relevant population? Not always easy to define…
Sampling frame: A list of elements (e.g. a
membership list, a student email list) from which a sample may be drawn– If a researcher was interested in surveying doctors in
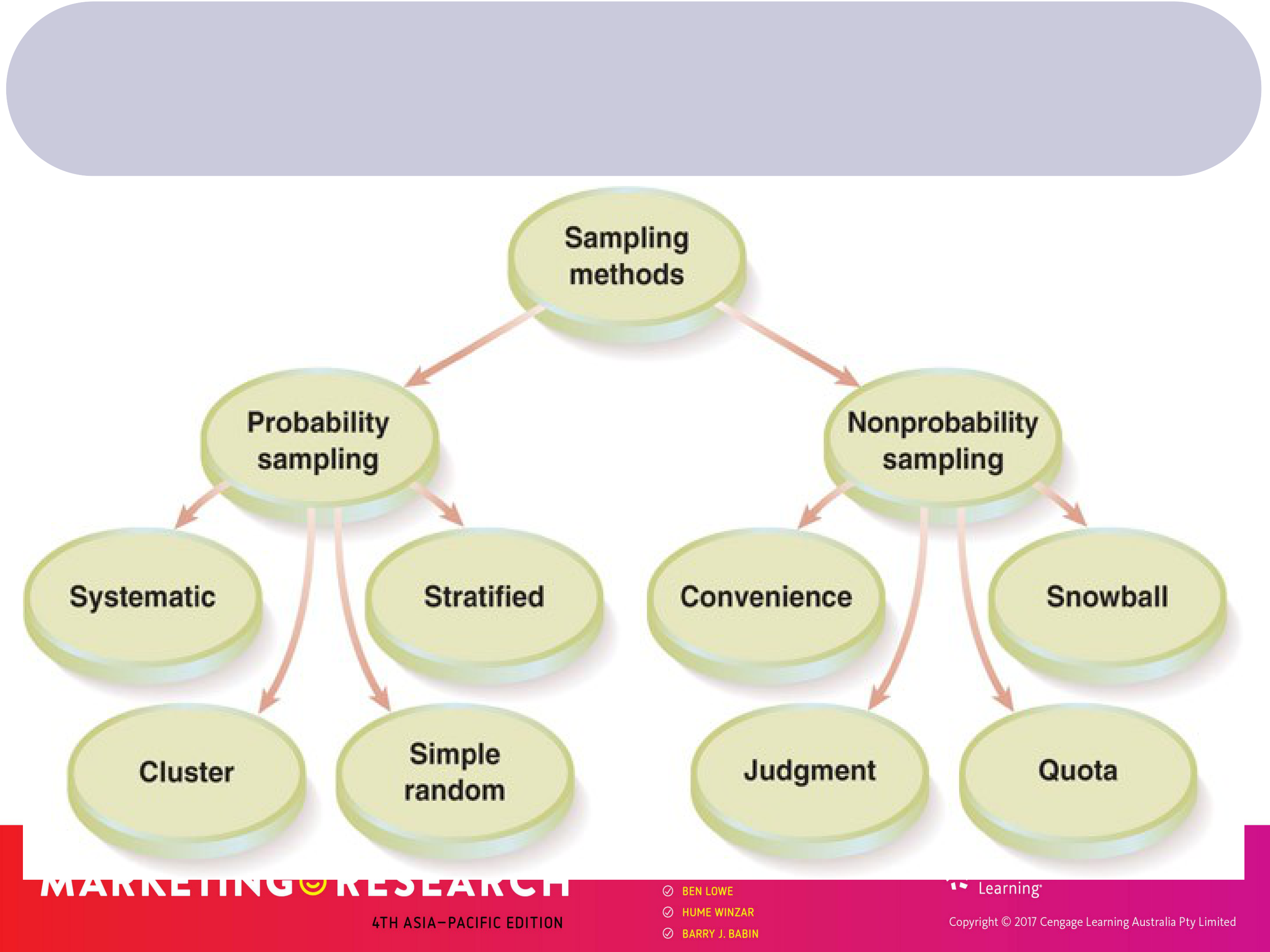
Australia, a sampling frame might be a list of all members of the Australian Medical Association.Nonprobability sampling: A sampling technique in which members are selected on the basis of
personal judgement or convenience.
| Please try to understand these! I would like you to specify what |
|---|
– Results appear to be random if there is no other systematic pattern to the list (ex: you are standing by the men’s bathroom…)
PROBABILITY SAMPLING METHODS (CONTINUED)
PROBABILITY SAMPLING METHODS (CONTINUED)
Cluster sampling
-0
Probability sampling
– It’s … convenient! A lecturer who uses students for a study; you ask your friends to complete a survey or participate in a focus group.
– Convenient, but potential respondents may be unwilling or unrepresentative. Are my friends representative of technology trends or political opinions?!
NONPROBABILITY SAMPLING (CONTINUED)
Quota sampling
– Respondents are obtained from information
provided by the initial respondents, they refer other individuals.– Common if dealing with rare populations, e.g., a teddy bear collector would provide contact details for other teddy bear collectors.
– Nonprobability methods are better for projects with financial and human resource constraints. If we are thoughtful (any reason to believe respondents are not representative?!), non-probability samples are often “good enough”.
EVALUATING SAMPLE DESIGN CRITERIA (CONTINUED)
Web surveys are increasing in popularity
– Option to reach a large sample rapidly (but verify that the survey you show formats properly on different devices).
• The confidence level (e.g. 90%, 95% or 99% CL) – Higher confidence requires a larger sample.
There are math formulas to determine an appropriate sample size – the ‘power’ of the study.
DETERMINING SAMPLE SIZE ON THE BASIS OF JUDGEMENT (COMMON)
• Sample size may be determined on the basis of managerial judgements.
• Sampling involves selecting a subset of the target population for the purposes of being able to draw general conclusions about that
population.• Why sample?
Findings will be reasonably accurate (there are formulas to determine the ‘confidence interval’).






