You are able move the object and the lens and change the characteristics the lens
We will use the technique of ray tracing along with the equations of geometrical optics to investigate aspects of a single lens with a single object. The lens we will use in this simulation is a thin double-convex lens.
a)What happens to the image formed on the other side of the lens?
|
|---|
|
|---|
a)Use the appropriate equation above to solve for the focal distance (f). Describe the equation you used and give your result.
|
distance object (do) | distance image (di) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
c) Make sure you fill in the table above.
3.Repeat the previous exercise, but with a very different lens with the following
characteristics: R = 80cm, n = 1.25
b) For virtual images what should the sign of di be?
|
|---|
| 120. cm |
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 90. cm |
|
||
| 60. cm | |||
| 30. cm |
|
||
| 15 cm |
|
b)As the radius of curvature of the lens increases, the focal point of that lens becomes closer to / further away from that lens.
|
|---|
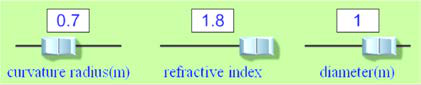
e)What was the focal distance (f) when the radius of curvature was .70 and index of refraction was 1.8?
h)Define lens magnification?