Case Study H&M Sample Assignment
H&M – Case Study
1.0 Introduction
H&M (Mennes & Mauritz AB) is a Swedish conglomerate that deals in retail clothing all over the globe. The company is known for its fast fashion clothing for women, men, children and as well as teenagers.
This paper is going to be focusing on the strategic analysis of H&M, i.e. the paper is going to be discussing the environmental (this is going to include PESTEL analysis), industry (this is going to include the Porter’s 5 forces analysis and the industry life cycle model), and competitive analysis (this is going to include the SWOT analysis and the Porter’s 5 forces framework along with the identification of competitors within the market). It shall be focusing on the strategic options (this would be focusing on generic strategy, value chain, competitive advantages, and CSR) and the methods and lastly strategic recommendations (this will be focusing on different actions that will be taken) will be given.
2.0 H&M Background
H&M (Mennes & Mauritz AB) is a Swedish multinational that deals in retail clothing all over the globe. The company is known for its fast fashion clothing for women, men, children and as well as teenagers. The company operates in 55 counties and online shopping in 13 countries and has 3500 stores. H&M employs 116,000 people as of 2013 (H&M, 2015). H&M is the second largest clothing retail that deals with fast fashion in the world after Zara, but it leads over the American company Gap Inc.
The company operates in the retail industry, was founded in 1947by Erling Persson. The headquarters of the company are located in Stockholm, Sweden. The key personnel of the company are Stefan Persson (chairman) and Karl-Johan Persson (CEO and President). The products that are sold by the company include clothes and accessories. The subsidiaries of the company include Monki, Weekday, Cheap Monday, COS and other retail outlets all over the globe. (H&M, 2015)
2.1 Mission
The mission of the company is to provide its customers with top quality products are best prices which the customers deem to be affordable. Quality is crucial to the company and has stressed over it considerably, so that the products they are selling meet the requirements of their customers. H&M is constantly innovating and finding new ways to improve its products so that they are able to exceed the expectations of their customers. H&M is also highly committed to environmental and social concerns. The company strongly believes in giving back to the society and therefore has a number of programs and is associated with a number of charities like Fashion against Aids and UNICEF etc. (H&M, 2015).
2.2 Vision
The vision of the company is to run its operations in a manner that is considered to be economically, environmentally and socially sustainable. It can be said that the company is able to meet the needs of both present and future generations. The company believes strongly in quality and making sure that its products are of top notch quality. Therefore the company is highly cost conscious and has a very efficient distribution channels (H&M 2015).
2.3 Goals and Objectives of the Company
- The goals and objectives of the company are basically to find new and innovative ways to improve their products.
- Making sure that their products are of top notch quality to meet the expectations of their customers.
- With the help of strong values the company is able to energy and commitment in regards to employees. The company make sure that the workplace is open and dynamic, where everyone is working together to achieve the goals that have been set by the company. (H&M, 2013)
- The objective of the company is to expand themselves all over the globe. In 2014 the company expanded itself to 375 new stores. It can be said that the pace of the company is strong in regards to growth. (H&M, 2015)
2.4 Financial Aspects
H&M is very strong financially, as of 2013; the company has sales inclusive of VAT increased by 9 percent compared with 2012. The gross profit of the company amounted SEK 76,033 million, which is an increase by 6 percent and the gross margin of the company is 59.1 percent (H&M, 2013). H&M in the last year has a little change in its net income and the contributing factor to this is the increase in cost of goods sold from 40.50 percent to 40.87 percent. The following table shows the financial ratio of the company (FT, 2015).
|
Financial Ratios SEK (as of 2013) | |
|
Current Ratio |
1.89 |
|
Quick Ratio |
0.9827 |
|
Net Profit margin |
13.29% |
|
Gross margin |
59.1 % |
|
ROE |
46.08 % |
|
ROI |
43.15 % |
2.5 Organizational Structure
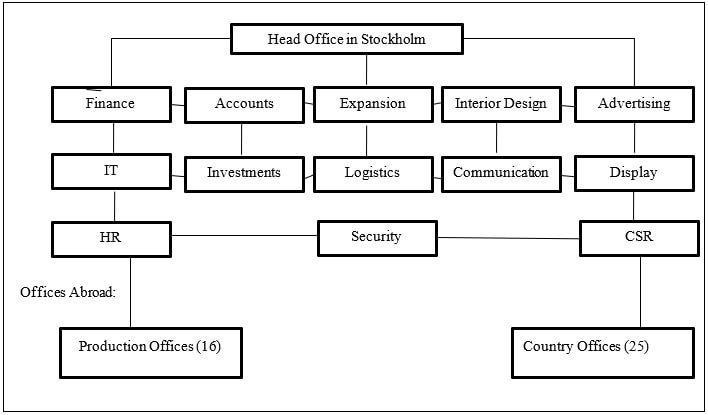
The headquarters of the company are located in Stockholm. The corporate culture of the company is that of a common global organization. H&M is known for outsourcing all its production. The company has over 700 independent suppliers which are mostly located in Asia and Europe along with 16 production offices. (H&M, 2013)
H&M organizational structure is a matrix, i.e. where there are wide spread departments, the organization is completely product based, the managers are required to accomplish common goals and the organization is highly flexible. The organizational structure of the company is as follows;
3.0 Environmental, Industry and Competitive Analysis
Environment, industry and competitive analysis is going to help H&M understand its position within its chosen industry. It will help to identify its weaknesses and strengths, along with opportunities that are present and the challenges it faces, plus it will also help to identify its competitors, the needs and requirements of the targeted customers along with other external forces.
3.1 Environmental Analysis
It is essential to understand the external environment in which the company operates, therefore to understand its environment the company needs to conduct a PESTLE analysis.
3.1.1 PESTLE
According to Kotler & Armstrong (2008), this analysis is used to conduct an audit for the influences the external environment has on the company. The following table shows the PESTLE analysis of H&M.
|
PESTLE Analysis | |
|
Political |
The major factor that tends to affect H&M in this element is the constraints and restriction it faced in regard to importing and exporting of its goods. Another issue for the company would be the continuous relocation for its manufacturing and outsourcing due to low costs |
|
Economical |
The consumer spending on clothes and apparel is increasing in a slow but a continuous pace. The financial crisis in 2008 played a major role in the spending of the consumer and its buying patterns Increase in the labor costs, especially in East Asia |
|
Social |
There is an increase in the green issues, as more and more companies are becoming green The company believes in ethics and morals |
|
Technological |
The company has introduced online shopping stores, since there is an increase in the shopping online trend, because it helps to save time and money |
|
Legal |
the company follows EU laws as well as international laws regarding labor practices and Swedish legation The company follows proper code of conduct |
|
Environmental |
The company focuses on sustainable development; therefore CSR is one of its essential values. The company believes in decreasing waste and increasing energy efficiency (H&M 2013) |
3.2 Industry Analysis
According to Porter (2008), industry analysis is essential for the success of the company. With the help of an industry analysis a company like H&M will be able to find out about the needs and requirements of its customers, the threats it is facing along with other aspects. The industry in which H&M operates is the fast fashion industry, where the company provides its customers with clothes, accessories and footwear. Therefore to understand the industry is essential to conduct the Porter’s Five Forces analysis along with a lifecycle model.
3.2.1 Porter’s Five Forces
According to Porter (2008), the five forces analysis is a very useful tool for companies. This analysis tends to observe the profit margins of the industry and tends to explain the structure of the industry itself. The five forces analysis is based on 5 elements. These elements are defined in the following illustration.
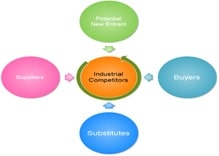
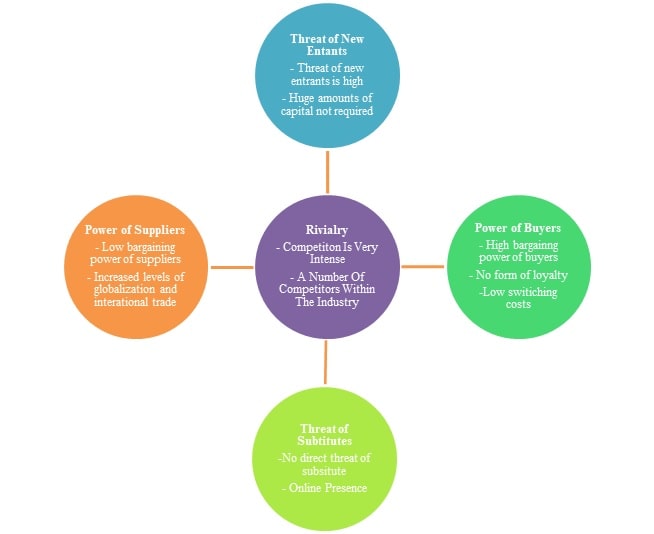
- Competitors/ Industry Rivalry: competition between companies within this industry is high, because there are a number of companies that are selling clothes and accessories related to fat fashion. The industry is growing but a slow pace after the recession that took place in 2008. The major competitors of the company are Zara and Gap. But the major competitor of H&M is Zara. When compared with H&M, Zara is considered to be the market leader in the fast fashion industry, closely followed by H&M and then GAP.
- Supplier Power: the bargaining power of the suppliers within this industry is low, why because there are a number of suppliers providing the same kind of clothes without any kind of differentiation. Due to globalization and international trade has provided the retailers to source from international manufacturers, for example, from countries like China, India and Bangladesh where the wages are low but there is extreme competition. (H&M, 2013)
- Barriers to Entry: the threat of new entrants within this particular industry is extremely high, because entering this industry does not require huge amounts of investments. And there are a number of individuals who have the means to open their own clothing lines. For example, the company can face threat from local boutiques and cloth retail shops. But there is one thing that needs to be kept in mind is that the costs of advertising and distribution channels are extremely high.
- Buyer Power: The customers play a crucial part in the success of the company, therefore it can be said that the bargaining power of the customers is very high. The customers who tend to purchase clothing and accessories from H&M are generally urban population, especially females from the ages of 18-30 years. But these customers tend to look for items that provide them with quality, affordable price and style. Therefore they are switiching from one brand to another and are not loyal at all.
- Threats of Substitutes: it can be said that there is no direct substitute for apparel, but there are substitutes for retail. For example, online shopping channels through which companies are able to sell their products all over the globe without have retail outlets.
3.2.2 Product Lifecycle Model
It has been suggested by Mullins & Williams (2012), that product lifecycle is one of the essential models of marketing. It can be considered as a stage process through which a product has to go through. The product has to go through four stages to reach from introduction to decline. The following illustration shows the product lifecycle curve.
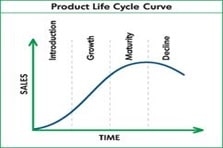
H&M is about to complete with growth stage and reaching its maturity. The still is in the process of expansion and is spreading itself globally. The company is also expanding through online sales, for example the company has online stores in 13 counties. (H&M, 2015)
3.3 Competitive Analysis
The part is going to be focusing on the competitors of the company. The major competitors of the company are Zara and Gap. But the major competitor of H&M is Zara. The competitive analysis is going to be defining the major competitor, will conduct a SWOT analysis and provide a Porter’s 5 forces framework.
3.3.1 Major Competitor - ZARA
The major competitor of H&M is Zara a Spanish clothing retail that also deal is fast fashion. Zara is a major selling brand of Inditex, who is the largest fashion retailers on the globe. Zara has over 2000 outlets all over the world (Inditex, 2014). Zara is highly innovative and the biggest seller of clothes even without an advertising campaign. When compared with H&M, Zara is considered to be the market leader in the fast fashion industry, closely followed by H&M and then GAP.
The major strategy of the company is to open its outlets in areas that are considered to be high profile, like 5th Avenue in New York City. The company also tends to focus on its product quality and it makes sure that it provides its customers with new design every two to three weeks (Levine, 2013). The target market of the company is extremely broad, because the company is not known for defining its targeted market. Zara mostly focuses on the desires and wants of their customers in regards to what they want in actual, i.e. what they are going to purchase, so that they are able to provide their customers with complete satisfaction, therefore the company strongly believes in getting feedback from its customers.
3.3.2 SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is conducted so that the company is able to understand its internal (which includes strengths and weaknesses) and external (which includes opportunities and threats) environment. According to Daft (2008), SWOT analysis is very essential for a company’s growth and development. The SWOT analysis of H&M is as follows.
- Strengths; the biggest strength of H&M is awareness of its brand image. People are quite aware of the H&M brand and that is all due to their marketing campaigns which are also the strength of the company. The quality of the products sold at affordable prices is another strength for H&M. The prices help the company to differentiate itself from its competitors. The global presence of H&M is also considered to be an advantage for the company, i.e. the company as of 2013 has 3000 stores in over 55 countries around the globe (H&M, 2015).
- Weaknesses; H&M completely depends’ on its suppliers, i.e. the company heavily relies on outside suppliers to manufacture its products. The company has over 900 independent suppliers therefore this suggests that it does not have control over that are creating its products (H&M, 2015). Another disadvantage for the company is poor quality based products when it has not control. Another weakness for the company is that its distribution warehouses are mostly located within Europe; therefore it is difficult for the company to open more online stores. There is considerable amount of uncertainty when it comes to no control over outside factories and this could lead to unfilled orders or late shipment.
- Opportunities; Online shopping is the fastest growing trend in the retail business, as more and more people shop online to save time and money. Therefore online expansion is one of the biggest opportunities for H&M. The company has opened online stores in 13 countries including US (H&M, 2015). Another opportunity for the company is to grow its presence within the Asian market like India. India is one of the biggest markets in the world. And the company needs to focus on the South American market, especially Brazil, which is an upcoming market.
- Threats; H&M faces intense rivalry in the industry from companies like Zara and Gap who also deal in fast fashion retail. Currency fluctuation will also be considered a threat for H&M, because it tends to deal in Swedish Krona (SEK), due to the fluctuations in the US dollar and Euro.
3.3.3 Porter’s 5 Forces Framework
4.0 Corporate, Business and Functional Analysis
The corporate, business and functional analysis tends to focus on the strategies that are being used by the company in regards to its operations.
4.1 Corporate Strategy
The corporate strategy tends to focus on the overall purpose and scope of the company along with the vision of the company. The corporate strategy of the company is to provide its customers with top quality products are cheap prices and making sure to give back to the community as well. (H&M, 2015)
4.2 Business Strategy
The business strategy of the company is global expansion, for example in 2013; the company opened its 3000th store in over 55 countries and has online stores in over 13 countries. The company is making its presence known within the industry through expansion and growth. (H&M, 2015)
4.3 Functional Strategy
The functional strategy of H&M is based on quality of the products, innovation in regards to new ad trendy clothes and accessories which are up to date with the fashion industry and customer feedback. The functional strategy of the company are also based on three strategic goals and they are profitability, expansion to gain competitive advantage over its competitors and technological leadership.
5.0 Strategic Options
According to Hill & Jones (2009), are different options that are available to the company, when it is carrying out its decisions in regards to strategy.
5.1 Generic Strategy
The strategy that is being followed by H&M is cost leadership. The company provides similar clothes as its competitors like Zara and Gap but at lower prices, therefore this helps the company to differentiate itself and gain a competitive advantage over its competitors, therefore this is one of the reasons why the company is ranked at second place after Zara in the fast fashion industry. The major reason that the company provides good quality products at lower process is because it has no manufacturing factories of its own and outsources its requirements to over 900 independent suppliers all over the globe (H&M, 2015).
5.2 Value Chain
The primary activities of H&M chain value are the design department, the purchasing department and the sales channels. The company makes sure that it purchases the best raw materials to collaborating with designers to create new and trendy designs to fabric production to clothes and accessories production to sales by providing the customers with a hand on experience, where they can touch, feel and try on clothes and accessories which meet their requirements. (H&M, 2015)
5.3 Competitive Advantages
- Providing customers quality products at affordable and cheap prices
- The stores of the company are located in convenient locations
- H&M has a good marketing and advertising campaign
- The company is focusing on online stores
5.4 Corporate Social Responsibility
H&M is also highly committed to environmental and social concerns. The company strongly believes in giving back to the society and therefore has a number of programs and is associated with a number of charities like Fashion against Aids and UNICEF etc. (H&M, 2015).
6.0 Strategic Method
Strategic method helps an organization to create or evolve it business strategy. The strategic method that is most commonly used is the SWOT analysis, because it helps to understand the internal and the external environment of the company. The SWOT analysis of H&M can be reviewed under the competitor analysis above.
7.0 Strategic Recommendations
- H&M needs to focus more on online shopping, even though it operates in 13 countries, it needs to expand its online stores, so that the company able to create more awareness about its brand on the internet.
- The company needs to move some of their distribution warehouses from Europe so that they are able to open more online outlets. For example, it can move some of its distribution centers to Dubai this way the company will be able to cover the entire Asia.
- Outsourcing is good, it saves time and money, but H&M needs to have some of its own manufacturing factories to have some control over its manufacturing.
References
Daft, R L. (2008), New Era of Management. USA: Cengage Learning
FT (2015), Equities – H&M. Viewed on 9th January 2015: http://markets.ft.com/research/Markets/Tearsheets/Financials?s=HM+B:STO
Hill, C W L. & Jones, GR. (2009), Essentials of Strategic Management 2nd Edition. USA: Cengage Learning
H&M (2015), From Idea to Store: Production Process. Viewed on 9th January 2015: http://about.hm.com/en/About/facts-about-hm/idea-to-store/production-process.html
H&M (2015), The H&M Group. Viewed on 9th January 2015: http://about.hm.com/en/About/facts-about-hm/about-hm/hm-group.html#cm-menu
H&M (2015), H&M – Our History. Viewed on 9th January 2015: http://about.hm.com/en/About/facts-about-hm/people-and-history/history.html#cm-menu
H&M (2013), Annual Report – 2013. Viewed on 9th January 2015: http://about.hm.com/content/dam/hm/about/documents/en/Annual%20Report/Annual-Report-2013_en.pdf
H&M (2015), Global Expansion. Viewed on 9th January 2015
Inditex, (2014), Brand: Zara. Viewed on 10th January 2015: http://www.inditex.com/en/brands/zara
Jeffs, C, (2008), Strategic Management. UK: Sage Publications
Kotler, P, & Armstrong, G, (2008), Principles of Marketing 12/e. India: Pearson Education India
Levine, S, (2013), How Zara Took Customer Focus to New Heights. Viewed on 10th January 2015: http://www.cutimes.com/2013/04/09/how-zara-took-customer-focus-to-new-heights
Mullins, J & Walker, O, (2012), Marketing Management: A Strategic Decision-Making Approach. USA: McGraw-Hill Companies
Porter, M E. (2008), Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors. USA: Simon & Schuster
Stokes, D & Lomax, W, 2008, Marketing: A Brief Introduction. USA: Cengage Learning EMEA
Resources
- 24 x 7 Availability.
- Trained and Certified Experts.
- Deadline Guaranteed.
- Plagiarism Free.
- Privacy Guaranteed.
- Free download.
- Online help for all project.
- Homework Help Services
Testimonials
Urgenthomework helped me with finance homework problems and taught math portion of my course as well. Initially, I used a tutor that taught me math course I felt that as if I was not getting the help I needed. With the help of Urgenthomework, I got precisely where I was weak: Sheryl. Read More

