Introduction to Wireless Communications
Review
- Wireless communications: transmission of digital data without the use of wires
- Various forms of wireless data communications:
- Wi-Fi-based wireless LANs
- Bluetooth
- ZigBee
- WiGig
- Satellite
- Cellular
- Fixed broadband wireless communications
Wireless Metropolitan Area and Wide Area Networks
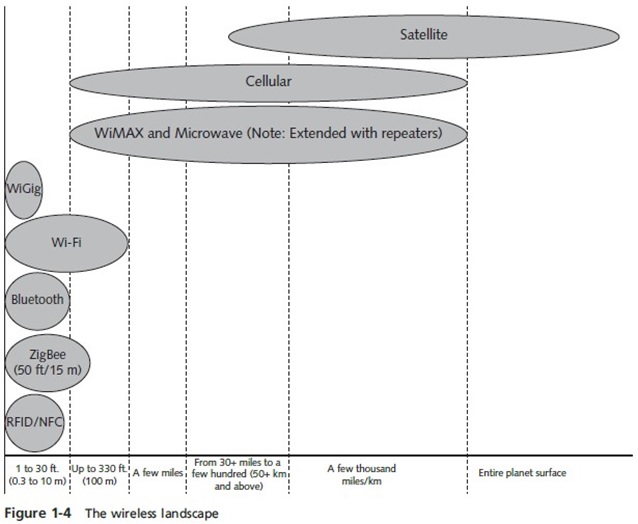
- This section covers wireless technologies that can cover areas ranging from an entire city to the entire planet
- Some of these technologies:
- Satellite networks
- Cellular networks
- Microwave links
Satellite Networks
- Commonly used in locations where a wired connection to the Internet is not easily available
- Used to transmit data over very long distance
- Repeater
- Located in the satellite itself
- “Repeats” the same signal to another location down on the surface
- Used to transmit data from one earth station to another
- Transmission time can be up to 250 milliseconds
- Satellite communications
- Often handled through third-party, dedicated providers
- Global Positioning System (GPS)
- Also based on satellite technology
- Satellite radio
- Another example of a technology that is not strictly data communications
Cellular Networks
- Maximizes the use of a limited range of frequency channels
- Located a few miles away to avoid interference
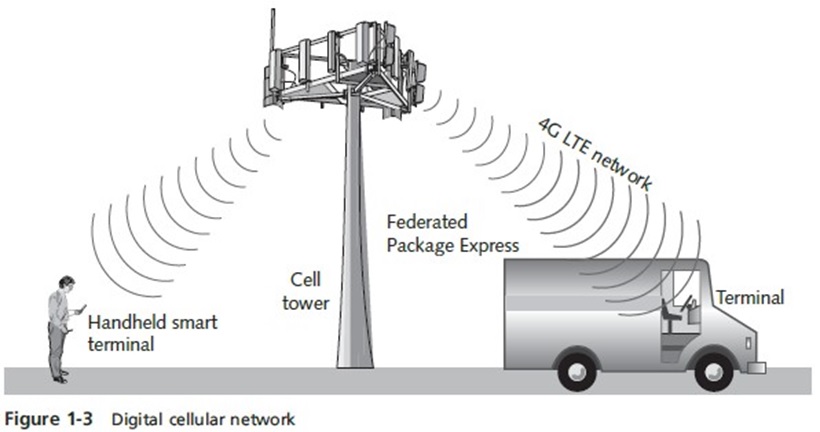
- The modern cellular telephone network
- Built around the concept of low-power transmitters
- With each “cell” handling a number of users
- Transmission towers are spread throughout a geographical area
- The same radio frequency channels can be reused by another tower
- Tablet computers can also be equipped with cellular technology
- Most smartphones also allow wireless tethering
- Use them to create a Wi-Fi hotspot and wirelessly connect a tablet or laptop computer to the smartphone
- Then let you access the Internet
- Many passenger cards offer connectivity to the Internet via the cellular network
- Public transportation also offers Wi-Fi capability
- 4G (fourth generation) technology
- Uses 100% digital transmission for both voice and data
- Transmission speed
- 50 Mbps for slow-moving pedestrians
- Over 100 Mbps when stationary
- 20 Mbps in a fast-moving vehicle
- 3G (third-generation) technology
- Realistic speeds are between 3 to 11 Mbps
Cellular Networks
Fixed Broadband Wireless
- In areas where wired Internet connectivity may not be available
- Solution may be to deploy wireless links based on microwave data equipment or WiMAX
- These technologies are commonly called fixed broadband wireless
- T1 lines
- Very costly option
- Cable modems
- Generally only available in residential areas
- Digital subscriber lines (DSL)
- Use either regular or special telephone lines – Speed is dependent on distance between FPE’s main office and nearest telephone switching office
- Wireless metropolitan area network (WMAN)
- Covers a distance of up to 25 miles
- Based on the IEEE 802.16 WIMAX Fixed Broadband Wireless standard
- Uses radio waves and small custom antennas on the roof of each building in WMAN
- WMAN (WiMax)
– Transmission speeds
- 75 Mbps at distances of up to 4 miles (6.4 km)
- 17 to 50 Mbps at distances over 6 miles (10 km)
– Recent amendment of IEEE 802.16m standard can achieve average speeds up to 100 Mbps and up to 1
Gbps in a point-to-point link
The Wireless Landscape
Digital Convergence and Future Trends
- Digital convergence
- Refers to the power of digital devices to combine voice, video, and text-processing capabilities
- As well as to be connected to business and home networks and to the Internet
- The same concept applies to the development of VoIP networks
- Use the same protocols and media that once only carried data
- Wireless technologies are used to fulfill many daily activities
Wireless Advantages and Challenges
- As with any new technology, wireless communications offers both advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of Wireless Networking
- Mobility
- Freedom to move about without being tethered by wires
- Permits many industries to shift toward an increasingly mobile workforce
- Creating “flatter” organizations with fewer management levels between top executives and regular employees
Advantages of Wireless Networking
- Easier and Less Expensive Installation
- Installing network cabling in older buildings can be a difficult, slow, and costly task
- Makes it easier for any office to be modified with new cubicles or furniture
- Installing network cabling can usually take days or even weeks to complete
- In countries where labor costs are high, this can make it very expensive
Advantages of Wireless Networking
- Increased reliability
- Network cable failures may be the most common source of network problems
- Eliminating cable failures increases the overall reliability of the network
- Disaster recovery
- In the event of a disaster, managers can quickly relocate the office
- Some planners keep laptop computers with wireless NICs and access points in reserve
Challenges of Wireless Networking
- Radio signal interference
- The potential for two signals to interfere exists
- Common office devices that could cause interference:
- Microwave ovens
- Elevator motors
- Heavy electrical equipment
- Outdoor lighting systems
- Theft protection systems
- Cordless telephones
- Solution: locate the source of interference and eliminate it
Challenges of Wireless Networking
- Security
- It is possible for an intruder to be lurking outdoors with a laptop computer and wireless NIC
- With the intent of intercepting the signals from a nearby wireless network
- Some wireless technologies can provide added levels of security
- Network managers can limit access to the network by programming it with a list of approved devices
- Rogue APs can be connected to a wired network by a disgruntled employee
Challenges of Wireless Networking
- Health risks
- High levels of RF can produce biological damage through heating effects
- Wireless devices emit low levels of RF while being used
- No clear picture of the biological effects of this type of radiation has been found to date
- Science today does not yet permit anyone to draw a definitive conclusion on the safety of wireless mobile devices
- Be aware of the possibility and monitor ongoing scientific research
Summary
- Wireless communications is quickly becoming the standard in the business world
- There are many different types of wireless networks and devices
- Wireless wide area networks will enable companies of all sizes to interconnect their offices
- Without the high cost charged by telephone carriers for their landline connections
- RFID and NFC short-range wireless have revolutionized counting inventory, item identification, and payment systems
- Digital convergence refers to the fact that data networks today carry digitized audio, video, and graphics in addition to other types of data
- Mobility is the primary advantage of a WLAN
- Other advantages include easier and less expensive installation, increased network reliability, and support for disaster recovery
- Challenges to a WLAN include:
- Radio signal interference, security issues, and health risks may slow down growth of these technologies
Resources
- 24 x 7 Availability.
- Trained and Certified Experts.
- Deadline Guaranteed.
- Plagiarism Free.
- Privacy Guaranteed.
- Free download.
- Online help for all project.
- Homework Help Services

