ITEC417 Wireless Communications and Security
Introduction to Wireless Communications
ITEC417 Wireless Communications and Security
Objectives
- Describe the various types of wireless communications technologies used today
- Discuss some trends in wireless data communications
- Outline the advantages and challenges of wireless communications technology
Wireless Communications Technologies
- Wireless: describes all types of devices and technologies not connected by a wire
- Wireless communications: transmission of digital data without the use of wires
- Various forms of wireless data communications:
- Wi-Fi-based wireless LANs
- Bluetooth
- ZigBee
- WiGig
- Satellite
- Cellular
- Fixed broadband wireless communications
Wi-Fi (Wireless LAN)
Wi-Fi or Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
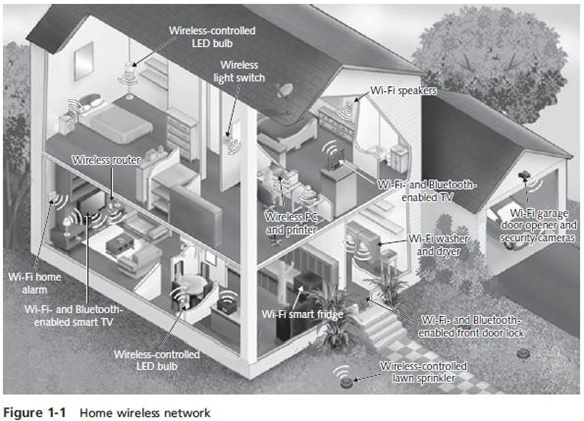
- Allows you to access all digital-data-enabled devices in the house
Wi-Fi (Wireless LAN)
- Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
- Extension of a wired LAN
- Connecting to it through a device called a wireless access point
- Access point (AP or wireless AP)
- Relays data signals among all of the devices on the wired network
- Each computer on the WLAN has a wireless network interface card (NIC)
- Used to communicate with your wireless residential gateway (often called a wireless router)
Wi-Fi (Wireless LAN)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) standards
- Established a series WLAN standards
- One of the latest standards provides for data transmission speeds of over 1 Gigabit per second
- Virtually all smartphones, tablets, and laptop computers are able to connect to a Wi-Fi network
- A few newer appliances include the ability to connect to the Internet
- Allows you to control them from wherever you may be
Bluetooth
– Wireless standard designed for very short ranges
- Typically a few inches to 33 feet (10 meters)
– Main purpose is to eliminate cables between devices
- Bluetooth communicates using small, low-power transceivers called radio modules
- Link manager
– Special software that helps identify other Bluetooth devices, create a link between them, and send and receive digital data
- Common implementations of Bluetooth:
- Headphones/headsets
- Smart TVs
- Keyboard/mouse
- Transfer pictures and files between tablets
- Connecting smartphones to car audio systems
- iBeacon
- Technology that uses Bluetooth
- Used to deliver coupons and direct customers to sale items while shopping
- Bluetooth is also used to connect smartwatches to smartphones and laptops
- Piconet
- Wireless personal area network (WPAN)
- Consists of two or more Bluetooth devices that are exchanging data with each other
- Up seven devices can belong to a single WPAN
ZigBee
- ZigBee
- A wireless communications specification based on IEEE standard 802.15.4
- Designed for applications that require devices with long battery life and can transmit data at distances of between 33 and 50 feet
- To pass certification
- Battery life on ZigBee devices must be at least 2 years
- Maximum data rate for ZigBee is 250 Kbps
- ZigBee-enabled devices can save power by turning off their transmitters for long periods of time
- Only wake up periodically to check status of network
- Most smart LED light bulbs support the ZigBee protocol and can be controlled by a central hub
- Accessed from a smartphone app
- ZigBee is used for automating entire commercial buildings
- Specification covers several other applications in addition to home and building automation
WiGig
- WiGig
- Another short-range wireless technology designed for use primarily in the home
- Can transfer video and sound at speeds between 7 Gbps and 10 Gbps using Ultra Wide Band (UWB)
- Distance: up to 2 meters at these high speeds
- Use is confined to the space within a room with few or no obstacles
RFID and NFC
- Radio frequency identification (RFID)
– Short-distance wireless technology – Developed to replace barcodes – Advantage over barcodes:
- Information can be read from the tag regardless of whether it is visible
– RFID tags are small chips containing a CPU, memory, and other electronic circuitry plus an antenna
RFID and NFC
- RFID reader emits electromagnetic waves that provide a small amount of current in the tag antenna
- The current powers the chip in the tag, which in turn transmits the information stored in the tag’s memory back to the reader
- Some RFID tags are called active tags
- Are battery-powered and have a longer range
- Common use for RFID today is for inventory control
- Some airlines use RFID to identify luggage
RFID and NFC
- Near field communication (NFC)
- Very similar to RFID
- Some RFID equipment can also read NFC tags
- Intended to work at an average distance of about 2 to 4 inches
- Transmission speed is approximately 250 Kbps
- Can include more flexible information like web addresses, commands, or instructions
- Smartphones and tablets equipped with NFC are sometimes able to write on the tags
Resources
- 24 x 7 Availability.
- Trained and Certified Experts.
- Deadline Guaranteed.
- Plagiarism Free.
- Privacy Guaranteed.
- Free download.
- Online help for all project.
- Homework Help Services

