Java Loop control Homework Help
Java Loop control:
If you want to execute particular part of code means use looping concept. In java we have three ways to running loop.
1. while loop
2. for loop
3. do … while loop
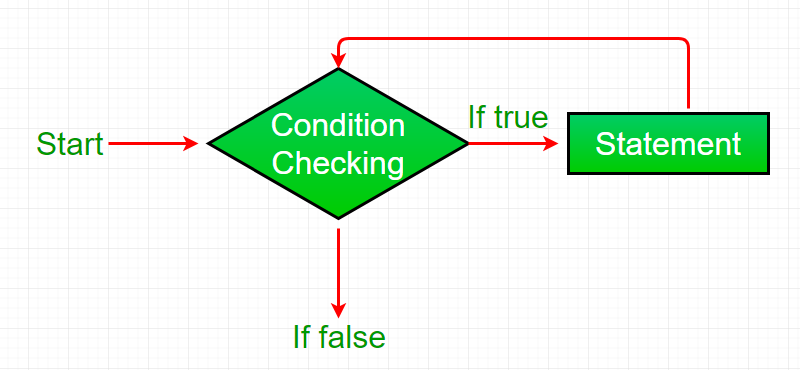
While loop:
It repeats the statement until the conditions get false.
Syntax:
while (condition)
{
code block to be executed
}
Example:
{`int a = 0;
while (a < 3) {
System.out.println(a);
a++;
}
`}
Output:
012
For loop:
It executes the set of statement multiple times until condition get false.
Syntax:
for ( initialization; condition; increment/decrement)
{Body of statement }
Example:
{`for (int i = 0; i <3; i++)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
`}
Output:
012
do .. while loop:
It not like that while loop. In this once the statement executes and then the condition will be checked.
Syntax:
do
{
Statement
}while(condition);
Example:
{`Int i=0;
do
{
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}while(i<3);
`}
Output:
012
Loop control statements:
It is used to change execution from normal process. Java supports two control statements.
i) break – when it is found the loop immediately terminate. It is used in switch case statements.
Syntax:
break;
Example:
{`public class sample {
public static void main(String args[])
}
int [] nums = {05, 10, 20, 25, 30 };
for(int i : nums )
{
if( i == 20 )
{
break;
}
System.out.print( i );
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
`}
Output:
05
10
ii) continue –
it is used for skip the few of statements when reach the particular condition.
Syntax:
continue:
Example:
{`public class sample {
int [] nums = {05, 10, 20, 25, 30 };
for(int i : nums )
{
if( i == 20 )
{
continue;
}
System.out.print( i );
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
`}
Output:
5
10
25
30
Java Tutorials
- Environment setup
- Basic concept
- Object Classes
- Constructors
- OOPS in java
- data abstraction
- Variable Types
- Modifiers
- Operators
- Loop Controls
- Decision Making
- Strings
- Arrays
- Date and Time
- Methods in java
Java sample assignments
Programming Topics
- Ada
- Assembly Language
- AutoCAD
- BASIC
- Computer virus
- C Programming
- Euphoria
- Fortran Homework Help
- Game programming language
- Java Assignment Help
- JavaScript
- Java Servlets Help
- Machine Language
- Matlab
- Pascal
- Perl
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
- Servlet Life Cycle
- Smalltalk
- SOAP
- Visual Basic
- COBOL
- Lisp
- Logo Help
- Plankalkul Help
- Prolog
- REBOL
- Rexx
- Scheme Help
- TCL
- ToonTalk Help

