|
C Language has following data types:
Char | 1 byte | Short Int | 2 bytes | Int | 4 bytes | Float | 4 bytes | Double | 8 bytes |
To declare a constant, you must specify its Data Type. For example:
int x=0;
char ch = ’a’;
All statements in C must terminate with ; (semi-colon).
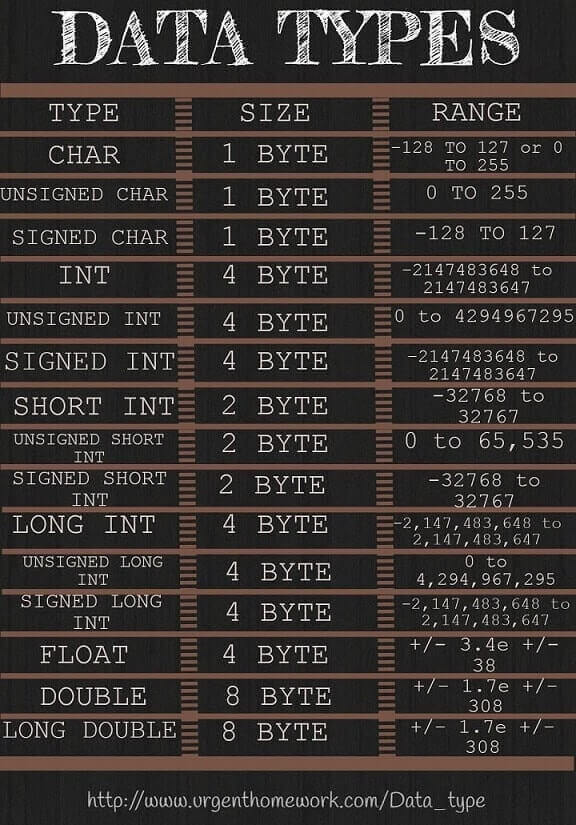
Data Type Conversion
Following are important points:
- Any operation involving Int and Int will result into Int.
- Any operation with Float and Float will result Float.
- Operations involving int and Float will result Float.
In operations involving int and Float, Int will be promoted automatically to the Float and then the evaluation of expression will take place, which will result Float.
You can convert type of any variable in the expression. For example, let us define a function 'f:double™double', if we want to apply that function on Int, we have to change the typecast.
int i,j;
i = f( (double) j);
|