Arrhythmia in Nursing
Arrhythmia & EP
Introduction: Heart arrhythmia also called as irregular heartbeat or cardiac dysrhythmia is a group of conditions where the heartbeat is irregular, too slow, or too fast. Arrhythmias are broken down into:
- Slow heartbeat: bradycardia.
- Fast heartbeat: tachycardia.
- Irregular heartbeat: flutter or fibrillation.
- Early heartbeat: premature contraction.
Cardiac Electrophysiology (EP) is the study of electrical system of heart aiming at analysing, diagnosis and treating its electrical activities. The human heart pumps 4,300 gallons of blood each day through the body’s intricate vascular network and although displacement of blood is its principal function. The heart regulates electrical impulses to create the beats.
Causes of arrhythmia: Arrhythmia may be caused by any type of interruption to the electrical impulses. A number of factors can cause the heart to work incorrectly those are:
alcohol abuse, diabetes, drug abuse, excessive coffee consumption, congestive heart failure, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, mental stress, heart attack, smoking, dietary supplements, medications.
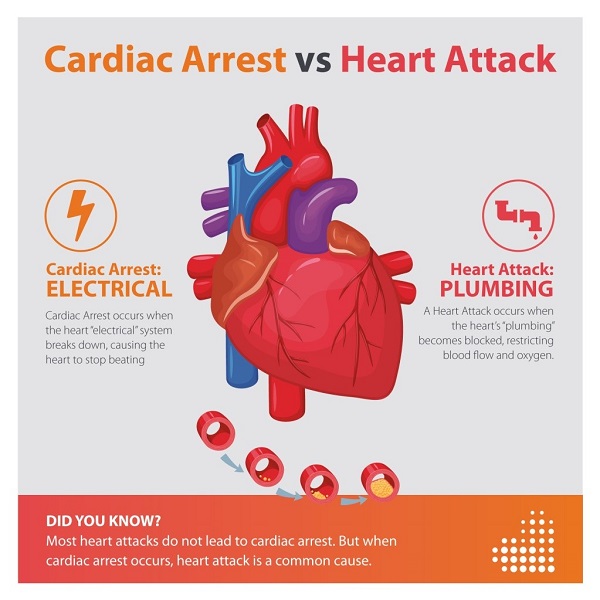
Diagnosis: The following test may involve under arrhythmia diagnosis:
- Blood and urine test
- Electrocardiogram
- Holtermonitor- a device that records heart for 1 or 2 days.
- Echocardiogram
- Chest X-ray
- Electro-physiologic testing
- Heart catheterization
Treatment: Electrophysiology (EP) procedure:
The patient is applied with local anaesthesia a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel through a site in the neck and the catheter is guided by fluoroscope images of the catheter and the heart muscles.
Once the catheter reaches the heart, electrodes at its tip gather data and a variety of electrical measurements are made. This “electrical mapping” helps the cardiac arrhythmia specialist identify the location of the area disrupting the electrical flow.
The Electrophysiologist then administers different medications or electrical impulses to determine their ability to terminate the arrhythmia.
Nursing Topics
- Registered Nurses Standards For Practice
- Reflection on Registered Nurse Standards for Practice
- Ambulatory care Nursing Homework Assignments Help
- Australian Healthcare System assignment help
- Clinical Judgment and Decision Making in Nursing
- Critical Thinking In Nursing Homework Assignments Help
- Families in Sickness and Health assignment answers
- Healthcare Management assignment help
- Spiritual Needs Assessment answers
- Therapeutic Nursing Homework Assignments Help
- Anxiety Disorders
- Arrhythmia
- Arthroplasty
- Autism
- Zika Virus
- Glaucoma
- Gallbladder and Biliary disease
- GERD
- GOUT
- Colorectal cancer
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Heart failure
- Hodgkin’s disease
- HPV and cervical cancer
- Hypertension
- Hypogonadism
- Immunization
- Infertility
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Insulin Therapy
- Influenza
⯈ Child Nursing Help
- Benefits of pet therapy in children on the autism disorder spectrum
- The use of cough and cold medicines in very young children
- Improving asthma management in schools
- Does obesity in children cause risks for influenza complications?
- Management of pain in pediatric nursing
- Children's health insurance: a right or a privilege?
⯈ Adult Nursing Help
- Effects of abdominal massage in critically ill patients
- Do whole grains in an adult's diet prevent cardiovascular diseases?
- Mirror therapy for brain-injured or stroke patients with partial paralysis
- The role of self-care management in sickle cell adult patients
- The role of nurses in weight loss programs for adults
- Cardiovascular risk scores in relation to age and gender
⯈ Elderly Care Nursing Help
- Ways to identify an abused elderly patient
- Clinical trials in older patients
- Change in health care for the elderly in your country
- Measures to take when the elderly refuse to eat
- Alcohol use among elderly patients in nursing homes
⯈ Women’s Health Nursing Help
- Acne prevention and treatment in women
- Increased risk factors for osteoporosis in women
- Factors that alter breast milk content
- Ways to teach patients about menopause management options
⯈ Pain Management Nursing Help
- Emerging ethical issues in pain management
- Influence of patient’s race and gender on pain management decisions
- Effects of cold therapy (a non-pharmacological method) for pain management
- Effective end-of-life care interventions
⯈Primary Health Care Nursing
- How well are nurses prepared for primary health care in your country?
- Primary health care: comparing public health nursing models in different countries
- Patient and family engagement in primary care

